Kubernetes Pod 管理
一、Workload 与 Pod 基础概念
1. Workload(工作负载)
- Workload:在 Kubernetes 集群中运行的应用程序
- 所有 Workload 最终都运行在 Pod 中
- Kubernetes 中的 Workload 分为两类:
- Pod
- Controller(控制器)
Controller 负责:
- Pod 副本数量
- 扩容 / 缩容
- 升级 / 回滚
2. Pod 与 Controller 的关系
- Pod 与 Controller 通过 Label + Selector 关联
- 这是 唯一的关联方式
yaml
# Pod 中定义标签
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
# Controller 中使用 selector 匹配
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx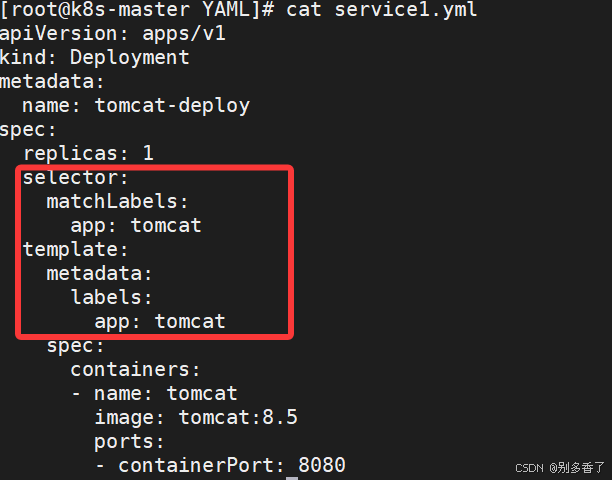
二、Pod 定义与分类
1. Pod 定义
- Pod 是 Kubernetes 调度和管理的最小计算单元
- Pod 不是进程,而是容器运行的环境
- 一个 Pod 可以包含:
- 单个容器
- 多个容器(主容器 + sidecar)
Pod 内共享的资源:
- 网络命名空间(IP 相同)
- IPC / UTS Namespace
- 存储卷(Volume)
2. Pod 分类
① 静态 Pod
- 由 kubelet 直接管理
- 不经过 API Server
- 常见于系统级组件
② 控制器管理的 Pod(常用)
- 由 Deployment / StatefulSet 等管理
- 支持副本、滚动升级、回滚
三、Pod 的基本操作
1. 查看 Pod
bash
kubectl get pod
kubectl get pod -n kube-system
kubectl get pods -o wide
kubectl describe pod pod-name
kubectl top pod pod-name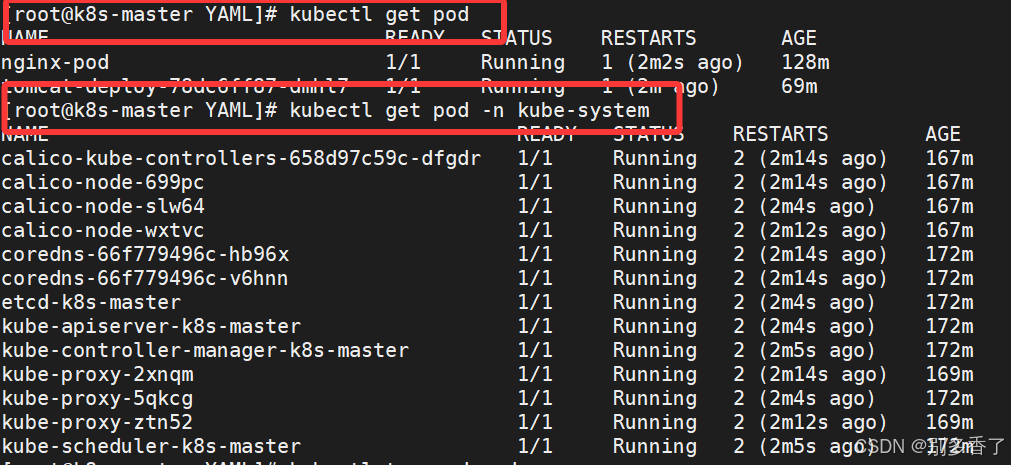
2. Pod YAML 基本结构
yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: demo-pod
namespace: default
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.26-alpine四、Pod 创建方式
1. 命令行创建(快速测试)
bash
kubectl run nginx1 --image=nginx:1.26-alpine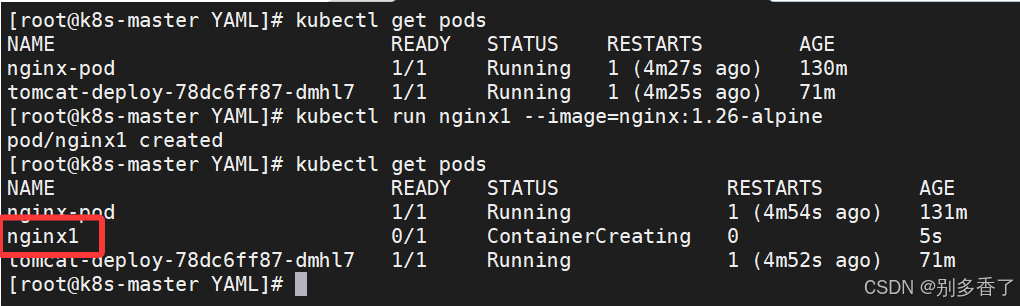
2. YAML 创建(推荐)
yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-stress
spec:
containers:
- name: c1
image: polinux/stress
command: ["stress"]
args: ["--vm","1","--vm-bytes","150M","--vm-hang","1"]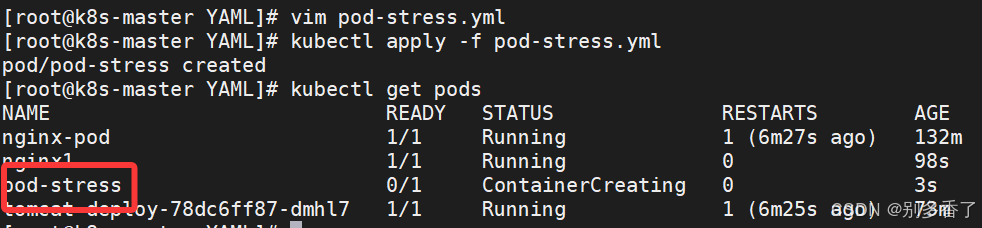
五、镜像拉取策略(imagePullPolicy)
1. 三种策略
| 策略 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Always | 只从仓库拉取 |
| IfNotPresent | 本地有就用,本地没有就去仓库拉取 |
| Never | 只用本地 |
默认规则:
latest→ Always- 指定版本 → IfNotPresent
yaml
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent修改YAML
bash
[root@k8s-master YAML]# vim pod-stress.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-stress
spec:
containers:
- name: c1
image: polinux/stress
command: ["stress"]
args: ["--vm","1","--vm-bytes","150M","--vm-hang","1"]
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent #添加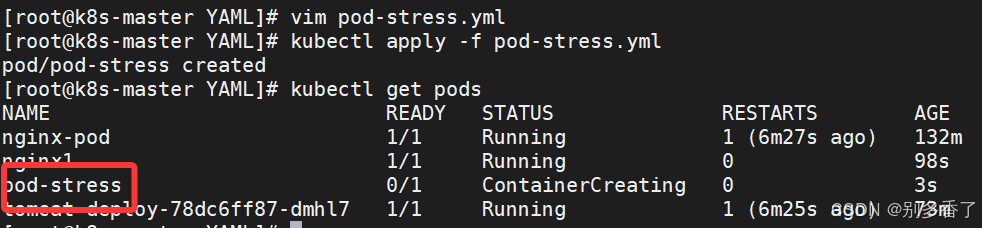
六、Pod 标签(Label)
1. 给 Pod 打标签
bash
kubectl label pod pod-stress env=test region=nanjing2. 按标签查询
bash
kubectl get pods -l env=test
kubectl get pods -l "region in (nanjing,beijing)"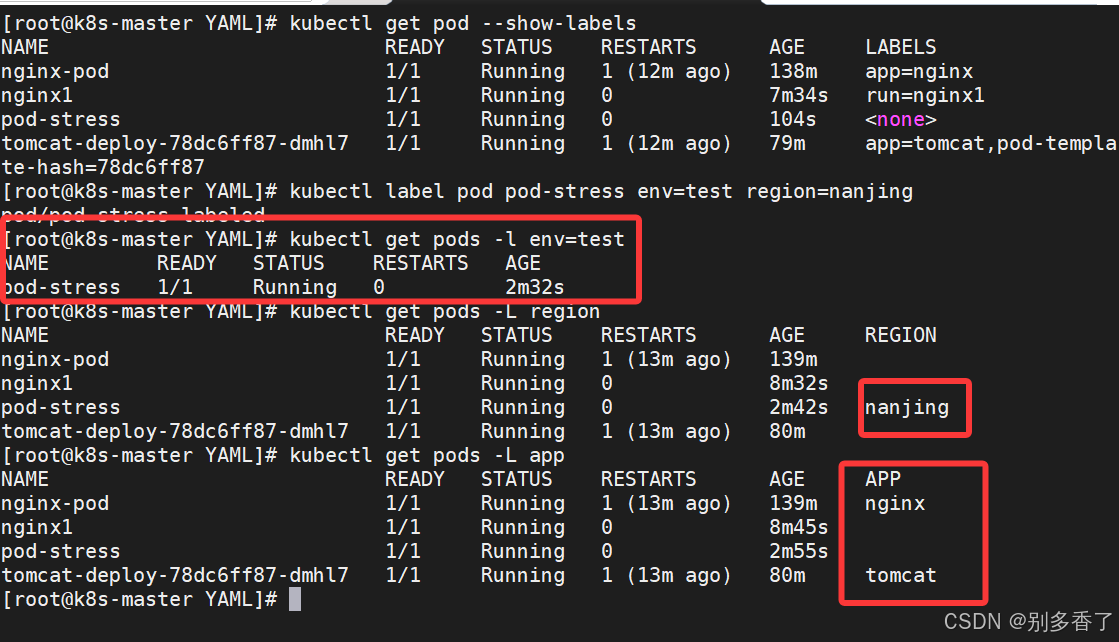
3. 删除标签
bash
kubectl label pod pod-stress env-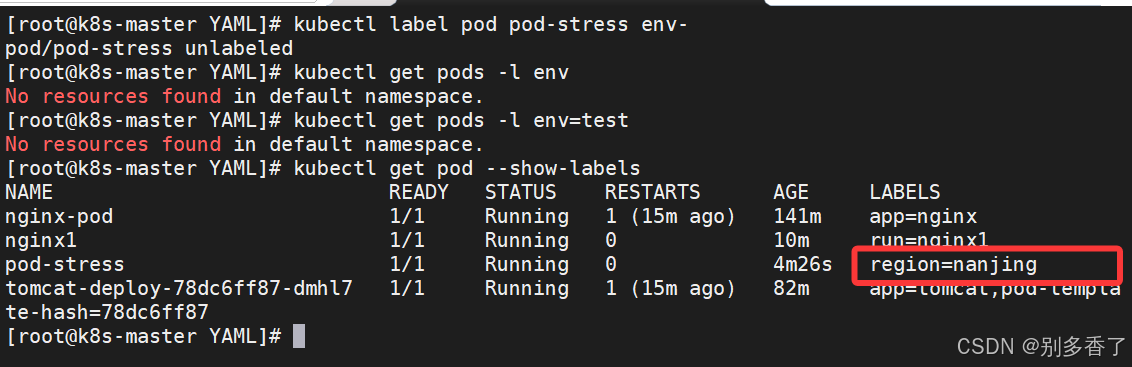
七、Pod 资源限制(Resources)
1. Requests & Limits
yaml
resources:
requests:
memory: "100Mi"
limits:
memory: "200Mi"- requests:调度时至少要有的资源
- limits:运行时最大允许使用
2. 超出限制的结果
创建pod的yaml文件
bash
[root@master ~]# vim pod3.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: namespace1
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-stress3
namespace: namespace1
spec:
containers:
- name: c1
image: polinux/stress
command: ["stress"]
args: ["--vm","1","--vm-bytes","250M","--vm-hang","1"]
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
resources:
limits:
memory: "200Mi"
requests:
memory: "150Mi"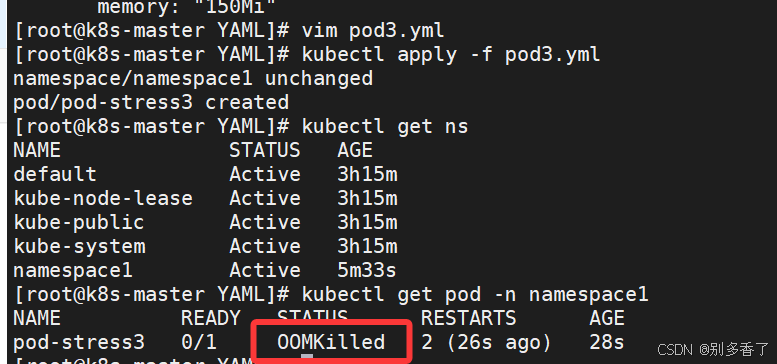
- 超出 memory limit →
OOMKilled - Pod 状态:
CrashLoopBackOff
八、Pod 多容器机制
1. 一个 Pod 多个容器
yaml
spec:
containers:
- name: c1
image: nginx
- name: c2
image: nginx📌 特点:
- IP 相同
- localhost 互通
- 端口不能冲突(否则 CrashLoop)
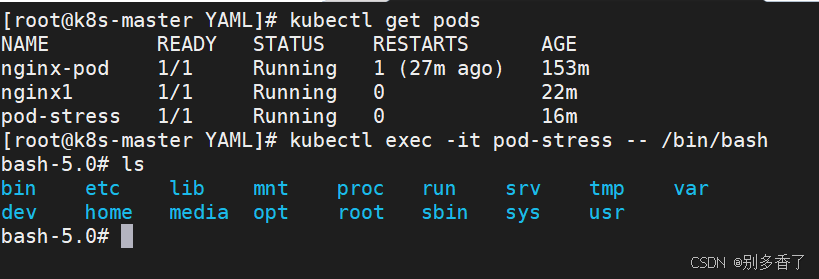
九、Pod 中容器操作(exec)
bash
[root@k8s-master YAML]# kubectl exec nginx-pod -- date
Fri Feb 13 06:22:09 UTC 2026
[root@k8s-master YAML]# kubectl exec -it pod-stress -- /bin/bash- 单容器 Pod:可省略
-c - 多容器 Pod:默认进入第一个
十、Pod 调度机制
1. nodeName(强制指定)
yaml
spec:
nodeName: node2- 不经过 scheduler
- 强制绑定节点
2. nodeSelector(推荐)
yaml
spec:
nodeSelector:
bussiness: game
kubectl label node node1 bussiness=game编写YAML文件
bash
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-nodeselect
spec:
nodeSelector:
bussiness: game # 匹配标签为 bussiness=game 的节点
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.26-alpine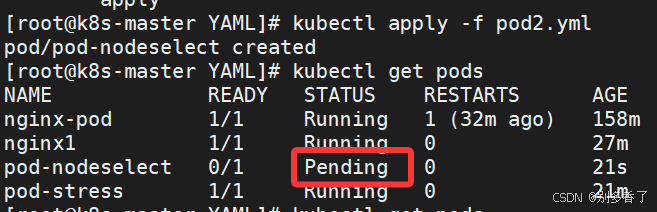
先确认目标节点已打上对应标签(否则 Pod 会 Pending):
bash
[root@k8s-master YAML]# kubectl delete -f pod2.yml
pod "pod-nodeselect" deleted
[root@k8s-master YAML]# kubectl label node k8s-node1 bussiness=game
node/k8s-node1 labeled
[root@k8s-master YAML]# kubectl apply -f pod2.yml
pod/pod-nodeselect created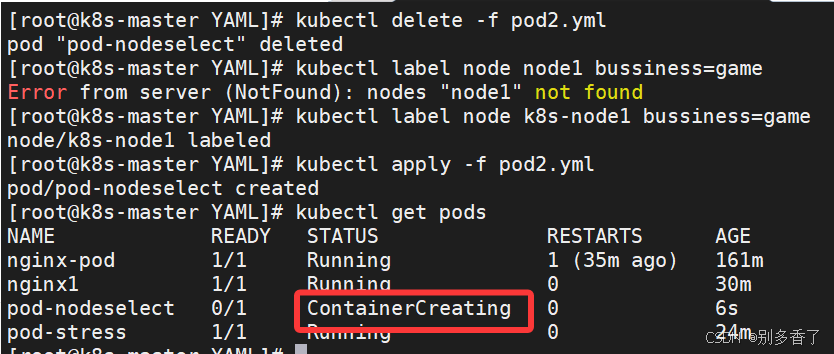
十一、Pod 生命周期
1. 启动流程
- Init Container(可选)
- 主容器启动
- postStart 钩子
- 健康检查
2. 终止流程
- preStop 钩子
- 等待 30 秒
- 强制终止
- 是否重启取决于策略
3. 重启策略
| 策略 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Always | 默认,挂了就重启 |
| OnFailure | 异常才重启 |
| Never | 不重启 |
十二、健康检查(Probe)
1. 探针类型
| 类型 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| liveness | 是否存活 |
| readiness | 是否可接流量 |
| startup | 是否完成启动 |
2.Probe探测方式
| 方式 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Exec | 执行命令 |
| HTTPGet | http请求某一个URL路径,查看返回状态码 |
| TCP | tcp连接某一个端口 |
| gRPC | 使用gRPC执行一个远程过程调用。目标应该实现gRPC健康检查。如果响应的状态是 "SERVING",则认为诊断成功。gRPC探针是一个alpha特性,只有在你启动了"GRPC ContainerProbe"特性门控时才能使用。 |
Exec 探针示例
yaml
livenessProbe:
exec:
command: ["cat","/tmp/healthy"]
initialDelaySeconds: 5
periodSeconds: 5HTTP 探针示例
yaml
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /index.html
port: 80TCP 探针示例
yaml
livenessProbe:
tcpSocket:
port: 805. readiness 特点
- 探测失败 → Pod 变为
NotReady - 不会重启容器
- Service 不再转发流量
十三、生命周期钩子
1. postStart
yaml
lifecycle:
postStart:
exec:
command: ["mkdir","-p","/data"]2. preStop
yaml
lifecycle:
preStop:
exec:
command: ["/bin/sh","-c","sleep 30"]十四、总结
TCP 探针示例
yaml
livenessProbe:
tcpSocket:
port: 805. readiness 特点
- 探测失败 → Pod 变为
NotReady - 不会重启容器
- Service 不再转发流量
十三、生命周期钩子
1. postStart
yaml
lifecycle:
postStart:
exec:
command: ["mkdir","-p","/data"]2. preStop
yaml
lifecycle:
preStop:
exec:
command: ["/bin/sh","-c","sleep 30"]十四、总结
Pod 是容器的运行环境,Controller 管 Pod,Label 是一切关联的核心,Probe 决定生死,Resources 决定稳定性。