目录
一、实验目的
了解动态分区分配方式中使用的数据结构和分配算法,并进一步加深对动态分区存储管理方式及其实现过程的理解。
二、实验环境
硬件环境:计算机一台,局域网环境;
软件环境: Windows或Linux操作系统, C语言编程环境。
三、实验内容
1、用C语言分别实现采用首次适应算法和最佳适应算法的动态分区分配过程alloc( )和回收过程free( )。其中,空闲分区通过空闲分区链来管理:在进行内存分配时,系统优先使用空闲区低端的空间。
2、假设初始状态下,可用的内存空间为640KB,并有下列的请求序列:
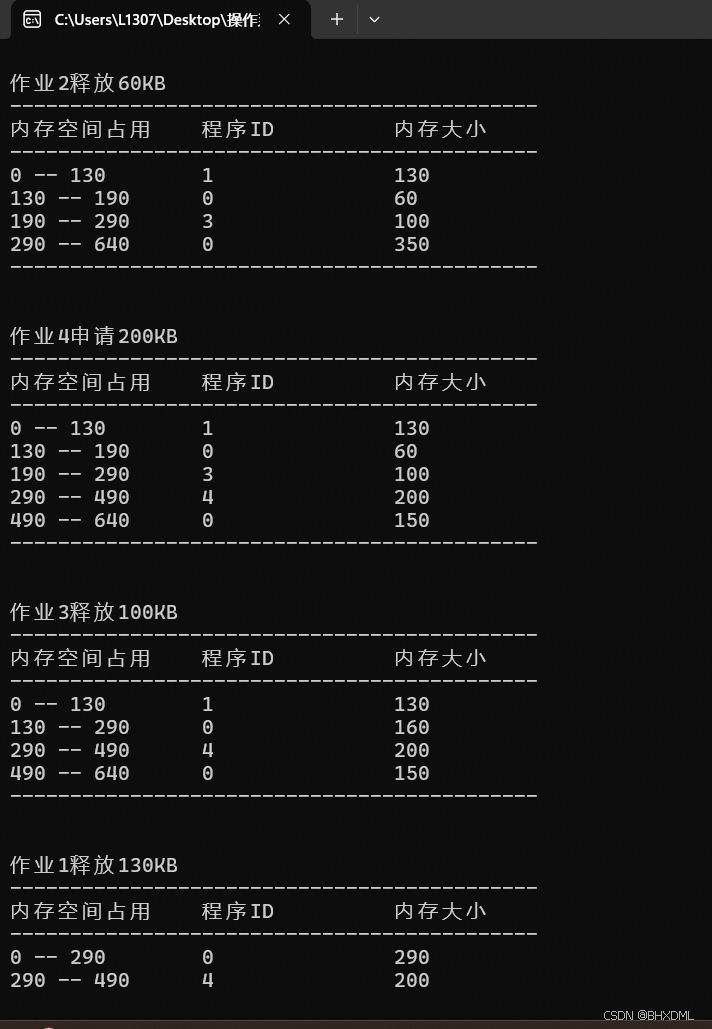
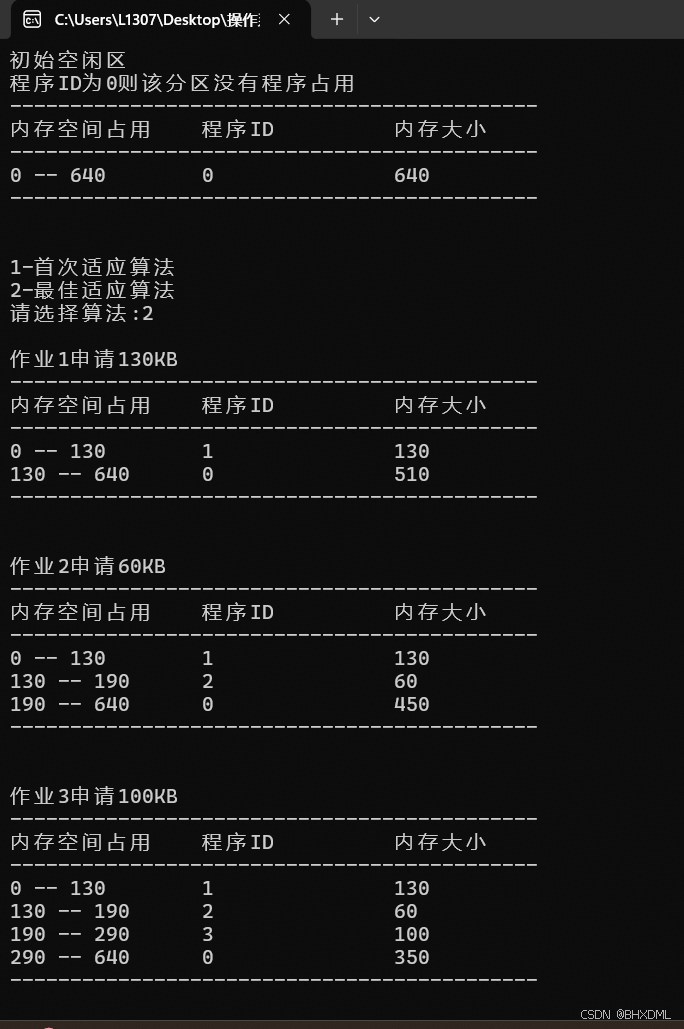
•作业1申请130KB。
•作业2申请60KB。
•作业3申请100KB。
•作业2释放60KB。
•作业4申请200KB。
•作业3释放100KB。
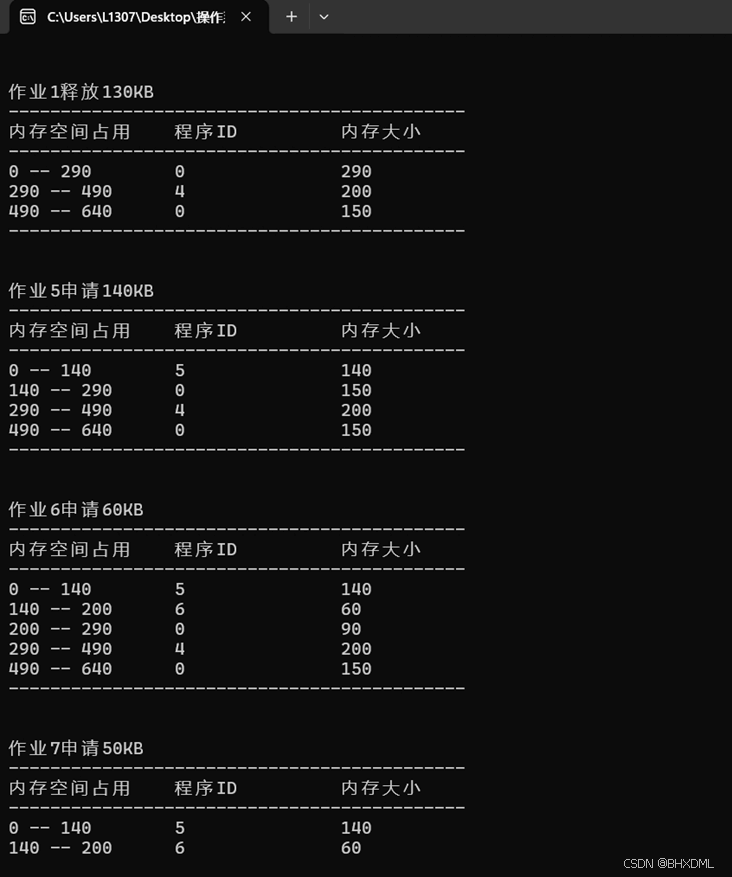
•作业1释放130KB。
•作业5申请140KB。
•作业6申请60KB。
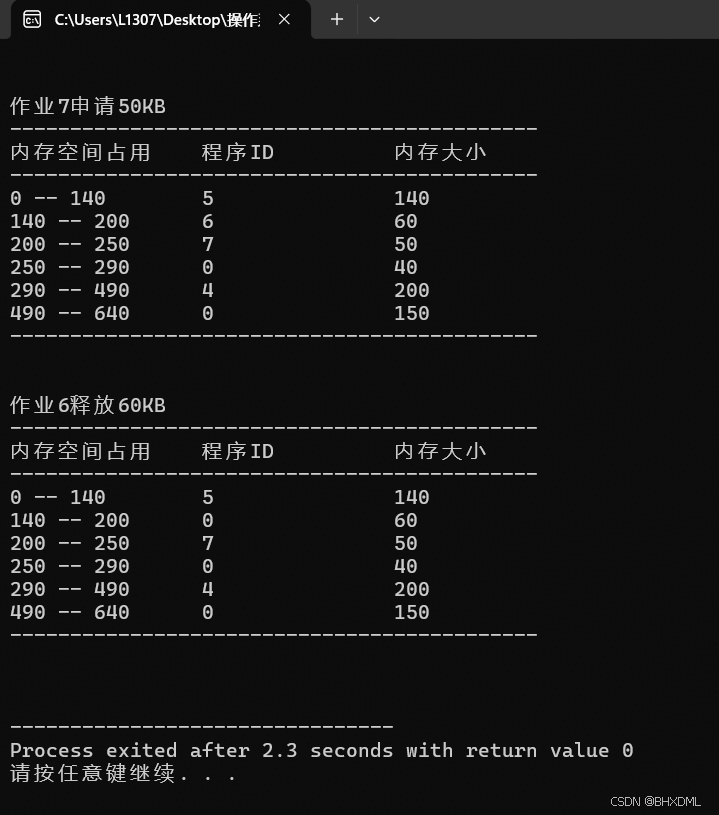
•作业7申请50KB。
•作业6释放60KB。
请分别采用首次适应算法和最佳适应算法,对内存块进行分配和回收,要求每次分配和回收后显示出空闲分区链的情况。
3、实验报告要求:
(1)给出具体的设计过程,贴出相应的代码,截图给出试验结果。
(2)结合实验情况,谈谈你对存储管理的理解和体会。
1.设计过程
- 确定数据结构:
-
首先,确定了三个主要的数据结构:
-
`Jobs`:表示作业的结构体,包含作业ID、起始地址和结束地址等信息。
-
`Unoccupied_block`:表示未分配的内存块的结构体,包含起始地址和结束地址等信息。
-
`Blocking_queue`:表示阻塞队列中的作业的结构体,包含作业ID和需要的空间等信息。
- 编写函数:
- 编写了一系列操作这些数据结构的函数,包括插入作业到作业队列、插入作业到阻塞队列、从作业队列删除作业、从阻塞队列删除作业、释放作业分配的内存等。
- 实现内存分配算法:
-
实现了首次适应算法(`first_fit`函数)和最佳适应算法(`best_fit`函数),在这两个函数中调用了内存分配和释放的相关函数。
-
在首次适应算法中,按照作业的空间大小首次找到满足要求的内存块进行分配,如果没有足够的内存,则将作业放入阻塞队列。
-
最佳适应算法中,选择大小最合适的空闲内存块进行分配。
- 输入输出处理:
- 设计了文件读取和输出函数,从文件中读取作业信息,并输出分配结果。
- 排序算法:
- 实现了排序函数`sort`和`sort2`,用于对未分配的内存块按照空闲空间大小和起始地址进行排序,以支持最佳适应算法。
- 主函数:
- 在主函数中,首先初始化数据结构,然后调用首次适应算法和最佳适应算法进行内存分配,最后输出结果。
2.设计过程
- 数据结构设计
Work结构体: 表示作业,其中包含作业ID和作业所需的内存大小。
Memory结构体: 表示内存块,其中包含起始地址、结束地址、占用程序ID、是否被占用的标志和内存块大小。
- 内存初始化
初始化一个640KB的内存块,设为未被占用。
- 内存分区管理
使用动态数组(M_queue)来管理内存分区,初始时包含两个分区:一个表示内存未使用的部分,一个表示内存的结束。
- 空闲分区合并
合并相邻的空闲分区,以减少内存碎片。
- 内存分配算法
首次适应算法: 遍历内存分区,找到第一个可以满足作业需求的空闲分区进行分配。
最佳适应算法: 遍历内存分区,找到最适合的(即最小的且可以满足作业需求的)空闲分区进行分配。
- 内存释放
找到对应的作业,标记为未占用,并进行内存分区合并。
- 输出内存状态
输出当前内存分区的状态,显示每个分区的起始地址、结束地址、占用程序ID和大小。
实验代码
1.
cs
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct Jobs {
int jobID;
int addr_start;
int addr_end;
struct Jobs *next;
};
struct Unoccupied_block {
struct Unoccupied_block *previous;
int addr_start;
int addr_end;
struct Unoccupied_block *next;
};
struct Blocking_queue {
int jobID;
int space;
struct Blocking_queue *next;
};
struct Jobs *jobhead;
struct Blocking_queue *bqhead;
struct Unoccupied_block *ubhead;
bool empty() {
// Check if the blocking queue is empty
if (bqhead->next == NULL)
return true;
return false;
}
// Sort the unoccupied blocks by size (ascending order)
void sort() {
// Bubble sort
struct Unoccupied_block *t = ubhead->next;
int length = 0;
// Get length
while (t) {
length++;
t = t->next;
}
t = ubhead->next;
// Bubble sort
for (int i = 0; i < length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < length - i - 1; j++) {
struct Unoccupied_block *a, *b, *temp;
temp = (struct Unoccupied_block *)malloc(sizeof(struct Unoccupied_block));
int count = j;
while (count--) {
t = t->next;
}
a = t;
b = t->next;
if (a->addr_end - a->addr_start > b->addr_end - b->addr_start) {
temp->addr_start = a->addr_start;
temp->addr_end = a->addr_end;
a->addr_start = b->addr_start;
a->addr_end = b->addr_end;
b->addr_start = temp->addr_start;
b->addr_end = temp->addr_end;
}
t = ubhead->next;
}
}
}
// Sort by start position
void sort2() {
// Bubble sort
struct Unoccupied_block *t = ubhead->next;
int length = 0;
// Get length
while (t) {
length++;
t = t->next;
}
t = ubhead->next;
// Bubble sort
for (int i = 0; i < length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < length - i - 1; j++) {
struct Unoccupied_block *a, *b, *temp;
temp = (struct Unoccupied_block *)malloc(sizeof(struct Unoccupied_block));
int count = j;
while (count--) {
t = t->next;
}
a = t;
b = t->next;
if (a->addr_start > b->addr_start) {
temp->addr_start = a->addr_start;
temp->addr_end = a->addr_end;
a->addr_start = b->addr_start;
a->addr_end = b->addr_end;
b->addr_start = temp->addr_start;
b->addr_end = temp->addr_end;
}
t = ubhead->next;
}
}
}
// Output unoccupied blocks
void Output() {
struct Unoccupied_block *t = ubhead->next;
int count = 0;
printf("------------------------------------\n");
printf("Current unoccupied blocks:\n");
while (t) {
count++;
printf("%d %d %d\n", count, t->addr_start, t->addr_end);
t = t->next;
}
printf("------------------------------------\n\n");
}
// Insert a job into job queue
void InsertJob(struct Jobs newJob) {
struct Jobs *t1 = jobhead;
while (t1->next)
t1 = t1->next;
struct Jobs *t = (struct Jobs *)malloc(sizeof(struct Jobs));
t->jobID = newJob.jobID;
t->addr_start = newJob.addr_start;
t->addr_end = newJob.addr_end;
t->next = NULL;
t1->next = t;
}
// Insert a job into blocking queue
void InsertBQ(struct Blocking_queue newJob) {
struct Blocking_queue *t = bqhead;
while (t->next)
t = t->next;
struct Blocking_queue *t2 = (struct Blocking_queue *)malloc(sizeof(struct Blocking_queue));
t2->jobID = newJob.jobID;
t2->space = newJob.space;
t2->next = NULL;
t->next = t2;
}
// Delete a job from job queue
void DeleteJob(int id, int *start, int *end) {
struct Jobs *t = jobhead;
while (t->next) {
if (t->next->jobID == id)
break;
t = t->next;
}
*start = t->next->addr_start;
*end = t->next->addr_end;
t->next = t->next->next;
printf("Recovery successful\n");
printf("Job information: ID: %d Space: %d\n", id, *end - *start);
}
// Delete a job from blocking queue
struct Blocking_queue *DeleteBQ(int id) {
struct Blocking_queue *t = bqhead;
while (t->next) {
if (t->next->jobID == id)
break;
t = t->next;
}
t->next = t->next->next;
return t->next;
}
// Arrange jobs in memory
bool Arrange(int newJobID, int newJobSpace, bool blockFlag) {
struct Unoccupied_block *head1 = ubhead->next;
struct Jobs *head2 = jobhead->next;
struct Blocking_queue *head3 = bqhead->next;
bool flag = false;
while (head1) {
if (head1->addr_end - head1->addr_start > newJobSpace) {
printf("Allocation successful\n");
printf("Job information: ID: %d Space: %d\n", newJobID, newJobSpace);
struct Jobs newjob;
newjob.addr_start = head1->addr_start;
newjob.addr_end = newjob.addr_start + newJobSpace;
newjob.jobID = newJobID;
newjob.next = NULL;
InsertJob(newjob);
head1->addr_start += newJobSpace;
flag = true;
break;
} else if (head1->addr_end - head1->addr_start == newJobSpace) {
printf("Allocation successful\n");
printf("Job information: ID: %d Space: %d\n", newJobID, newJobSpace);
struct Jobs newjob;
newjob.addr_start = head1->addr_start;
newjob.addr_end = head1->addr_end;
newjob.jobID = newJobID;
newjob.next = NULL;
InsertJob(newjob);
head1->previous->next = head1->next;
flag = true;
break;
} else {
head1 = head1->next;
}
}
if (!flag) {
printf("Allocation failed\n");
printf("Job information: ID: %d Space: %d\n", newJobID, newJobSpace);
struct Blocking_queue newJob;
newJob.jobID = newJobID;
newJob.space = newJobSpace;
newJob.next = NULL;
if (!blockFlag)
InsertBQ(newJob);
return false;
}
return true;
}
// Free memory allocated by a job
void Free(int newJobID) {
struct Unoccupied_block *head1 = ubhead->next;
struct Jobs *head2 = jobhead->next;
struct Blocking_queue *head3 = bqhead->next;
int jobAddrStart, jobAddrEnd;
DeleteJob(newJobID, &jobAddrStart, &jobAddrEnd);
sort2();
struct Unoccupied_block *indexInsert = ubhead;
while (indexInsert) {
if (head1 == NULL || head1->addr_start >= jobAddrEnd) {
indexInsert = ubhead;
break;
} else if (indexInsert->addr_end <= jobAddrStart && (indexInsert->next == NULL || indexInsert->next->addr_start >= jobAddrEnd))
break;
else
indexInsert = indexInsert->next;
}
if (indexInsert->next == NULL) {
struct Unoccupied_block *newItem = (struct Unoccupied_block *)malloc(sizeof(struct Unoccupied_block));
newItem->addr_start = jobAddrStart;
newItem->addr_end = jobAddrEnd;
indexInsert->next = newItem;
newItem->previous = indexInsert;
newItem->next = NULL;
return;
}
if (indexInsert->addr_end < jobAddrStart && indexInsert->next->addr_start > jobAddrEnd) {
struct Unoccupied_block *newItem = (struct Unoccupied_block *)malloc(sizeof(struct Unoccupied_block));
newItem->addr_start = jobAddrStart;
newItem->addr_end = jobAddrEnd;
indexInsert->next->previous = newItem;
newItem->next = indexInsert->next;
newItem->previous = indexInsert;
indexInsert->next = newItem;
return;
} else if (indexInsert->addr_end == jobAddrStart && indexInsert->next->addr_start == jobAddrEnd) {
indexInsert->addr_end = indexInsert->next->addr_end;
struct Unoccupied_block *t = indexInsert->next;
if (t->next == NULL) {
indexInsert->next = NULL;
return;
}
t->next->previous = indexInsert;
indexInsert->next = t->next;
return;
} else if (indexInsert->addr_end == jobAddrStart) {
indexInsert->addr_end = jobAddrEnd;
return;
} else if (indexInsert->next->addr_start == jobAddrEnd) {
indexInsert->next->addr_start = jobAddrStart;
return;
}
}
void first_fit(bool altype) {
FILE *fp;
printf("Enter the file name:\n");
char filename[20];
scanf("%s", filename);
if ((fp = fopen(filename, "r")) == NULL) {
printf("Failed to open file\n");
return;
}
jobhead = (struct Jobs *)malloc(sizeof(struct Jobs));
jobhead->next = NULL;
bqhead = (struct Blocking_queue *)malloc(sizeof(struct Blocking_queue));
bqhead->next = NULL;
ubhead = (struct Unoccupied_block *)malloc(sizeof(struct Unoccupied_block));
struct Unoccupied_block *first = (struct Unoccupied_block *)malloc(sizeof(struct Unoccupied_block));
first->addr_start = 0;
first->addr_end = 640;
first->next = NULL;
first->previous = ubhead;
ubhead->next = first;
ubhead->previous = NULL;
ubhead->addr_start = -1;
ubhead->addr_end = -1;
while (!feof(fp)) {
struct Jobs newJob;
int id, type, space;
fscanf(fp, "%d %d %d", &id, &type, &space);
if (type == 1) {
Arrange(id, space, false);
if (altype)
sort();
Output();
} else if (type == 0) {
Free(id);
if (altype)
sort();
if (!empty()) {
struct Blocking_queue *t = bqhead->next;
while (t) {
printf("Processing job %d from the blocking queue\n", t->jobID);
if (Arrange(t->jobID, t->space, true)) {
if (altype)
sort();
t = DeleteBQ(t->jobID);
continue;
}
t = t->next;
}
}
Output();
}
}
}
int main(void) {
printf("*******************************************************\n\n");
printf("First Fit Algorithm:\n\n");
first_fit(false);
printf("*******************************************************\n\n");
printf("Best Fit Algorithm:\n\n");
first_fit(true);
return 0;
}代码调试过程中用到的测试数据
2.txt
1 1 130
2 1 60
3 1 20
1 0 130
2 0 60
2.
cs
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<string.h>
#define MAX 640
struct work {
int id;
int size;
};
struct memory {
int front_number; //开始地址
int number; //结束地址
int id; //占用程序的id
bool flag;//0为未被占用,可被回收
int size; //大小
};
struct memory M[2] = {
{0, 0, 0, 1, 0},
{0, MAX, 0, 0, MAX}
}; //内存空间初始化,从1开始
struct memory temp;
int chose;
struct memory *M_queue; //内存分区队列
int M_queue_size = 0;
//空闲分区合并
void M_merge(int mer_id) {
//回收区地址小
if ((mer_id < M_queue_size - 1) && (M_queue[mer_id + 1].flag == 0)) {
M_queue[mer_id + 1].size += M_queue[mer_id].size;
M_queue[mer_id + 1].front_number = M_queue[mer_id].front_number;
for (int i = mer_id; i < M_queue_size - 1; i++) {
M_queue[i] = M_queue[i + 1];
}
M_queue_size--;
}
//空闲区地址小
if (M_queue[mer_id - 1].flag == 0) {
M_queue[mer_id - 1].size += M_queue[mer_id].size;
M_queue[mer_id - 1].number = M_queue[mer_id].number;
for (int i = mer_id; i < M_queue_size - 1; i++) {
M_queue[i] = M_queue[i + 1];
}
M_queue_size--;
}
}
void M_print() {
printf("--------------------------------------------\n");
printf("内存空间占用\t程序ID\t\t内存大小\n");
printf("--------------------------------------------\n");
for (int i = 1; i < M_queue_size; i++) {
printf("%d -- %3d\t%d\t\t%d\n", M_queue[i].front_number, M_queue[i].number, M_queue[i].id, M_queue[i].size);
}
printf("--------------------------------------------\n");
printf("\n\n");
}
void alloc(struct work p1) {
if (chose == 1) { //首次适应算法
for (int i = 1; i < M_queue_size; i++) {
if ((M_queue[i].flag == 0) && p1.size < M_queue[i].size) {
temp.flag = 1;
temp.id = p1.id;
temp.size = p1.size;
temp.front_number = M_queue[i].front_number;
temp.number = temp.front_number + temp.size;
//更新空闲区
M_queue[i].front_number = temp.number;
M_queue[i].size -= temp.size;
for (int j = M_queue_size; j > i; j--) {
M_queue[j] = M_queue[j - 1];
}
M_queue[i] = temp;
M_queue_size++;
break;
}
}
} else if (chose == 2) { //最佳适应算法
int best_num = MAX; //记录目标空闲区大小
int best_id = 1; //记录目标空闲区编号
for (int i = 1; i < M_queue_size; i++) { //找到只比p1.size大一点的空闲区,即目标空闲区
if ((M_queue[i].flag == 0) && (M_queue[i].size >= p1.size) && (M_queue[i].size <= best_num)) {
best_num = M_queue[i].size;
best_id = i;
}
}
temp.flag = 1;
temp.id = p1.id;
temp.size = p1.size;
temp.front_number = M_queue[best_id].front_number;
temp.number = temp.front_number + temp.size;
//更新空闲区
M_queue[best_id].front_number = temp.number;
M_queue[best_id].size -= p1.size;
for (int j = M_queue_size; j > best_id; j--) {
M_queue[j] = M_queue[j - 1];
}
M_queue[best_id] = temp;
M_queue_size++;
}
M_print();
}
void free_mem(struct work p2) {
int id;
for (int i = 0; i < M_queue_size; i++) {
if (p2.id == M_queue[i].id) {
M_queue[i].flag = 0;
M_queue[i].id = 0;
id = i;
break;
}
}
M_merge(id);
M_print();
}
int main() {
M_queue = (struct memory *) malloc(sizeof(struct memory) * (MAX / 2));
M_queue[M_queue_size++] = M[0];
M_queue[M_queue_size++] = M[1]; //初始化内存分区队列
printf("初始空闲区\n");
printf("程序ID为0则该分区没有程序占用\n");
M_print();
printf("1-首次适应算法\n2-最佳适应算法\n请选择算法:");
scanf("%d", &chose);
if (chose != 1 && chose != 2) {
printf("错误!\n");
return 0;
}
printf("\n");
struct work process1 = {1, 130};
struct work process2 = {2, 60};
struct work process3 = {3, 100};
struct work process4 = {4, 200};
struct work process5 = {5, 140};
struct work process6 = {6, 60};
struct work process7 = {7, 50};
printf("作业1申请130KB\n");
alloc(process1);
printf("作业2申请60KB\n");
alloc(process2);
printf("作业3申请100KB\n");
alloc(process3);
printf("作业2释放60KB\n");
free_mem(process2);
printf("作业4申请200KB\n");
alloc(process4);
printf("作业3释放100KB\n");
free_mem(process3);
printf("作业1释放130KB\n");
free_mem(process1);
printf("作业5申请140KB\n");
alloc(process5);
printf("作业6申请60KB\n");
alloc(process6);
printf("作业7申请50KB\n");
alloc(process7);
printf("作业6释放60KB\n");
free_mem(process6);
free(M_queue);
return 0;
}实验结果:
1.


2.

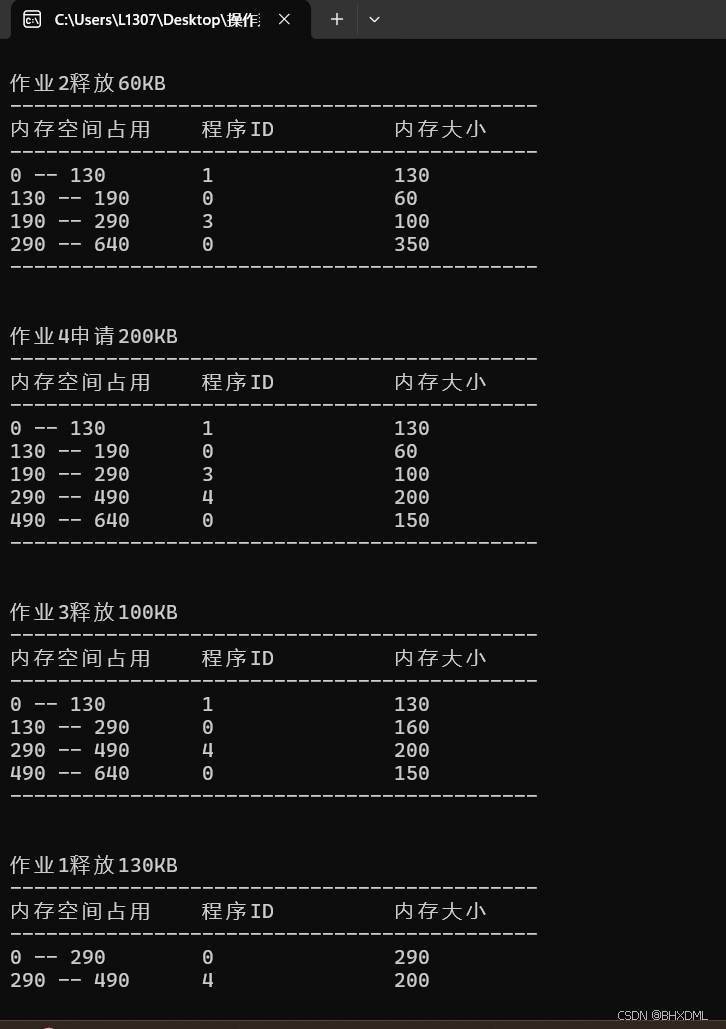
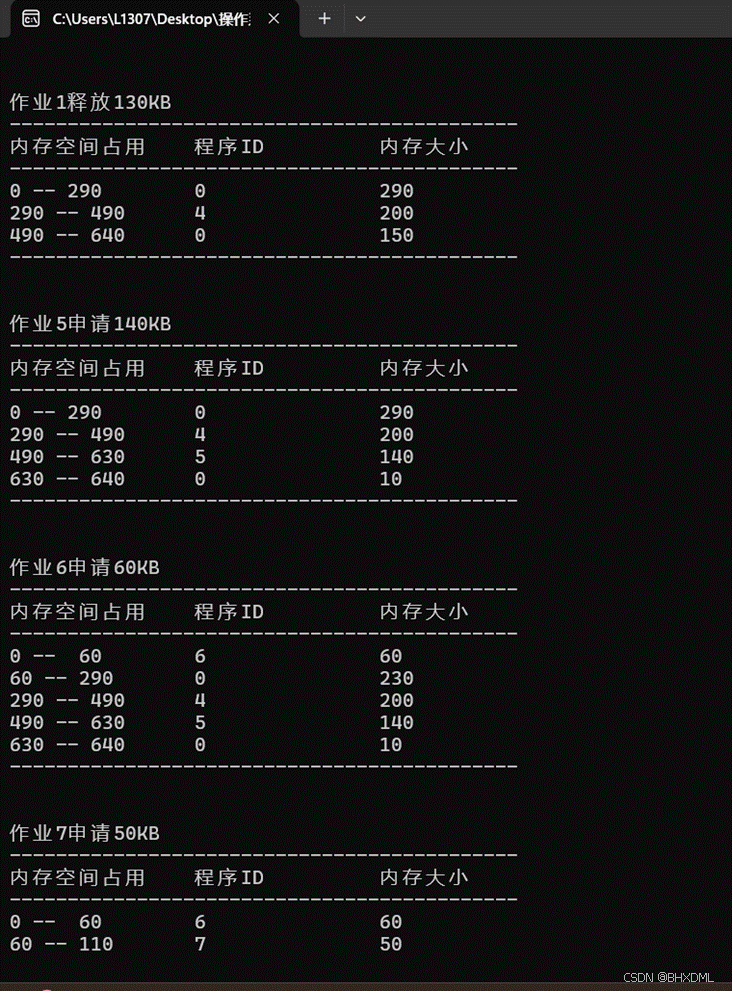
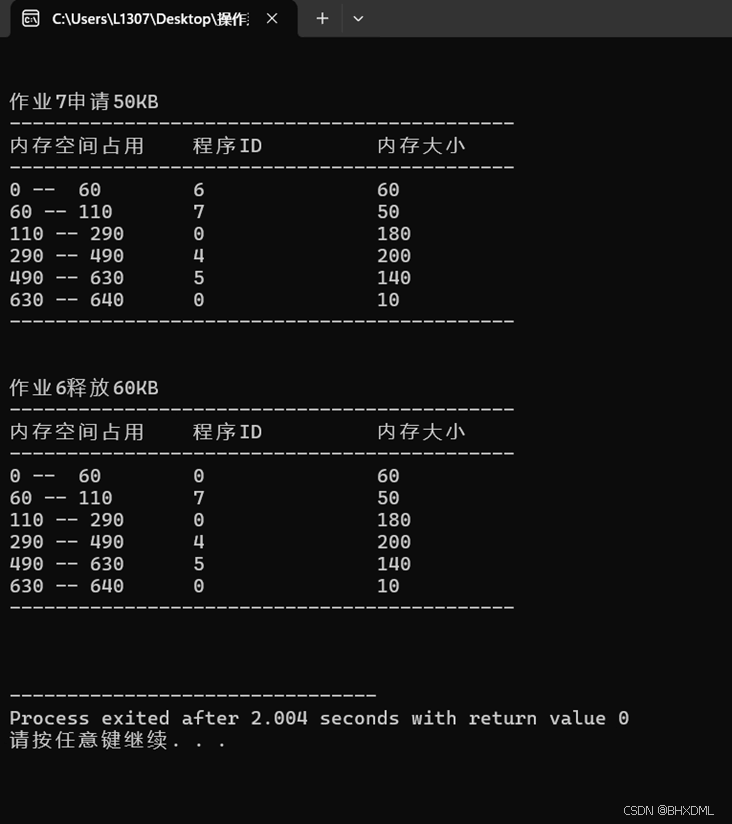
理解:
- 内存分配与回收
内存分配
操作系统负责将内存分配给进程或线程。在多任务操作系统中,多个进程或线程同时运行,操作系统需要根据每个进程或线程的需求分配适当的内存。
静态分配: 在程序运行前确定内存分配,如全局变量和静态变量。
动态分配: 在程序运行时进行内存分配,如堆和栈的内存分配。
内存回收
当一个进程或线程结束时,操作系统需要回收其占用的内存,以便分配给其他进程或线程。
自动回收: 操作系统自动回收已终止进程的内存。
手动回收: 程序通过系统调用(如free()或delete)主动释放内存。
- 内存保护
内存保护确保一个进程不能访问其他进程的内存,从而保护进程的私有数据,防止意外或恶意的访问和修改。操作系统通过硬件(如MMU,内存管理单元)和软件机制实现内存保护。
基址寄存器和限长寄存器: 用于保护进程的内存空间。
页表和段表: 用于管理虚拟内存,实现进程间内存隔离。
- 内存共享
内存共享允许多个进程共享同一段内存,以便进程之间高效通信。
共享内存: 进程通过共享内存段进行数据交换。
内存映射文件: 进程将文件映射到内存空间,实现文件的共享和访问。
- 虚拟内存管理
虚拟内存管理扩展了物理内存的容量,使程序可以使用比实际物理内存更大的地址空间。虚拟内存通过分页或分段实现。
分页: 将内存分为固定大小的页和页框,通过页表映射虚拟地址到物理地址。
分段: 将内存分为不定长的段,通过段表管理段的分配和保护。
- 内存分页
内存分页是虚拟内存管理的一种实现方式。分页将内存分为固定大小的页(通常为4KB),通过页表将虚拟地址映射到物理地址。
页表: 保存页号到页框的映射关系。
多级页表: 解决大内存地址空间管理问题,通过多级映射减少页表大小。
- 内存碎片管理
内存碎片分为内部碎片和外部碎片。操作系统需要管理和减少内存碎片,以提高内存利用率。
内部碎片: 分配的内存块比实际需要的要大,导致内存浪费。
外部碎片: 内存中有足够的空闲空间,但不连续,无法满足新内存块的分配需求。
内存紧缩: 通过移动内存块合并碎片,提高内存利用率。
- 内存交换(Swapping)
内存交换将不活动的进程或内存页从内存移到磁盘,以腾出内存空间给其他进程使用。当被交换的进程或页再次需要时,再从磁盘加载回内存。
进程交换: 将整个进程从内存移到磁盘。
页交换: 只将不活动的页移到磁盘,实现更细粒度的内存管理。
首次适应算法(First-Fit Algorithm)
工作原理
首次适应算法是一种简单的内存分配算法,按照内存中空闲块的顺序查找第一个满足请求大小的空闲块,并将内存分配给该请求。具体步骤如下:
- 从内存的低地址开始,查找第一个能够满足内存请求的空闲块。
- 如果找到合适的空闲块,则将其分配给请求并调整空闲块的大小和位置。
- 如果没有找到合适的空闲块,则请求失败。
优点
- 实现简单:首次适应算法的实现相对简单,只需要顺序扫描内存空闲块即可。
- 分配速度快:在找到第一个合适的空闲块后立即分配,无需进一步搜索,因此分配速度较快。
缺点
- 容易产生外部碎片:由于总是从低地址开始分配,容易在内存中留下大量的小碎片,难以利用。
- 内存利用率低:碎片化问题会导致内存利用率下降,特别是在系统运行较长时间后,碎片化问题更加严重。
适用场景
- 系统负载较轻,对内存利用率要求不高的场景。
- 实现简单、效率优先的场景。
最佳适应算法(Best-Fit Algorithm)
工作原理
最佳适应算法通过查找最适合的空闲块来分配内存,即查找能够满足请求大小的最小空闲块。具体步骤如下:
- 遍历所有空闲块,查找能够满足内存请求的最小空闲块。
- 如果找到最合适的空闲块,则将其分配给请求并调整空闲块的大小和位置。
- 如果没有找到合适的空闲块,则请求失败。
优点
- 内存利用率高:最佳适应算法能够找到最适合的空闲块进行分配,减少内存碎片,提高内存利用率。
- 减少外部碎片:通过分配最适合的空闲块,最大限度地减少内存碎片。
缺点
- 实现复杂:需要遍历所有空闲块,寻找最适合的空闲块,算法实现和维护相对复杂。
- 分配速度慢:每次分配内存时都需要遍历所有空闲块,查找最适合的空闲块,分配速度较慢。
适用场景
- 系统负载较重,对内存利用率要求较高的场景。
- 需要减少内存碎片,提高内存利用率的场景。
对比总结
| 特性 | 首次适应算法 | 最佳适应算法 |
|---|---|---|
| 实现复杂度 | 简单 | 复杂 |
| 分配速度 | 快 | 慢 |
| 内存利用率 | 较低 | 较高 |
| 外部碎片 | 容易产生 | 较少 |
| 适用场景 | 负载较轻、实现简单的场景 | 负载较重、内存利用率高的场景 |
实验体会:
- 理解存储管理的重要性
存储管理是操作系统中至关重要的一部分,通过本次实验,我体会到了存储管理在确保系统稳定性和资源高效利用方面的重要性。正确的内存分配和回收机制不仅能够提高系统性能,还能避免内存泄漏和碎片问题。
- 数据结构设计的合理性
在实验中,我设计了work和memory两个结构体分别表示作业和内存分区。通过链表管理内存分区的方式,使得内存的分配和回收变得直观和高效。这让我体会到,在实际系统设计中,选择合适的数据结构是解决问题的关键。
- 内存分配算法的实现
通过实现首次适应算法和最佳适应算法,我深入理解了两种算法的区别和各自的优缺点。首次适应算法实现相对简单,但可能导致较多的外部碎片;最佳适应算法能有效减少碎片,但实现较复杂,需要频繁排序和查找。这让我意识到,算法的选择需要根据具体应用场景权衡复杂度和性能。
- 内存回收和碎片合并
实验中,我还实现了内存回收和碎片合并的功能。这部分实现让我认识到,内存管理不仅仅是分配问题,更重要的是如何有效地回收和合并碎片,以保持内存的连续性和高效利用率。通过设计合并相邻空闲分区的机制,有效减少了内存碎片问题。