Rust的原生类型包括标量类型和复合类型。
标量类型
- 有符号整型:i8, i16, i32, i64, isize
- 无符号整型:u8, u16, u32, u64, usize
- 浮点型:f32, f64
- 字符:单个Unicode字符(每个占4字节)
- 布尔型:true, false
- 单元型:()(空元组)
复合类型
- 数组
一组拥有相同类型的对象的集合,在内存中连续存储,大小在编译时会被确定。
切片:类型和数组类似,其大小在编译时不确定。切片是一个双字对象,第一个字是一个指向数据的指针,第二个字是切片的长度。字的宽度和 usize 相同,由处理器架构决定。切片可以用来借用数组的一部分,类型标记为 &[T].
- 元组
元组可以包含各种类型的值,使用括号 () 来构成,可以使用元组来返回多个值。
新建文件mytry.rs, 输入如下代码:
rust
fn reverse(pair: (i32, bool)) -> (bool, i32) {
let (integer, boolean) = pair;
(boolean, integer)
}
#[derive(Debug)]
struct Matrix(f32, f32, f32, f32);
fn main() {
let long_tuple = (1u8, 2u16, 3u32, 4u64, -1i8, -2i16, -3i32, -4i64,
0.1f32, 0.2f64, 'a', true);
println!("long tuple first value: {}", long_tuple.0);
println!("long tuple second value: {}", long_tuple.1);
let tuple_of_tuples = ((1u8, 2u16, 2u32), (4u64, -1i8), -2i16);
println!("tuple of tuples: {:?}", tuple_of_tuples);
let pair = (1, true);
println!("pair is {:?}", pair);
println!("the reversed pair is {:?}", reverse(pair));
println!("one element tuple: {:?}", (5u32,));
println!("just an integer: {:?}", (5u32));
let tuple = (1, "hello", 4.5, true);
let (a, b, c, d) = tuple;
println!("{:?}, {:?}, {:?}, {:?}", a, b, c, d);
let matrix = Matrix(1.1, 1.2, 2.1, 2.2);
println!("{:?}", matrix)
}执行结果如下:
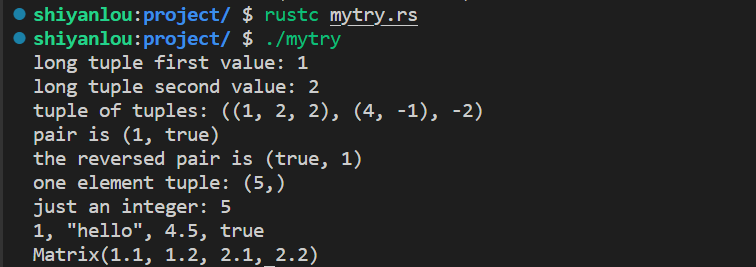
修改代码如下:
rust
fn reverse(pair: (i32, bool)) -> (bool, i32) {
let (integer, boolean) = pair;
(boolean, integer)
}
use std::fmt; // 添加这行
struct Matrix(f32, f32, f32, f32);
// 添加下述代码
impl fmt::Display for Matrix {
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut fmt::Formatter) -> fmt::Result {
write!(f, "({}, {})\n({}, {})", self.0, self.1, self.2, self.3)
}
}
fn main() {
let long_tuple = (1u8, 2u16, 3u32, 4u64, -1i8, -2i16, -3i32, -4i64,
0.1f32, 0.2f64, 'a', true);
println!("long tuple first value: {}", long_tuple.0);
println!("long tuple second value: {}", long_tuple.1);
let tuple_of_tuples = ((1u8, 2u16, 2u32), (4u64, -1i8), -2i16);
println!("tuple of tuples: {:?}", tuple_of_tuples);
let pair = (1, true);
println!("pair is {:?}", pair);
println!("the reversed pair is {:?}", reverse(pair));
println!("one element tuple: {:?}", (5u32,));
println!("just an integer: {:?}", (5u32));
let tuple = (1, "hello", 4.5, true);
let (a, b, c, d) = tuple;
println!("{:?}, {:?}, {:?}, {:?}", a, b, c, d);
let matrix = Matrix(1.1, 1.2, 2.1, 2.2);
println!("{}", matrix)
}结果如下(使用Display将Matrix按行显示):
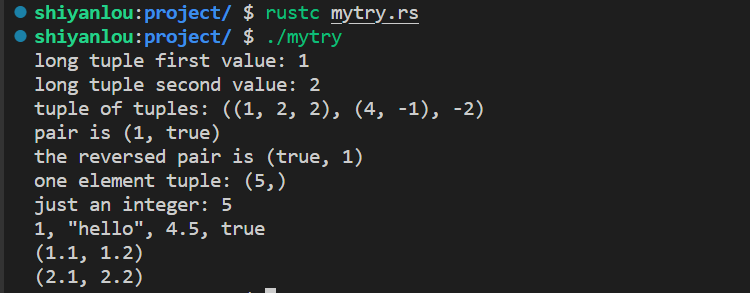
修改代码:
rust
fn reverse(pair: (i32, bool)) -> (bool, i32) {
let (integer, boolean) = pair;
(boolean, integer)
}
// 添加如下代码
fn transpose(matrix: Matrix) -> Matrix {
Matrix(matrix.0, matrix.2, matrix.1, matrix.3)
}
use std::fmt;
struct Matrix(f32, f32, f32, f32);
impl fmt::Display for Matrix {
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut fmt::Formatter) -> fmt::Result {
write!(f, "({}, {})\n({}, {})", self.0, self.1, self.2, self.3)
}
}
fn main() {
let long_tuple = (1u8, 2u16, 3u32, 4u64, -1i8, -2i16, -3i32, -4i64,
0.1f32, 0.2f64, 'a', true);
println!("long tuple first value: {}", long_tuple.0);
println!("long tuple second value: {}", long_tuple.1);
let tuple_of_tuples = ((1u8, 2u16, 2u32), (4u64, -1i8), -2i16);
println!("tuple of tuples: {:?}", tuple_of_tuples);
let pair = (1, true);
println!("pair is {:?}", pair);
println!("the reversed pair is {:?}", reverse(pair));
println!("one element tuple: {:?}", (5u32,));
println!("just an integer: {:?}", (5u32));
let tuple = (1, "hello", 4.5, true);
let (a, b, c, d) = tuple;
println!("{:?}, {:?}, {:?}, {:?}", a, b, c, d);
let matrix = Matrix(1.1, 1.2, 2.1, 2.2);
println!("Matrix:\n{}", matrix); // 修改这行
println!("Transpose:\n{}", transpose(matrix)); // 添加这行
}结果如下:

变量可以显示/后缀声明,整型默认i32,浮点型默认f64
字面量和运算符
字面量相当于变量
Rust运算符的优先级和类C语言类似