linux--实时性优化
- [1 介绍](#1 介绍)
- [2 实时性需求](#2 实时性需求)
- [3 代表性实时系统](#3 代表性实时系统)
- [4 嵌入式系统](#4 嵌入式系统)
- [5 cyclictest 测试工具](#5 cyclictest 测试工具)
- [6 linux 实时性改进](#6 linux 实时性改进)
- 参考
1 介绍
Linux本身为分时操作系统,其系统目标为较好的平均响应时间和较高的吞吐量,而实时系统则主要考虑任务的按量完成、尽量降低进程运行的不可预测性等。
2 实时性需求
AGV、机械臂等机器人,在控制伺服,读取雷达、PGV等传感器数据时,需要一定的实时性。如伺服控制周期要在 10ms 甚至更低,这就需要相应线程工作时,能稳定在相应周期内。
3 代表性实时系统
| 实时系统 | 开源/商业 | 地区 |
|---|---|---|
| μc/os-III | 商业 | 国外 |
| FreeRTOS | 开源 | 国外 |
| Vxworks | 商业 | 国外 |
| RT-Thread | 开源 | 国内 |
| Liteos | 开源 | 国内 |
4 嵌入式系统
嵌入式软件系统结构
目前常见的嵌入式软件结构可以分为轮询系统、前后台系统和多任务系统。
ISR是Interrupt Service Routines的缩写,即中断服务程序。
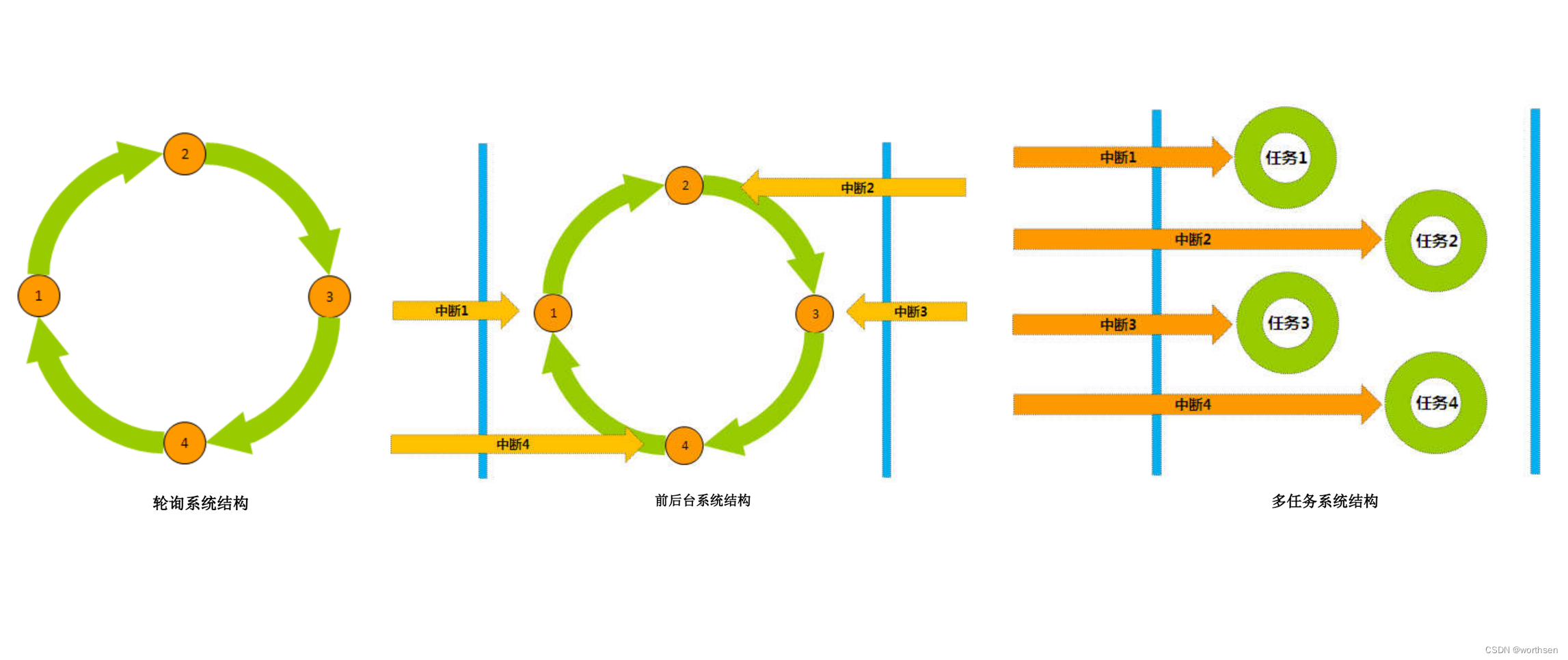
| 模型 | 事件响应 | 事件处理 | 特点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 轮询系统 | 主程序 | 主程序 | 轮询响应事件,轮询处理事件 |
| 前后台系统 | 前台多个中断程 | 后台单个主程序 | 实时响应事件,轮询处理事件 |
| 多任务系统 | 多个中断程序 | 多个任务 | 实时响应事件,实时处理事件 |
处理器时钟节拍
多任务机制
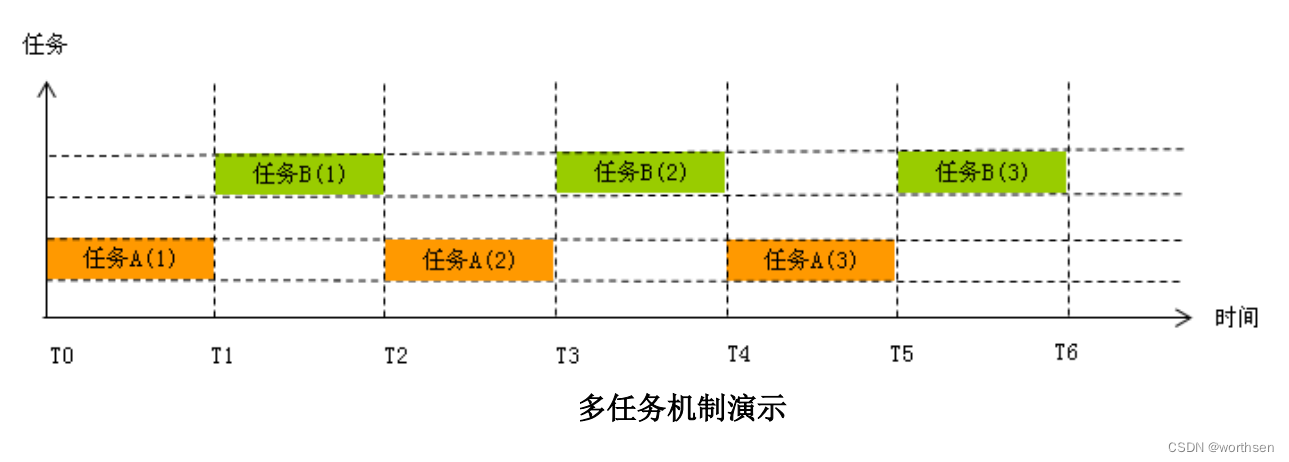
在上图中,任务 A 和任务 B 按照等长时间轮流占用处理器,在单处理器上造成多
个任务同时运行的假象。
任务调度方式
任务调度方式可分为可抢占调度和不可抢占式调度两类。
基于优先级的可抢占式调度的实时性好,任何优先级高的任务只要具备了运行的条
件,即进入了就绪态,就可以立即得到调度和运行。任务在运行过程中都随时可能被比它优先级高的任务抢占。这种方式的任务调度保证了系统的实时性。
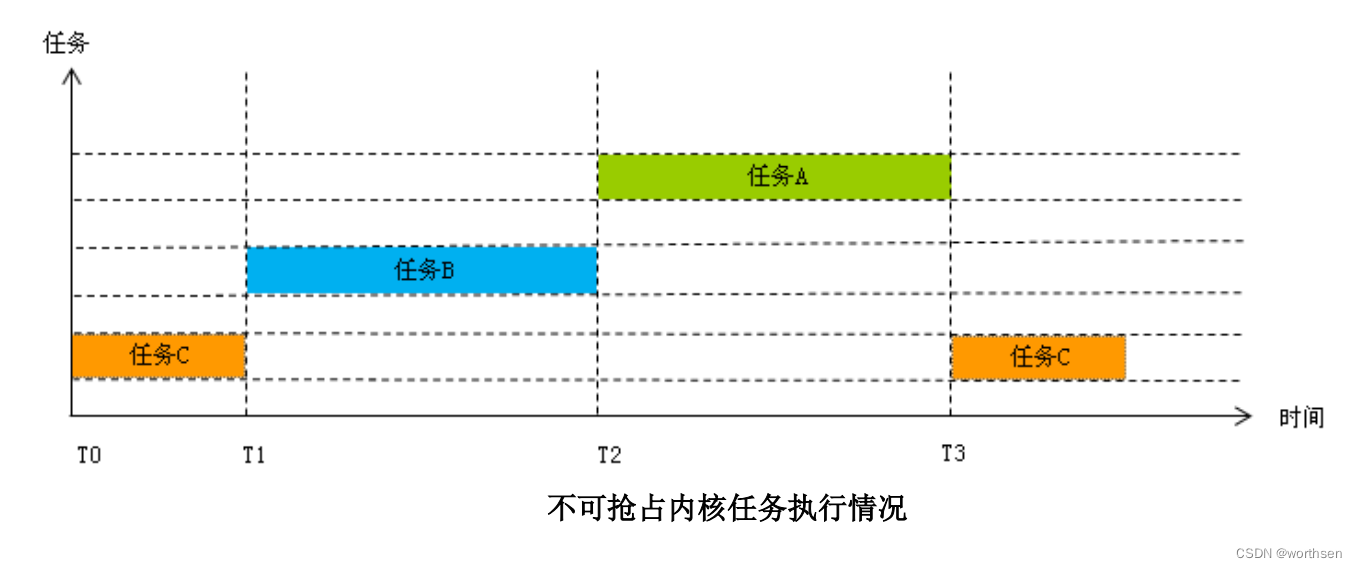
上图演示了不可抢占内核中的任务执行情况。例子中有三个任务需要运行。系统的
执行流程如下:
- T0 时刻任务 C 得到处理器,它开始执行。在它执行过程中,任务 B 和任务 C 就
绪,但是因为内核不支持抢占式调度,所以它们只好等待机会。 - T1 时刻任务 C 完成操作,主动让出处理器。内核选择任务 B 来运行
- T2 时刻任务 B 完成操作,主动让出处理器。内核选择任务 A 来运行
- T3 时刻任务 A 完成操作,主动让出处理器。内核再次选择任务 C 来运行
任务调度算法
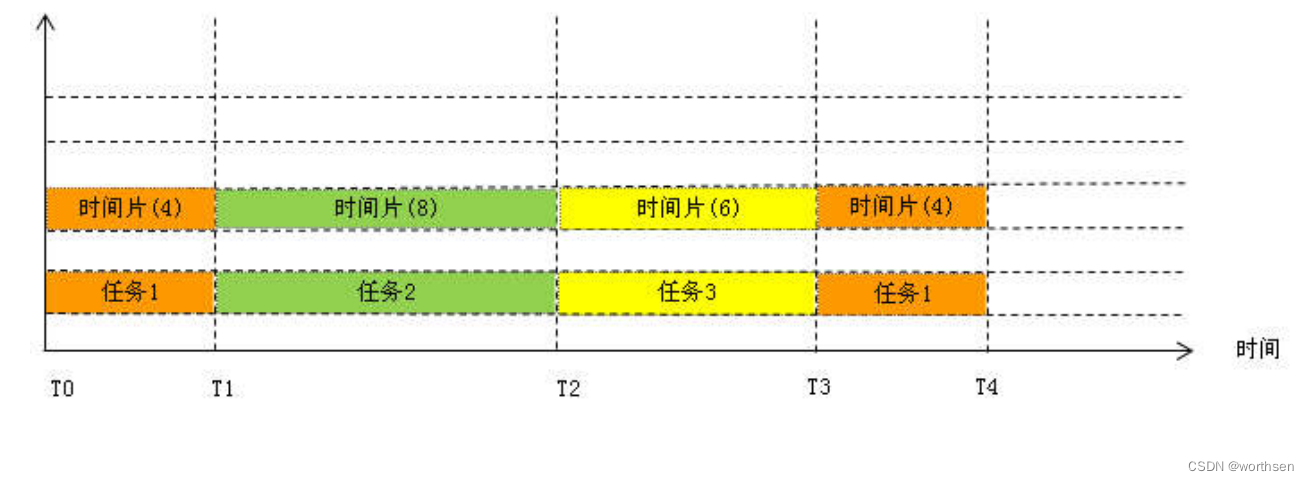
时间片调度算法
指的是内核先让某个任务运行一个时间片(多个时钟节拍),然后再切换给另一个
任务。
缺点:在任务占有处理器的时间段内,即是有更紧急任务就绪,也不能立刻执行它。
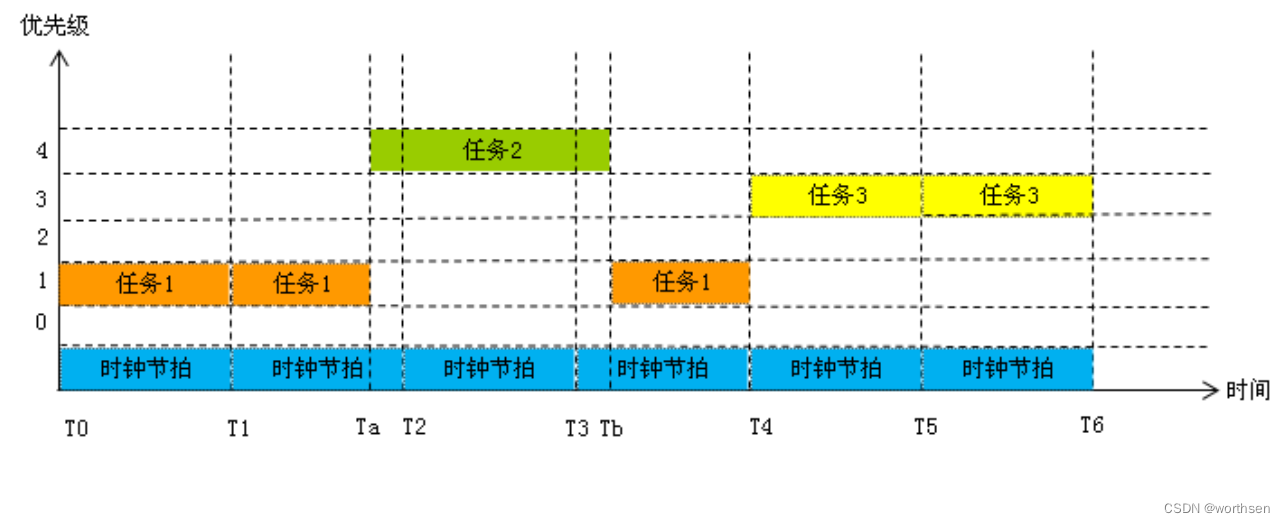
优先级调度算法
指的是内核总是让具有最高优先级的就绪任务优先运行。这种内核最大的提升了系统的实时性。
缺点:当最高优先级任务在运行时,它将持续占有处理器直到任务结束或者阻塞,否则其它任务无法获得运行的机会。
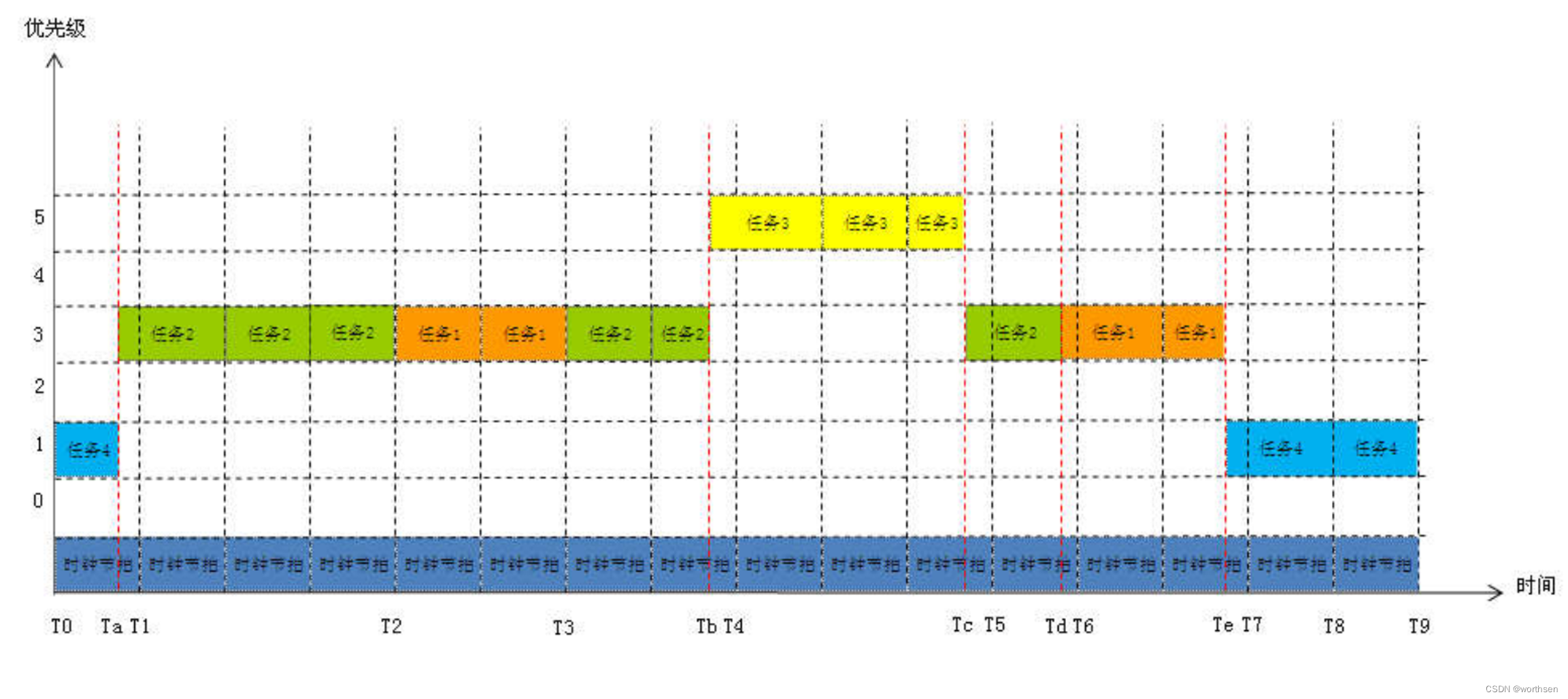
基于优先级的时间片调度算法
吸收了以上两种算法的优点,同时又解决了它们的不足。
这种算法为每个任务都安排了优先级和时间片。在不同优先级的任务间采用优先级调度算法,在相同优先级的任务间使用时间片轮转调度算法。任务调度策略首先考虑任务的优先级,优先级高的任务必定会抢占低优先级的任务。相同优先级的任务则按照时间片长度比例共享处理器时间。
这样既保证了能够尽快响应紧急任务,又保证相优先级的任务都有机会轮流占有处理器。
5 cyclictest 测试工具
可以在centos,ubuntu,加补丁的linux中使用。
命令说明
(base) root@orangepiaipro:/opt/worthsen/rt-tests# ./cyclictest --help
cyclictest V 1.00
Usage:
cyclictest <options>
-a [NUM] --affinity run thread #N on processor #N, if possible
with NUM pin all threads to the processor NUM
-A USEC --aligned=USEC align thread wakeups to a specific offset
-b USEC --breaktrace=USEC send break trace command when latency > USEC
-B --preemptirqs both preempt and irqsoff tracing (used with -b)
-c CLOCK --clock=CLOCK select clock
0 = CLOCK_MONOTONIC (default)
1 = CLOCK_REALTIME
-C --context context switch tracing (used with -b)
-d DIST --distance=DIST distance of thread intervals in us, default=500
-D --duration=TIME specify a length for the test run.
Append 'm', 'h', or 'd' to specify minutes, hours or days.
--latency=PM_QOS write PM_QOS to /dev/cpu_dma_latency
-E --event event tracing (used with -b)
-f --ftrace function trace (when -b is active)
-F --fifo=<path> create a named pipe at path and write stats to it
-h --histogram=US dump a latency histogram to stdout after the run
US is the max latency time to be be tracked in microseconds
This option runs all threads at the same priority.
-H --histofall=US same as -h except with an additional summary column
--histfile=<path> dump the latency histogram to <path> instead of stdout
-i INTV --interval=INTV base interval of thread in us default=1000
-I --irqsoff Irqsoff tracing (used with -b)
-l LOOPS --loops=LOOPS number of loops: default=0(endless)
--laptop Save battery when running cyclictest
This will give you poorer realtime results
but will not drain your battery so quickly
-m --mlockall lock current and future memory allocations
-M --refresh_on_max delay updating the screen until a new max
latency is hit. Userful for low bandwidth.
-n --nanosleep use clock_nanosleep
--notrace suppress tracing
-N --nsecs print results in ns instead of us (default us)
-o RED --oscope=RED oscilloscope mode, reduce verbose output by RED
-O TOPT --traceopt=TOPT trace option
-p PRIO --priority=PRIO priority of highest prio thread
-P --preemptoff Preempt off tracing (used with -b)
--policy=NAME policy of measurement thread, where NAME may be one
of: other, normal, batch, idle, fifo or rr.
--priospread spread priority levels starting at specified value
-q --quiet print a summary only on exit
-r --relative use relative timer instead of absolute
-R --resolution check clock resolution, calling clock_gettime() many
times. List of clock_gettime() values will be
reported with -X
--secaligned [USEC] align thread wakeups to the next full second
and apply the optional offset
-s --system use sys_nanosleep and sys_setitimer
-S --smp Standard SMP testing: options -a -t -n and
same priority of all threads
--spike=<trigger> record all spikes > trigger
--spike-nodes=[num of nodes]
These are the maximum number of spikes we can record.
The default is 1024 if not specified
-t --threads one thread per available processor
-t [NUM] --threads=NUM number of threads:
without NUM, threads = max_cpus
without -t default = 1
--tracemark write a trace mark when -b latency is exceeded
-T TRACE --tracer=TRACER set tracing function
configured tracers: hwlat blk function_graph wakeup_dl wakeup_rt wakeup function nop
-u --unbuffered force unbuffered output for live processing
-v --verbose output values on stdout for statistics
format: n:c:v n=tasknum c=count v=value in us
-w --wakeup task wakeup tracing (used with -b)
-W --wakeuprt rt task wakeup tracing (used with -b)
--dbg_cyclictest print info useful for debugging cyclictest
(base) root@orangepiaipro:/opt/worthsen/rt-tests#命令分析
| 参数 | 完整参数 | 参数含义 |
|---|---|---|
| 常用的基本选项 | ||
| -a | --affinity | 设置测试线程的亲核性,或设置线程的cpuset |
| -A | --aligned=USEC | align thread wakeups to a specific offset |
| -d | --distance=DIST | 当每个CPU上只有一个线程时,建议将它设置为0。若CPU上有多个实时线程,需要设置一个distance用来隔开线程唤醒的时间,distance会累加到interval的值上,默认是500us |
| -D | --duration=TIME --latency=PM_QOS | 指定测试持续事件,可以加单位 'm' 'h' 'd' 分钟 小时 天 write PM_QOS to /dev/cpu_dma_latency |
| -F | --fifo= | 在指定路径下创建一个管道,用来向它写stats |
| -i | --interval=INTV | 线程睡眠的时间,默认是1000us,即实时线程1000us被唤醒一次 |
| -l | --loops=LOOPS --laptop | 循环次数,默认次数是0(无数次),cyclictest运行的时间等于interval×loops,或是--duration=TIME 省电模式运行cyclictest,得到的结果相对不那么realtime。 |
| -m | --mlockall | 将当前和接下来的内存通过mlock锁定,防止发生swap影响测试 |
| -n | --nanosleep --notrace | 使用精度更高的纳秒睡眠api:clock_nanosleep 抑制追踪的行为(因为ftrace会有一定的overhead) |
| -p | --priority=PRIO | 指定实时线程的优先级 |
| 关于timer和时间的选项 | ||
| -c | --clock=CLOCK | 选择时钟类型。默认是=0 0代表CLOCK_MONOTONIC 1代表CLOCK_REALTIME |
| -N | --nsecs | 测试结果使用精度更高的ns显示(默认是us) |
| -r | --relative | 使用相对时间的timer来代替绝对时间的timer |
| -R | --resolution --secaligned [USEC] | check clock resolution. align thread wakeups to the next full second |
| -s | --system | 使用sys_nanosleep()和sys_setitimer()设置定时器 |
| -t | --threads --tracemark | 每个处理器分配一个线程 write a trace mark when -b latency is exceeded |
| -t | --threads=NUM | 指定总线程数,若不指定,线程数等于max_cpus;若不使用-t参数,则线程数为1。 |
| -S | --smp --smi | 标准smp架构测试,所有的线程将使用相同的-a -t -n和优先级 Enable SMI counting |
| 关于输出打印的选项 | ||
| -h | --histogram=US | 测试完成后输出一个直方图,并输出延时小于US的次数统计。 |
| -H | --histofall=US --histfile= | 类似于-h,输出一个柱状图 指定输出文件的路径 |
| -M | --refresh_on_max | delay updating the screen until a new max latency is hit. Userful for low bandwidth. |
| -q | --quiet | 测试结束后再输出结果 |
| -o | --oscope=RED | 使用'示波器'模式,以减少RED冗长的输出信息 |
| -u | --unbuffered | force unbuffered output for live processing |
| -v | -verbose | 把测试信息输出到stdout |
| tracing相关的选项 | ||
| -b | --breaktrace=USEC | 当出现大于USEC的延时后,立即退出测试 |
| -O | --traceopt=TOPT | trace option |
| -T | --tracer=TRACER | (同-b一起使用)用来指定ftrace的tracer类型,例如:function_graph function nop blk |
| -B | --preemptirqs | (同-b一起使用)追踪preempt和irqoff |
| -E | --event | (同-b一起使用)进行event tracing |
| -I | --irqsoff | (同-b一起使用)追踪irqsoff |
| -P | --preemptoff --policy=NAME --priospread | (同-b一起使用)追踪Preempt off 设置实时进程的调度策略:other, normal, batch, idle, fifo or rr. spread priority levels starting at specified value |
| -w | --wakeup | (同-b一起使用)追踪wakeup |
| -f | --ftrace | (同-b一起使用)使用ftrace |
| -C | --context | (同-b一起使用)追踪context switch |
| -W | --wakeuprt --dbg_cyclictest | (同-b一起使用)追踪wakeuprt。 打印cyclictest的调试信息。 |
参数含义
| T | 线程 |
|---|---|
| P | 线程优先级 |
| C | 计数器。线程的时间间隔每达到一次,计数器加1 |
| I | 时间间隔(us) |
| Min | 最小延时(us) |
| Act | 最近一次的延时(us) |
| Avg | 平均延时(us) |
| Max | 最大延时(us) |
6 linux 实时性改进
目前影响Linux内核实时性因素主要有时钟精度、系统中断、进程调度算法和内核可抢占性等。
某版本上发布实时补丁或者内核改造
| 性能 | 直接修改内核 | 直接修改内核 | 双内核 | 双内核 | 双内核 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RT-patch | 其他 | RT-Linux | RTAI | xenomai | |
| 实时性 | 好 | 差 | 好 | 较好 | 较好 |
| 硬件支持 | 较好 | 好 | 一般 | 一般 | 较好 |
| API | 丰富 | 一般 | 一般 | 一般 | 丰富 |
| 维护难度 | 易 | 易 | 难 | 难 | 难 |
| 社区活跃度 | 较好 | 差 | 较差 | 一般 | 良好 |
| 用户态实时任务 | 支持 | 支持 | 不支持 | 支持 | 支持 |
| 内核实时任务 | 不支持 | 不支持 | 支持 | 支持 | 支持 |
打补丁【RT-patch】
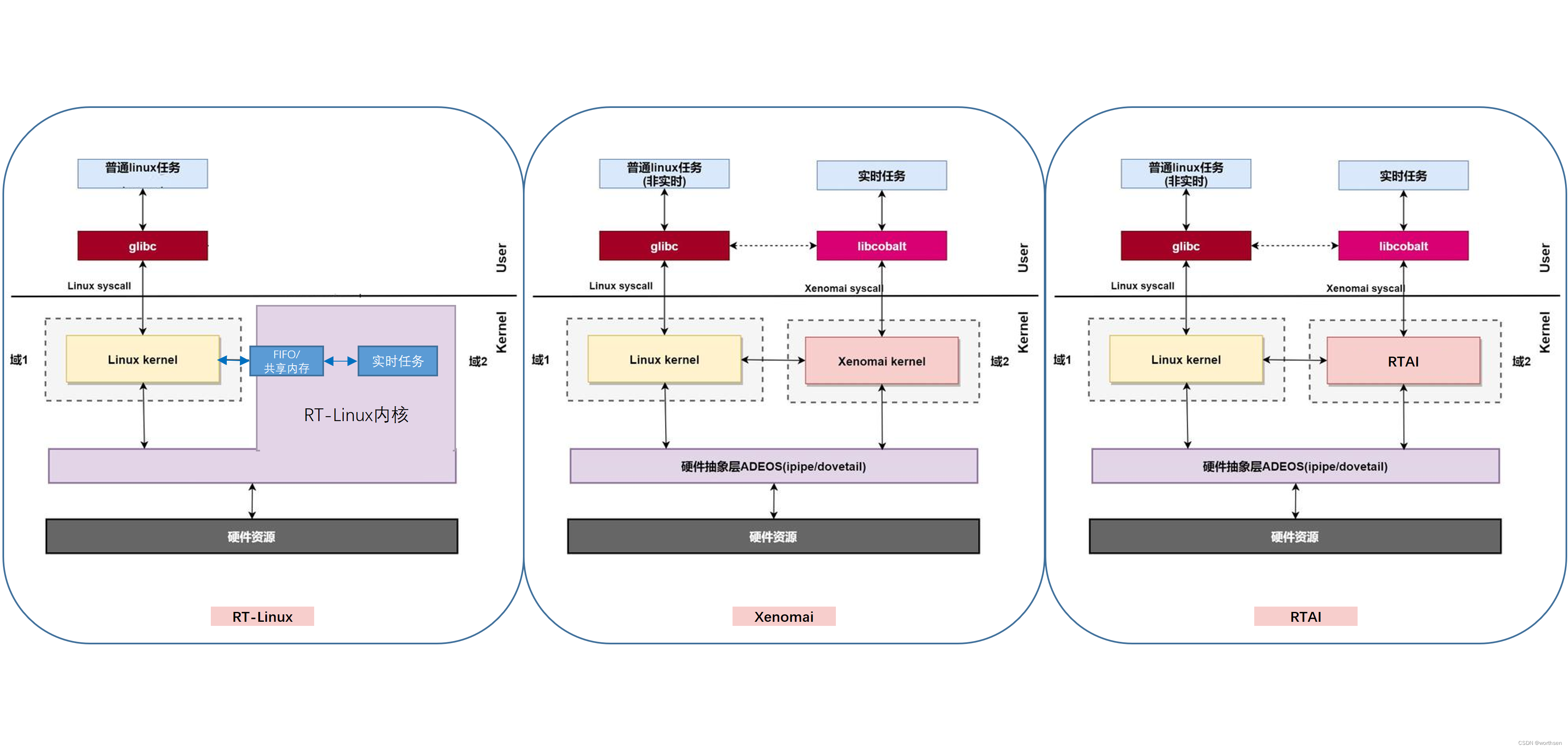
双内核【RT-Linux、RTAI、Xenomai】
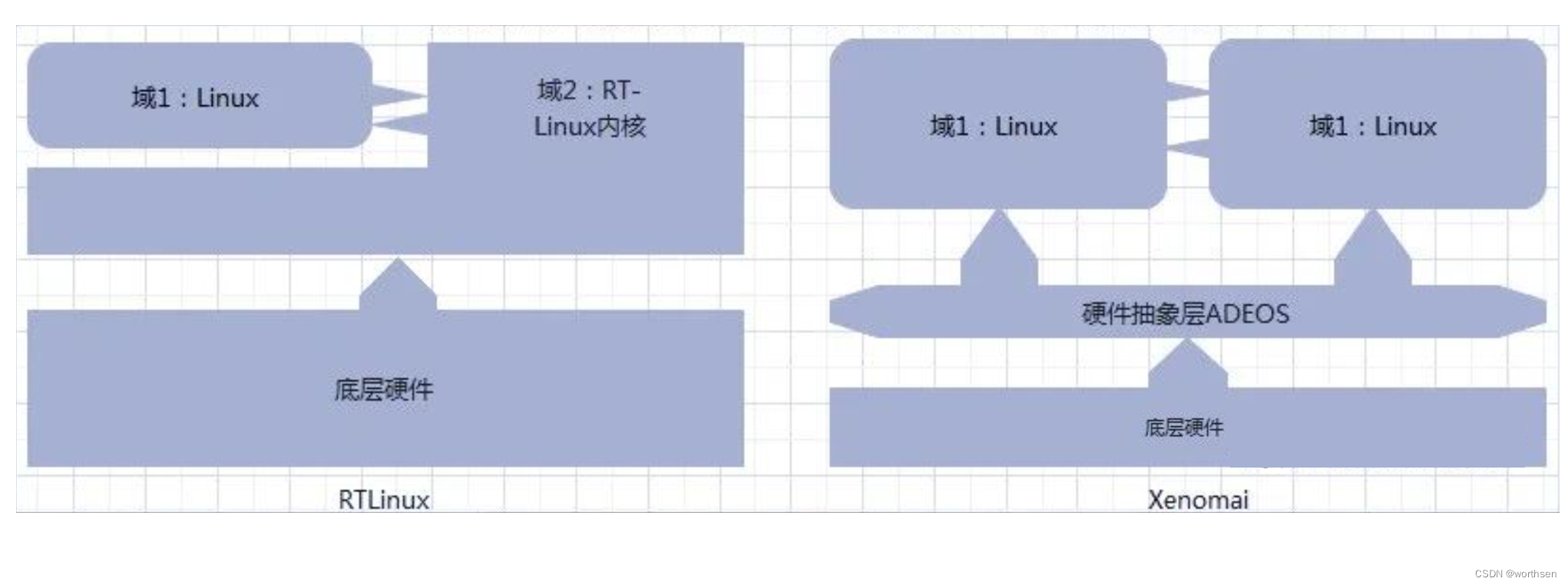
代表有RT-Linux、RTAI(Real-Time Application Interface)和Xenomai。
-
RT-Linux(Real-Time Linux)【停止更新】
采用了双内核的做法。简单理解就是系统中存在两个内核,实时核和非实时核。底层硬件资源和实时的内核打交道绕开非实时核,来自硬件的中断源由实时核全面接管,
-
Xenomai【更新中】
借鉴了RT-Linux的双内核做法,内部也有实时核和非实时核。但不同的是Xenomai在底层硬件和两个内核之间还加了一层硬件抽象层ADEOS(Adoptive Domain Environment for Operating System),实时核和非实时核作为硬件抽象层的两个域而存在,Xenomai内核属于实时域,Linux内核属于非实时域。ADEOS在系统的关键路径中对中断进行拦截,优先响应Xenomai实时域的中断,当没有实时任务和中断需要处理的时候才会轮到Linux内核执行。两者对比如下。
-
RTAI
同样借鉴RT-Linux。
时钟精度调整
提升时钟精度,系统中的调度会加快,优点是进程的响应提高,缺点进程切换开销增加,要根据具体使用场景来评估合理性。
中断调整
RTOS和Linux中,硬件中断的响应优先级永远是最高的。
OrangePi AIpro(8T) 开发板【昇腾310B4】查看系统的所有中断
cat /proc/interrupts
(base) root@orangepiaipro:~# cat /proc/interrupts
CPU0 CPU1 CPU2 CPU3
9: 0 0 0 0 GICv3 25 Level vgic
11: 0 0 0 0 GICv3 30 Level kvm guest ptimer
12: 0 0 0 0 GICv3 27 Level kvm guest vtimer
13: 4728702 1741435 1607592 1272102 GICv3 26 Level arch_timer
14: 1 0 0 0 GICv3 201 Level uart-pl011
15: 0 0 0 0 GICv3 298 Level c42e0000.watchdog
18: 0 0 0 0 GICv3 23 Level arm-pmu
19: 1 0 0 0 GICv3 319 Edge APEI:HED
20: 0 0 0 0 GICv3 177 Level gpio
21: 0 0 0 0 GICv3 178 Level gpio
22: 0 0 0 0 GICv3 179 Level gpio
23: 0 0 0 0 GICv3 181 Level gpio
24: 0 0 0 0 GICv3 182 Level gpio
25: 0 0 0 0 GICv3 183 Level gpio
26: 0 0 0 0 GICv3 249 Edge hns3-a7100000.xge0-TxRx-0
27: 0 0 0 0 GICv3 250 Edge hns3-a7100000.xge0-TxRx-2
28: 0 0 0 0 GICv3 251 Edge hns3-a7100000.xge0-TxRx-4
29: 0 0 0 0 GICv3 252 Edge hns3-a7100000.xge0-TxRx-6
42: 0 0 0 0 GICv3 265 Level hnsplf-abn-a7100000.xge0
43: 1 0 0 0 GICv3 269 Level hnsplf-mac-a7100000.xge0
44: 0 0 0 0 GICv3 241 Level hnsplf-rtc-a7100000.xge0
54: 5 0 0 0 GICv3 133 Level dvpp_ipcm0
55: 0 0 0 0 GICv3 134 Level dvpp_ipcm1
56: 0 0 0 0 GICv3 135 Level dvpp_ipcm2
58: 0 0 0 0 GICv3 286 Level MIPI_RX
59: 0 0 0 0 GICv3 291 Level SLVS_EC
60: 8 0 0 0 GICv3 290 Level tc_ns_client
61: 0 0 0 0 GICv3 279 Level hisi-i2c
62: 0 0 0 0 GICv3 280 Level hisi-i2c
63: 0 0 0 0 GICv3 281 Level hisi-i2c
64: 0 0 0 0 GICv3 282 Level hisi-i2c
65: 158 0 0 0 GICv3 185 Level hisi-i2c
66: 0 0 0 0 GICv3 186 Level hisi-i2c
67: 0 0 0 0 GICv3 187 Level hisi-i2c
68: 27 0 0 0 GICv3 188 Level hisi-i2c
69: 448 0 0 0 GICv3 189 Level hisi-i2c
70: 0 0 0 0 GICv3 192 Level hisi-i2c
71: 0 0 0 0 GICv3 193 Level 82020000.spi0
72: 0 0 0 0 GICv3 194 Level 82030000.spi1
73: 0 0 0 0 GICv3 283 Level 3001b0000.spi3
74: 0 0 0 0 GICv3 284 Level 3001c0000.spi4
75: 0 0 0 0 GICv3 195 Level c40b0000.spi5
80: 0 0 0 0 ITS-pMSI 75776 Edge arm-smmu-v3-evtq
81: 0 0 0 0 ITS-pMSI 75777 Edge arm-smmu-v3-gerror
82: 0 0 0 0 ITS-pMSI 77824 Edge arm-smmu-v3-evtq
83: 0 0 0 0 ITS-pMSI 77825 Edge arm-smmu-v3-gerror
84: 0 0 0 0 ITS-pMSI 79872 Edge arm-smmu-v3-evtq
85: 0 0 0 0 ITS-pMSI 79873 Edge arm-smmu-v3-gerror
86: 0 0 0 0 ITS-pMSI 81920 Edge arm-smmu-v3-evtq
87: 0 0 0 0 ITS-pMSI 81921 Edge arm-smmu-v3-gerror
88: 0 0 0 0 ITS-pMSI 83968 Edge arm-smmu-v3-evtq
89: 0 0 0 0 ITS-pMSI 83969 Edge arm-smmu-v3-gerror
90: 0 0 0 0 ITS-pMSI 86016 Edge arm-smmu-v3-evtq
91: 0 0 0 0 ITS-pMSI 86017 Edge arm-smmu-v3-gerror
92: 0 0 0 8 mbigen-v2 916 Level mmc0
93: 48205 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 917 Level mmc1
95: 0 1 0 0 ITS-MSI 0 Edge PCIe PME, aerdrv, pciehp
96: 0 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 699 Level mailbox-0-lp-rx-acpu0
97: 0 0 0 3089 mbigen-v2 700 Level mailbox-1-lp-rx-acpu1
98: 69 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 701 Level mailbox-2-lp-rx-acpu2
99: 0 5 0 0 mbigen-v2 702 Level mailbox-3-lp-rx-acpu3
100: 0 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 628 Level ts_ipc_done_interrupt
101: 0 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 629 Level ts_ipc_done_interrupt
102: 0 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 630 Level ts_ipc_done_interrupt
103: 0 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 631 Level ts_ipc_done_interrupt
104: 0 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 632 Level ts_ipc_done_interrupt
105: 0 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 633 Level ts_ipc_done_interrupt
106: 0 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 634 Level ts_ipc_done_interrupt
107: 0 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 635 Level ts_ipc_done_interrupt
108: 0 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 636 Level mailbox-8-ts-rx-acpu0
109: 0 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 637 Level mailbox-9-ts-rx-acpu1
110: 0 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 638 Level mailbox-10-ts-rx-acpu2
111: 0 5 0 0 mbigen-v2 639 Level mailbox-11-ts-rx-acpu3
112: 0 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 594 Level irq_route_to_ts
113: 0 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 595 Level irq_route_to_ts
114: 0 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 596 Level irq_route_to_ts
115: 0 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 597 Level irq_route_to_ts
116: 0 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 598 Level irq_route_to_ts
117: 0 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 599 Level irq_route_to_ts
118: 0 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 600 Level irq_route_to_ts
119: 0 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 601 Level irq_route_to_ts
120: 0 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 602 Level irq_route_to_ts
121: 0 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 603 Level irq_route_to_ts
122: 0 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 604 Level irq_route_to_ts
123: 0 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 605 Level irq_route_to_ts
124: 0 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 606 Level irq_route_to_ts
125: 0 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 607 Level irq_route_to_ts
126: 0 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 608 Level sq_trigger
127: 15 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 609 Level trs-mbox-0-0
128: 1551 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 610 Level maint_cq
132: 0 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 614 Level cqe_done
138: 0 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 620 Level topic_sched_ccpu
141: 0 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 623 Level topic_sched_aicpu
146: 0 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 934 Level VI_CAP0
147: 0 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 935 Level VI_PROC0
148: 0 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 936 Level VPSS
155: 0 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 663 Level VEDU_0
156: 0 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 665 Level VEDU_1
160: 0 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 831 Level VGS
161: 0 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 830 Level GDC
162: 0 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 590 Level asp_dma_irq
163: 0 0 0 0 mbigen-v2 918 Level xhci-hcd:usb1
164: 0 695298 0 0 mbigen-v2 922 Level xhci-hcd:usb3
165: 0 0 1152 0 mbigen-v2 926 Level xhci-hcd:usb5
166: 0 190 0 0 mbigen-v2 930 Level xhci-hcd:usb7
167: 0 0 0 0 gpio-dwapb 2 Edge drv_power_off
168: 0 0 568143 0 mbigen-v2 910 Level DRM_0
IPI0: 753334 324877 530484 343726 Rescheduling interrupts
IPI1: 1424 6291 6018 12370 Function call interrupts
IPI2: 0 0 0 0 CPU stop interrupts
IPI3: 0 0 0 0 CPU stop (for crash dump) interrupts
IPI4: 0 0 0 0 Timer broadcast interrupts
IPI5: 0 0 0 0 IRQ work interrupts
IPI6: 0 0 0 0 CPU wake-up interrupts
IPI7: 0 0 0 0 User function call interrupts
Err: 0
(base) root@orangepiaipro:~#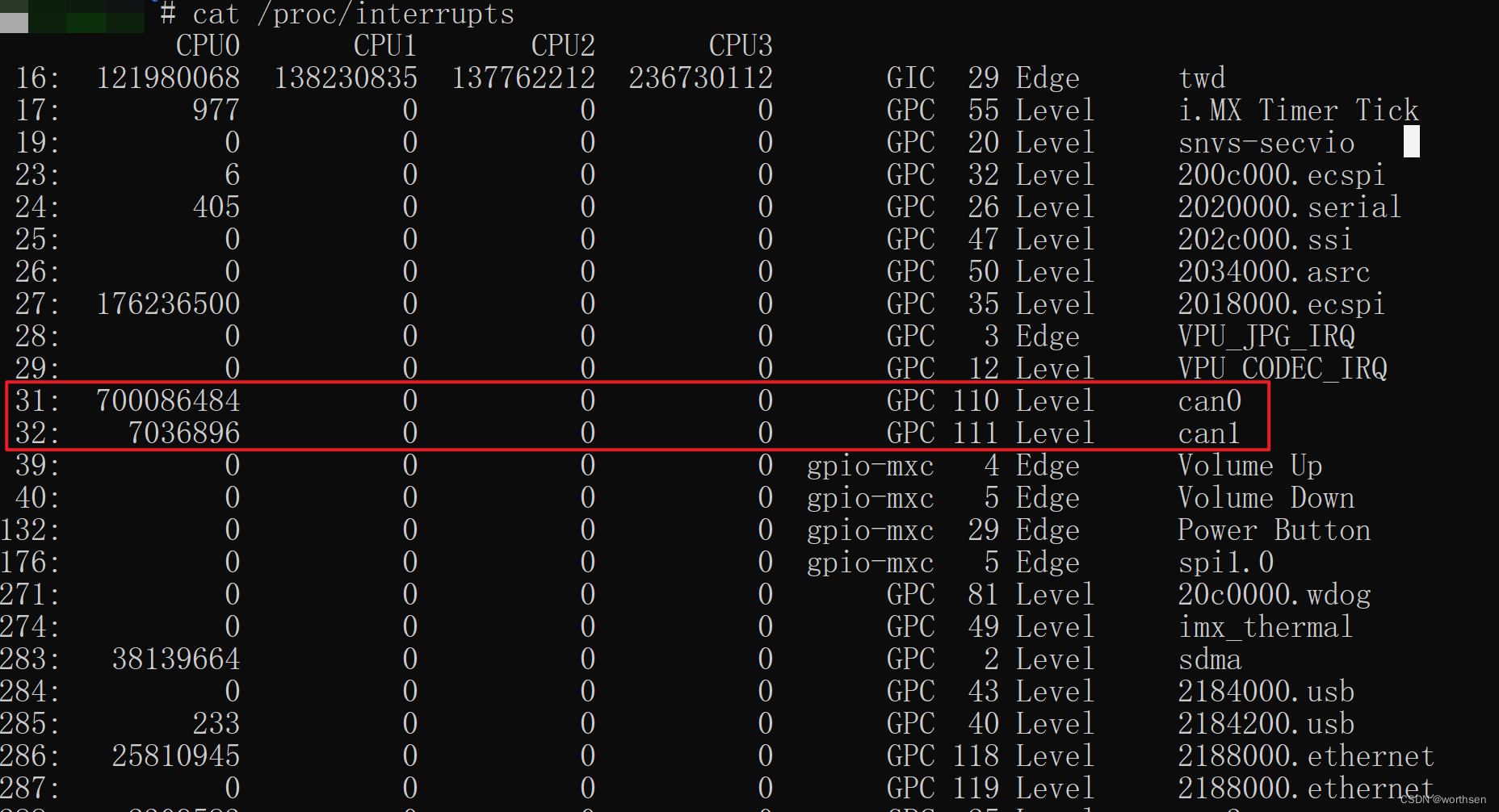
将某中断绑定到某CPU
echo "1" > /proc/irq/30/smp_affinity进程调度算法
Linux系统目前默认采用的是完全公平调度算法(CFS),它按照各个进程的权重来分配运行时间。
使用CFS的情况下,我们可以给有实时性需求的进程分配更高的优先级和权重。
Linux内核目前支持的调度类有:stop、deadline、realtime、CFS、idle。、它们的优先级依次由高到底排序。
deadline调度类包含如下调度策略:
- SCHED_DEADLINE
realtime调度类包含如下调度策略:
- SCHED_FIFO
- SCHED_RR
CFS调度类包含如下调度策略:
- SCHED_NORMAI
- SCHED_BATCH
- SCHED_IDLE
其他策略,绑核
如果核多,可以将实时性要求高的进程绑核。
参考
3、嵌入式Linux实时系统的特点和Linux内核在实时应用方面的不足
6、开源IgH EtherCAT主站方案,基于IMX8、ZYNQ、AM335x、T3等平台