【问】如何描述一个字符设备?
dev结构体
其中需要关心三个成员变量:
所属模块 :struct module *owner;
文件操作结构体: const struct file_operations *ops
设备号 : dev_t
当应用层使用指令open("/dev/hello", HELLO),系统就会进入驱动程序中执行cdev_open函数
【问】 如何连接系统调用open和驱动程序dev_open函数
file_operations结构体中就将这两个函数进行连接:
cs
static struct file_operations cdev_ops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE;
.open = cdev_open;
}【问】应用程序和驱动程序的桥梁是什么?
设备节点,设备节点创建在/dev目录下。
比如 open("/dev/hello" ,HELLO);
【问】如何创建设备节点?
使用udev机制,在注册设备的时候自动创建,在注销设备的时候自动销毁。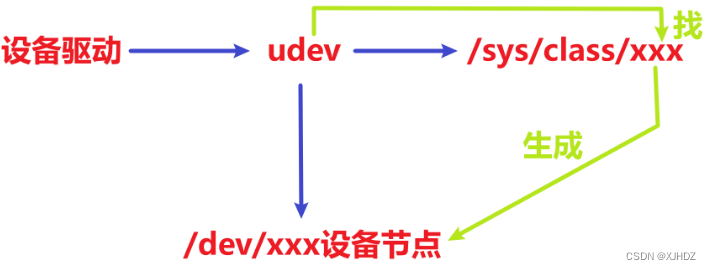
1.创建类:
class_creat(struct module *owner ,const char *name)
THIS_MODULE 和 类的名字
对应删除:class_destroy(struct class *cls) 类
2.在类下创建设备:
device_creat(struct class *cls ,struct device *parent, dev_t devt , NULL ,const char *fmt )
1.哪个类 2.父设备是谁? NULL一般 3.设备号 4.NULL 5.设备节点的名字
3.删除类:
device_destroy(struct class *cls, dev_t devt)
类 设备号
【注册字符设备模版 】
cs
static int major = 0;
static int minor = 0;
module_param(major ,int ,S_IRUGO);
module_param(minor ,int ,S_IRUGO);
dev_t dev_num;
static int cdev_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
printk("cdev_open success\n");
return 0;
}
static ssize_t cdev_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t cnt, loff_t *offt)
{
printk("cdev_read success\n");
return 0;
}
static ssize_t cdev_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t cnt, loff_t *offt)
{
printk("cdev_write success\n");
return 0;
}
static int cdev_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
printk("cdev_release success\n");
return 0;
}
struct file_operations cdev_file_operations = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE;
.open = cdev_open;
.read = cdev_read;
.write = cdev_write;
.release = cdev_release;
}
struct cdev cdev_test;
static int moduleparam_init()
{
int ret;
/* 动态申请 */
ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&dev_num,0,1);
if(ret<0)
{
printk("alloc_chrdev_region error\n");
}
//动态注册设备号成功,则打印
printk("alloc_chrdev_region ok\n");
major_num =MAJOR(dev_num); //将主设备号取出来
minor_num = MINOR(dev_num);//将次设备号取出来
printk("major_num = %d\n",major_num);//打印传入进来的主设备号
printk("minor_num = %d\n",minor_num);//打印传入进来的次设备号
cdev_test.owner = THIS_MODULE;
cdev_init(cdev_test, cdev_file_operations);
cdev_add(&cdev_test, dev_num, 1);
class = class_creat(THIS_MODULE, "test");
device = device_creat(class,NULL,dev_num,,NULL,"/dev/test")
return 0;
}
static void hello_exit(void)
{
unregister_chrdev_region(MKDEV(major_num,minor_num),DEVICE_NUMBER);//注销设备号
cdev_del(&cdev_test); //销毁字符设备
device_destroy(class,dev_num);
class_destroy(class);
printk("gooodbye! \n");
}
module_init(moduleparam_init);
module_init(moduleparam_exit);【应用程序验证】
cs
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int fd;
char buf[64] = 0;
fd = open("/dev/test", HELLO); /* 打开设备节点 */
close(fd);
return 0;
}【问】app.c如何编译?
使用3568开发板对应的交叉编译器
linux源码 / prebuilts /gcc /linux-x86 / aarch64 / gcc ..............................
然后进入bin文件夹找到 gnu - gcc
编译命令:
进入app.c目录:
交叉编译器的绝对路径 加 / 交叉编译器的名字 加 app.c
生成a.out文件
拷贝 a.out 和 file .ko 文件进开发板
加载:insmod file.ko
手动创建设备节点 : mknod /dev/test c 2350 (设备名字和驱动中一致)
(在dev/test中可以看到设备节点)
执行 a.out 应用程序: ./a.out
成功调用,打印出驱动中的这两句话:

实验效果:
加载:insmod file.ko
因为是自动创建设备节点,所以ls /dev/test直接看
执行:./a.out
---------------------------------------------
-----------------------打印出打开设备和卸载设备信息