数据结构进阶------并查集
- [1. 并查集的原理](#1. 并查集的原理)
- [2. 并查集的实现](#2. 并查集的实现)
- [3. 练习题](#3. 练习题)
-
- [3.1 省份的数量](#3.1 省份的数量)
- [3.2 等式方程的可满足性](#3.2 等式方程的可满足性)
1. 并查集的原理
1. 什么是并查集:
- 在一些应用问题中,需要将n个不同的元素划分成一些不相交的集合。开始时,每个元素自成一个单元素集合,然后按一定的规律将归于同一组元素的集合合并 。在此过程中要反复用到查询某一个元素归属于那个集合的运算 。适合于描述这类问题的抽象数据类型称为并查集(union-find set)。
2. 并查集的原理:
- 假设现在有一个10个人的小班,郑州的4人,上海的3人,北京的3人。起初每个人都互相不认识,各自为一个独立的小团体。现在给这些学生进行编号:
{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}。用以下数组来存储这些小团体,数组下标对应每一个不同的人,下标对应的值的绝对值表示每一个小集体中的人数(至于为什么要存负数我们到后面慢慢体会):
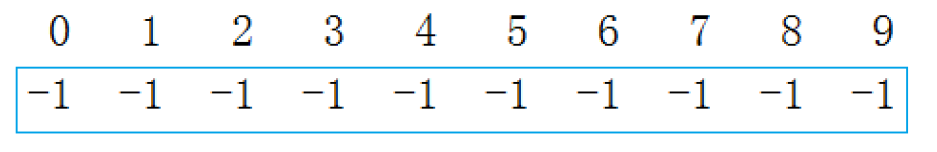
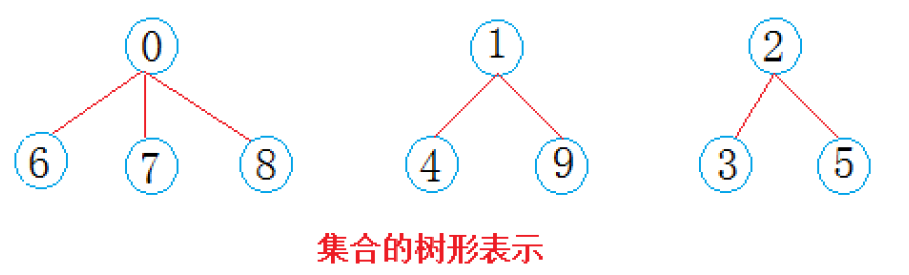
- 后来,同一个城市的人玩到了一起,形成了三个小团体,郑州小分队
s1 = {0, 6, 7, 8},上海小分队s2 = {1, 4, 9},北京小分队s3 = {2, 3, 5}。每一个小团体中都有一个队长,我们假设是编号小的人当队长(其实谁当队长都可以):
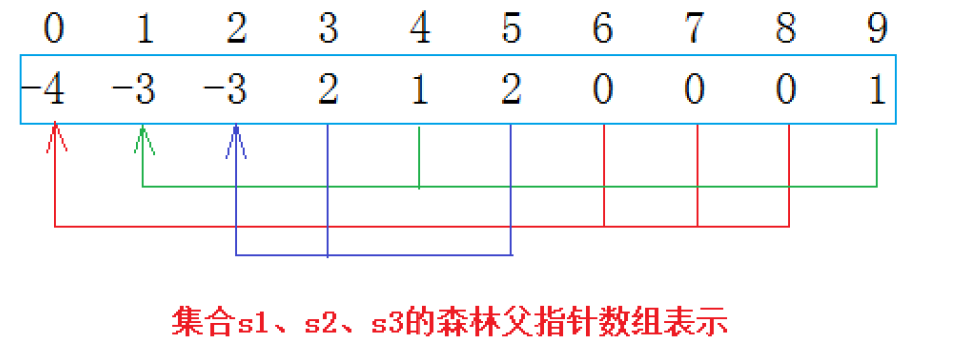
- 将上述关系存储在数组中:
- 数组的下标对应集合中每个人的编号;
- 数组中如果为负数,负号代表根,也就是队长,数值部分代表该小团体中的人数;
- 数组中如果为非负数,代表此人所在小团体的队长在数组中的下标。
- 在一起相处一段时间后,郑州小分队的8号同学,和上海小分队的1号同学玩到了一起,于是郑州小分队和上海小分队合并成了一个大分队:
- 将其用数组形式表示,先找到8号同学所在小分队的队长,和1号同学所在小分队的队长;
- 判断8号同学和1号同学小分队的队长是否是同一个人(判断是否已经是同一分队),是的话就不做处理;不是的话,就让任意一个小分队的队长,成为另一个小分队的队员即可;
- 注意要更新新大分队的人数,只需要让两个小分队的人数相加即可得到大分队的人数。

3. 路径压缩(建议看完实现再来看路径压缩):
- 一般在数据量非常大,或者某些对性能极致追求的场景中,会用到路径压缩;平时几乎用不上,用了就是给自己找麻烦,这里简单介绍一下思路,感兴趣的同学可以手动实现。
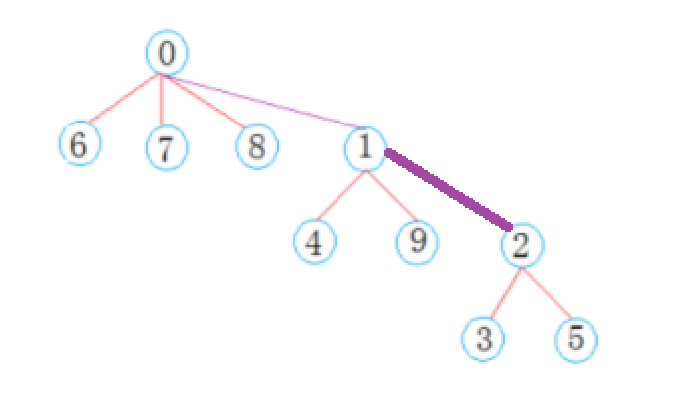
- 找某一个元素的根时,可能出现路径太长,耗时严重的情况。比如上面这个集合,我们想找5的根,就要找3次。先找到2,再找到1,最后才找到0。
- 所谓路径压缩,就是将路径变短,例如可以把5节点直接链接在0节点下。
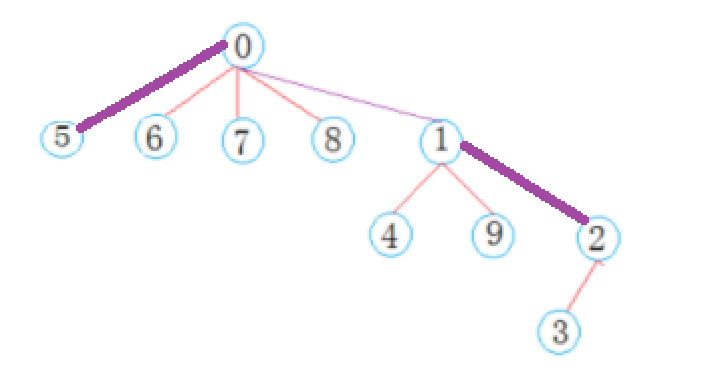
- 建议在
FindRoot函数内实现路径压缩,即在找的时候顺便压缩了。比如我们在上面这棵树中,找3节点的根,得到的路径是{3, 2, 1, 0},我们就可以记录这个路径,然后将这条路径上的所有节点,都连接到0节点下,完成路径压缩。 - 找哪个节点的根,顺带压缩一下它的路径,这样下次找的时候就快了。
4. 通过以上例子可知,并查集一般可以解决以下问题:
- 查找元素属于哪个集合。
- 沿着数组表示树形关系往上一直找到根(即树中中元素为负数的位置)。
- 查看两个元素是否属于同一个集合。
- 沿着数组表示的树形关系往上一直找到树的根,如果根相同表明在同一个集合,否则不在。
- 将两个集合归并成一个集合。
- 将两个集合中的元素合并;
- 将一个集合名称改成另一个集合的名称。
- 集合的个数。
- 遍历数组,数组中元素为负数的个数即为集合的个数。
2. 并查集的实现
1. 带映射关系的并查集:
- 实际应用中,可能我们更多的是拿到一个字符串数组,比如人员名单。我们需要根据这份人员名单,建立一个人名与编号的映射关系,即可以通过人名快速找到编号,也可以通过编号快速找到对应的人。
cpp
template<class T>
class UnionFindSet
{
public:
UnionFindSet(const vector<T>& a, size_t n)
:_ufs(n, -1) // vector的初始化,开n个空间,并且全部初始化为-1
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
_a.push_back(a[i]);
_indexMap[a[i]] = i;
}
}
// 返回队长名字
string FindRoot(const string& person)
{
int index = _indexMap[person];
while (_ufs[index] >= 0)
{
index = _ufs[index];
}
return _a[index];
}
// 集合的合并操作
void Union(const string& person1, const string& person2)
{
string root1 = FindRoot(person1);
string root2 = FindRoot(person2);
if (root1 != root2)
{
int index1 = _indexMap[root1];
int index2 = _indexMap[root2];
// 保证编号小的成为队长
if (index1 > index2)
swap(index1, index2);
_ufs[index1] += _ufs[index2];
_ufs[index2] = index1;
}
}
// 返回集合数量
size_t SetCount()
{
size_t count = 0;
for (auto e : _ufs)
{
if (e < 0)
count++;
}
return count;
}
private:
vector<int> _ufs; // 数组表示的集合
vector<T> _a; // 编号找人
map<string, int> _indexMap; // 人找编号
};2. 不带映射关系的简化版并查集:
- 平常大家做OJ题时,大概率用到是这种,及给你的就是正数数组,映射关系已经给好了。
cpp
class UnionFindSet
{
public:
UnionFindSet(size_t size)
: _ufs(size, -1)
{}
// x是元素的编号
size_t FindRoot(int x)
{
while (_ufs[x] >= 0)
{
x = _ufs[x];
}
return x;
}
void Union(int x1, int x2)
{
int root1 = FindRoot(x1);
int root2 = FindRoot(x2);
if (root1 != root2)
{
if (root1 > root2)
swap(root1, root2);
_ufs[root1] += _ufs[root2];
_ufs[root2] = root1;
}
}
size_t SetCount()
{
size_t count = 0;
for (auto e : _ufs)
{
if (e < 0)
{
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
private:
vector<int> _ufs;
};3. 练习题
3.1 省份的数量
1. leedcode链接:
2. 分析:
- a和b连通,b又和c连通,说明a也和c连通。即a和b是一个小团体,b和c是一个小团体,现在b和c又玩的好了,大家形成了一个大团体。这种问题完全可以用并查集解决。
3. 第一种解决方式,手撕并查集类:
cpp
class UnionFindSet
{
public:
UnionFindSet(size_t size)
: _ufs(size, -1)
{}
// x是元素的编号
size_t FindRoot(int x)
{
while (_ufs[x] >= 0)
{
x = _ufs[x];
}
return x;
}
void Union(int x1, int x2)
{
int root1 = FindRoot(x1);
int root2 = FindRoot(x2);
if (root1 != root2)
{
if (root1 > root2)
swap(root1, root2);
_ufs[root1] += _ufs[root2];
_ufs[root2] = root1;
}
}
size_t SetCount()
{
size_t count = 0;
for (auto e : _ufs)
{
if (e < 0)
{
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
private:
vector<int> _ufs;
};
class Solution {
public:
int findCircleNum(vector<vector<int>>& isConnected)
{
UnionFindSet ufs(isConnected.size());
for (int i = 0; i < isConnected.size(); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < isConnected[i].size(); j++)
{
if (isConnected[i][j] == 1)
{
ufs.Union(i, j);
}
}
}
return ufs.SetCount();
}
};4. 第二种解决方式,不封装,只手撕功能:
cpp
class Solution {
public:
int findCircleNum(vector<vector<int>>& isConnected)
{
vector<int> ufs(isConnected.size(), -1);
auto findRoot = [&ufs](int x)
{
while (ufs[x] >= 0)
{
x = ufs[x];
}
return x;
};
for (int i = 0; i < isConnected.size(); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < isConnected[i].size(); j++)
{
if (isConnected[i][j] == 1)
{
int root1 = findRoot(i);
int root2 = findRoot(j);
if (root1 != root2)
{
ufs[root1] += ufs[root2];
ufs[root2] = root1;
}
}
}
}
int n = 0;
for (auto e : ufs)
{
if (e < 0)
++n;
}
return n;
}
};3.2 等式方程的可满足性
1. leedcode链接:
2. 分析:
=号是具有传递性的,如果a = b,b = c,那么说明a = c。如果这时出现了一个a != c,肯定就要返回false了。- 所以我们的思路就是,先将相等的字母,全部放到一个集合中;再去判断不相等的字母,有没有出现在相等字母的集合中,如果出现了,就返回
false,没有就返回true。 - 我们直接用一个从0到25的数组,来对字母
a到z做映射。
cpp
class Solution {
public:
bool equationsPossible(vector<string>& equations)
{
vector<int> ufs(26, -1); // 26个英文字母,从a到z编号为0到25
auto findRoot = [&ufs](int x)
{
while (ufs[x] >= 0)
{
x = ufs[x];
}
return x;
};
// 先把相等的值加到一个集合中
for (auto& str : equations)
{
if (str[1] == '=')
{
int root1 = findRoot(str[0] - 'a');
int root2 = findRoot(str[3] - 'a');
if (root1 != root2)
{
ufs[root1] += ufs[root2];
ufs[root2] = root1;
}
}
}
// 看看不相等的在不在一个集合,在就相悖了,返回false
for (auto& str : equations)
{
if (str[1] == '!')
{
int root1 = findRoot(str[0] - 'a');
int root2 = findRoot(str[3] - 'a');
if (root1 == root2)
{
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
};