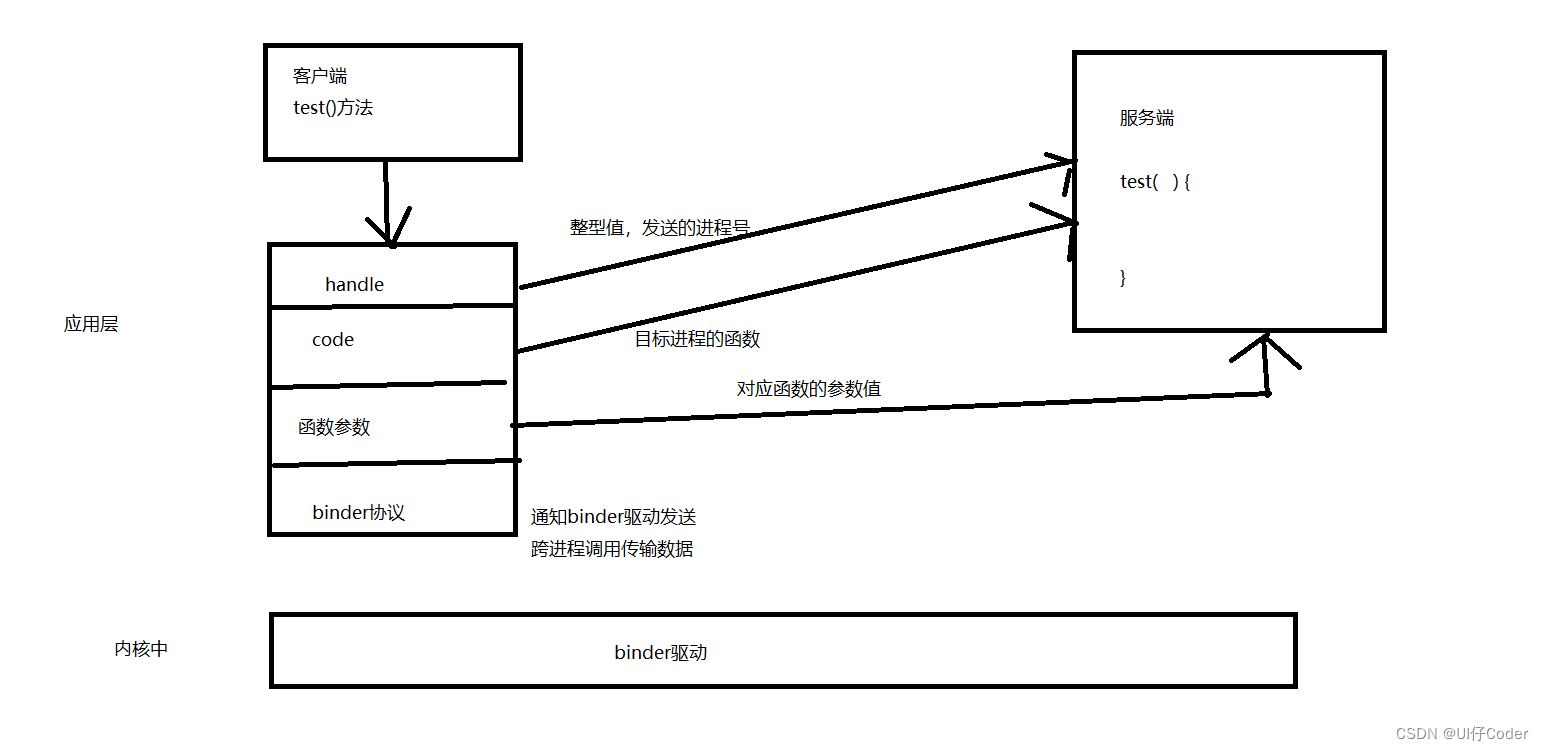
RPC原理图
Binder C语言层的Demo演示
新建目录
把两个文件拷贝到我们的Demo下面
1.binder_server.c
c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "binder.h"
#define LOG_TAG "BinderServer"
#include <log/log.h>
#define HELLO_BINDER 1
#define HELLO_BINDER_TO 2
//服务就是被调用的函数
void hellobinder(void)
{
static int cnt = 0;
ALOGW("hello : %d\n", ++cnt);
}
int hellobinder_to(char *name)
{
static int cnt = 0;
ALOGW("hello to %s : %d\n", name, ++cnt);
return cnt;
}
//回调函数
int hellobinder_service_handler(struct binder_state *bs,
struct binder_transaction_data_secctx *txn_secctx,
struct binder_io *msg,
struct binder_io *reply)
{
struct binder_transaction_data *txn = &txn_secctx->transaction_data;
/* 根据txn->code知道要调用哪一个函数
* 参数, 从msg取出
* 返回结果, 把结果放入reply
*/
/* sayhello
* sayhello_to
*/
uint16_t *s;
char name[512];
size_t len;
//uint32_t handle;
uint32_t strict_policy;
int i;
// Equivalent to Parcel::enforceInterface(), reading the RPC
// header with the strict mode policy mask and the interface name.
// Note that we ignore the strict_policy and don't propagate it
// further (since we do no outbound RPCs anyway).
strict_policy = bio_get_uint32(msg);
//code 用于判断我们需要调用哪一个函数,客户端远程调用哪个服务端函数
switch(txn->code) {
case HELLO_BINDER:
hellobinder();
//给reply写一个值为0
bio_put_uint32(reply, 0); /* no exception */
return 0;
case HELLO_BINDER_TO:
/* 从msg里取出字符串 */
s = bio_get_string16(msg, &len); //"IHelloService"
s = bio_get_string16(msg, &len); // name
if (s == NULL) {
return -1;
}
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
name[i] = s[i];
name[i] = '\0';
/* 处理 */
i = hellobinder_to(name);
/* 把结果放入reply 给回客户端*/
bio_put_uint32(reply, 0); /* no exception */
bio_put_uint32(reply, i);
break;
default:
fprintf(stderr, "unknown code %d\n", txn->code);
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
// 进程的 Binder 回调函数
//binder_transaction_data_secctx主要的数据,msg客户端传递过来的函数的参数,reply返回给客户端的数据
int test_server_handler(struct binder_state *bs,
struct binder_transaction_data_secctx *txn_secctx,
struct binder_io *msg,
struct binder_io *reply)
{
//取出数据,
struct binder_transaction_data *txn = &txn_secctx->transaction_data;
//函数指针,
int (*handler)(struct binder_state *bs,
struct binder_transaction_data *txn,
struct binder_io *msg,
struct binder_io *reply);
// txn->target.ptr 是 svcmgr_publish 传入的第二个参数
handler = (int (*)(struct binder_state *bs,
struct binder_transaction_data *txn,
struct binder_io *msg,
struct binder_io *reply))txn->target.ptr;
//调用函数指针,那么就会调用txn->target.ptr;这个指针,那么就是hellobinder_service_handler
return handler(bs, txn, msg, ,reply);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
struct binder_state *bs;
//值为 0
uint32_t svcmgr = BINDER_SERVICE_MANAGER;
uint32_t handle;
int ret;
//初始化驱动
bs = binder_open("/dev/binder", 128*1024);
if (!bs) {
fprintf(stderr, "failed to open binder driver\n");
return -1;
}
//添加服务hellobinder_service_handler 是 hello 服务对应的回调函数
//bs打开启动返回的一个int值,句柄,svcmgr表示把数据发到这个进程中,是ServiceManager,hello是注册的服务的名字
//当我们注册的时候把这个hellobinder_service_handler指针传给驱动,驱动就记住hello服务回调是它,客户端需要调用hello服务的时候
ret = svcmgr_publish(bs, svcmgr, "hello", hellobinder_service_handler);
if (ret) {
fprintf(stderr, "failed to publish hello service\n");
return -1;
}
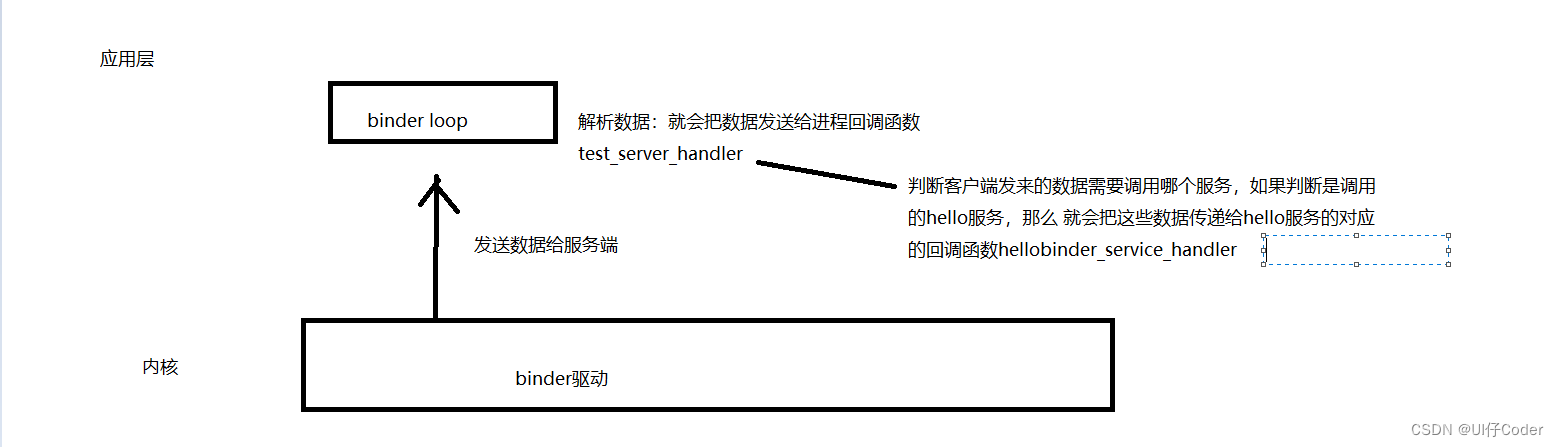
//test_server_handler 进程的 Binder 回调函数,进入循环服务端就不会挂掉,一直执行
//binder收到数据,就解析,解析好就传给test_server_handler
binder_loop(bs, test_server_handler);
return 0;
}
binder_transaction_data_secctx
主要的数据结构是在这里
2.binder_client.c
c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "binder.h"
#define HELLO_BINDER 1
#define HELLO_BINDER_TO 2
int g_handle = 0;
struct binder_state *g_bs;
void sayhello(void)
{
unsigned iodata[512/4];
struct binder_io msg, reply;
/* 构造binder_io */
//初始化msg数据,表示的是所调用的服务端函数所需的参数
bio_init(&msg, iodata, sizeof(iodata), 4);
/* 放入参数 */
//把数据写入msg中
bio_put_uint32(&msg, 0); // strict mode header
bio_put_string16_x(&msg, "IHelloService");
/* 调用binder_call */
//发起远程调用,g_bs是binder_open返回的一个句柄,msg函数的参数,reply服务端返回值,g_handle是hello服务在客户端的一个句柄索引,通过它才能找到对应的服务端,HELLO_BINDER是code,表示要调用服务端的哪个函数
if (binder_call(g_bs, &msg, &reply, g_handle, HELLO_BINDER))
return ;
/* 从reply中解析出返回值 */
//解析服务端返回的数据
binder_done(g_bs, &msg, &reply);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd;
struct binder_state *bs;
uint32_t svcmgr = BINDER_SERVICE_MANAGER;
int ret;
bs = binder_open("/dev/binder", 128*1024);
if (!bs) {
fprintf(stderr, "failed to open binder driver\n");
return -1;
}
g_bs = bs;
/* get service 查找服务,bs是binder_open的返回值,svcmgr是servicemanager表示数据要发送给它,hello是查找服务的名字*/
//g_handle句柄,索引
g_handle = svcmgr_lookup(bs, svcmgr, "hello");
if (!g_handle) {
return -1;
}
//调用服务,发起远程调用
sayhello();
}编写bp文件
sh
cc_defaults {
name: "bindertestflags",
cflags: [
"-Wall",
"-Wextra",
"-Werror",
"-Wno-unused-parameter",
"-Wno-missing-field-initializers",
"-Wno-unused-parameter",
"-Wno-unused-variable",
"-Wno-incompatible-pointer-types",
"-Wno-sign-compare",
],
product_variables: {
binder32bit: {
cflags: ["-DBINDER_IPC_32BIT=1"],
},
},
shared_libs: ["liblog"],
}
//c的可执行程序
cc_binary {
name: "binderclient",
defaults: ["bindertestflags"],
vendor: true,
srcs: [
"binder_client.c",
"binder.c",
],
}
cc_binary {
name: "binderserver",
defaults: ["bindertestflags"],
vendor: true,
srcs: [
"binder_server.c",
"binder.c",
],
}
// cc_binary {
// name: "myservicemanager",
// defaults: ["mybindertest_flags"],
// srcs: [
// "service_manager.c",
// "binder.c",
// ],
// shared_libs: ["libcutils", "libselinux"],
// }把编译出来的两个二进制文件push到设备中测试
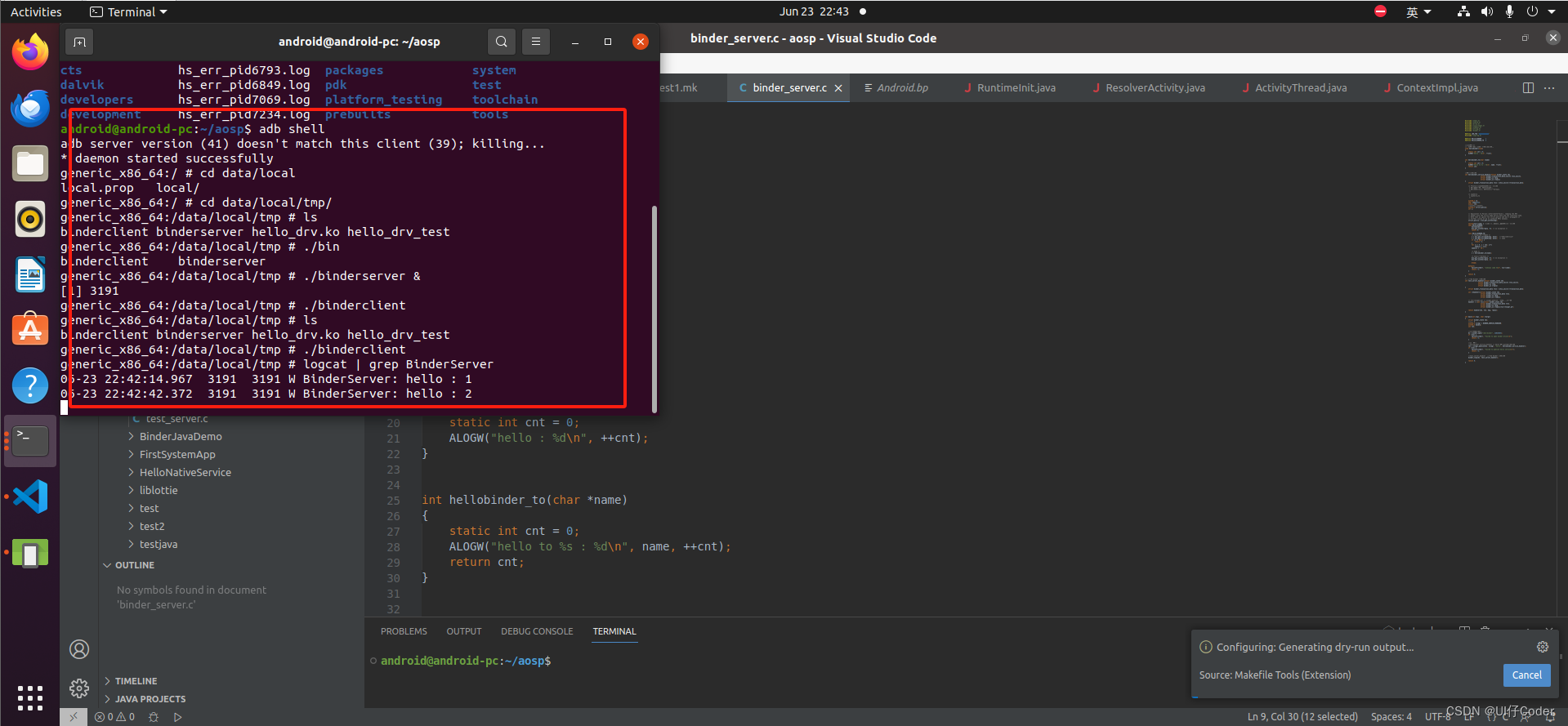
看到hello已经被调用了说明跨进程通信成功了