CentOS中使用SSH远程登录
准备工作
两台安装CentOS系统的虚拟机
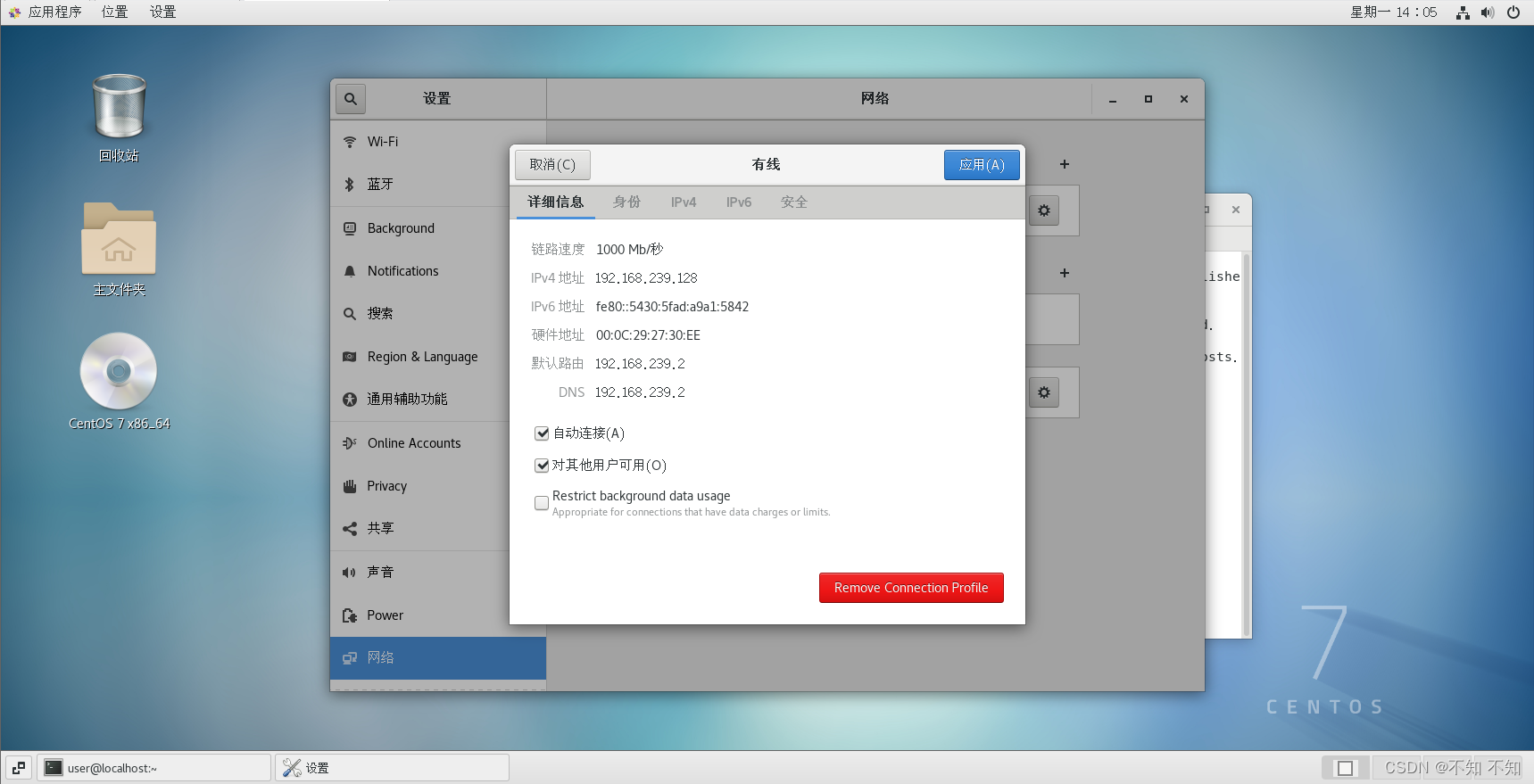
客户机(192.168.239.128)
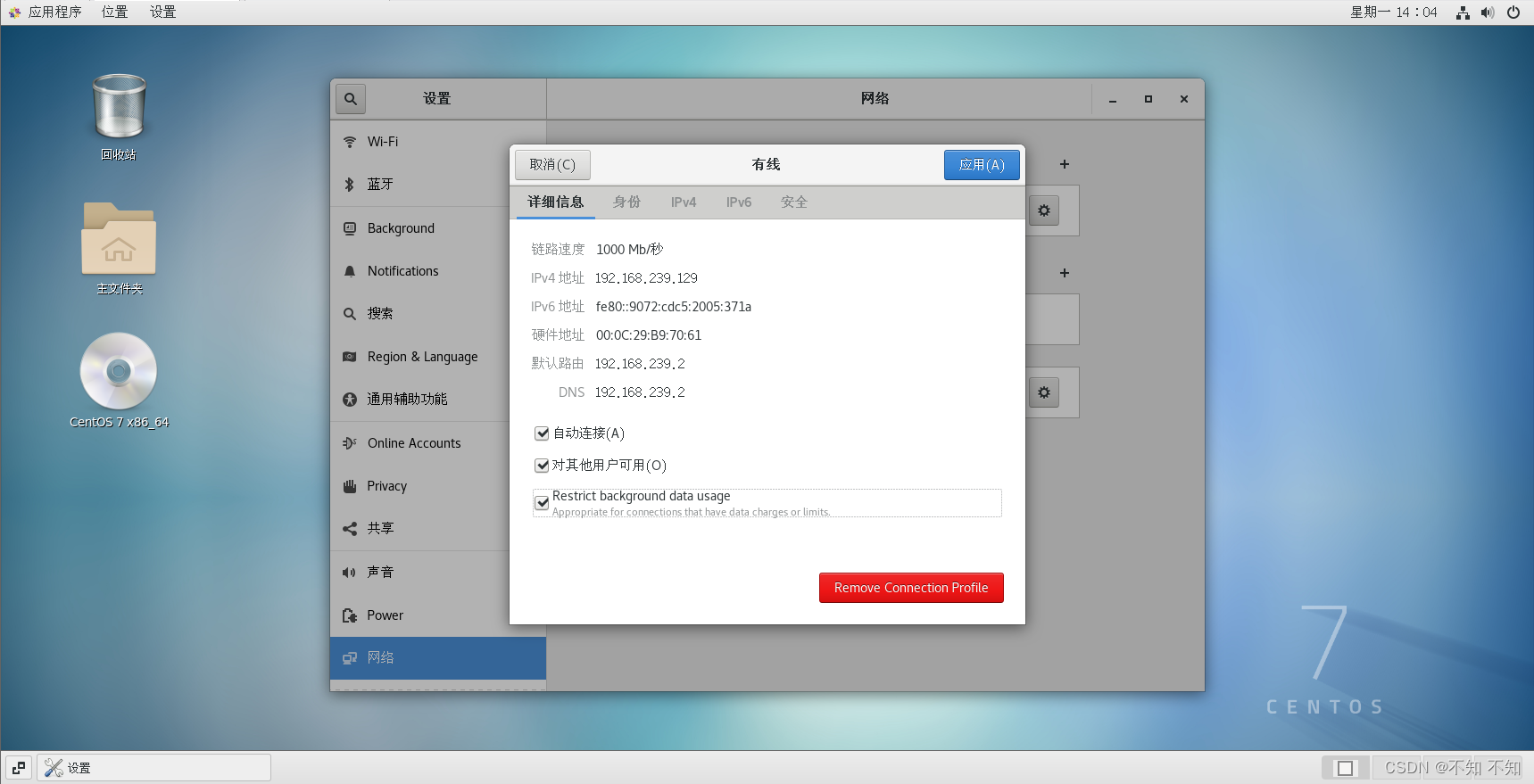
服务器(192.168.239.129)
SSH概述
Secure Shell(SSH) 是由 IETF(The Internet Engineering Task Force) 制定的建立在应用层基础上的安全网络协议。
它是专为远程登录会话(甚至可以用Windows远程登录Linux服务器进行文件互传)和其他网络服务提供安全性的协议,可有效弥补网络中的漏洞。通过SSH,可以把所有传输的数据进行加密,也能够防止DNS欺骗和IP欺骗。还有一个额外的好处就是传输的数据是经过压缩的,所以可以加快传输的速度。
SSH服务的安装与启动
- 查看当前的centos是否安装了openssh-server服务。默认安装openssh-server服务。
bash
rpm -qa|grep -E "openssh"查看是否安装了以下三个服务
bash
[user@localhost ~]$ rpm -qa|grep -E "openssh"
openssh-clients-7.4p1-21.el7.x86_64
openssh-7.4p1-21.el7.x86_64
openssh-server-7.4p1-21.el7.x86_64- 如果没有,通过以下命令安装openSSH
bash
yum install openssh-server -y- 启动SSH服务
bash
service sshd start建立SSH连接
基于口令的安全验证:只要你知道自己帐号和口令,就可以登录到远程主机。所有传输的数据都会被加密,但是不能保证你正在连接的服务器就是你想连接的服务器。可能会有别的服务器在冒充真正的服务器,也就是受到"中间人攻击"这种方式的攻击。格式如下:
bash
ssh 用户名@服务器IP示例 客户机连接服务器
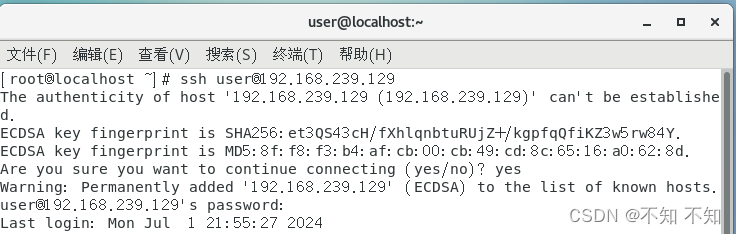
基于密钥的安全验证:你必须为自己创建一对密钥,并把公钥放在需要访问的服务器上。如果你要连接到SSH服务器上,客户端软件就会向服务器发出请求,请求用你的密钥进行安全验证。服务器收到请求之后,先在该服务器上你的主目录下寻找你的公钥,然后把它和你发送过来的公钥进行比较。如果两个密钥一致,服务器就用公钥加密"质询"(challenge)并把它发送给客户端软件。客户端软件收到"质询"之后就可以用你的私钥在本地解密再把它发送给服务器完成登录。与第一种级别相比,第二种级别不仅加密所有传输的数据,也不需要在网络上传送口令,因此安全性更高,可以有效防止中间人攻击。
- 创建密钥对命令:
bash
ssh-keygen示例 客户机创建密钥对命令
bash
[root@localhost ~]# ssh-keygen
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
//密钥对存放位置(回车默认)
Enter file in which to save the key (/root/.ssh/id_rsa):
//设置密钥对密码(回车默认)
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:817WC5/GOz2ozvF+iGd8WgwnyhN9mr9YZiCYtxX2zbc root@localhost.localdomain
The key's randomart image is:
+---[RSA 2048]----+
| |
| |
| o |
| o o o..|
| So + * ++|
| oo *.X o|
| .**++E |
| ..++O@*.|
| o+=*O=o|
+----[SHA256]-----+2.查看密钥对是否生成(id_rsa为私钥,id_ras.pub为公钥)
bash
[root@localhost ~]# cd .ssh
[root@localhost .ssh]# ls
id_rsa id_rsa.pub known_hosts3.将密钥发送至服务器,命令格式如下:
bash
ssh-copy-id 用户名@服务器IP示例 客户机将密钥发送至服务器
bash
[root@localhost .ssh]# ssh-copy-id user@192.168.239.129
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed -- if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys
user@192.168.239.129's password:
Number of key(s) added: 1
Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh 'user@192.168.239.129'"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.
[root@localhost .ssh]# 4.使用ssh免密登录到服务器
bash
[root@localhost .ssh]# ssh user@192.168.239.129
Last login: Mon Jul 1 13:58:22 2024 from 192.168.239.128SSH配置文件
OpenSSH的主配置文件:/etc/ssh/sshd_config,通过vim命令编辑主配置文件。
bash
vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config各参数详情:
bash
Port=22 设置SSH的端口号是22(默认端口号为22)
Protocol 2 启用SSH版本2协议
ListenAddress 192.168.0.222 设置服务监听的地址
DenyUsers user1 user2 foo 拒绝访问的用户(用空格隔开)
AllowUsers root osmond vivek 允许访问的用户(用空格隔开)
PermitRootLogin no 禁止root用户登陆
PermitEmptyPasswords no 用户登陆需要密码认证
PasswordAuthentication yes 启用口令认证方式修改SSH默认端口
SSH的默认端口为22 ,在实际生产环境中为了保证服务器安全,通常会修改SSH的默认端口。步骤如下:
1.打开服务器的SSH主配置文件,设置新的端口号
bash
vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config
/Port进行查找
Vim中输入
i 进行编辑
ESE 退出编辑
:wq! 强制保存退出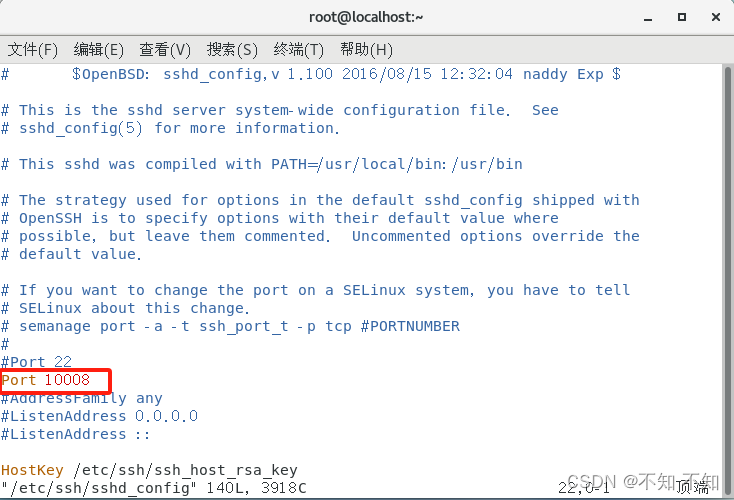
2.查看22端口相关值
bash
[root@localhost .ssh]# semanage port -l grep ssh
ssh_port_t tcp 223.将10008端口的值修改为上面22端口的相关值
bash
[root@localhost .ssh]# semanage port -a -t ssh_port_t -p tcp 10008
semanage(管理SELinux安全策略) 命令参数
-a 添加
-t 设置类型
-p 设置协议查看是否添加成功
bash
[root@localhost .ssh]# semanage port -l grep ssh
ssh_port_t tcp 10008,224.防火墙中放行10008端口
bash
[root@localhost]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=10008/tcp
success
firewall-cmd命令参数:
--permanent 永久生效
--add-port 设置端口号/协议5.重新加载防火墙
bash
[root@localhost]# firewall-cmd --reload
success
firewall-cmd命令参数:
--reload 重新加载6.重新启动SSH服务
bash
systemctl restart sshd7.在客户机上测试连接
默认22端口无法连接
bash
[user@localhost ~]$ ssh user@192.168.239.129
ssh: connect to host 192.168.239.129 port 22: Connection refused指定修改后的10008端口可以进行连接
bash
[user@localhost ~]$ ssh -p user@192.168.239.129
Bad port 'user@192.168.239.129'
[user@localhost ~]$ ssh -p 10008 user@192.168.239.129
The authenticity of host '[192.168.239.129]:10008 ([192.168.239.129]:10008)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:et3QS43cH/fXhlqnbtuRUjZ+/kgpfqQfiKZ3w5rw84Y.
ECDSA key fingerprint is MD5:8f:f8:f3:b4:af:cb:00:cb:49:cd:8c:65:16:a0:62:8d.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
Warning: Permanently added '[192.168.239.129]:10008' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
user@192.168.239.129's password:
Last login: Mon Jul 1 15:02:34 2024 from 192.168.239.128SSH文件传输
服务器文件下载到客户机
bash
scp [选项] [服务器用户名@]服务器IP地址或域名:服务器文件 本地目录示例
bash
[root@localhost ~]# scp -P 10008 user@192.168.239.129:/home/user /home/user
scp: /home/user: not a regular file
[root@localhost ~]# scp -P 10008 user@192.168.239.129:/home/user/11.txt /home/user
11.txt 100% 4 0.8KB/s 00:00
[root@localhost ~]# 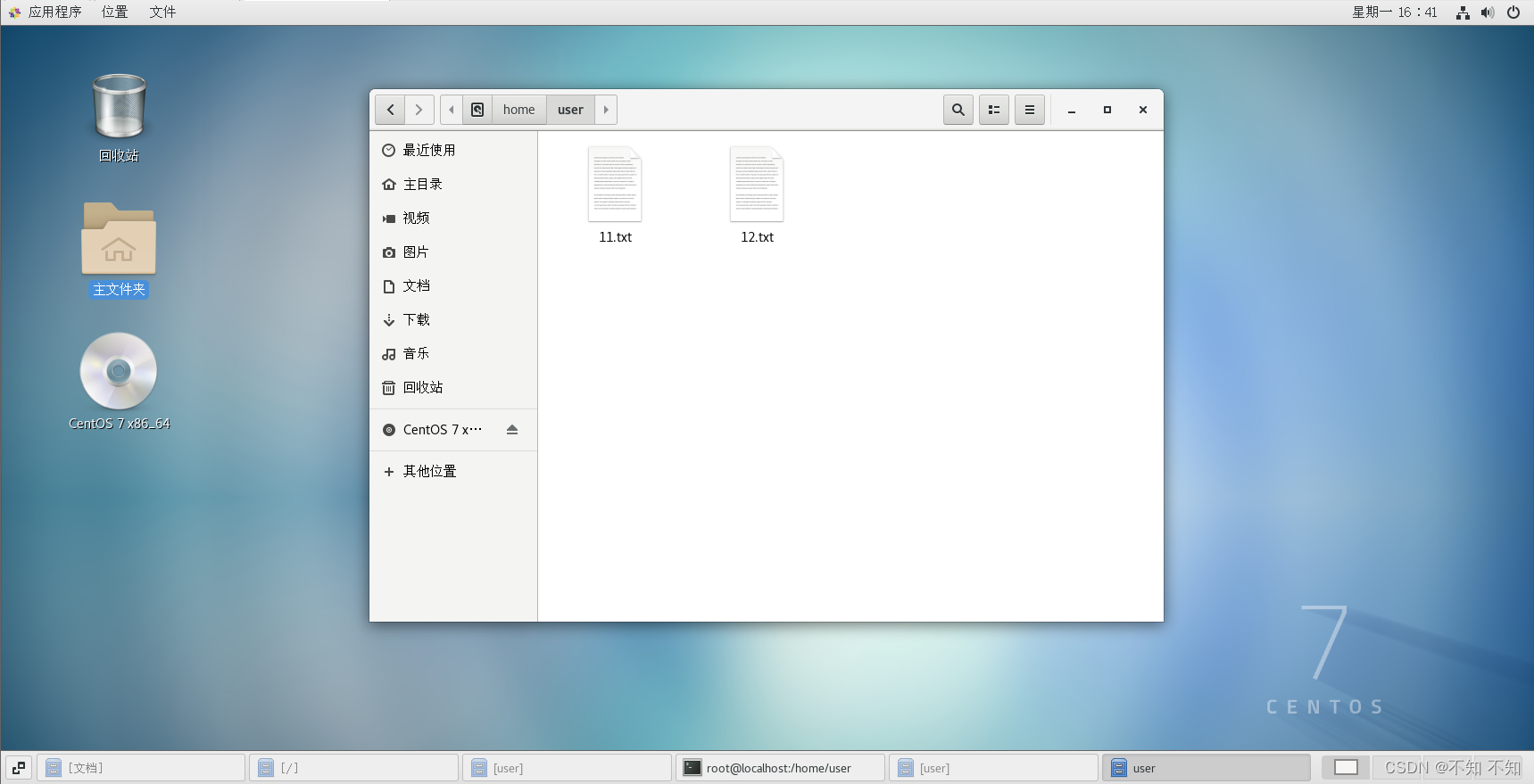
客户机文件文件上传服务器
bash
scp [选项] 本地文件 [服务器用户名@]服务器IP地址或域名:服务器目录示例
bash
[root@localhost home]# cd /home/user
[root@localhost user]# ls
11.txt 12.txt
[root@localhost user]# scp -P 10008 12.txt user@192.168.239.129:/home/user
12.txt 100% 4 0.9KB/s 00:00
[root@localhost user]#