minist数据集训练
训练方法:利用pytorch来实现minist数据集的分类模型训练
训练模型如下图所示
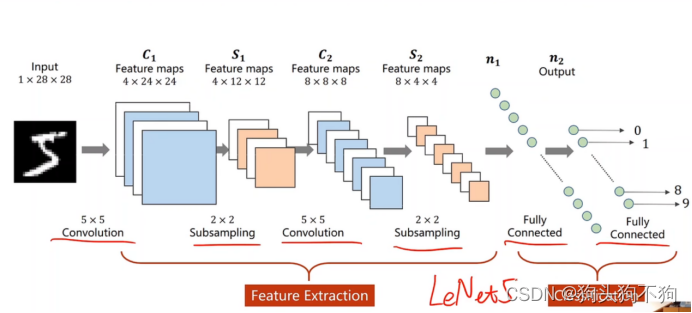
模型代码:
python
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import Flatten
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.module = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1,4,5,1,0),
nn.MaxPool2d(2),
nn.Conv2d(4,8,5,1,0),
nn.MaxPool2d(2),# torch.Size([8, 4, 4])
Flatten(),# torch.Size([64, 128])
nn.Linear(8*16,16),# torch.Size([64, 16])
nn.Linear(16, 10) #torch.Size([64, 10])
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.module(x)
return x
if '__name__' == '__mian__':
net = Net()
input = torch.ones((64,1, 28, 28))
output = net(input)
print(output.shape)现在开始编写代码训练模型
基本思路:
- 读取数据集并整理
- 将数据集放入模型中训练,每次记录训练的损失loss以及准确率
实测训练大概10轮后,正确率能达到98%以上
python
import torch.optim
import torchvision
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
from module import *
dataset_transform = torchvision.transforms.Compose([torchvision.transforms.ToTensor()])
train_set = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(root='../dataset_MNIST',train=True,transform=dataset_transform,download=True)
test_set = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(root='../dataset_MNIST',train=False,transform=dataset_transform,download=True)
print('训练数据集size{}'.format(len(train_set)))
print('测试数据集size{}'.format(len(test_set)))
train_loader = DataLoader(dataset=train_set, batch_size=64)
test_loader = DataLoader(dataset=test_set,batch_size=64)
# for data in train_loader:
# imgs,target = data
# print('imgs',imgs.shape) # torch.Size([64, 1, 28, 28])
# print('target',target)
# break
writer = SummaryWriter('../p10')
cuda_available = torch.cuda.is_available()
net = Net()
if cuda_available:
net = net.cuda()
# 定义损失函数
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
if cuda_available:
loss_fn = loss_fn.cuda()
# 优化器
learning_rate = 0.01
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
# 设置训练参数
# 训练次数
total_train_step = 0
total_test_step = 0
# 训练轮数
epoch = 10
for i in range(10):
print('------------第{}轮训练开始------------'.format(i))
net.train()
for data in train_loader:
imgs,targets = data
if cuda_available:
imgs = imgs.cuda()
targets = targets.cuda()
outputs = net(imgs)
loss = loss_fn(outputs,targets)
#优化器优化模型
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
total_train_step += 1
if total_train_step % 100 == 0:
print('训练次数:{} loss:{}'.format(total_train_step, loss.item()))
# 开始测试
net.eval()
total_test_loss = 0
total_accuracy = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for data in test_loader:
imgs,targets = data
if cuda_available:
imgs = imgs.cuda()
targets = targets.cuda()
outputs = net(imgs)
loss = loss_fn(outputs, targets)
total_test_loss += loss.item()
accuracy = (outputs.argmax(1) == targets).sum()
total_accuracy += accuracy
print("整体测试集的Loss:{}".format(total_test_loss))
writer.add_scalar("test_loss", total_test_loss, total_test_step)
total_test_step += 1
print("整体测试集的正确率:{}".format(total_accuracy / len(test_set)))
if i == 9:
torch.save(net, "train_model_{}.pth".format(i))
print('模型已保存')
writer.close()上面已经将最后一次训练的的模型保存了,那么现在就可以用一个图片来测试一下这个模型
python
from module import *
import torchvision.transforms
from PIL import Image
dataset_transform = torchvision.transforms.Compose([torchvision.transforms.ToTensor()])
test_set = torchvision.datasets.MNIST('../dataset_MNIST',train=False,transform=dataset_transform,download=False)
model = torch.load("train_model_9.pth")
model.eval()
for i in range(10):
img, target = test_set[i]
print('--------------第{}张图片--------------'.format(i))
print("图片尺寸",img.shape)
print("标签",target)
img = torch.reshape(img,(1,1,28,28))
img = img.cuda()
with torch.no_grad():
output = model(img)
print(output)
print(output.argmax(1))这里要注意的一点是,因为训练模型时使用了nvida的cuda驱动,那么在使用模型的时候,也需要将图片进行一点修改,具体是
python
img = img.cuda()测试结果如下:
shel
--------------第0张图片--------------
图片尺寸 torch.Size([1, 28, 28])
标签 7
tensor([[ 0.1551, -2.2232, 5.1375, 3.1896, -9.0812, -3.7413, -16.3016,
16.5437, -2.3190, 2.7608]], device='cuda:0')
tensor([7], device='cuda:0')
--------------第1张图片--------------
图片尺寸 torch.Size([1, 28, 28])
标签 2
tensor([[ 8.5477, 6.7017, 15.3023, 6.9958, -12.9011, -3.1987, 2.8130,
-12.9218, 4.8305, -17.2936]], device='cuda:0')
tensor([2], device='cuda:0')
--------------第2张图片--------------
图片尺寸 torch.Size([1, 28, 28])
标签 1
tensor([[-1.4329, 9.1416, 0.7603, -2.0579, 1.7856, -3.9744, 0.1253, 2.0046,
-0.6214, -2.1419]], device='cuda:0')
tensor([1], device='cuda:0')
--------------第3张图片--------------
图片尺寸 torch.Size([1, 28, 28])
标签 0
tensor([[13.5426, -6.6119, 1.1040, -5.3236, -6.8938, 2.2850, 3.4611, -2.5504,
-0.0393, -0.4295]], device='cuda:0')
tensor([0], device='cuda:0')
--------------第4张图片--------------
图片尺寸 torch.Size([1, 28, 28])
标签 4
tensor([[-2.2200, -3.2653, -3.9221, -7.7044, 12.9432, -5.3840, -0.3826, 1.3231,
-2.7672, 6.4946]], device='cuda:0')
tensor([4], device='cuda:0')
--------------第5张图片--------------
图片尺寸 torch.Size([1, 28, 28])
标签 1
tensor([[-2.1054, 10.7492, -0.0951, -2.4075, 3.1492, -5.6566, -1.9704, 4.0755,
-0.5151, -0.8886]], device='cuda:0')
tensor([1], device='cuda:0')
--------------第6张图片--------------
图片尺寸 torch.Size([1, 28, 28])
标签 4
tensor([[-7.6890, 0.1027, -5.0862, -4.9066, 10.8449, -1.0489, -2.3638, 2.8111,
4.3393, 3.6312]], device='cuda:0')
tensor([4], device='cuda:0')
--------------第7张图片--------------
图片尺寸 torch.Size([1, 28, 28])
标签 9
tensor([[-7.3084, -1.4986, -1.5550, 2.7101, 2.4086, 2.5202, -7.5940, 0.3350,
2.0277, 7.9211]], device='cuda:0')
tensor([9], device='cuda:0')
--------------第8张图片--------------
图片尺寸 torch.Size([1, 28, 28])
标签 5
tensor([[ -0.5667, -15.0522, -2.6193, -2.5653, -1.2110, 13.1138, 5.9642,
-7.2953, 4.0217, 1.9577]], device='cuda:0')
tensor([5], device='cuda:0')
--------------第9张图片--------------
图片尺寸 torch.Size([1, 28, 28])
标签 9
tensor([[-2.5326, -8.8390, -2.7222, -2.3805, 2.1510, -1.2283, -7.7543, 5.7798,
5.2312, 11.3871]], device='cuda:0')
tensor([9], device='cuda:0')
Process finished with exit code 0
s说明准确率都还挺高的,这么模型训练的还可以
好了,这就是minist数据集训练了
写完这个就算是入门了
b站上有一个pytorch很好的入门视频
讲的很不错的,学完就能入门了