搭建好python后对于内部的很多函数还是不太了解,按照下面的学习博客,理解内部具体的网络实现并代码实现一个线性回归模型并训练。
【从零开始学习深度学习】3. 基于pytorch手动实现一个线性回归模型并进行min--batch训练_pytorch mini batch-CSDN博客
网络模型:矩阵乘法-输入矩阵*权重 = 输出
损失函数:预测值与真实值的误差平方
优化函数:小批量随机梯度下降
pytorch中对梯度自动计算,存储tensor计算图,所以应该着重理解并注意是否梯度参与计算
python
import numpy.random
import torch
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from IPython import display
import random
import os
os.environ['KMP_DUPLICATE_LIB_OK'] = 'True'
num_inputs = 2
num_examples = 1000
w0 = [2,-3.4]
b0 = 4.2
data = torch.randn(num_examples, num_inputs,dtype=torch.float)
labels = w0[0] * data[:,0] + w0[1] * data[:,1] + b0
labels += torch.tensor(np.random.normal(0,0.01,size=labels.size())).float()
def data_iter(batch_size,data,labels):
num_examples = data.shape[0]
indices = list(range(num_examples)) #返回0-1000的序列
random.shuffle(indices) #原地打乱indices列表的顺序
for i in range(0,num_examples,batch_size):
j = torch.LongTensor(indices[i:min(i+batch_size,num_examples)]) #返回indices打乱后从i-barch_size段的值,用作索引
yield data.index_select(0,j), labels.index_select(0,j) #yield 惰性生成,每次只生成一组数据暂停,等第二次调用生成第二组
#将权重初始化成均值0,标准差0.01的正态随机数,偏差b初始化为0
w = torch.tensor(numpy.random.normal(0,0.01,(num_inputs,1)),dtype=torch.float)
b = torch.zeros(1).float()
#后续模型训练中,需要对这些参数求梯度来迭代参数的值,因此必须为true
w.requires_grad_(True)
b.requires_grad_(True)
#线性回归模型
def linreg(X, w, b):
return torch.mm(X,w) + b #mm函数-矩阵乘法 输入*权重+偏差=输出 一个简单的线性回归网络模型
#损失函数
def squared_loss(y_hat,y):
return (y_hat - y.view(y_hat.size()))**2/2 # 注意这里返回的是向量
#优化算法
def sgd(params, lr,batch_size):
for param in params:
param.data -= lr * param.grad / batch_size #这里更改param时用的param.data,想要修改param的值,又不希望被autograd记录(不会影响反向传播),就对data操作
lr = 0.03
num_epochs = 3
batch_size = 10
net = linreg
loss = squared_loss
losses = []
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
for X,y in data_iter(batch_size,data,labels):
output = net(X,w,b)
l = loss(output,y).sum() # l是有关小批量X和y的损失
l.backward() # 小批量的损失对模型参数求梯度
sgd([w,b],lr,batch_size) # 使用小批量随机梯度下降迭代模型参数
w.grad.data.zero_() #梯度清零
b.grad.data.zero_()
train_l = loss(net(data,w,b),labels) # 计算第一个迭代周期的损失
losses.append(train_l.mean().item())
print('echo %d,loss %f' % (epoch+1, train_l.mean().item()))
plt.plot(losses, label ="loss")
plt.xlabel('epoch')
plt.ylabel('loss')
plt.title('Training Loss')
plt.show()
print(f"True_W={ w0 },\n learn w ={ w.detach().numpy() }") #detach()脱离计算图,numpy转到数组
print(f"True_b={ b0},\n learn b ={ b.detach().numpy() }")输出
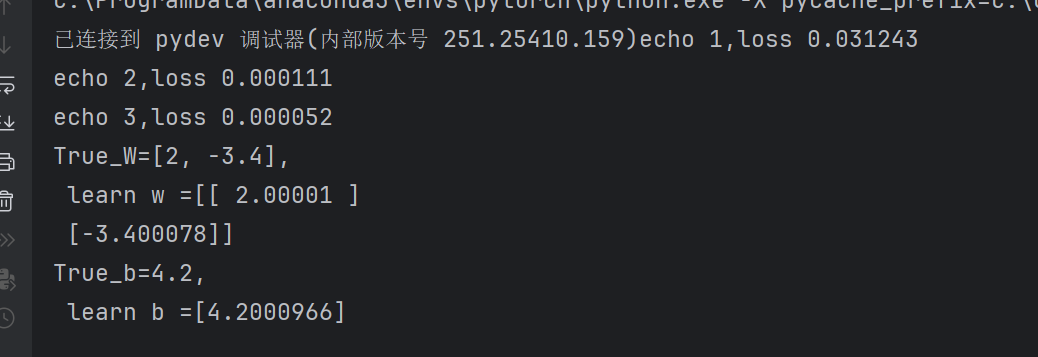
真实值和学习值很接近。