文章目录
引言
- 今天又要面试字节,不过这次没有上次那么紧张了,平常心,然后去面对就行了,行就行,不行也没有办法撒!反正得好好准备提前批还有秋招的正式批!好好准备吧!
- 今天多复习几题,整体来说,复习还是挺快的!
- 对了,今天还得整理一下MySQL中关于锁的相关内容,背八股的时候,总是有点疑惑,今天全过一遍!
复习
每日温度
复习实现
- 我记得这道题我是做出来了,然后当时方法和参考方法不同,但是思想大致是相同的,应该要维护两个栈。我是从前往后进行遍历,他是从后往前进行遍历。
- 整体来说还是很好做的,两个判定情况
- 当前元素比栈顶元素大,栈内元素弹出,直到一个比他本身大的元素,
- 当前元素比栈顶元素小,直接入栈。
- 从后往前进行遍历
cpp
class Solution {
public int[] dailyTemperatures(int[] tempe) {
// define the result array
int m = tempe.length;
int[] res = new int[m];
// define the compare stack
Deque<Integer> stk = new LinkedList<>();
// trasverse the tempe
stk.push(m - 1);
for(int i = m - 2;i >= 0;i --){
if(tempe[stk.peek()] > tempe[i]){
res[i] = stk.peek() - i ;
stk.push(i);
}else{
while( !stk.isEmpty() && tempe[stk.peek()] <= tempe[i]){
stk.pop();
}
if(!stk.isEmpty()) res[i] = stk.peek() - i;
stk.push(i);
}
}
return res;
}
}总结
- 我这里还调整了蛮久的,不行呀,写出来的代码还那么繁琐!
- 关于多态有了更加深刻的理解,你要使用队列或者堆栈的功能,就要使用对应的父类接口来承接对应接口实现类的实例对象,才能调用对应的方法。
- 不要子类直接调用,这样方法太多了,代码可读性也不好!

- 不要子类直接调用,这样方法太多了,代码可读性也不好!
参考学习
参考代码
cpp
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> dailyTemperatures(vector<int>& temp) {
int m = temp.size();
vector<int> f(m);
stack<int> upst;
for(int i = temp.size() - 1;i >= 0;i --){
while(!upst.empty() && temp[i] >= temp[upst.top()]) upst.pop();
if(upst.size()) f[i] = upst.top() - i;
upst.push(i);
}
return f;
}
};修改之后的代码
- 确实更加简洁了,继续再弄吧!
cpp
class Solution {
public int[] dailyTemperatures(int[] tempe) {
// define the result array
int m = tempe.length;
int[] res = new int[m];
// define the compare stack
Deque<Integer> stk = new LinkedList<>();
// trasverse the tempe
for(int i = m - 1;i >= 0;i --){
while( !stk.isEmpty() && tempe[stk.peek()] <= tempe[i]) stk.pop();
if(!stk.isEmpty()) res[i] = stk.peek() - i;
stk.push(i);
}
return res;
}
}还是得记录模板,不然做不下去!自己推,根本没有那么多时间!
关于背包集合的问题模板,可以看一下"铅笔大佬"的总结
完全平方数
复习实现
- 第二次再看,这个题目就是一个完全背包的问题,背包的物品就是对应的平方数,然后容量就是当前的数字。
cpp
class Solution {
public int numSquares(int n) {
// define the square number of n
List<Integer> sqt = new LinkedList<>();
for(int i = 1;i * i <= n;i++ ) sqt.add(i * i);
// travser all the situation based on the bag problem
int[] f = new int[n + 1];
Arrays.fill(f,n);
int m = sqt.size();
for(int i = m - 1;i >= 0;i --){
for(int j = n ;j >= sqt.get(i);j --)
for(int k = 0;k * sqt.get(i) <= j;k ++)
f[j] = Math.min(f[j],f[j - k * sqt.get(i)] + k);
}
return f[n - 1];
}
}
总结
- 完全背包的模板没有背下来,没整明白,然后优化模板也没有背下来,不能每次都推导,在浪费时间。
- 这应该不全是一个完全背包问题,还是不够扎实!
完全背包模板
- 这多香,往上一套,直接用,可惜你没背出来
- "找个就放,放满为止;剩余容量,加上价值"
cpp
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i)
for (int j = v[i]; j <= m; ++ j)
f[j] = max(f[j], f[j - v[i]] + w[i]);参考学习
- 真的是愚蠢呀,那道题一看到用什么数学定理,你直接跳过了,真行!不是还有完全背包这种解法吗?你不也是没弄好!
- 完全背包解决!加上模板,直接修改,秒过,这个模板还是得背!
cpp
class Solution {
public int numSquares(int n) {
// define the square number of n
List<Integer> sqt = new LinkedList<>();
for(int i = 1;i * i <= n;i++ ) sqt.add(i * i);
// travser all the situation based on the bag problem
int[] f = new int[n + 1];
Arrays.fill(f,n);
f[0] = 0;
int m = sqt.size();
for(int i = 0;i < m;i ++){
for(int j = sqt.get(i) ;j <= n;j ++)
f[j] = Math.min(f[j],f[j - sqt.get(i)] + 1);
}
return f[n ];
}
}
算法二
- 这里是使用了两个定理,一个是一个数一定能够4个完全平方数表示,所以这题返回的结果最多就是4,然后的如果满足一个等式,就可以用三个数表示,否则不行,这里就需要记住一个东西
判定一个数是否是完全平方数
cpp
// 这是一个完全平放数的判定
Math.pow(Math.sqrt(x),2) == x- 其他的直到就行了
无重复字符的最长子串
-
笑死,这是华为笔试的那道题,如果今天是华为的笔试,你能做出来吗?再来呗,不知道你能不能在一个题上跌三次跟头!
复习实现
- 典型的滑动窗口,并且是不包含重复字符的,使用hash实现,整整,看看能不能做出来
cpp
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
// define dict to remove the multiple word
Map<Character,Integer> dict = new HashMap<>();
// travrese the whole s
int m = s.length();
int res = 0;
for(int l = 0,r = 0;r < m;r ++){
// judge wherther the new char is exists
while(dict.getOrDefault(s.charAt(r),0) >= 1) {
dict.put(s.charAt(l),dict.get(s.charAt(l)) - 1);
l ++;
}
dict.put(s.charAt(r),dict.getOrDefault(s.charAt(r),0) + 1 );
res = Math.max(res,r - l + 1);
}
return res;
}
}
这里补充了关于String的一些操作
- 获取字符串的长度 length()
- 获取某一个特定的字符,chatAt()
- 获取子串,substring(beignIdx,endIdx);
参考学习
- 这里完全可以先添加元素,然后在判定,大概的方式是一样的!
cpp
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
unordered_map<char,int> heap;
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0 ,j = 0; i < s.size(); ++i) {
heap[s[i]] ++;
while(heap[s[i]] > 1)
heap[s[j ++]] --;
res = max(res,i - j + 1);
}
return res;
}新作
控制多线程输出
- 线程一,循环输出的1,线程二,循环输出2,线程三,循环输出3,写一个程序,控制这三个线程循环输出1,2,3,1,2,3,...
- 这个欠缺的知识有点多,一时间不知道怎么弄,这里先补充一下
Java实现线程------不使用锁实现
- 实现runnable接口的具体类
- 重写runnable方法,然后在一个thread对象中传入对应的新实例,创建对应线程,然后进行运行
java
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(new ThreadTest(1));
Thread t2 = new Thread(new ThreadTest(2));
Thread t3 = new Thread(new ThreadTest(3));
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
static class ThreadTest implements Runnable{
int num = 0;
ThreadTest(int val){
num = val;
}
// define recursive function
private void printNum() throws InterruptedException {
while(true){
System.out.print(num);
Thread.sleep(100);
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
printNum();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}下述是直接实现的效果,并不是完全的123顺序,所以这个方法并不合理!

版本一,通过全局变量实现控制输出的123
- 这里虽然有多个线程,但是他们都是Main的内部类,以及内部实例,是共享一个静态变量的current,所以通过current进行设置即可!
cpp
public class Main {
private static int current = 1;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(new ThreadTest(1));
Thread t2 = new Thread(new ThreadTest(2));
Thread t3 = new Thread(new ThreadTest(3));
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
static class ThreadTest implements Runnable{
int num = 0;
ThreadTest(int val){
num = val;
}
// define recursive function
private void printNum() throws InterruptedException {
while(true){
if (current == num){
System.out.print(num);
current ++;
}
if(current == 4) current = 1;
Thread.sleep(100);
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
printNum();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}问题
- 如果不使用对应锁进行控制,三个线程同时在输出前阻塞,然后输出顺序就没有办法控制了!仅仅是在这个简单程序出问题的概率比较低,如果复杂程序出问题的概率就高了!
使用synchronized关键实现------使用锁实现
synchronized关键字介绍
- 修饰函数,多个线程只能互斥访问这个函数
- 修饰代码块,多个线程只能访问特定的代码块(需要使用对象锁)
不使用synchronized实现方法

使用synchronized方法效果
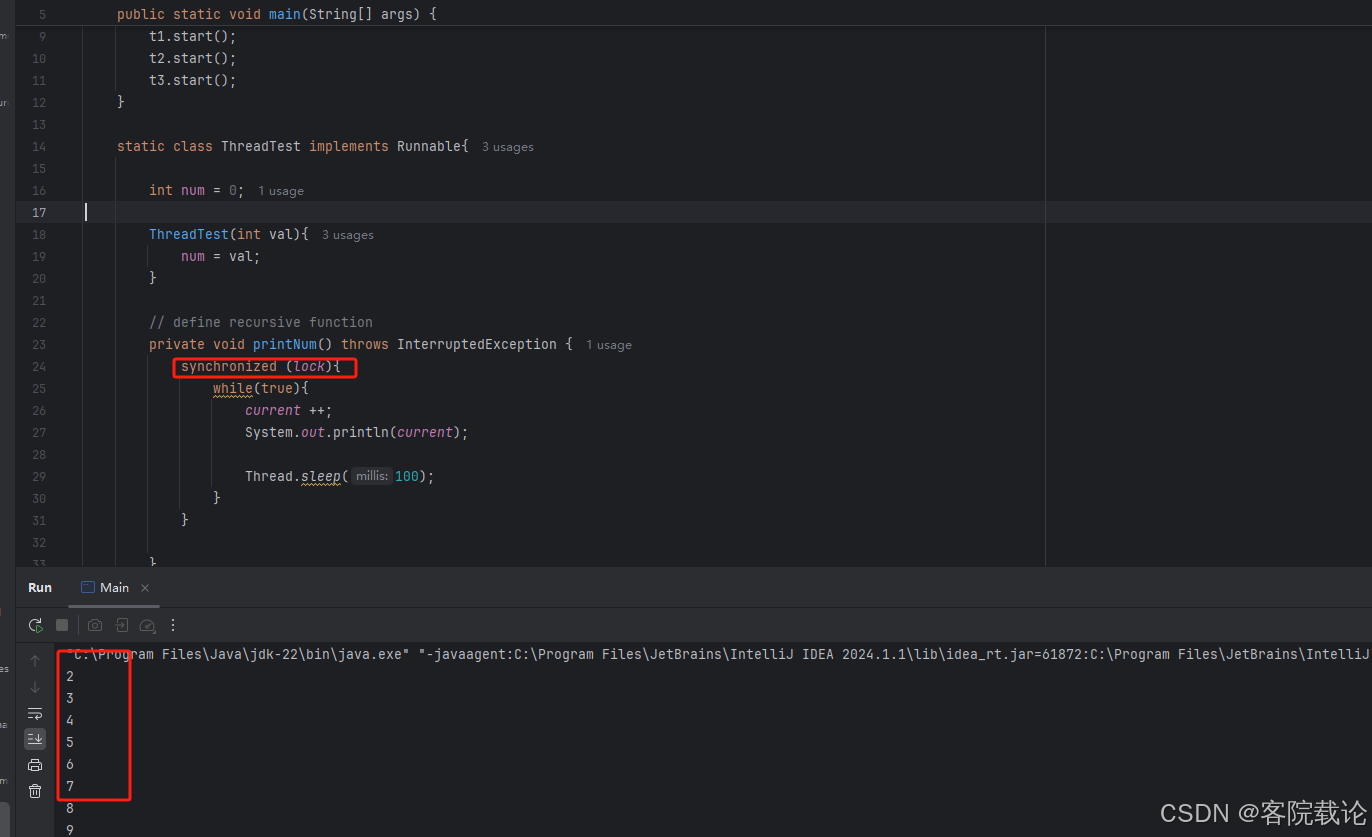
- 下文使用了synchronized方法之后的效果
cpp
public class Main {
private static int current = 1;
private static final Object lock = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(new ThreadTest(1));
Thread t2 = new Thread(new ThreadTest(2));
Thread t3 = new Thread(new ThreadTest(3));
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
static class ThreadTest implements Runnable{
int num = 0;
ThreadTest(int val){
num = val;
}
// define recursive function
private void printNum() throws InterruptedException {
synchronized (lock){
while(true){
current ++;
System.out.println(current);
Thread.sleep(100);
}
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
printNum();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
使用synchronized、wait和notify关键字实现
具体实现思路
- 使用state来表示当前应该的打印那个字母,
- 每一个线程打印字母之后,就要更新state并且唤醒正在等待的线程
cpp
public class Main {
private static int current = 1;
private static final Object lock = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run(){
for(int i = 0;i < 100;i ++){
synchronized(lock){
// judge whether th current thread should print the num
try {
// if the current thread should not print num ,wait until the current changed
while (current % 3 != 1) {
lock.wait();
}
System.out.println(1);
current ++;
lock.notifyAll();
}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run() {
// traverse 100 times
for(int i = 0;i < 100;i ++){
synchronized(lock){
try{
while(current % 3 != 2){
lock.wait();
}
System.out.println(2);
current ++;
lock.notifyAll();
}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
});
Thread t3 = new Thread(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run(){
for(int i = 0;i < 100;i ++){
synchronized(lock){
try{
while(current % 3 != 0) {
lock.wait();
}
System.out.println(3);
current ++;
lock.notifyAll();
}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}这里有几个东西还是需要记住的
- 重写的是Overirde,第一个字母是大写
- notify和wait是会出现interruptedException异常
- 打印输出异常信息是e.printStackTrace()
总结
- 不行,太晚了,今天搞得太晚了,放弃,明天在弄吧,面试完了,整个人又开始放松了,然后开始摆烂了!明天得有好多东西需要补充学习,尤其是多线程编程那里,需要好好补充!趁着周六,加油,好好看看!
- 今天面试字节应该是凉了,感觉没戏了!
- 不想了,继续往下做吧!