首先分别介绍一下这几种引用
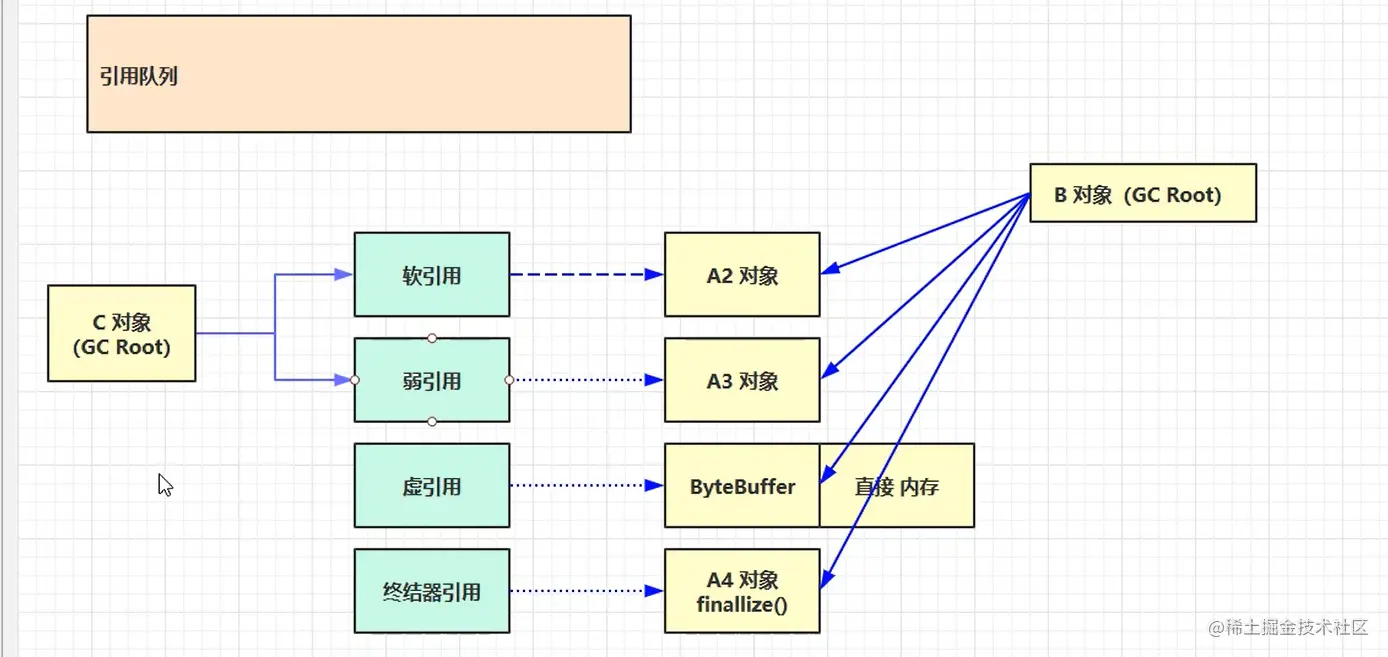
强引用: 只要能通过GC ROOT根对象引用链找到就不会被垃圾回收器回收,当所有的GC Root都不通过强引用引用该对象时,才能被垃圾回收器回收。
软引用(SoftReference): 当只有软引用引用该对象时,在垃圾回收之后内存仍然不足会再次发起垃圾回收,这时会回收掉软引用对象,我们可以配合引用队列来释放软引用自身。
弱引用: 当发生垃圾回收时,无论内存是否够用,只有软引用的对象都会被垃圾回收器回收
虚引用: 必须配合引用队列使用,主要配合 ByteBuffer 使用,被引用对象回收时,会将虚引用入引用队列, 由 Reference Handler 线程调用虚引用相关方法释放直接内存。
终结器引用: 无需手动编码,但其内部配合引用队列使用,在垃圾回收时,终结器引用入队(被引用对象 暂时没有被回收),再由 Finalizer 线程通过终结器引用找到被引用对象并调用它的 finalize 方法,第二次 GC 时才能回收被引用对象
实例
强引用 首先我们设置内存大小为20MB

java
public class Demo2_3 {
private static final int _4MB = 4 * 1024 * 1024;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ArrayList<byte[]> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
list.add(new byte[_4MB]);
}
System.in.read();
}
}启动main,因为强引用无法被垃圾回收会发生内存溢出,报错内存不足无法启动 
弱引用 应用场景
java
public class Demo2_4 {
private static final int _4MB = 4 * 1024 * 1024;
//软引用,当堆内存空间不足时,会回收来释放内存空间
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//list ---> SoftReference ---> byte[] list先引用了软引用对象SoftReference,软引用对象SoftReference再间接引用byte
List<SoftReference<byte[]>> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
//引用对象关联引用队列,当软引用所关联的byte[]被回收时,软引用自己会加入到引用队列queue中去
SoftReference<byte[]> ref = new SoftReference<>(new byte[_4MB]);
System.out.println(ref.get());
list.add(ref);
System.out.println(list.size());
}
System.out.println("循环结束:" + list.stream());
for (SoftReference<byte[]> softReference : list) {
System.out.println(softReference.get());
}
}
}运行:
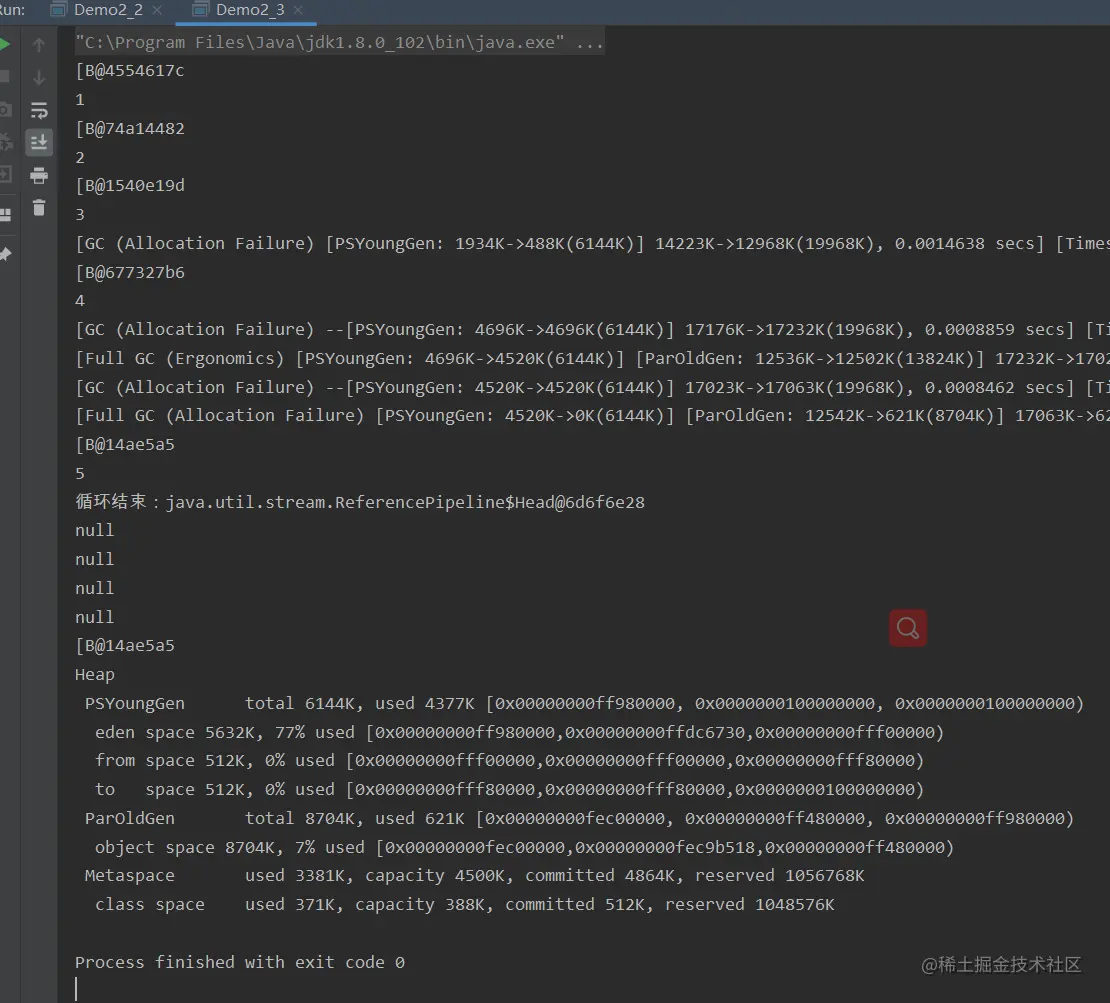
查看打印结果,程序在第四次循环的时候内存不足触发了垃圾回收,此时将前面的软引用的对象给回收了,所以我们最后打印结果只有第五个对象不为null
同时我们还可以配合引用队列来释放软引用自身
java
public class Demo2_3 {
private static final int _4MB = 4 * 1024 * 1024;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//list ---> SoftReference ---> byte[] list先引用了软引用对象SoftReference,软引用对象SoftReference再间接引用byte
List<SoftReference<byte[]>> list = new ArrayList<>();
//引用队列
ReferenceQueue<byte[]> queue = new ReferenceQueue<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
//引用对象关联引用队列,当软引用所关联的byte[]被回收时,软引用自己会加入到引用队列queue中去
SoftReference<byte[]> ref = new SoftReference<>(new byte[_4MB],queue);
System.out.println(ref.get());
list.add(ref);
System.out.println(list.size());
}
//poll方法就是从队列中获取最先放入队列的元素移除队列
//从队列中获取无用的软引用对象并移除
Reference<? extends byte[]> poll = queue.poll();
while (poll != null){
list.remove(poll);
poll = queue.poll();
}
System.out.println("循环结束:" + list.stream());
for (SoftReference<byte[]> softReference : list) {
System.out.println(softReference.get());
}
}
}运行程序:

前四次循环的软引用自身已经被释放
弱引用: 应用场景举例
java
public class Demo2_5 {
private static final int _4MB = 4 * 1024 * 1024;
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<WeakReference<byte[]>> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
WeakReference<byte[]> ref = new WeakReference<>(new byte[_4MB]);
list.add(ref);
for (WeakReference<byte[]> w : list) {
System.out.print(w.get()+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("循环结束:"+list.size());
}
}运行程序:
