✨✨ 欢迎大家来到贝蒂大讲堂✨✨
🎈🎈养成好习惯,先赞后看哦~🎈🎈
所属专栏:C++学习
贝蒂的主页:Betty's blog
为了让我们更加深入理解
list,接下来我们将模拟实现一个·简易版的list。而为了和STL库中的list以示区分,我们将使用命名空间namespace对其封装。
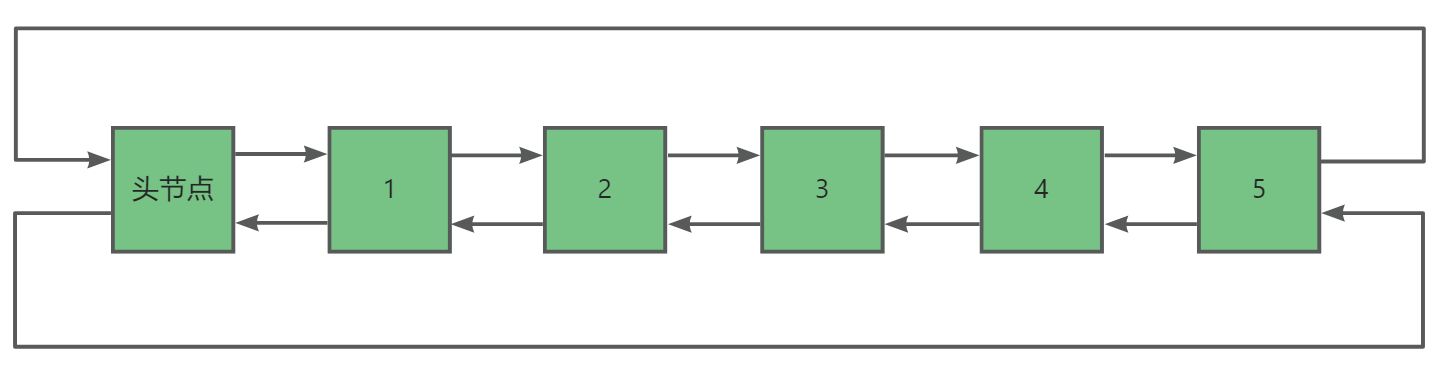
1. list的成员变量
list的底层其实就是我们之前在数据结构学习的双向循环链表,它由一个节点指针_head以及记录有效节点个数的_size
下面是list的成员变量以及主体架构:
cpp
namespace betty
{
template<class T>
struct _list_node//节点
{
_list_node<T>* _prev;
_list_node<T>* _next;
T _data;
_list_node(const T& x = T())
:_prev(nullptr)
,_next(nullptr)
,_data(x)
{
;
}
};
template<class T>
class list
{
public:
typedef _list_node<T> node;
//...成员函数
private:
node* _head;
size_t _size;
};
}
2. list的成员函数
在知道list的成员变量之后,接下来我们将探究list的成员函数,而常见成员函数的用法我们早在之前就已经介绍过了 ,下面我们将来具体实现一下:
2.1 list的迭代器
首先我们来模拟实现一下迭代器iterator,而在list中迭代器iterator与vector,string中的迭代器都不同,因为list每个节点在物理空间都不连续,所以我们不可能直接使用原生指针,而是要对原生指针进行封装形成一个list_iterator类。然后再这个类中进行运算符重载++,--,*,->,==,!=等操作符。
而我们知道迭代器又分为iterator与const_iterator两种,常规情况下我们这两个类都要实现。但他们功能就显得过于冗余了,所以我们可以采用增加模版参数的方法简化。第一个模版参数T代表节点类型,第二个模版参数Ref代表迭代器引用,第三个模版参数Ptr代表迭代器指针类型。
cpp
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct _list_iterator
{
typedef _list_node<T> node;//节点
typedef _list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;//迭代器本身
node* _node;//节点指针
_list_iterator(node* n)
:_node(n)//通过节点构建迭代器
{
;
}
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &(_node->_data);
}
Self& operator++()//前置++
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
Self operator++(int)//后置++
{
Self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_next;
return tmp;
}
Self& operator--()//前置--
{
_node = _node->_prev;
return *this;
}
Self operator--(int)//后置--
{
Self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_prev;
return tmp;
}
bool operator==(const Self& s)
{
return _node == s._node;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s)
{
return _node != s._node;
}
};然后再list中对不同迭代器类型进行typedef简化。
cpp
typedef _list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef _list_iterator< T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;接下来我们来实现begin()与end(),其中begin()指向的是列表的起始位置即第一个有效节点,而end()指向有效长度最后的下一位即头节点的位置,这些我们直接通过相应节点构造迭代器即可。
cpp
iterator begin()
{
return iterator(_head->_next);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(_head);
}实现完普通迭代器之后,我们可以顺便重载一个const_iterator的版本。
cpp
const_iterator begin()const
{
return const_iterator(_head->_next);
}
const_iterator end()const
{
return const_iterator(_head);
}我们知道在list中还有一个反向迭代器,这个我们在之后会统一实现。
2.2 list的初始化与销毁
2.2.1 构造函数与拷贝构造
我们之前在学习list时知道其初始化方式有很多,可以通过默认构造函数给其初始化,n个val初始化,也可以通过迭代器区间初始化。
首先我们写一个默认构造函数,构造出一个头节点指向自己。
cpp
void empty_initialize()
{
_head = new node;
_head ->_next = _head;
_head ->_prev = _head;
_size = 0;
}
list()
{
empty_initialize();
}这里有个问题就是empty_initialize是非const成员函数,那定义const成员是否还能来调用呢?答案自然是可以的,因为const变量在定义的时候是不具有const属性的,定义完成之后才有。比如说:
cpp
//如果在定义之前就具有const属性,那么n就无法赋值
const int n = 10;
const list<int> l1;接下来我们来实现迭代器初始化,而因为我们可以通过其他容器的迭代器对其初始化,所以要通过模版来实现。
cpp
template<class Iterator>
list(Iterator first, Iterator last)
{
empty_initialize();
while (first != last)
{
push_back(*first);
++first;
}
}最后我们来实现n个val初始化,这个构造我们可以直接复用resize()函数。
cpp
list(size_t n, const T& val = T())
{
empty_initialize();
resize(n, val);
}
list(int n, const T& val = T())
{
empty_initialize();
resize(n, val);
}至于为什么要同时重载int与size_t两种不同类型,那是为了防止在传两个int类型的参数时被编译器交给模版InputIterator识别,然后报错。
拷贝构造也十分简单,直接拷贝就行。
cpp
list(const list<T>& lt)
{
empty_initialize();
list tmp(lt.begin(),lt.end());
swap(tmp);//交换
}首先通过构造出一个与原列表it相同的列表tmp,然后让this所指向的列表与其交换,这样出了作用域之后销毁的就是原this所指向的列表。
2.2.2 赋值重载与析构函数
赋值运算符重载与拷贝构造的实现就非常类似了,直接实现即可。
cpp
list<T>& operator=(list<T> lt)
{
swap(lt);
return *this;
}最后我们实现析构函数,只需要清理资源即可
cpp
~list()
{
clear();//先清空其他节点
delete _head;//释放头节点
_head = nullptr;
}2.3 list的容量操作
2.3.1 size()与empty()
首先size()直接返回有效元素的个数,empty()判断有效元素个数是否为0。
cpp
size_t size()
{
return _size;
}
bool empty()
{
return _size == 0;
}2.3.2 clear()与resize()
首先clear()要清理掉除头节点外的所有节点,我们可以直接复用earse删除即可。
cpp
void clear()
{
iterator it = begin();
while (it != end())
{
it = erase(it);
}
}当使用 resize(n) 时,如果 n 大于当前列表的大小,那么会在列表末尾添加足够数量的默认值元素,使列表大小达到 n 。如果 n 小于当前列表的大小,那么会从列表末尾删除一些元素,使列表大小变为 n 。
cpp
void resize(size_t n, const T& val = T())
{
if (n < _size)
{
while (_size != n)
{
pop_back();//尾删
}
}
else
{
while (_size != n)
{
push_back(val);//尾插
}
}
}2.4 list的访问操作
因为列表并不支持重载operator[],我们只能实现front()与back()函数。可读可写与可读不可写。并且使用引用返回,减少不必要的拷贝。
cpp
// 可读可写
T& front()
{
return *(begin());
}
T& back()
{
return *(--end());
}
// 可读不可写
const T& front()const
{
return *(begin());
}
const T& back()const
{
return *(--end());
}2.5 list的修改操作
2.5.1 常见的修改操作
首先我们将实现两个常用的修改函数:push_back()与pop_back()。这两个函数也都可以复用insert()与·earse()
cpp
void push_back(const T& x)
{
insert(end(), x);
}
void pop_back()
{
erase(--end());
}然后我们同理可以实现push_front()与pop_front()。
cpp
void push_front(const T&x)
{
insert(begin(), x);
}
void pop_front()
{
erase(begin());
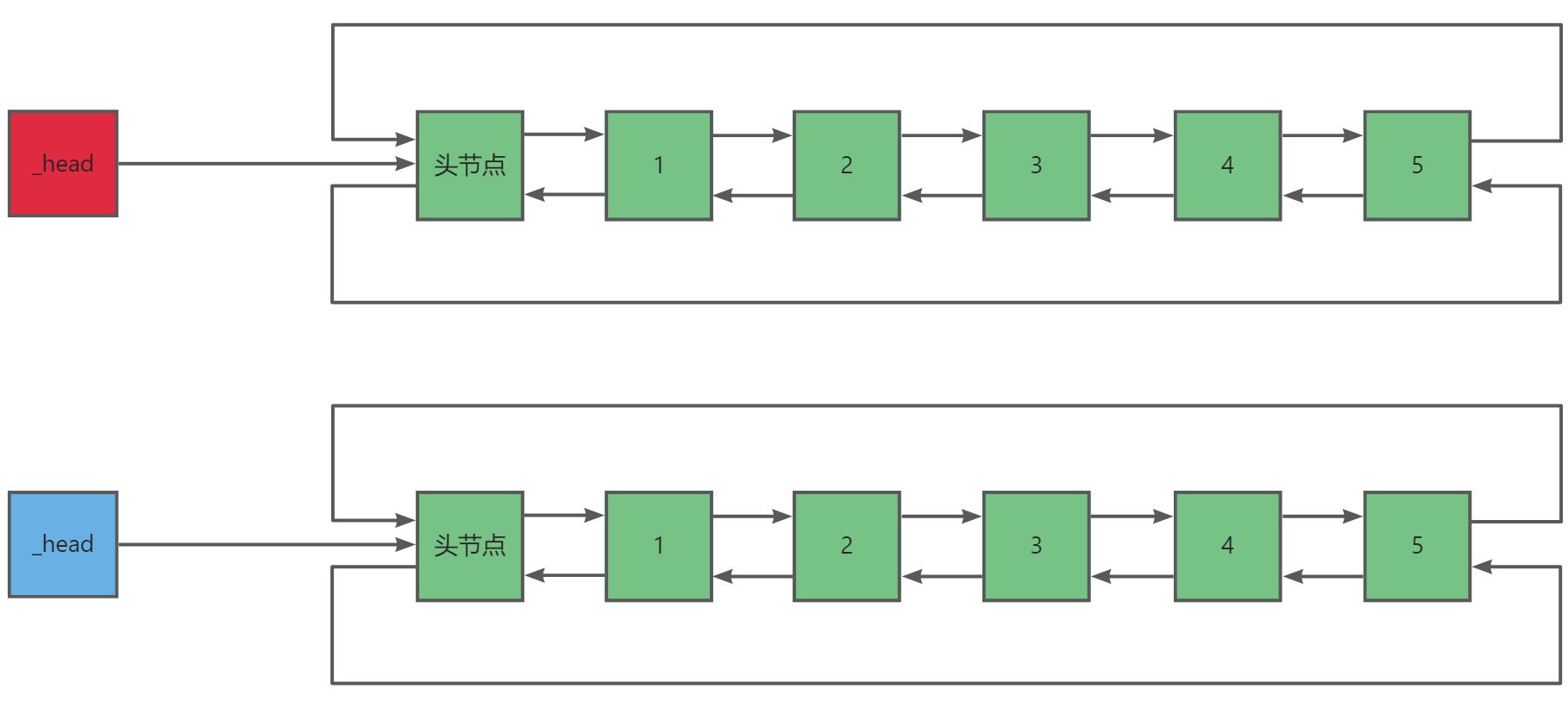
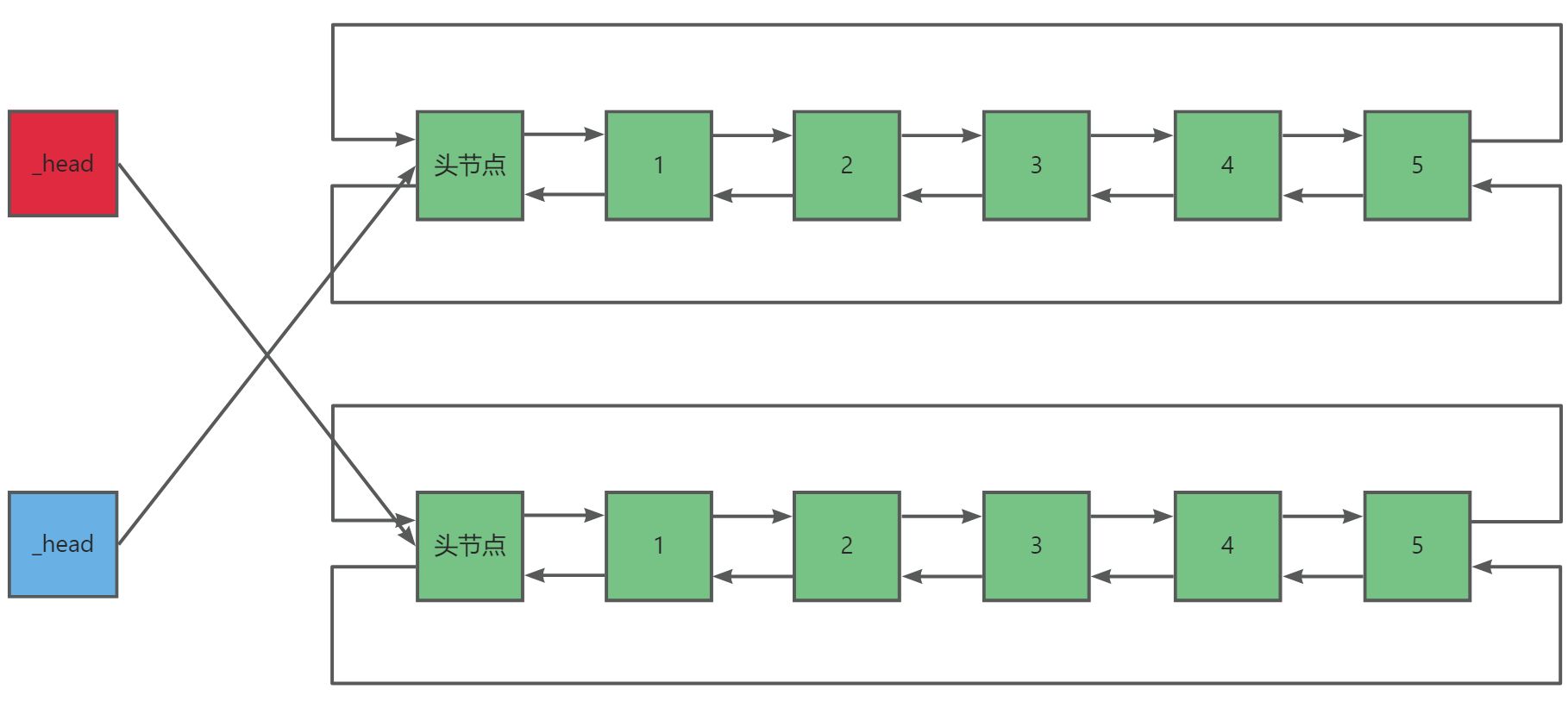
}随后我们来实现数组的交换swap()函数,我们知道list的交换其实就是指针_head,与有效个数_size的交换。
cpp
void swap(list<T>& lt)
{
std::swap(_head, lt._head);
std::swap(_size, lt._size);
}
2.5.2迭代器失效
接下来我们实现insert()与erase()两个函数。虽然插入并没有使迭代器失效,但为了与其他容量的功能视频,迭代器应指向新插入的节点。
cpp
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x)
{
node* newnode = new node(x);
node* cur = pos._node;
node* prev = cur->_prev;
prev->_next = newnode;
newnode->_prev = prev;
newnode->_next = cur;
cur->_prev = newnode;
++_size;
return iterator(newnode);
}erase为了防止迭代器失效,需要返回删除元素下一个元素的迭代器。
cpp
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
node* cur = pos._node;
node* prev = cur->_prev;
node* next = cur->_next;
prev->_next = next;
next->_prev = prev;
delete cur;
cur = nullptr;
--_size;
return iterator(next);
}3. 源码
cpp
#pragma once
#include<assert.h>
namespace betty
{
template<class T>
struct _list_node
{
_list_node<T>* _prev;
_list_node<T>* _next;
T _data;
_list_node(const T& x = T())
:_prev(nullptr)
,_next(nullptr)
,_data(x)
{
;
}
};
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct _list_iterator
{
typedef _list_node<T> node;//节点
typedef _list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;//迭代器本身
node* _node;//节点指针
_list_iterator(node* n)
:_node(n)
{
;
}
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &(_node->_data);
}
Self& operator++()//前置++
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
Self operator++(int)//后置++
{
Self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_next;
return tmp;
}
Self& operator--()//前置--
{
_node = _node->_prev;
return *this;
}
Self operator--(int)//后置--
{
Self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_prev;
return tmp;
}
bool operator==(const Self& s)
{
return _node == s._node;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s)
{
return _node != s._node;
}
};
template<class T>
class list
{
public:
typedef _list_node<T> node;
typedef _list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef _list_iterator< T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return iterator(_head->_next);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(_head);
}
const_iterator begin()const
{
return const_iterator(_head->_next);
}
const_iterator end()const
{
return const_iterator(_head);
}
void empty_initialize()
{
_head = new node;
_head ->_next = _head;
_head ->_prev = _head;
_size = 0;
}
list()
{
empty_initialize();
}
template<class Iterator>
list(Iterator first, Iterator last)
{
empty_initialize();
while (first != last)
{
push_back(*first);
++first;
}
}
list(size_t n, const T& val = T())
{
empty_initialize();
resize(n, val);
}
list(int n, const T& val = T())
{
empty_initialize();
resize(n, val);
}
list(const list<T>& lt)
{
empty_initialize();
list tmp(lt.begin(),lt.end());
swap(tmp);//交换
}
list<T>& operator=(list<T> lt)
{
swap(lt);
return *this;
}
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x)
{
node* newnode = new node(x);
node* cur = pos._node;
node* prev = cur->_prev;
prev->_next = newnode;
newnode->_prev = prev;
newnode->_next = cur;
cur->_prev = newnode;
++_size;
return iterator(newnode);
}
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
node* cur = pos._node;
node* prev = cur->_prev;
node* next = cur->_next;
prev->_next = next;
next->_prev = prev;
delete cur;
cur = nullptr;
--_size;
return iterator(next);
}
// 可读可写
T& front()
{
return *(begin());
}
T& back()
{
return *(--end());
}
// 可读不可写
const T& front()const
{
return *(begin());
}
const T& back()const
{
return *(--end());
}
void push_back(const T& x)
{
insert(end(), x);
}
void push_front(const T&x)
{
insert(begin(), x);
}
void pop_back()
{
erase(--end());
}
void pop_front()
{
erase(begin());
}
size_t size()
{
return _size;
}
bool empty()
{
return _size == 0;
}
void clear()
{
iterator it = begin();
while (it != end())
{
it = erase(it);
}
}
void resize(size_t n, const T& val = T())
{
if (n < _size)
{
while (_size != n)
{
pop_back();//尾删
}
}
else
{
while (_size != n)
{
push_back(val);//尾插
}
}
}
void swap(list<T>& lt)
{
std::swap(_head, lt._head);
std::swap(_size, lt._size);
}
~list()
{
clear();//先清空其他节点
delete _head;//释放头节点
_head = nullptr;
}
private:
node* _head;
size_t _size;
};
}