
❄专栏传送门:《C语言》、《数据结构与算法》、C语言刷题12天IO强训、LeetCode代码强化刷题、洛谷刷题、C/C++基础知识知识强化补充、C/C++干货分享&学习过程记录
🍉学习方向:C/C++方向
⭐️人生格言:为天地立心,为生民立命,为往圣继绝学,为万世开太平
前言:本文主要用C语言和C++跟大家做一下洛谷的一些入门题,主要是分支机构的部分。

目录
[1 Apples Prologue / 苹果和虫子](#1 Apples Prologue / 苹果和虫子)
[2 数的性质](#2 数的性质)
[3 闰年判断](#3 闰年判断)
[4 Apples](#4 Apples)
[5 洛谷团队系统](#5 洛谷团队系统)
[6 肥胖问题](#6 肥胖问题)
[7 三位数排序](#7 三位数排序)
C++的两个参考文档:
老朋友(非官方文档):cplusplus
官方文档(同步更新):cppreference
正文
1 Apples Prologue / 苹果和虫子
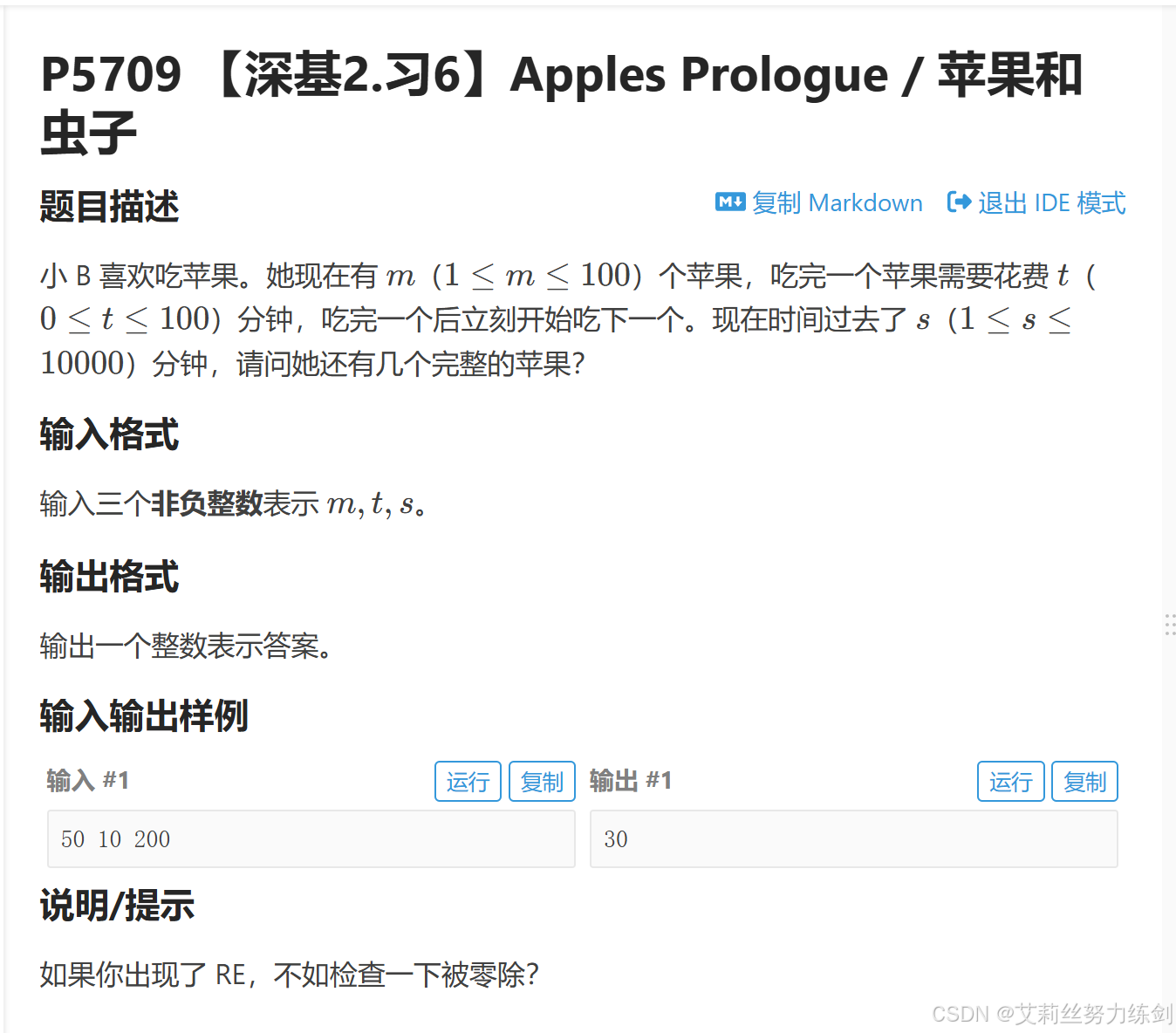
题目描述:
代码演示:
cpp
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int m,t,s;
cin>>m>>t>>s;
if(t==0)
{
cout<<0<<endl;
return 0;
}
if(s % t==0)
cout<<max(m-s/t,0);
if(s % t != 0)
cout<<max(m-s/t-1,0);
}博主用的是C++的写法,关于C++,大家可以关注一下博主的专栏,会介绍许多C++方向的干货:
这道题我们主要注意要用到分类讨论的思想------
(1)先判断t 是否为 0,为 0 我们直接打印,程序就结束了;
(2)如果t 不为 0,我们再分类讨论------s % t是否为 0,输出的就是对应的答案。
2 数的性质
题目链接:P5710 【深基3.例2】数的性质
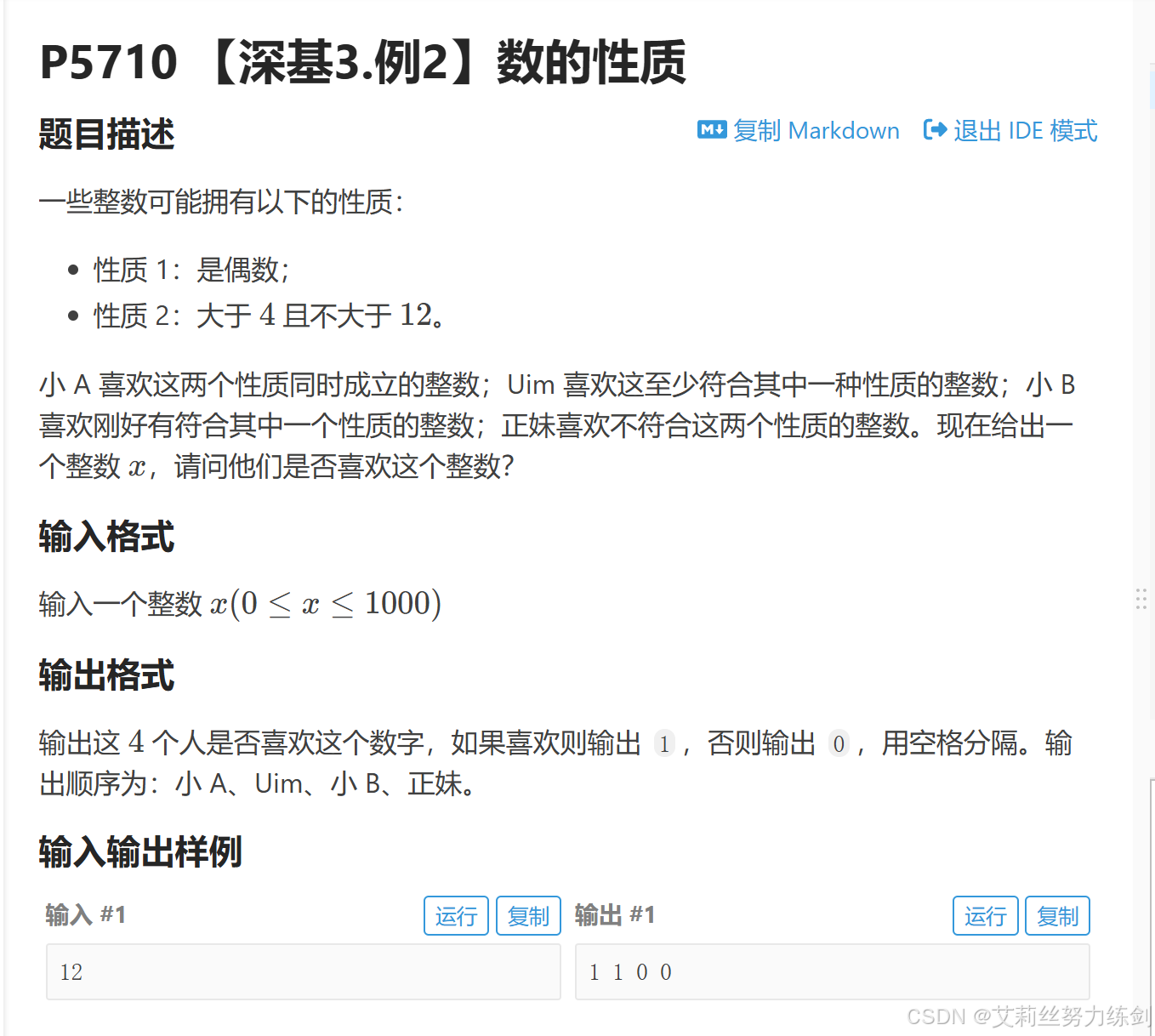
题目描述:
代码演示:
cpp
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x;cin>>x;
if(x%2==0&&x>4&&x<=12)
cout<<1<<' ';
else
cout<<0<<' ';
if((x%2==0)||(x>4&&x<=12))
cout<<1<<' ';
else
cout<<0<<' ';
if((x%2==0&&!(x>4&&x<=12))||(!(x%2==0)&&(x>4&&x<=12)))
cout<<1<<' ';
else
cout<<0<<' ';
if((x%2!=0)&&!(x>4&&x<=12))
cout<<1<<' ';
else
cout<<0<<' ';
return 0;
}这道题我们逐个讨论,用if/else语句一个一个实现分别满足4个人要求的结果就可以了。
3 闰年判断
题目链接:P5711 【深基3.例3】闰年判断
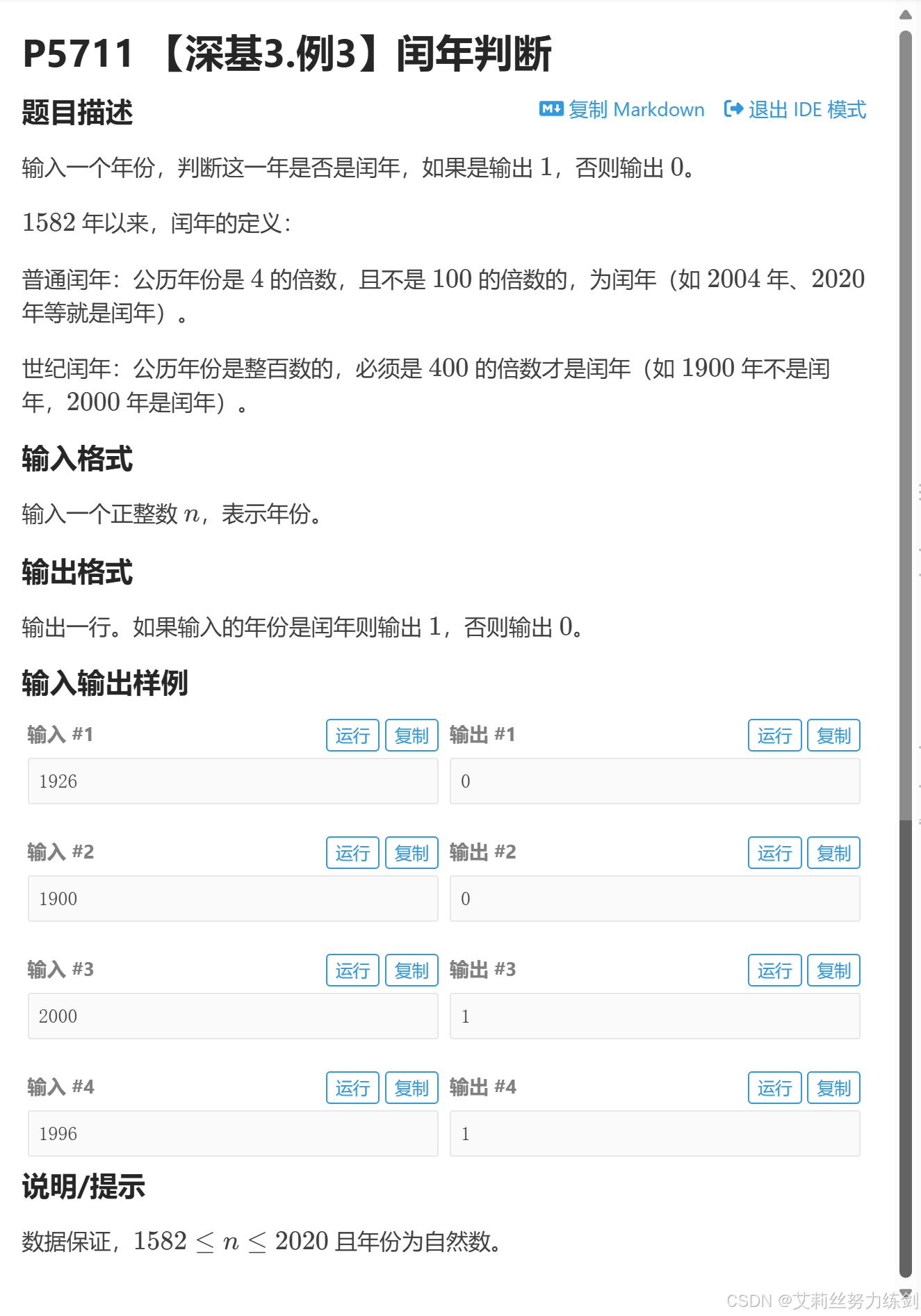
题目描述:
代码演示:
cpp
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;cin>>n;
if((n%4==0) && (n%100!=0)
||(n%400==0))
cout<<1<<endl;
else
cout<<0<<endl;
return 0;
}这道题是C语言中一道老生常谈的经典题目,只不过我们这次是要用C++来实现。
根据题目所给闰年满足的条件,我们就能写出代码:要么能被4整除且不能100整除(这是一个小的"且"的关系),要么就是能被400整除,这是一个大的"或"的关系。
4 Apples
题目链接:P5712 【深基3.例4】Apples
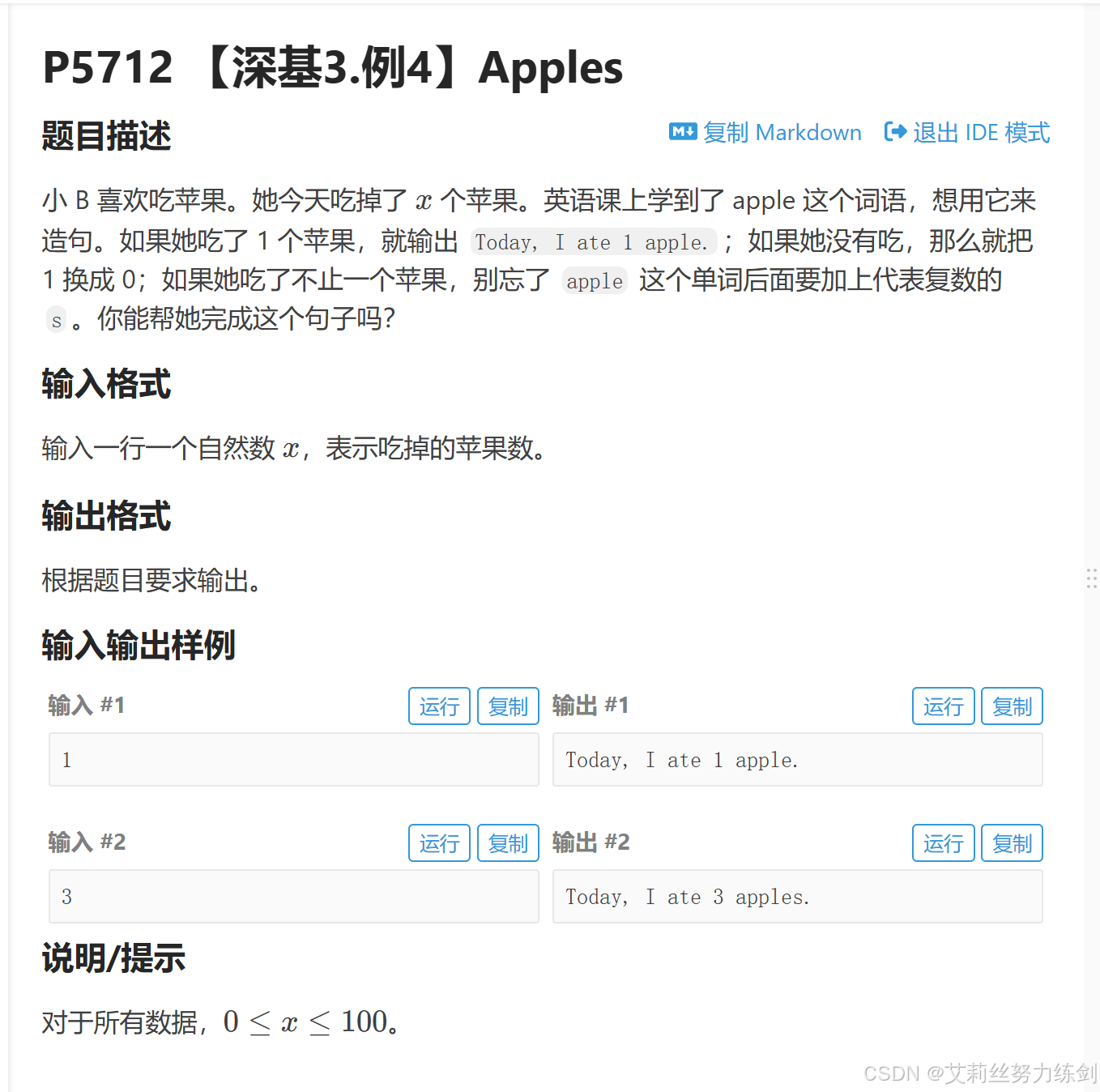
题目描述:
代码演示:
cpp
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x;cin>>x;
if(x==1)
cout<<"Today, I ate 1 apple."<<endl;
else if(x==0)
cout<<"Today, I ate 0 apple."<<endl;
else
printf("Today, I ate %d apples.",x);
return 0;
}这道题也是一道老生常谈的经典题目,我们根据题目给出的条件写就没有问题了。
根据题目所给吃掉苹果的数量,我们分成三种情况,就能写出代码:
吃了1个、没吃和吃了超过1个三种情况,我们直接if/else if/else,关键是最后一个条件要传一个未知数x,我们不确定到底是多少,所以直接用占位符%d代替,传一个x,输出直接用printf,C++就是在C语言中生长出来的语言,可以用printf。
5 洛谷团队系统
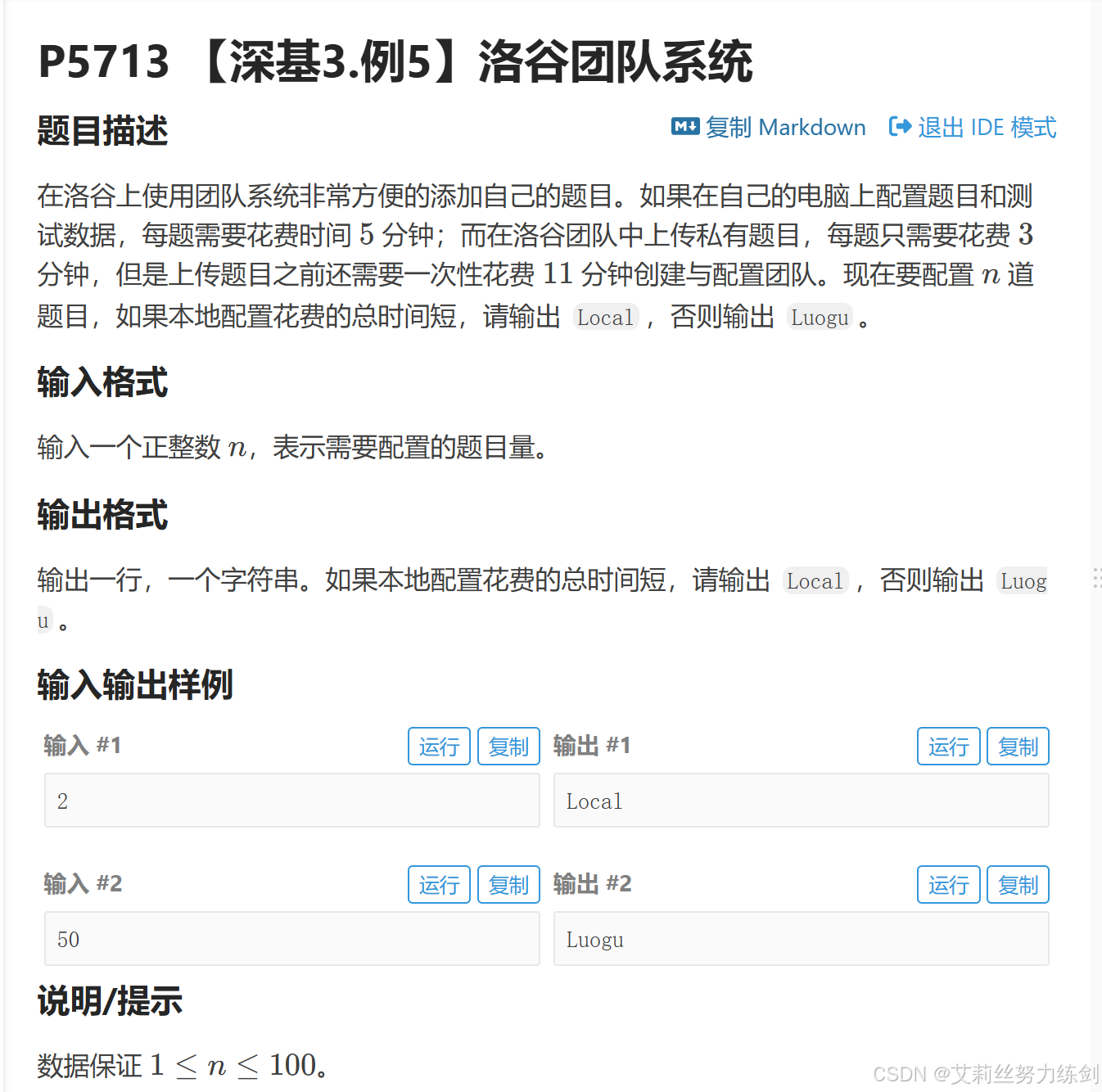
题目链接:P5713 【深基3.例5】洛谷团队系统
题目描述:
代码演示:
写法(1):
cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n; cin >> n;
int Jqj, Lmt;
Jqj = 5 * n;
Lmt = 11 + 3 * n;
if (Jqj < Lmt)
cout << "Local" << endl;
else
cout << "Luogu" << endl;
return 0;
}写法(2):
cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n; cin >> n;
if ((5 * n) < (3 * n + 11))
cout << "Local" << endl;
if ((5 * n) > (3 * n + 11))
cout << "Luogu" << endl;
return 0;
}这道题依然是一道老生常谈的经典题目,我们根据题目给出的条件写就没有问题了。
本题我们只要比较5 * n 和 3 * n + 11 就可以了。
6 肥胖问题
题目链接:P5714 【深基3.例7】肥胖问题
题目描述:

代码演示:
cpp
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
double m,h; cin>>m>>h;
double bmi=m/(h*h);
if(bmi<18.5)
cout<<"Underweight"<<endl;
else if(bmi>=18.5&&bmi<24)
cout<<"Normal"<<endl;
else
cout<<bmi<<'\n'<<"Overweight"<<endl;
return 0;
}这道题也是一道老生常谈的经典题目,我们根据题目给出的条件写就没有问题了。
这道题我们只要知道BMI的几个结点值:18.5、24就可以了。
7 三位数排序
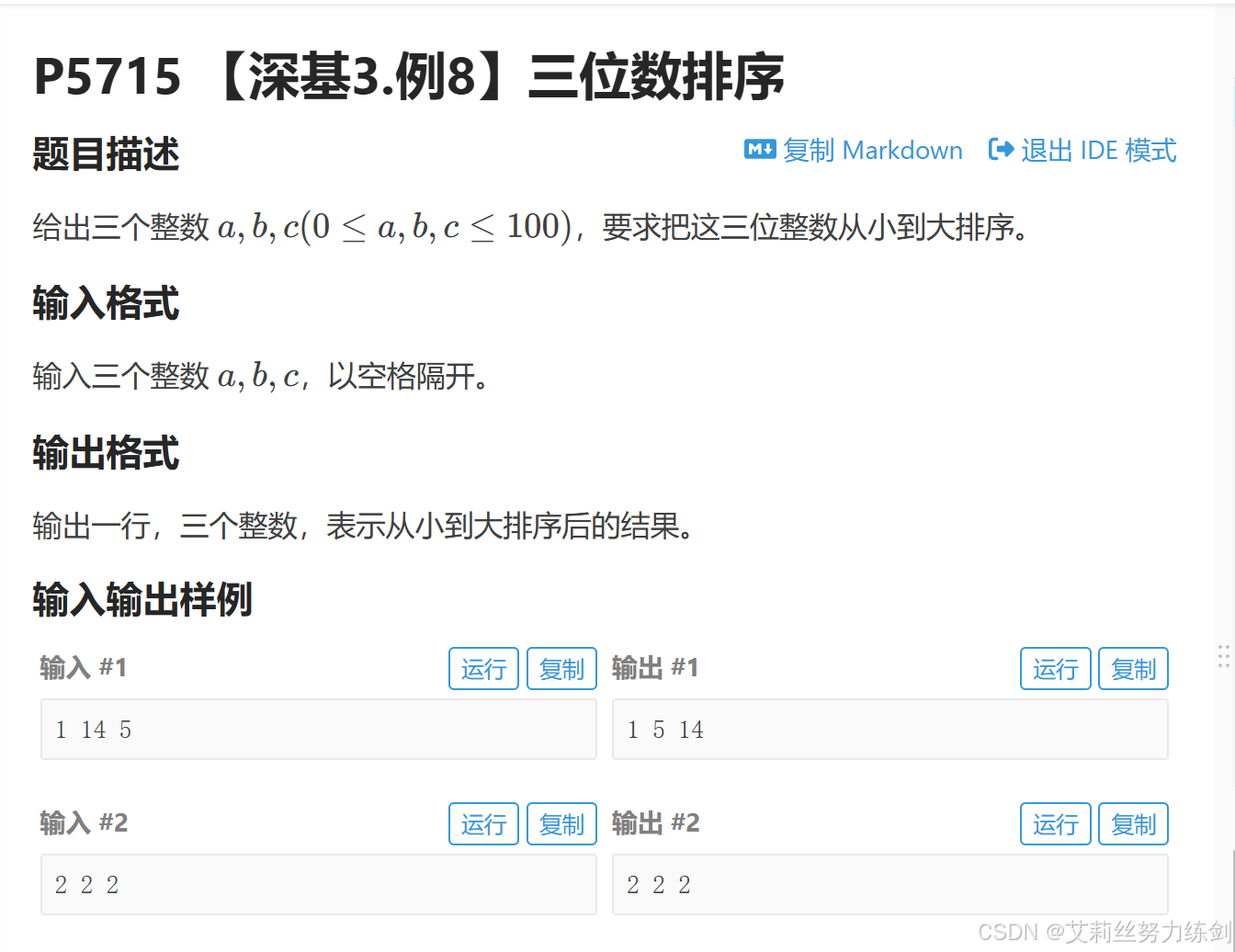
题目链接:P5715 【深基3.例8】三位数排序
题目描述:
代码演示:
cpp
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=105;
int a[N];
int main()
{
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
}
sort(a,a+3);
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
{
cout<<a[i]<<' '<<endl;
}
return 0;
}我们如果完全用C++的STL的sort排序就会异常简洁,代码演示如下:
cpp
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[3];
cin>>arr[0]>>arr[1]>>arr[2];
//C++的STL的sort排序
sort(arr,arr+3);
cout<<arr[0]<<" "<<arr[1]<<" "<<arr[2];
return 0;
}当然,用C语言也是可以写的,代码演示:
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d %d %d", &a, &b, &c);
// 比较交换法排序
if (a > b)
{
int tmp = a;
a = b;
b = tmp;
}
if (a > c)
{
int tmp = a;
a = c;
c = tmp;
}
if (b > c)
{
int tmp = b;
b = c;
c = tmp;
}
printf("%d %d %d", a, b, c);
return 0;
}这道题是一道老生常谈的经典题目,我们根据题目给出的条件写就没有问题了。
如果选择用C语言写,就直接比较交换进行排序,题目说从小到大,我们就用if语句分别判断a>c、a>b、b>c三种情况,再创建一个空的数组,把比较出来大的那个放到空数组tmp里面,再让大的那个的变量和小的那个变量一交换,再让原来存放小的那个变量(现在"空了")等于数组tmp,让tmp里面存放的那个大的数覆盖这个变量里面存放的小的那个数,这样进行三次if语句判断,分别完成交换,我们就把小的全部交换到前面了,完成三位数排序了。
结尾
**结语:**本文的内容到这里就结束了,记得给博主"一键四连"哦!感谢支持!