329. Longest Increasing Path in a Matrix
Given an m x n integers matrix, return the length of the longest increasing path in matrix.
From each cell, you can either move in four directions: left, right, up, or down. You may not move diagonally or move outside the boundary (i.e., wrap-around is not allowed).
Example 1:
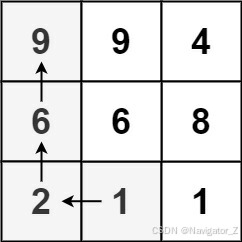
Input: matrix = [[9,9,4],[6,6,8],[2,1,1]]
Output: 4
Explanation: The longest increasing path is [1, 2, 6, 9].
Example 2:
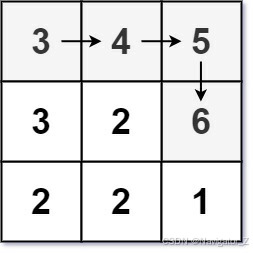
Input: matrix = [[3,4,5],[3,2,6],[2,2,1]]
Output: 4
Explanation: The longest increasing path is [3, 4, 5, 6]. Moving diagonally is not allowed.
Example 3:
Input: matrix = [[1]]
Output: 1
Constraints:
- m == matrix.length
- n == matrix[i].length
- 1 <= m, n <= 200
- 0 < = m a t r i x [ i ] [ j ] < = 2 31 − 1 0 <= matrix[i][j] <= 2^{31} - 1 0<=matrix[i][j]<=231−1
From: LeetCode
Link: 329. Longest Increasing Path in a Matrix
Solution:
Ideas:
- DFS with Memoization: The solution uses Depth-First Search (DFS) combined with memoization to explore all possible paths starting from each cell in the matrix.
- Memoization: An array memo is used to store the length of the longest path starting from each cell to avoid redundant calculations.
- Directions Array: The array directions stores the four possible directions (up, down, left, right) in which one can move.
Code:
c
int dfs(int** matrix, int m, int n, int** memo, int i, int j) {
if (memo[i][j] != 0) return memo[i][j];
int directions[4][2] = {{1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}};
int maxLength = 1;
for (int d = 0; d < 4; d++) {
int x = i + directions[d][0];
int y = j + directions[d][1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && matrix[x][y] > matrix[i][j]) {
int len = 1 + dfs(matrix, m, n, memo, x, y);
maxLength = (len > maxLength) ? len : maxLength;
}
}
memo[i][j] = maxLength;
return maxLength;
}
int longestIncreasingPath(int** matrix, int matrixSize, int* matrixColSize) {
if (matrixSize == 0 || matrixColSize[0] == 0) return 0;
int m = matrixSize;
int n = matrixColSize[0];
int** memo = (int**)malloc(m * sizeof(int*));
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
memo[i] = (int*)calloc(n, sizeof(int));
}
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
int len = dfs(matrix, m, n, memo, i, j);
result = (len > result) ? len : result;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
free(memo[i]);
}
free(memo);
return result;
}