Springboot整合J2Cache
一、J2Caceh多级缓存
J2Cache 是 OSChina 目前正在使用的两级缓存框架(要求至少 Java 8)。
第一级缓存使用内存(同时支持 Ehcache 2.x、Ehcache 3.x 和 Caffeine),第二级缓存使用 Redis(推荐)/Memcached 。
-
L1: 进程内缓存 caffeine(默认使用) / ehcache
-
L2: 集中式缓存 Redis(推荐使用) / Memcached
由于大量的缓存读取会导致 L2 的网络成为整个系统的瓶颈,因此 **L1 的目标是降低对 L2 的读取次数**。 该缓存框架主要用于集群环境中。单机也可使用,用于**避免应用重启导致的缓存冷启动后对后端业务的冲击**、重启导致的ehcache缓存数据丢失。 J2Cache **默认使用Caffeine(https://gitee.com/link?target=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.oschina.net%2Fp%2Fben-manes-caffeine)作为一级缓存**,使用 Redis 作为二级缓存(https://so.csdn.net/so/search?q=%E4%BA%8C%E7%BA%A7%E7%BC%93%E5%AD%98&spm=1001.2101.3001.7020) 。你还可以选择 Ehcache2 和 Ehcache3 作为一级缓存。J2Cache 从 1.3.0 版本开始支持 JGroups 和 Redis Pub/Sub 两种方式进行缓存事件的通知。在某些云平台上可能无法使用 JGroups 组播方式,可以采用 Redis 发布订阅的方式。详情请看 j2cache.properties 配置文件的说明。
1.1 设计思路
将Ehcache和Redis结合起来,将Ehcache(也可以使用caffeine cache)作为一级缓存、将redis(也可以使用memcached )作为二级缓存,取长补短。
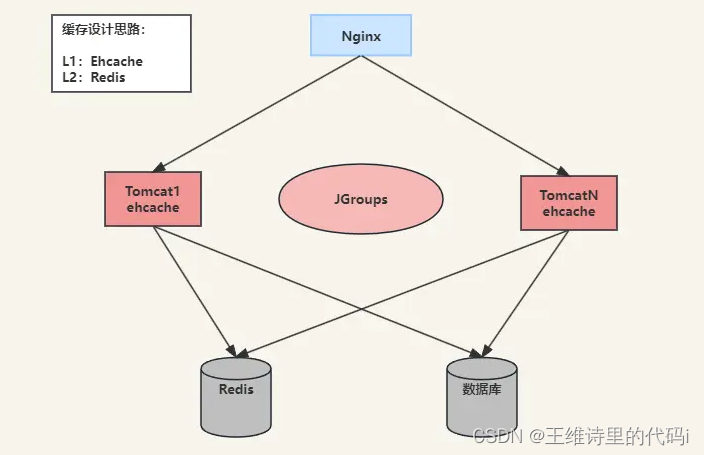
尽量从本机取数据,取不到的时候再去redis里面取。这样结合可以保证高性能。数据基本上都是从Ehcache里面取得,有效的缓解应用冷启动对数据库的压力,应用和redis之间不会频繁的有大量数据传输。数据传输只存在应用冷启动及缓存变更时。
- 数据读取顺序:-> L1(进程内缓存) -> L2(集中式缓存) -> DB(数据库缓存)
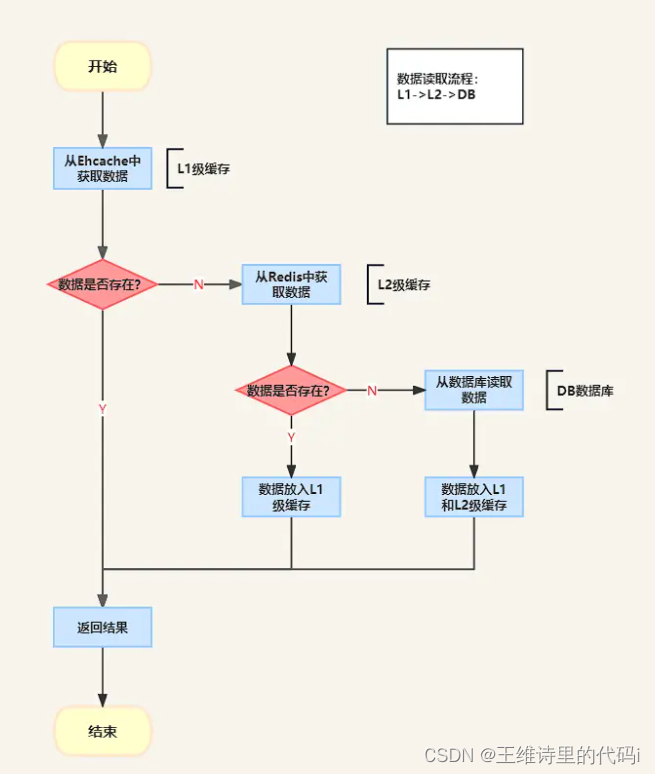
J2Cache 目前提供两种节点间数据同步的方案 ------ Redis Pub/Sub 和 JGroups 。当某个节点的缓存数据需要更新时,J2Cache 会通过 Redis 的消息订阅机制或者是 JGroups 的组播来通知集群内其他节点。当其他节点收到缓存数据更新的通知时,它会清掉自己内存里的数据,然后重新从 Redis 中读取最新数据。这就完成了 J2Cache 缓存数据读写的闭环。
- 数据更新顺序:
- 从数据库中读取最新数据,依次更新 L1 -> L2 ,发送广播清除某个缓存信息
- 接收到广播(手工清除缓存 & 一级缓存自动失效),从 L1 中清除指定的缓存信息
二、J2Cache二级缓存的实现
J2Cache 默认使用 Caffeine 作为一级缓存,使用 Redis 作为二级缓存。你还可以选择 Ehcache2 和 Ehcache3 作为一级缓存。
准备工作:
-
安装 Redis
-
新建一个基于 Maven 的 Java 项目
2.1 引入Maven
xml
<!-- J2Cache(两级缓存): 一个基于Redis的Java缓存框架,支持多种缓存策略,并提供了多种缓存注解,可以方便的集成到Spring、Spring Boot等主流框架中。 -->
<!-- j2cache与spring bott整合的工具 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>net.oschina.j2cache</groupId>
<artifactId>j2cache-spring-boot2-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.8.0-release</version>
</dependency>
<!-- j2cache 的核心包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>net.oschina.j2cache</groupId>
<artifactId>j2cache-core</artifactId>
<version>2.8.4-release</version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-simple</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>2.2 配置文件的准备
拷贝 j2cache.properties 和 caffeine.properties 到你项目的源码目录,并确保这些文件会被编译到项目的 classpath 中。
-
j2cache.properties 配置文件内容
properties## 1级缓存 #j2cache.L1.provider_class = ehcache #ehcache.configXml = ehcache.xml # ## 2级缓存 #j2cache.L2.provider_class =net.oschina.j2cache.cache.support.redis.SpringRedisProvider #j2cache.L2.config_section = redis #redis.hosts = localhost:6379 ## 1级缓存中的数据如何到达2级缓存 #j2cache.broadcast =net.oschina.j2cache.cache.support.redis.SpringRedisPubSubPolicy #J2Cache configuration ######################################### # Level 1&2 provider # values: # none -> disable this level cache # ehcache -> use ehcache2 as level 1 cache # ehcache3 -> use ehcache3 as level 1 cache # caffeine -> use caffeine as level 1 cache(only in memory) # redis -> use redis as level 2 cache (using jedis) # lettuce -> use redis as level 2 cache (using lettuce) # readonly-redis -> use redis as level 2 cache ,but never write data to it. if use this provider, you must uncomment `j2cache.L2.config_section` to make the redis configurations available. # memcached -> use memcached as level 2 cache (xmemcached), # [classname] -> use custom provider ######################################### # 一级缓存 j2cache.L1.provider_class = caffeine caffeine.properties = /caffeine.properties # 内嵌的方式配置caffeine 中的配置信息 #caffeine.default = 1000, 30m #caffeine.rx=50, 2h #caffeine.users=50, 2h # 二级缓存 # 启用L2缓存 Redis #j2cache.L2.provider_class = redis # 是否启用同步一级缓存的Time-To-Live超时时间到Redis TTL(true启用,false不启用则永不超时) j2cache.sync_ttl_to_redis = true j2cache.serialization = json # 启用L2缓存 lettuce j2cache.L2.provider_class = lettuce # xxx使用rabbitmq广播通知 #j2cache.broadcast = lettuce j2cache.broadcast =net.oschina.j2cache.cache.support.redis.SpringRedisPubSubPolicy # When L2 provider isn't `redis`, using `L2.config_section = redis` to read redis configurations # j2cache.L2.config_section = redis # Enable/Disable ttl in redis cache data (if disabled, the object in redis will never expire, default:true) # NOTICE: redis hash mode (redis.storage = hash) do not support this feature) # Whether to cache null objects by default (default false) j2cache.default_cache_null_object = true ######################################### # Cache Serialization Provider # values: # fst -> using fast-serialization (recommend) # kryo -> using kryo serialization # json -> using fst's json serialization (testing) # fastjson -> using fastjson serialization (embed non-static class not support) # java -> java standard # fse -> using fse serialization # [classname implements Serializer] ######################################### #json.map.person = net.oschina.j2cache.demo.Person ######################################### # Ehcache configuration ######################################### # ehcache.configXml = /ehcache.xml # ehcache3.configXml = /ehcache3.xml # ehcache3.defaultHeapSize = 1000 ######################################### # Caffeine configuration # caffeine.region.[name] = size, xxxx[s|m|h|d] # ######################################### ######################################### # Redis connection configuration ######################################### ######################################### # Redis Cluster Mode # # single -> single redis server # sentinel -> master-slaves servers # cluster -> cluster servers (\u6570\u636e\u5e93\u914d\u7f6e\u65e0\u6548\uff0c\u4f7f\u7528 database = 0\uff09 # sharded -> sharded servers (\u5bc6\u7801\u3001\u6570\u636e\u5e93\u5fc5\u987b\u5728 hosts \u4e2d\u6307\u5b9a\uff0c\u4e14\u8fde\u63a5\u6c60\u914d\u7f6e\u65e0\u6548 ; redis://user:password@127.0.0.1:6379/0\uff09 # ######################################### redis.mode = single #redis storage mode (generic|hash) redis.storage = generic ## redis pub/sub channel name redis.channel = j2cache ## redis pub/sub server (using redis.hosts when empty) redis.channel.host = #cluster name just for sharded redis.cluster_name = j2cache ## redis cache namespace optional, default[empty] redis.namespace = ## redis command scan parameter count, default[1000] #redis.scanCount = 1000 ## connection # Separate multiple redis nodes with commas, such as 192.168.0.10:6379,192.168.0.11:6379,192.168.0.12:6379 redis.hosts = 119.91.255.122:6379 redis.timeout = 5000 redis.password = lcjRedis123.. redis.database = 10 redis.ssl = false ## redis pool properties # 最大连接数(获取连接时进行判断,也即连接数的上限) redis.maxTotal = 100 # 最大空闲连接数(在归还连接时判断,若当前连接数超过maxIdle连接数,则释放归还的连接) redis.maxIdle = 10 # 获取连接的最大等待时长ms(当连接池已耗尽时) redis.maxWaitMillis = 5000 # 驱逐空闲连接的最小间隔时间 redis.minEvictableIdleTimeMillis = 60000 # 最小空闲连接数(超过maxIdle则使用maxIdle值,单独的Evict任务负责清理超时的连接) redis.minIdle = 1 redis.numTestsPerEvictionRun = 10 # 获取资源后进先出(false则对应先进先出) redis.lifo = false redis.softMinEvictableIdleTimeMillis = 10 # 是否测试连接可用 redis.testOnBorrow = true redis.testOnReturn = false redis.testWhileIdle = true redis.timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis = 300000 # 当资源池耗尽,获取连接时是否需要等待 redis.blockWhenExhausted = false redis.jmxEnabled = false ######################################### # Lettuce scheme # # redis -> single redis server # rediss -> single redis server with ssl # redis-sentinel -> redis sentinel # redis-cluster -> cluster servers # ######################################### ######################################### # Lettuce Mode # # single -> single redis server # sentinel -> master-slaves servers # cluster -> cluster servers (\u6570\u636e\u5e93\u914d\u7f6e\u65e0\u6548\uff0c\u4f7f\u7528 database = 0\uff09 # sharded -> sharded servers (\u5bc6\u7801\u3001\u6570\u636e\u5e93\u5fc5\u987b\u5728 hosts \u4e2d\u6307\u5b9a\uff0c\u4e14\u8fde\u63a5\u6c60\u914d\u7f6e\u65e0\u6548 ; redis://user:password@127.0.0.1:6379/0\uff09 # ######################################### ## redis command scan parameter count, default[1000] #lettuce.scanCount = 1000 lettuce.mode = single lettuce.namespace = lettuce.storage = hash lettuce.channel = j2cache lettuce.scheme = redis lettuce.hosts = 119.91.255.122:6379 lettuce.password = lcjRedis123.. lettuce.database = 10 lettuce.sentinelMasterId = lettuce.sentinelPassword = lettuce.maxTotal = 100 lettuce.maxIdle = 10 lettuce.minIdle = 10 # timeout in milliseconds lettuce.timeout = 10000 # redis cluster topology refresh interval in milliseconds lettuce.clusterTopologyRefresh = 3000 ## 1级缓存中的数据如何到达2级缓存 ######################################### # Cache Broadcast Method # values: # jgroups -> use jgroups's multicast # redis -> use redis publish/subscribe mechanism (using jedis) # lettuce -> use redis publish/subscribe mechanism (using lettuce, Recommend) # rabbitmq -> use RabbitMQ publisher/consumer mechanism # rocketmq -> use RocketMQ publisher/consumer mechanism # none -> don't notify the other nodes in cluster # xx.xxxx.xxxx.Xxxxx your own cache broadcast policy classname that implement net.oschina.j2cache.cluster.ClusterPolicy ######################################### #j2cache.broadcast = redis #j2cache.broadcast =net.oschina.j2cache.cache.support.redis.SpringRedisPubSubPolicy # jgroups properties jgroups.channel.name = j2cache jgroups.configXml = /network.xml # RabbitMQ properties rabbitmq.exchange = j2cache rabbitmq.host = localhost rabbitmq.port = 5672 rabbitmq.username = guest rabbitmq.password = guest # RocketMQ properties rocketmq.name = j2cache rocketmq.topic = j2cache # use ; to split multi hosts rocketmq.hosts = 127.0.0.1:9876 -
caffeine作为一级缓存时的配置文件 caffeine.properties
properties######################################### # Caffeine configuration # [name] = size, xxxx[s|m|h|d] ######################################### # 定义缓存名default,对象大小1000,缓存数据有效时间30分钟。 可以定义多个不同名称的缓存。 default = 1000, 30m rx=50, 2h
注意:如果你选择了 ehcache 作为一级缓存,需要拷贝 ehcache.xml 或者 ehcache3.xml 到源码目录(后者对应的是 Ehcache 3.x 版本)2.3.1中有提供 。
-
采用application.yml 配置相关信息方案 [该方式也需要在resources下添加 对应的一级缓存配置文件]
yaml#L1: 进程内缓存 caffeine/ehcache #L2: 集中式缓存 Redis/Memcached j2cache: # config-location: j2cache.properties cache-clean-mode: passive allow-null-values: true redis-client: lettuce #指定redis客户端使用lettuce,也可以使用Jedis l2-cache-open: true #开启二级缓存 #利用Redis的发布/订阅功能实现的广播策略。通过这个配置,可以在使用J2Cache缓存时,实现缓存的广播通知,确保缓存的一致性。 broadcast: net.oschina.j2cache.cache.support.redis.SpringRedisPubSubPolicy # broadcast: jgroups L1: #指定一级缓存提供者为ehcache/caffeine provider_class: caffeine L2: #指定二级缓存提供者为redis provider_class: net.oschina.j2cache.cache.support.redis.SpringRedisProvider config_section: lettuce # 是否启用同步一级缓存的Time-To-Live超时时间到Redis TTL(true启用,false不启用则永不超时) sync_ttl_to_redis: true default_cache_null_object: false serialization: json #序列化方式:fst、kyro、Java\json caffeine: # 这个配置文件需要放在项目中 properties: /caffeine.properties lettuce: mode: single namespace: storage: generic channel: j2cache scheme: redis hosts: ${test.redis.ip}:${test.redis.port} password: ${test.redis.password} database: ${test.redis.database} pool: database: 15 # 连接池中的最小空闲连接 min-idle: 2 # 连接池中的最大空闲连接 max-idle: 5 # 连接池的最大数据库连接数 max-active: 10 # #连接池最大阻塞等待时间(使用负值表示没有限制) max-wait: -1ms sentinelMasterId: # =========== 配置文件参数设置 =========== test: redis: ip: 127.0.0.1 port: 6379 password: lcjRedis123.. database: 15
2.3 其它实行方案
2.3.1 使用ehcache作为一级缓存
首先修改 j2cache.properties 中的 j2cache.L1.provider_class 为 ehcache 或者 ehcache3,然后拷贝 ehcache.xml 或者 ehcache3.xml 到类路径,并配置好缓存,需要在项目中引入对 ehcache 的支持:
xml
<dependency><!-- Ehcache 2.x //-->
<groupId>net.sf.ehcache</groupId>
<artifactId>ehcache</artifactId>
<version>2.10.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency><!-- Ehcache 3.x //-->
<groupId>org.ehcache</groupId>
<artifactId>ehcache</artifactId>
<version>3.4.0</version>
</dependency>由于ehcache的配置有独立的配置文件格式,因此还需要指定ehcache的配置文件,以便于读取相应配置
-
ehcache.xml 配置文件
xml<!-- for ehcache 2.x --> <ehcache updateCheck="false" dynamicConfig="false"> <diskStore path="java.io.tmpdir"/> <cacheManagerEventListenerFactory class="" properties=""/> <!--Default Cache configuration. These will applied to caches programmatically created through the CacheManager. The following attributes are required for defaultCache: maxInMemory - Sets the maximum number of objects that will be created in memory eternal - Sets whether elements are eternal. If eternal, timeouts are ignored and the element is never expired. timeToIdleSeconds - Sets the time to idle for an element before it expires. Is only used if the element is not eternal. Idle time is now - last accessed time timeToLiveSeconds - Sets the time to live for an element before it expires. Is only used if the element is not eternal. TTL is now - creation time overflowToDisk - Sets whether elements can overflow to disk when the in-memory cache has reached the maxInMemory limit. --> <!--默认缓存策略 --> <!-- external:是否永久存在,设置为true则不会被清除,此时与timeout冲突,通常设置为false--> <!-- diskPersistent:是否启用磁盘持久化--> <!-- maxElementsInMemory:最大缓存数量--> <!-- overflowToDisk:超过最大缓存数量是否持久化到磁盘--> <!-- timeToIdleSeconds:最大不活动间隔,设置过长缓存容易溢出,设置过短无效果,可用于记录时效性数据,例如验证码--> <!-- timeToLiveSeconds:最大存活时间--> <!-- memoryStoreEvictionPolicy:缓存清除策略--> <defaultCache eternal="false" diskPersistent="false" maxElementsInMemory="1000" eternal="false" timeToIdleSeconds="1800" timeToLiveSeconds="1800" overflowToDisk="true"> </defaultCache> <!--Predefined caches. Add your cache configuration settings here. If you do not have a configuration for your cache a WARNING will be issued when the CacheManager starts The following attributes are required for defaultCache: name - Sets the name of the cache. This is used to identify the cache. It must be unique. maxInMemory - Sets the maximum number of objects that will be created in memory eternal - Sets whether elements are eternal. If eternal, timeouts are ignored and the element is never expired. timeToIdleSeconds - Sets the time to idle for an element before it expires. Is only used if the element is not eternal. Idle time is now - last accessed time timeToLiveSeconds - Sets the time to live for an element before it expires. Is only used if the element is not eternal. TTL is now - creation time overflowToDisk - Sets whether elements can overflow to disk when the in-memory cache has reached the maxInMemory limit. --> <cache name="example" maxElementsInMemory="5000" eternal="false" timeToIdleSeconds="1800" timeToLiveSeconds="1800" overflowToDisk="false" > </cache> </ehcache> -
ehcache3.xml 配置文件
xml<!-- for ehcache 3.x --> <config xmlns:xsi='http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance' xmlns='http://www.ehcache.org/v3' xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.ehcache.org/v3 http://www.ehcache.org/schema/ehcache-core.xsd"> <!-- Don't remote default cache configuration --> <cache-template name="default"> <key-type>java.lang.String</key-type> <value-type>java.io.Serializable</value-type> <expiry> <ttl unit="seconds">1800</ttl> </expiry> <resources> <heap>1000</heap> <offheap unit="MB">100</offheap> </resources> </cache-template> <cache alias="default" uses-template="default"/> </config>
2.3.2 使用 RabbitMQ 作为消息通知
首先修改 j2cache.properties 中的 j2cache.broadcast 为 rabbitmq,然后在 j2cache.properties 中配置 rabbitmq.xxx 相关信息。
需要在项目中引入对 rabbitmq 的支持:
xml
<dependency>
<groupId>com.rabbitmq</groupId>
<artifactId>amqp-client</artifactId>
<version>5.3.0</version>
</dependency>2.3.3 使用 memcached 作为二级缓存
首先修改 j2cache.properties 中的 j2cache.L2.provider_class 为 memcached,然后在 j2cache.properties 中配置 memcached.xxx 相关信息。
需要在项目中引入对 memcached 的支持:
xml
<dependency>
<groupId>com.googlecode.xmemcached</groupId>
<artifactId>xmemcached</artifactId>
<version>2.4.5</version>
</dependency>2.3.4 如何使用 JGroups组传播方式(无法在云主机中使用)
首先修改 j2cache.properties 中的 j2cache.broadcast 值为 jgroups,然后在 maven 中引入
xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jgroups</groupId>
<artifactId>jgroups</artifactId>
<version>3.6.13.Final</version>
</dependency>三、声明式缓存
使用j2cache可以将数据进行多级缓存。如果项目中很多模块都需要使用缓存功能,这些模块都需要调用j2cache的API来进行缓存操作,这种j2cache提供的原生API使用起来就比较繁琐了,并且操作缓存的代码和我们的业务代码混合到一起,即j2cache的API对我们的业务代码具有侵入性。
基于上述情况,我们可以采用声明式缓存。即:定义缓存注解,在需要使用缓存功能的方法上加入缓存注解即可自动进行缓存操作。
注意:j2cache原生API和我们实现的声明式缓存可以兼容,即在项目中可以同时使用,互为补充。例如在Controller的方法中需要将多类业务数据载入缓存,此时通过声明式缓存就无法做到(因为声明式缓存只能将方法的返回值载入缓存),这种场景下就需要调用j2cache的原生API来完成。
3.1 实现思路
声明式缓存底层实现原理是基于AOP,通过代理技术来实现的。更确切的说,就是通过Spring提供的拦截器来拦截Controller,在拦截器中动态获取Controller方法上的注解,从而进行缓存相关操作。
要实现声明式缓存,需要设计如下主要的类和注解:
-
Cache:缓存注解,在Controller的方法上使用,用于缓存此方法的返回值
-
CacheEvictor:清理缓存注解,在Controller的方法上使用,用于清理指定缓存数据
-
CacheMethodInterceptor:缓存拦截器,用于拦截加入缓存相关注解的Controller方法
-
AbstractCacheAnnotationProcessor:抽象缓存注解处理器,为缓存操作提供一些公共方法
-
CachesAnnotationProcessor:缓存注解处理器,当Controller的方法上加入Cache注解时由此处理器进行缓存处理
-
CacheEvictorAnnotationProcessor:失效缓存注解处理器,当Controller的方法上加入CacheEvictor注解时由此处理器进行缓存失效处理
-
EnableCache:开启缓存功能注解,一般在项目的启动类上使用,用于开启缓存功能
3.2 声明式缓存代码实现
3.2.1 自定义缓存注解类
-
自定义注解,用于指定对应方法,标记该方法的返回值进行缓存
javapackage com.test.test_redis_j2cache.J2cache.annotation; import java.lang.annotation.*; /** * @ClassName : Cache * @Description : 缓存注解 * 1. @Documented -- 表示使用该注解的元素应被javadoc或类似工具文档化,它应用于类型声明,类型声明的注解会影响客户端对注解元素的使用。如果一个类型声明添加了Documented注解,那么它的注解会成为被注解元素的公共API的一部分。 * 2. @Target -- 表示支持注解的程序元素的种类,一些可能的值有TYPE, METHOD, CONSTRUCTOR, FIELD等等。如果Target元注解不存在,那么该注解就可以使用在任何程序元素之上。 * 3. @Inherited -- 表示一个注解类型会被自动继承,如果用户在类声明的时候查询注解类型,同时类声明中也没有这个类型的注解,那么注解类型会自动查询该类的父类,这个过程将会不停地重复,直到该类型的注解被找到为止,或是到达类结构的顶层(Object)。 * 4. @Retention -- 表示注解类型保留时间的长短,它接收RetentionPolicy参数,可能的值有SOURCE, CLASS, 以及RUNTIME。 * @Author : AD */ @Documented @Target({ElementType.METHOD}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface Cache { String region() default "rx"; //缓存区域 String key() default ""; //缓存key String params() default ""; //缓存参数 }
-
自定义注解,用于标记清理指定方法的返回值缓存数据。(比如更新操作、删除操作中的缓存数据)
javapackage com.test.test_redis_j2cache.J2cache.annotation; import java.lang.annotation.*; /** * @ClassName : CacheEvictor * @Description : 失效缓存--清理缓存注解,用于清理指定缓存数据 * @Author : AD */ @Documented @Target({ElementType.METHOD}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface CacheEvictor { Cache[] value() default {}; }
3.2.2 自定义缓存注解模型映射对象
-
缓存处理数据映射对象实体类
javapackage com.test.test_redis_j2cache.J2cache.model; import com.alibaba.fastjson2.JSONObject; import lombok.Data; import java.lang.annotation.Annotation; /** * @ClassName : CacheAnnotationInfo * @Description : 自定义缓存注解Cache信息包装--缓存数据模型 * @Author : AD */ @Data public class CacheAnnotationInfo<T extends Annotation> { private T annotation; private String key; private String region; @Override public String toString(){ if (annotation == null){ return null; } return JSONObject.toJSONString(this); } } -
缓存数据处理结果实映射对象
javapackage com.test.test_redis_j2cache.J2cache.model; /** * @ClassName : CacheHolder * @Description : 缓存处理结果封装类 * @Author : AD */ public class CacheHolder { /** * 缓存的数据 * */ private Object value; /** * 缓存数据是否存在 * */ private boolean existsCache; /** * 异常信息 * */ private Throwable throwable; /** * 初始化缓存占位 */ private CacheHolder() { } /** * 获取值 * * @return */ public Object getValue() { return value; } /** * 是否存在缓存 * * @return */ public boolean isExistsCache() { return existsCache; } /** * 是否有错误 * * @return */ public boolean hasError() { return throwable != null; } /** * 生成缓存结果的占位 * * @param value 结果 * @param existsCache 是否存在缓存 * @return 缓存 */ public static CacheHolder newResult(Object value, boolean existsCache) { CacheHolder cacheHolder = new CacheHolder(); cacheHolder.value = value; cacheHolder.existsCache = existsCache; return cacheHolder; } /** * 生成缓存异常的占位 * * @param throwable 异常 * @return 缓存 */ public static CacheHolder newError(Throwable throwable) { CacheHolder cacheHolder = new CacheHolder(); cacheHolder.throwable = throwable; return cacheHolder; } }
3.2.3 缓存处理器工具类封装
-
缓存键生成工具 CacheKeyBuilder
javapackage com.test.test_redis_j2cache.J2cache.utils; import org.springframework.util.StringUtils; /** * 缓存键生成工具 */ public class CacheKeyBuilder { /** * 生成key * * @param key 键 * @param params 参数 * @param args 参数值 * @return * @throws IllegalAccessException 当访问异常时抛出 */ public static String generate(String key, String params, Object[] args) throws IllegalAccessException { StringBuilder keyBuilder = new StringBuilder(""); if (StringUtils.hasText(key)) { keyBuilder.append(key); } if (StringUtils.hasText(params)) { String paramsResult = ObjectAccessUtils.get(args, params, String.class, "_", "null"); keyBuilder.append(":"); keyBuilder.append(paramsResult); } return keyBuilder.toString(); } } -
Spring上下文工具类 SpringApplicationContextUtils
javapackage com.test.test_redis_j2cache.J2cache.utils; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import javax.annotation.PostConstruct; /** * Spring上下文工具类 */ @Primary @Component public class SpringApplicationContextUtils { private static ApplicationContext springContext; @Autowired private ApplicationContext applicationContext; @PostConstruct private void init() { springContext = applicationContext; } /** * 获取当前ApplicationContext * * @return ApplicationContext */ public static ApplicationContext getApplicationContext() { return springContext; } } -
字符串封装工具 StringGenius
javapackage com.test.test_redis_j2cache.J2cache.utils; import org.springframework.util.StringUtils; import java.util.regex.Pattern; /** * 字符串工具类 */ public class StringGenius { /** * 是否是整数 * * @param text 文本 * @return true:是;false:否 */ public static boolean isInteger(String text) { if (!StringUtils.hasText(text)) { return false; } Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("^[-\\+]?[\\d]*$"); return pattern.matcher(text).matches(); } } -
为访问对象提供路径支持 FieldAccessDescriptor
javapackage com.test.test_redis_j2cache.J2cache.utils; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap; import java.util.stream.Collectors; /** * 为访问对象提供路径支持 * <p> * address.id * <br> * detailList[0].name * <br> * payInfo.payMethodList[0].name * <br> * 0.text * <br> * data.address.city.text * <br> * ?0.text * <br> * detailList[?0].name * <br> * data.address?.city?.text * </p> */ public class FieldAccessDescriptor { private static ConcurrentHashMap<String, FieldAccessDescriptor> cacheMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(128); private String currentPath; private String currentField; private int currentIndex; private boolean isOptionalAccess; private FieldAccessDescriptor nextFieldAccessDescriptor; private FieldAccessDescriptor(String fieldPath) { this(fieldPath, true); } private FieldAccessDescriptor(String fieldPath, boolean isFirst) { try { // 移除[和.符号 if (fieldPath.startsWith("[") || fieldPath.startsWith(".")) { fieldPath = fieldPath.substring(1); } if (fieldPath.startsWith("?")) { this.isOptionalAccess = true; // 移除可选访问符[?] fieldPath = fieldPath.substring(1); // 如果是逗点开头,则移除逗点[.] if (fieldPath.startsWith(".")) { fieldPath = fieldPath.substring(1); } } int bracketIndex = fieldPath.indexOf('['); int commaIndex = fieldPath.indexOf('.'); int optionalIndex = fieldPath.indexOf('?'); List<Integer> indexList = Arrays.asList(bracketIndex, commaIndex, optionalIndex).stream().filter(i -> i > -1).collect(Collectors.toList()); int index = -1; if (indexList.size() > 0) { index = indexList.stream().min((i, i2) -> (i - i2)).get().intValue(); } if (index < 0) { // 解析终止 // 移除可能存在的右中括号 fieldPath = fieldPath.replace("]", ""); int accessIndex = getInt(fieldPath); this.currentIndex = accessIndex; this.currentField = fieldPath; if (accessIndex > -1) { this.currentPath = "[" + accessIndex + "]"; } else { this.currentPath = fieldPath; } } else { String left = fieldPath.substring(0, index); if (left == "") { throw new IllegalArgumentException("非法的fieldPath格式"); } String right = fieldPath.substring(index); left = left.replace("]", ""); int accessIndex = getInt(left); this.currentIndex = accessIndex; this.currentField = left; if (accessIndex > -1) { this.currentPath = "[" + accessIndex + "]"; } else { this.currentPath = left; } if (right != "") { this.nextFieldAccessDescriptor = new FieldAccessDescriptor(right, false); } } if (isFirst) { fixPath(); } } catch (Exception e) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("非法的fieldPath格式"); } } private void fixPath() { if (hasNext()) { String separator = this.nextFieldAccessDescriptor.currentIndex > -1 ? "" : "."; this.nextFieldAccessDescriptor.currentPath = this.currentPath + separator + this.nextFieldAccessDescriptor.currentPath; this.nextFieldAccessDescriptor.fixPath(); } } private int getInt(String text) { if (StringGenius.isInteger(text)) { return Integer.parseInt(text); } else { return -1; } } public String getCurrentPath() { return currentPath; } public String getCurrentField() { return currentField; } public int getCurrentIndex() { return currentIndex; } public boolean isOptionalAccess() { return isOptionalAccess; } public FieldAccessDescriptor getNextFieldAccessDescriptor() { return nextFieldAccessDescriptor; } public boolean accessArray() { return this.currentIndex > -1; } public boolean hasNext() { return this.nextFieldAccessDescriptor != null; } public String nextPath() { if (!hasNext()) { return ""; } else { if (this.nextFieldAccessDescriptor.accessArray()) { return String.format("[%s]", this.nextFieldAccessDescriptor.getCurrentIndex()); } else { return this.nextFieldAccessDescriptor.getCurrentField(); } } } public static FieldAccessDescriptor parse(String fieldPath) { if (cacheMap.containsKey(fieldPath)) { return cacheMap.get(fieldPath); } else { FieldAccessDescriptor fieldAccessDescriptor = new FieldAccessDescriptor(fieldPath); cacheMap.put(fieldPath, fieldAccessDescriptor); return fieldAccessDescriptor; } } } -
对象访问工具类 ObjectAccessUtils
javapackage com.test.test_redis_j2cache.J2cache.utils; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONArray; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject; import org.springframework.util.StringUtils; import java.util.ArrayList; /** * 对象访问工具类 * <br> * 支持的路径格式参考: * <p> * address.id * <br> * detailList[0].name * <br> * payInfo.payMethodList[0].name * <br> * 0.text * <br> * data.address.city.text * <br> * ?0.text * <br> * detailList[?0].name * <br> * data.address?.city?.text * </p> */ public class ObjectAccessUtils { /** * 以字段路径形式访问对象 * <br> * 字段路径支持所有常见访问场景。比如:<br> * address.id <br> * detailList[0].name <br> * payInfo.payMethodList[0].name <br> * 0.text <br> * data.address.city.text <br> * ?0.text <br> * detailList[?2].name <br> * data.address?.city?.text <br> * * @param target 要访问的目标对象 * @param fieldPath 字段路径 * @param clazz 要返回的类型的类 * @param <T> 要返回的类型 * @return 值 * @throws IllegalAccessException 当无法访问对象或者字段时触发 */ public static <T> T get(Object target, String fieldPath, Class<T> clazz) throws IllegalAccessException { return get(target, fieldPath, clazz, ""); } /** * 以字段路径形式访问对象 * <br> * 字段路径支持所有常见访问场景。比如:<br> * address.id <br> * detailList[0].name <br> * payInfo.payMethodList[0].name <br> * 0.text <br> * data.address.city.text <br> * ?0.text <br> * detailList[?2].name <br> * data.address?.city?.text <br> * * @param target 要访问的目标对象 * @param fieldPath 字段路径 * @param clazz 要返回的类型的类 * @param delimiter 分隔符 * @param <T> 要返回的类型 * @return 值 * @throws IllegalAccessException 当无法访问对象或者字段时触发 */ public static <T> T get(Object target, String fieldPath, Class<T> clazz, String delimiter) throws IllegalAccessException { return get(target, fieldPath, clazz, delimiter, null); } /** * 以字段路径形式访问对象 * <br> * 字段路径支持所有常见访问场景。比如:<br> * address.id <br> * detailList[0].name <br> * payInfo.payMethodList[0].name <br> * 0.text <br> * data.address.city.text <br> * ?0.text <br> * detailList[?2].name <br> * data.address?.city?.text <br> * * @param target 要访问的目标对象 * @param fieldPath 字段路径 * @param clazz 要返回的类型的类 * @param delimiter 分隔符 * @param nullText null时替代文本 * @param <T> 要返回的类型 * @return 值 * @throws IllegalAccessException 当无法访问对象或者字段时触发 */ public static <T> T get(Object target, String fieldPath, Class<T> clazz, String delimiter, String nullText) throws IllegalAccessException { if (target == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("要访问的目标对象不能为空"); } else if (fieldPath == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("要访问的目标对象的字段路径不能为空"); } else if (!StringUtils.hasText(fieldPath)) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("要访问的目标对象的字段路径不能为空"); } fieldPath = fieldPath.replaceAll(",", "+"); if (fieldPath.contains("+")) { if (!String.class.equals(clazz)) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("当字段路径中包含+时,clazz只能是String.class"); } String[] fieldPathList = fieldPath.split("\\+"); ArrayList<String> results = new ArrayList<>(); if (StringUtils.hasText("s.")) { results.add(get(target, fieldPathList[0], String.class)); } else { for (String fp : fieldPathList) { if (StringUtils.hasText(fp)) { String item = get(target, fp, String.class); if (item == null) { item = nullText; } results.add(item); } } } return (T) String.join(delimiter, results); } if (fieldPath.startsWith("*")) { // fieldPath = fieldPath.substring(1); throw new IllegalArgumentException("路径不能以*开头"); } JSON targetElement; if (target instanceof JSON) { targetElement = (JSON) target; } else { String jsonText = JSONObject.toJSONString(target); targetElement = (JSON) JSONObject.parse(jsonText); } if (targetElement == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("无法以json形式访问目标对象"); } FieldAccessDescriptor fieldAccessDescriptor = FieldAccessDescriptor.parse(fieldPath); Object valueElement = getValue(targetElement, fieldAccessDescriptor); Object result; if (valueElement == null) { result = null; } else { if (valueElement.getClass().equals(clazz)) { result = valueElement; } else if (String.class.equals(clazz)) { result = JSONObject.toJSONString(valueElement); } else { result = JSONObject.parseObject(JSONObject.toJSONString(valueElement), clazz); } } if (result == null && String.class.equals(clazz)) { result = nullText; } return (T) result; } /** * 获取值 * * @param targetElement 目标元素 * @param fieldAccessDescriptor 访问标识符 * @return 值 * @throws IllegalAccessException 访问出错时抛出 */ private static Object getValue(Object targetElement, FieldAccessDescriptor fieldAccessDescriptor) throws IllegalAccessException { Object valueElement; boolean needBreak = false; if (fieldAccessDescriptor.accessArray()) { if (!(targetElement instanceof JSONArray)) { throw new IllegalAccessException("要访问的索引的目标不是对象:" + fieldAccessDescriptor.getCurrentIndex()); } JSONArray jsonArray = (JSONArray) targetElement; if (fieldAccessDescriptor.getCurrentIndex() < 0 || jsonArray.size() <= fieldAccessDescriptor.getCurrentIndex()) { if (fieldAccessDescriptor.isOptionalAccess()) { valueElement = null; needBreak = true; } else { throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("索引超界:" + fieldAccessDescriptor.getCurrentPath()); } } else { valueElement = jsonArray.get(fieldAccessDescriptor.getCurrentIndex()); } } else { if (targetElement == null) { if (fieldAccessDescriptor.isOptionalAccess()) { valueElement = null; needBreak = true; } else { throw new IllegalAccessException("无法访问对象" + fieldAccessDescriptor.getCurrentPath()); } } else { if (!(targetElement instanceof JSONObject)) { // throw new IllegalAccessException("要访问的字段的目标不是对象:" + fieldAccessDescriptor.getCurrentField()); if (targetElement instanceof JSONArray) { JSONArray jsonArray = (JSONArray) targetElement; String s = ""; for (int i = 0; i < jsonArray.size(); i++) { s += jsonArray.getString(i) + "_"; } return s.substring(0, s.length() - 1); } } JSONObject jsonObject = (JSONObject) targetElement; if (!jsonObject.containsKey(fieldAccessDescriptor.getCurrentField())) { if (fieldAccessDescriptor.isOptionalAccess()) { valueElement = null; needBreak = true; } else { throw new IllegalAccessException("无法访问对象" + fieldAccessDescriptor.getCurrentPath()); } } else { valueElement = jsonObject.get(fieldAccessDescriptor.getCurrentField()); } } } if (!needBreak && fieldAccessDescriptor.hasNext()) { valueElement = getValue(valueElement, fieldAccessDescriptor.getNextFieldAccessDescriptor()); } return valueElement; } }
3.2.4 缓存处理器封装
这里需要注意需要创建三个缓存处理器。
一个用来处理对应 @Cache注解的处理器,用来处理需要缓存的接口;另一个是用来处理 @CacheEvictor 注解的缓存处理器,来用处理需要清理指定缓存数据。
最后一个缓存处理类为抽象类的缓存处理类,作为该两个处理器的父类,
-
提供了一种模板或者接口,规定了子类必须实现的抽象方法,同时提供了一些通用的实现。
-
提供了一种标准化的结构,可以被多个子类共享。
-
用于在设计接口时提供一些共同的实现逻辑,减少了代码的重复性。
-
AbstractCacheAnnotationProcessor 两个子处理器的父类
javapackage com.test.test_redis_j2cache.J2cache.aop; import com.test.test_redis_j2cache.J2cache.annotation.Cache; import com.test.test_redis_j2cache.J2cache.annotation.CacheEvictor; import com.test.test_redis_j2cache.J2cache.model.CacheAnnotationInfo; import com.test.test_redis_j2cache.J2cache.utils.CacheKeyBuilder; import com.test.test_redis_j2cache.J2cache.utils.SpringApplicationContextUtils; import net.oschina.j2cache.CacheChannel; import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.util.StringUtils; import java.lang.reflect.Method; /** * @ClassName : AbstractCacheAnnotationProcessor * @Description : @Cache 缓存注解处理器[抽象类] * @Author : AD */ public abstract class AbstractCacheAnnotationProcessor { protected CacheChannel cacheChannel; /** * Description: 初始化缓存注解处理器 * proceedingJoinPoint 切点 * @param * @return */ protected AbstractCacheAnnotationProcessor(){ ApplicationContext applicationContext = SpringApplicationContextUtils.getApplicationContext(); cacheChannel = applicationContext.getBean(CacheChannel.class); } /** * Description: 转换为注解信息 * * @param proceedingJoinPoint * @param cache 注解信息 * @return com.test.test_redis_j2cache.J2cache.model.CacheAnnotationInfo<com.test.test_redis_j2cache.J2cache.annotation.Cache> 注解信息实体类 */ protected CacheAnnotationInfo<Cache> getAnnotationInfo(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint, Cache cache){ CacheAnnotationInfo<Cache> annotationCacheAnnotationInfo = new CacheAnnotationInfo<>(); annotationCacheAnnotationInfo.setAnnotation(cache); annotationCacheAnnotationInfo.setRegion(cache.region()); try { annotationCacheAnnotationInfo.setKey(generateKey(proceedingJoinPoint, annotationCacheAnnotationInfo.getAnnotation())); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("生成键出错:", e); } return annotationCacheAnnotationInfo; } /** * 生成key字符串 * * @param cache 缓存注解 * @return key字符串 */ protected String generateKey(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint, Cache cache) throws IllegalAccessException { String key = cache.key(); if (!StringUtils.hasText(key)) { String className = proceedingJoinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getSimpleName(); MethodSignature methodSignature = (MethodSignature) proceedingJoinPoint.getSignature(); Method method = methodSignature.getMethod(); key = className + ":" + method.getName(); } key = CacheKeyBuilder.generate(key, cache.params(), proceedingJoinPoint.getArgs()); return key; } /** * 抽象方法,处理缓存操作,具体应该由子类具体实现 * * @param proceedingJoinPoint 切点 * @return 处理结果 */ public abstract Object process(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable; /** * 获得缓存注解处理器对象 * * @param proceedingJoinPoint 切点 * @param cache 注解 * @return 注解处理器 */ public static CachesAnnotationProcessor getProcessor(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint, Cache cache) { return new CachesAnnotationProcessor(proceedingJoinPoint, cache); } /** * 获得清理缓存注解处理器对象 * * @param proceedingJoinPoint 切点 * @param cacheEvictor 注解 * @return 注解处理器 */ public static CacheEvictorAnnotationProcessor getProcessor(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint, CacheEvictor cacheEvictor) { return new CacheEvictorAnnotationProcessor(proceedingJoinPoint, cacheEvictor); } }
- 缓存注解处理器:CachesAnnotationProcessor
java
package com.test.test_redis_j2cache.J2cache.aop;
import com.test.test_redis_j2cache.J2cache.annotation.Cache;
import com.test.test_redis_j2cache.J2cache.model.CacheAnnotationInfo;
import com.test.test_redis_j2cache.J2cache.model.CacheHolder;
import net.oschina.j2cache.CacheObject;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
/**
* @ClassName : CacheAnnotationProcessor
* @Description : Cache注解,缓存注解处理器
* @Author : AD
*/
public class CachesAnnotationProcessor extends AbstractCacheAnnotationProcessor{
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CachesAnnotationProcessor.class);
private CacheAnnotationInfo annotationInfo;
/**
* Description: 初始化处理器,同时将相关的对象进行初始化
*
* @param proceedingJoinPoint
* @param cache
* @return
*/
public CachesAnnotationProcessor(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint, Cache cache)
{
super();
//创建注解信息对象
annotationInfo = getAnnotationInfo(proceedingJoinPoint , cache);
}
/**
* Description: 具体缓存处理逻辑
*
* @param proceedingJoinPoint
* @return java.lang.Object
*/
@Override
public Object process(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {
Object result = null;
boolean existsCache = false;
//1、获取缓存数据
CacheHolder cacheHolder = getCache(annotationInfo);
if(cacheHolder.isExistsCache()){
//2、如果缓存数据存在则直接返回(相当于controller的目标方法没有执行)
result = cacheHolder.getValue();//缓存结果数据
existsCache = true;
}
//如果不存在数据,则执行方法,将方法数据存入缓存
if(!existsCache){
//3、如何缓存数据不存在,放行调用Controller的目标方法
result = invoke(proceedingJoinPoint);
//4、将目标方法的返回值载入缓存
setCache(result);
}
//5、将结果返回
return result;
}
/**
* 获取缓存数据
* @param annotationInfo
* @return
*/
private CacheHolder getCache(CacheAnnotationInfo<Cache> annotationInfo){
Object value = null;
String region = annotationInfo.getRegion();
String key = annotationInfo.getKey();
boolean exists = cacheChannel.exists(region, key);
int check = cacheChannel.check(region, key);
logger.info("@Cache缓存数据[{}.{}]存在状态为: {}。 存在级缓存某级缓存:{}",region, key, exists,check);
if(exists){
CacheObject cacheObject = cacheChannel.get(region, key);
//获得缓存结果数据
value = cacheObject.getValue();
return CacheHolder.newResult(value,true);
}
return CacheHolder.newResult(value,false);
}
/**
* 调用目标方法
* @param proceedingJoinPoint
* @return
*/
private Object invoke(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable{
return proceedingJoinPoint.proceed(proceedingJoinPoint.getArgs());
}
/**
* 设置缓存数据
* @param result
*/
private void setCache(Object result){
cacheChannel.set(annotationInfo.getRegion(),annotationInfo.getKey(),result);
}
}-
清除缓存数据处理器
javapackage com.test.test_redis_j2cache.J2cache.aop; import com.test.test_redis_j2cache.J2cache.annotation.Cache; import com.test.test_redis_j2cache.J2cache.annotation.CacheEvictor; import com.test.test_redis_j2cache.J2cache.model.CacheAnnotationInfo; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * @ClassName : CacheEvictorAnnotationProcessor * @Description : 清理缓存数据处理器 * @Author : AD */ public class CacheEvictorAnnotationProcessor extends AbstractCacheAnnotationProcessor{ private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CacheEvictorAnnotationProcessor.class); /** * 封装注解信息集合 * */ private List<CacheAnnotationInfo<Cache>> cacheList = new ArrayList<>(); /** * 初始化清理缓存注解处理器对象,同时初始化一些缓存操作的对象 * @param proceedingJoinPoint * @param cacheEvictor */ public CacheEvictorAnnotationProcessor(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint, CacheEvictor cacheEvictor) { super(); Cache[] value = cacheEvictor.value(); for(Cache cache : value){ CacheAnnotationInfo<Cache> annotationInfo = getAnnotationInfo(proceedingJoinPoint, cache); cacheList.add(annotationInfo); } } /** * Description: 具体清理缓存处理逻辑 * * @param proceedingJoinPoint * @return java.lang.Object */ @Override public Object process(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable { for (CacheAnnotationInfo<Cache> annotationInfo : cacheList) { String region = annotationInfo.getRegion(); String key = annotationInfo.getKey(); boolean exists = cacheChannel.exists(region, key); int check = cacheChannel.check(region, key); logger.info("@CacheEvictor清除缓存数据[{}.{}]存在状态为: {}。 存在级缓存某级缓存:{}",region, key, exists,check); //清理缓存数据 cacheChannel.evict(region,key); } //调用目标方法(就是Controller中的方法) return proceedingJoinPoint.proceed(proceedingJoinPoint.getArgs()); } }
3.2.5 自定义缓存拦截器
注意这里的Interceptor是org.aopalliance.intercept包下的Spring的AOP只能支持到方法级别的切入。换句话说,切入点只能是某个方法。
java
package com.test.test_redis_j2cache.J2cache.aop;
import com.test.test_redis_j2cache.J2cache.annotation.Cache;
import com.test.test_redis_j2cache.J2cache.annotation.CacheEvictor;
import com.test.test_redis_j2cache.J2cache.utils.SpringApplicationContextUtils;
import com.test.test_redis_j2cache.TestRedisJ2CacheApplication;
import org.aopalliance.intercept.Interceptor;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationUtils;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* @ClassName : 拦截方法上使用Cache注解的Controller
* @Description : 缓存拦截器Aop
* @Author : AD
*/
@Aspect
@Component
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = true) //指定使用cglib方式为Controller创建代理对象,代理对象其实是目标对象的子类
@Import(SpringApplicationContextUtils.class)
public class CacheMethodHandleInterceptor implements Interceptor {
//@Around注解,表示这是一个环绕通知。环绕通知是所有通知里功能最为强大的通知,可以实现前置通知、后置通知、异常通知以及返回通知的功能。目标方法进入环绕通知后,通过调用ProceedingJoinPoint对象的proceed方法使目标方法继续执行,开发者可以在此修改目标方法的执行参数、返回值等,并且可以在此处理目标方法的异常。
@Around("@annotation(com.test.test_redis_j2cache.J2cache.annotation.Cache)")
public Object invokeCacheAllMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable
{
MethodSignature methodSignature =(MethodSignature) proceedingJoinPoint.getSignature();
Cache cacheAnnotation = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(methodSignature.getMethod(), Cache.class);
if (cacheAnnotation!= null)
{
System.out.println("需要进行设置缓存数据处理。。。。");
//创建处理器,具体处理缓存逻辑
CachesAnnotationProcessor processor = AbstractCacheAnnotationProcessor.getProcessor(proceedingJoinPoint, cacheAnnotation);
return processor.process(proceedingJoinPoint);
}
//没有获取到Cache注解信息,直接放行
return proceedingJoinPoint.proceed(proceedingJoinPoint.getArgs());
}
/**
* Description: 拦截方法上使用CacheEvictor注解的Controller
*
* @param proceedingJoinPoint
* @return java.lang.Object
*/
@Around("@annotation(com.test.test_redis_j2cache.J2cache.annotation.CacheEvictor)")
public Object invokeCacheEvictorAllMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable
{
//获得方法前面对象
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) proceedingJoinPoint.getSignature();
//获得当前拦截到的Controller方法对象
Method method = signature.getMethod();
//获得方法上的Cache注解信息
CacheEvictor cacheEvictor = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(method, CacheEvictor.class);
if (cacheEvictor != null){
System.out.println("清理缓存处理...");
//创建清理缓存的处理器
CacheEvictorAnnotationProcessor processor = AbstractCacheAnnotationProcessor.getProcessor(proceedingJoinPoint, cacheEvictor);
return processor.process(proceedingJoinPoint);
}
return proceedingJoinPoint.proceed(proceedingJoinPoint.getArgs());
}
}3.2.6 声明式注解的配置
-
@EnableCache注解
javapackage com.test.test_redis_j2cache.J2cache.annotation; import com.test.test_redis_j2cache.J2cache.aop.CacheMethodHandleInterceptor; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import; import java.lang.annotation.*; /** * @ClassName : EnableCache * @Description : 开启缓存功能注解 * @Author : AD */ @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target({ElementType.TYPE}) @Documented @Import( CacheMethodHandleInterceptor.class) public @interface EnableCache { } -
在启动类上使用 @EnableCache
javapackage com.test.test_redis_j2cache; import com.test.test_redis_j2cache.J2cache.annotation.EnableCache; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; /** * @author AD */ @SpringBootApplication @EnableCache public class TestRedisJ2CacheApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(TestRedisJ2CacheApplication.class, args); } }
3.2.7 测试类的创建
-
测试类Controller创建
javapackage com.test.test_redis_j2cache.J2cache; import com.test.test_redis_j2cache.J2cache.annotation.Cache; import com.test.test_redis_j2cache.J2cache.annotation.CacheEvictor; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; /** * @ClassName : TestCacheAnnotationController * @Description : 测试 声明式缓存注解的使用 * @Author : AD */ @RestController @RequestMapping(value = "testCache") public class TestCacheAnnotationController { private String region = "testCache"; /** * 查询地址簿详情 * @param id * @return */ @GetMapping("detail/{id}") @Cache(region = "testCache",key = "ab",params = "id") public Map detail(@PathVariable(name = "id") String id) { System.out.println("L1 、 L2 均不存在该数据缓存:查询方法执行了 DB !!"); Map map = new HashMap<String, String>(); map.put("查询id",id); map.put("name", "测试查询功能1"); return map; } /** * 修改 * @param id * @param map * @return */ @PutMapping("put/{id}") @CacheEvictor(value = {@Cache(region = "testCache",key = "ab",params = "1.id")}) public Map update(@PathVariable(name = "id") String id, @RequestBody Map map) { map.put("传入待修改的id",id); return map; } /** * 删除 * @param id * @return */ @DeleteMapping("del/{id}") @CacheEvictor({@Cache(region = "testCache",key = "ab",params = "id")}) public Map del(@PathVariable(name = "id") String id) { Map map = new HashMap<String, String>(); map.put("待删除id",id); map.put("name", "测试查询功能1"); return map; } } -
查询接口 detail 测试
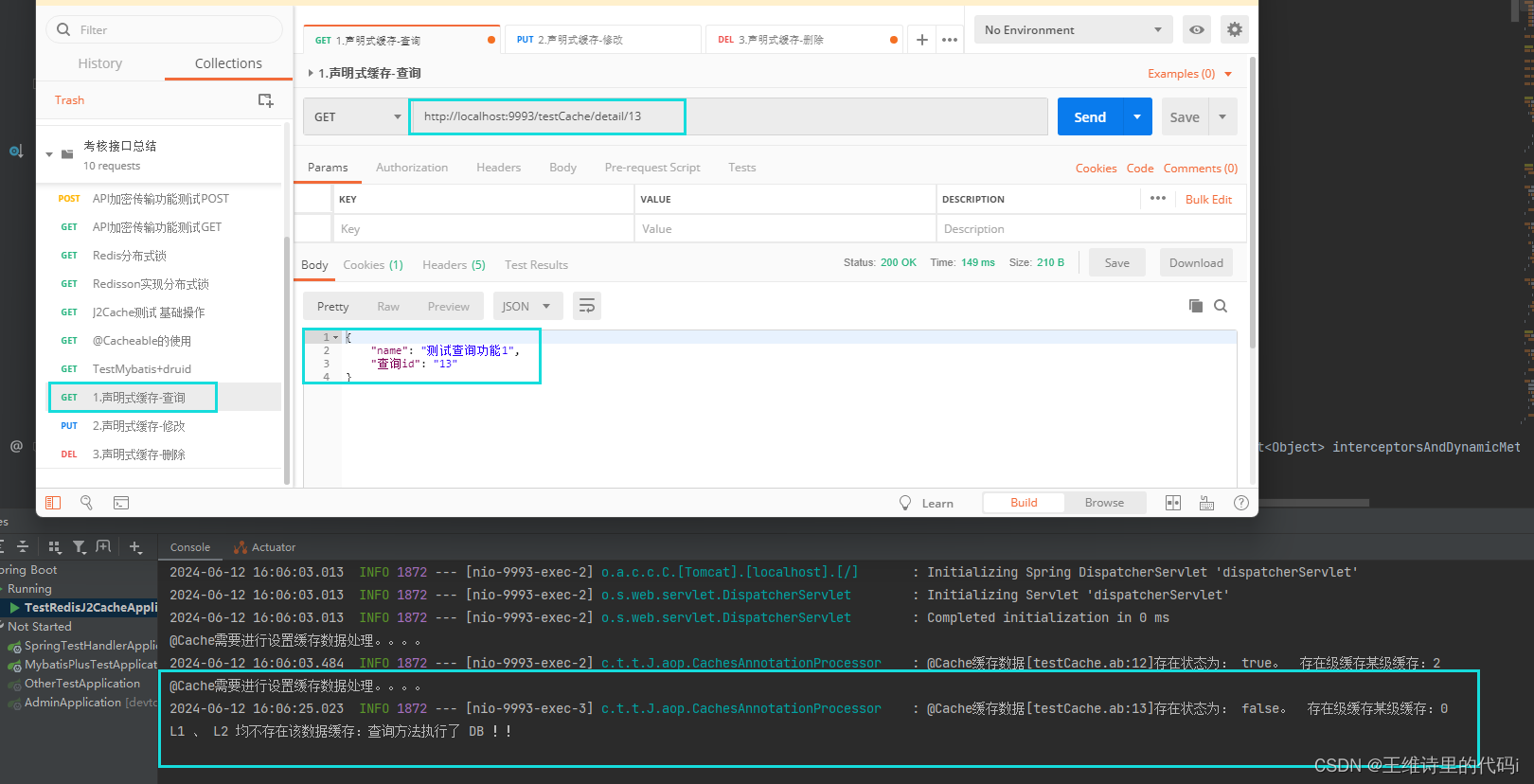
- 修改接口 update 调用效果
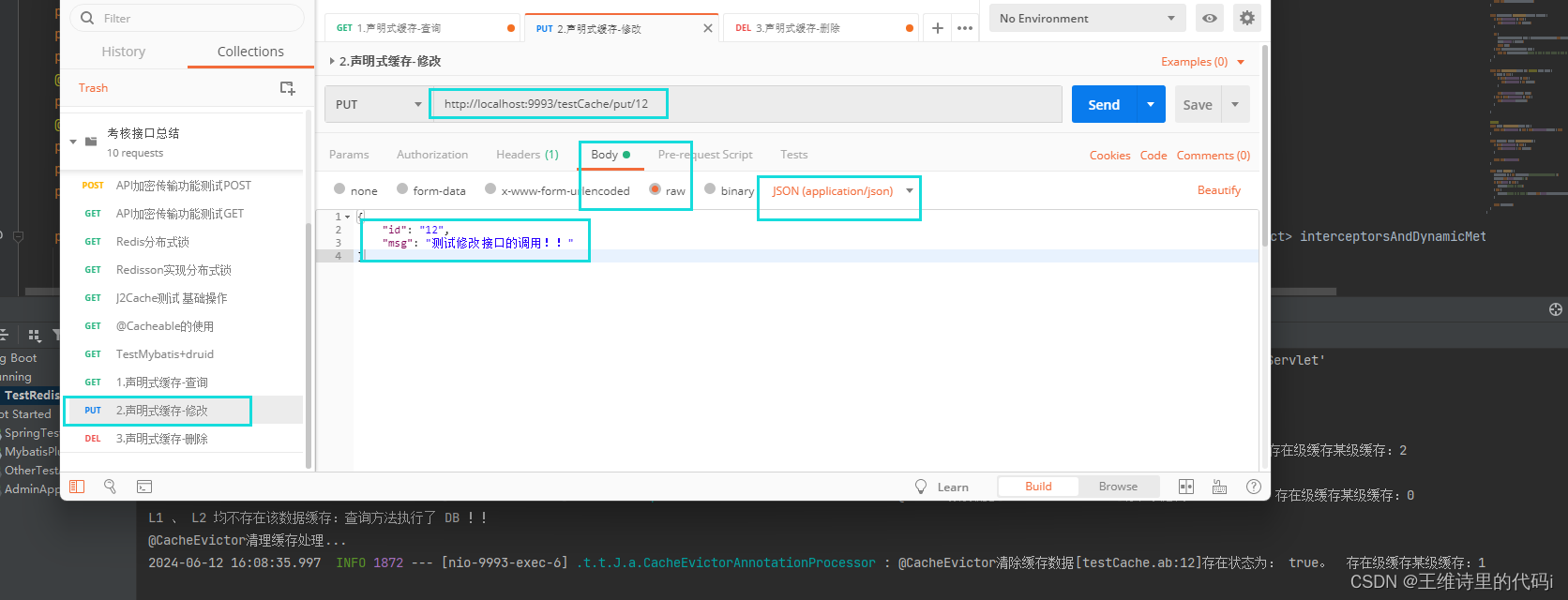
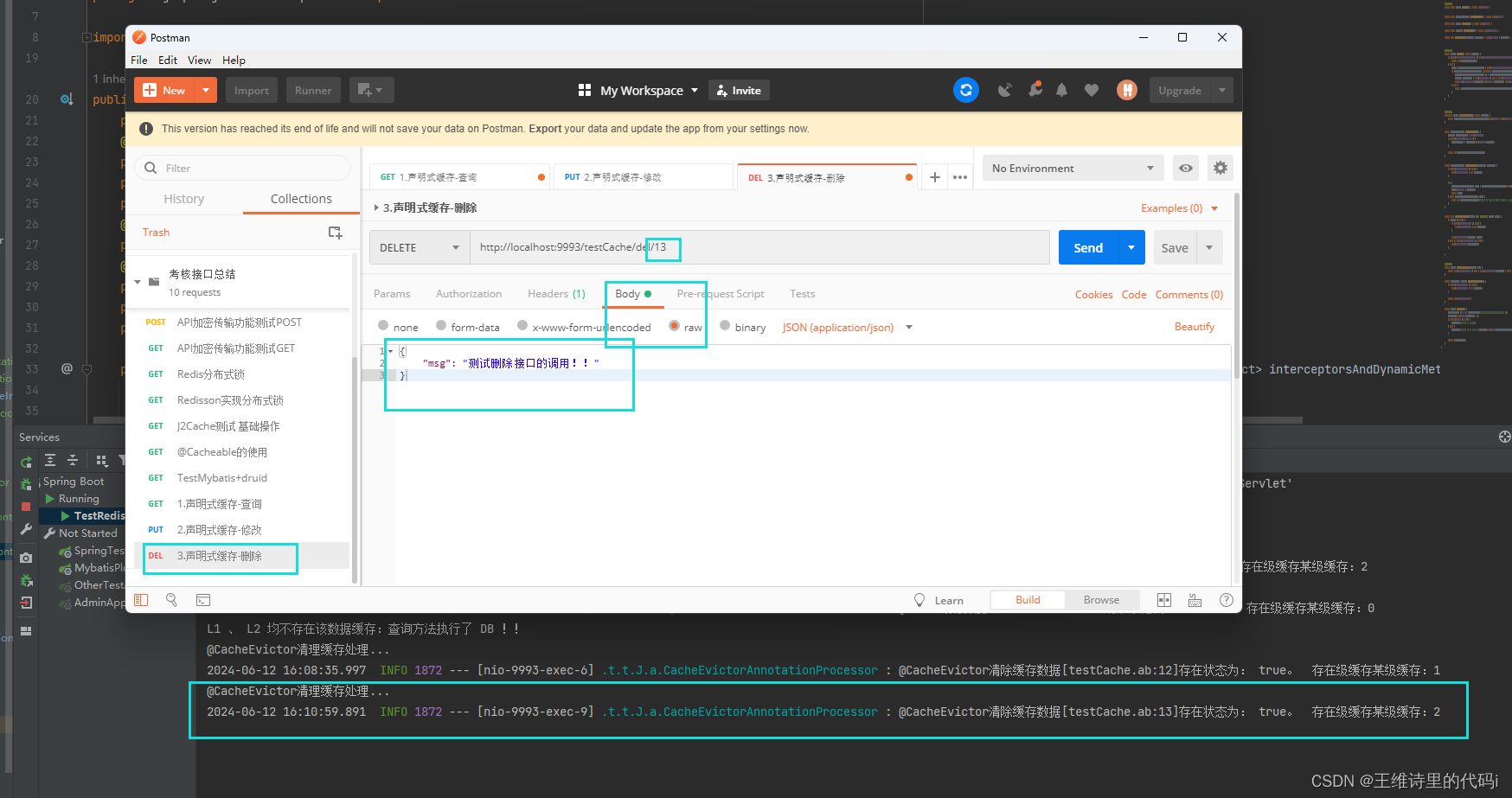
- 删除接口 del 测试效果
3.3 总结
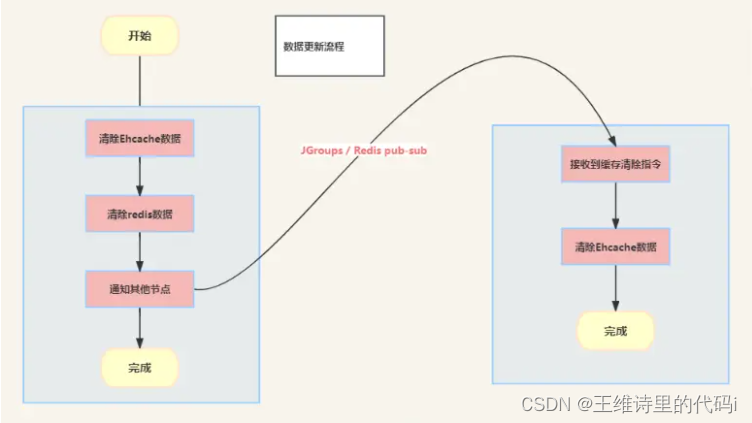
这里使用的是aspectj而非Springaop,故使用时用法有不一样。使用j2cache框架的整体逻辑:自定义缓存注解,类似springboot自带的cache,但是这里粒度更细,而且更好控制超时时间。
缓存层类似如下图:

然后需要用到aspectj的aop逻辑,自定义横切关注点,这里的连接点即是controller层的方法,需要判断每个方法上是否存在cahce注解,如果不存在则直接放行( proceedingJoinPoint.proceed),如果存在则交给缓存处理器进行处理,这里添加和删除缓存主要用的是j2cache组件的cachechannel,个人理解它这里类似一个连接到缓存服务器的通道,且有相应的api可以供增删操作(cacheChannel.set(annotationInfo.getRegion(),annotationInfo.getKey(),result))。在读取缓存时首先是从一级缓存中取,然后从二级缓存中取,如果没找到则查询数据库。对于缓存结果的获得通过封装一个缓存结果类和获得cache注解的信息类来获得( AnnotationInfo ,制定了这个类的数据类型是Annotation的子类)。