阻塞队列
概述和架构
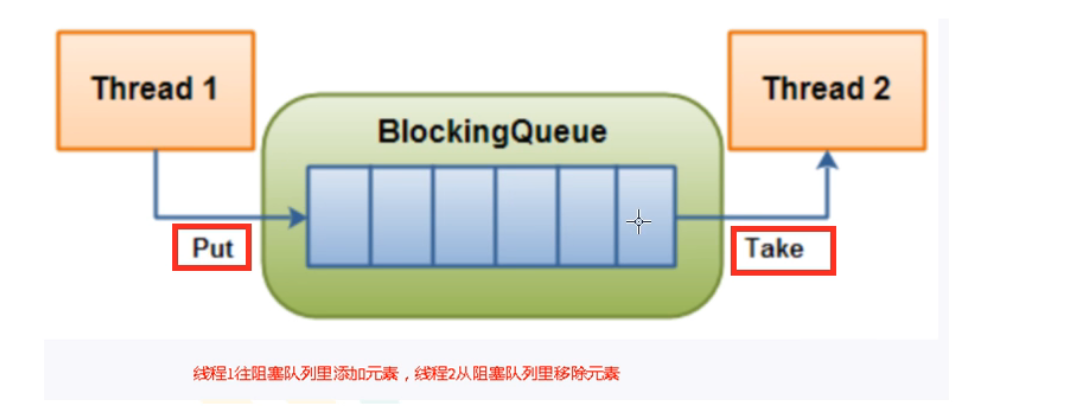


分类和核心方法
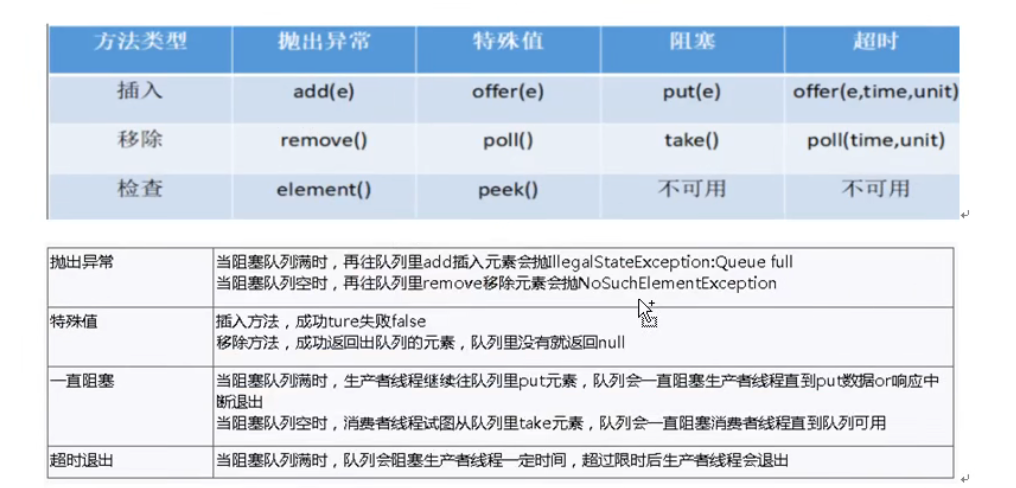
这里是在讲 为了区分在不同场景下 调用的不同组实现方法
核心方法演示
java
package com.example.juc.queue;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class BlockingQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
// 第一组
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("a"));
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("b"));
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("c"));
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.element());
// Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IllegalStateException: Queue full
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("d"));
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());
// Exception in thread "main" java.util.NoSuchElementException
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());
// 第二组
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("a"));
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("b"));
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("c"));
// // a
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.peek());
//
// // false
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("d"));
//
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
// // null
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
// 第三组
// blockingQueue.put("a");
// blockingQueue.put("b");
// blockingQueue.put("c");
// // 会阻塞住 由于用的是定长的 ArrayBlockingQueue
blockingQueue.put("www");
//
//
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());
// // 阻塞
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());
// 第四组
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("a"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("b"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("c"));
// 阻塞 3S 后退出 返回 false
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("w", 3L, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
// 阻塞 3S 后退出 返回 null
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll(3L, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
}
}线程池
概念


接口介绍以及提交任务方式对比
Executor
我们把实现了 Runnable或者 Callable接口的任务提交给线程池
Executor框架负责任务的执行
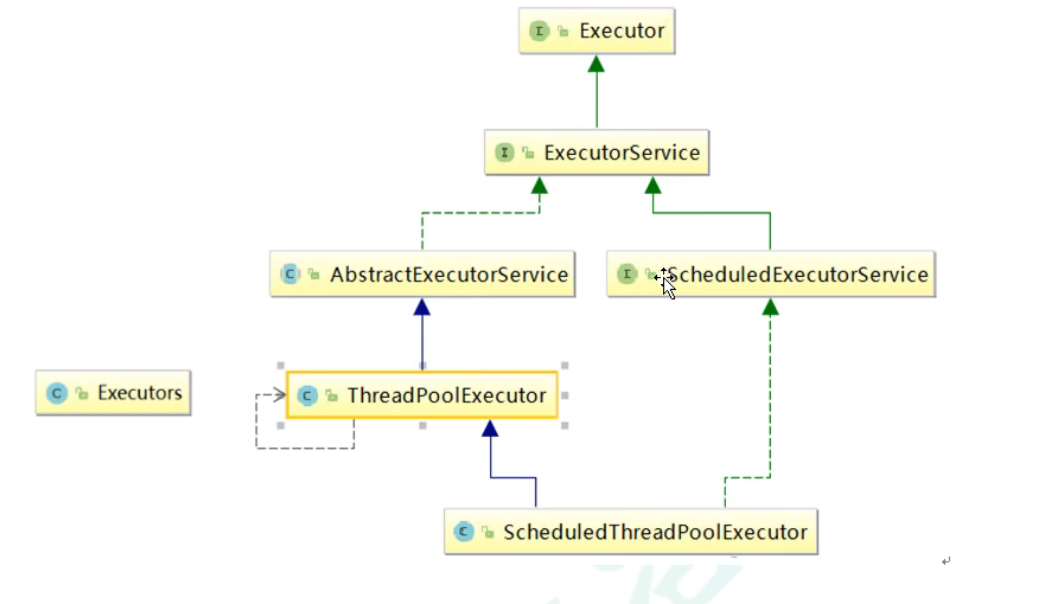
提交任务可以使用 submit和 execute
ExecutorService 中 execute 和 submit 的区别
ExecutorService 中的 execute 和 submit 方法都用于提交任务,但它们有一些关键区别:
1.返回类型:
execute(Runnable command): 这个方法没有返回值。它只接受一个 Runnable 对象并执行它。
submit(Callable task): 这个方法返回一个 Future 对象。它可以接受一个 Callable 对象或一个 Runnable 对象,并返回一个 Future,可以用来检查任务的状态或获取任务的结果。
- 异常处理:
execute: 如果任务在执行过程中抛出未捕获的异常,异常会直接传播到调用者线程。
submit: 如果任务在执行过程中抛出未捕获的异常,异常会被捕获并存储在返回的 Future 对象中。调用 Future.get() 方法时会抛出 ExecutionException,其 getCause() 方法返回实际的异常。
任务类型:
execute: 只能接受 Runnable 对象。
submit: 可以接受 Runnable 或 Callable 对象
java
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
// 使用 execute 提交任务
threadPool.execute(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 使用 execute 办理业务");
});
// 使用 submit 提交任务
Future<String> future = threadPool.submit(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 使用 submit 办理业务");
return "任务完成";
});
try {
// 获取 submit 任务的结果
String result = future.get();
System.out.println("submit 任务结果: " + result);
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}总结: execute 功能较简单,submit 可以看做增强版本,可以获取一个 future
ScheduledThreadThreadPoolExecutor添加了调度任务执行的功能
常见线程池和创建线程池的底层原理
java
package com.example.juc.pool;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
// 演示线程池 三种 常用分类
public class ThreadPoolDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 一池五线程
ExecutorService threadPool1 = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
// 一池一线程
ExecutorService threadPool2 = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
// 一池可扩容线程
ExecutorService threadPool3 = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
// 10 个顾客请求
try {
for (int i = 0; i <= 10; i++) {
// 执行
threadPool3.execute(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 办理业务");
});
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
threadPool3.shutdown();
}
}
}底层都是创建 ThreadPoolExecutor
java
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
}
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()));
}
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
}
// 引出下面的一小节,ThreadPoolExecutor 总共有 七个参数
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
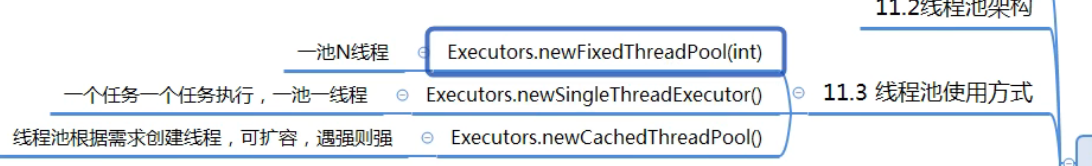
RejectedExecutionHandler handler)- newFixedThreadPool
- 没有救急线程,也就无需空闲时间,阻塞队列无限
- 适合任务量已知,相对耗时任务
- newSingleThreadExecutor
- 希望多个任务排队执行,线程数固定一个,多余任务排队执行
- newCachedThreadPool
- 全部是救急线程,60s空闲回收时间,救急线程无限创建
- 适合任务比较密集,任务执行时间短
七个参数介绍

重点注意 keepAliveTIme 和 unit ,是用于救急线程在空闲后的回收
常用阻塞队列
- 容量为
Integer.MAX_VALUE的<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">LinkedBlockingQueue</font>(无界队列):FixedThreadPool和SingleThreadExector。FixedThreadPool最多只能创建核心线程数的线程(核心线程数和最大线程数相等),SingleThreadExector只能创建一个线程(核心线程数和最大线程数都是 1),二者的任务队列永远不会被放满。
java
public class LinkedBlockingQueueExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个容量为 5 的 LinkedBlockingQueue 队列
LinkedBlockingQueue<String> queue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(5);
// 创建生产者线程
Thread producer = new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
String element = "Element-" + i;
System.out.println("Producer is putting: " + element);
queue.put(element); // 阻塞直到有空间可放入元素
System.out.println("Producer has put: " + element);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
});
// 创建消费者线程
Thread consumer = new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.println("Consumer is waiting to take an element...");
String element = queue.take(); // 阻塞直到有元素可取
System.out.println("Consumer has taken: " + element);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
});
// 启动生产者和消费者线程
producer.start();
consumer.start();
}
}<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">SynchronousQueue</font>(同步队列):CachedThreadPool。SynchronousQueue没有容量,不存储元素,插入时阻塞,直到元素被取出。DelayedWorkQueue(延迟阻塞队列):ScheduledThreadPool和SingleThreadScheduledExecutor。DelayedWorkQueue的内部元素并不是按照放入的时间排序,而是会按照延迟的时间长短对任务进行排序,内部采用的是"堆"的数据结构,可以保证每次出队的任务都是当前队列中执行时间最靠前的。DelayedWorkQueue添加元素满了之后会自动扩容原来容量的 1/2,即永远不会阻塞,最大扩容可达Integer.MAX_VALUE,所以最多只能创建核心线程数的线程。- ArrayBlockingQueue: 有界阻塞队列,内部是一个数组。需要指定队列的容量。适用于有界任务队列的场景。
- PriorityBlockingQueue:支持优先级排序的无界阻塞队列。元素按照优先级顺序出队。适用于需要任务优先级调度的场景。
工作流程和拒绝策略
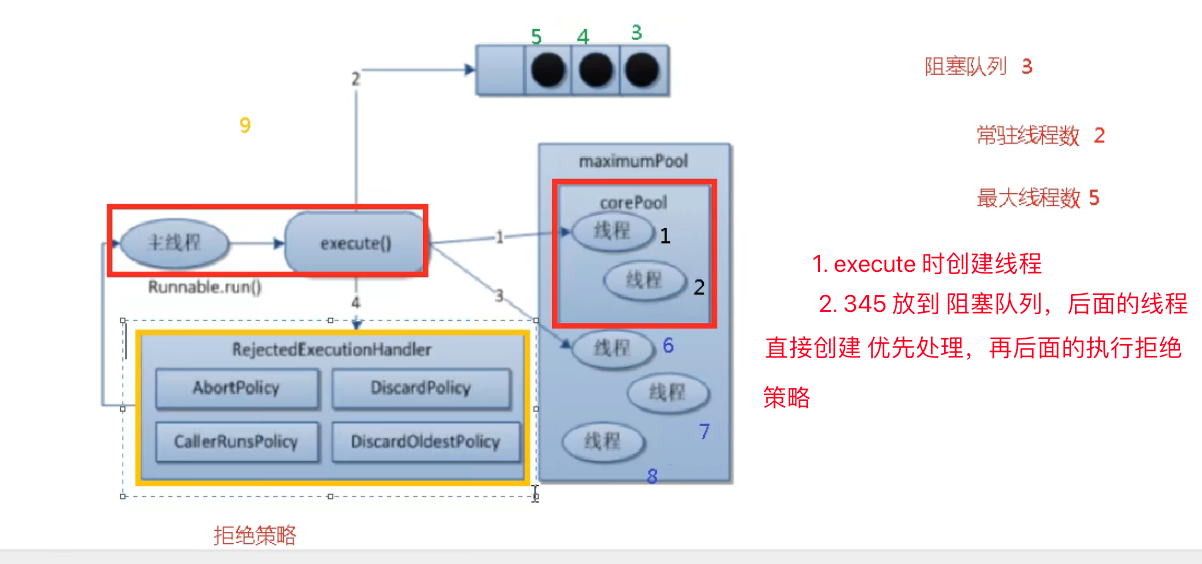
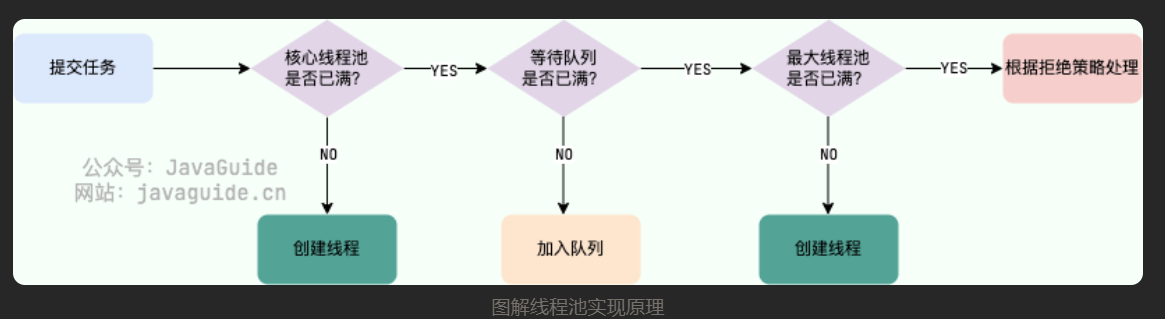
- 如果当前运行的线程数小于核心线程数,那么就会新建一个线程来执行任务。
- 如果当前运行的线程数等于或大于核心线程数,但是小于最大线程数,那么就把该任务放入到任务队列里等待执行。
- 如果向任务队列投放任务失败(任务队列已经满了),但是当前运行的线程数是小于最大线程数的,就新建一个线程来执行任务。
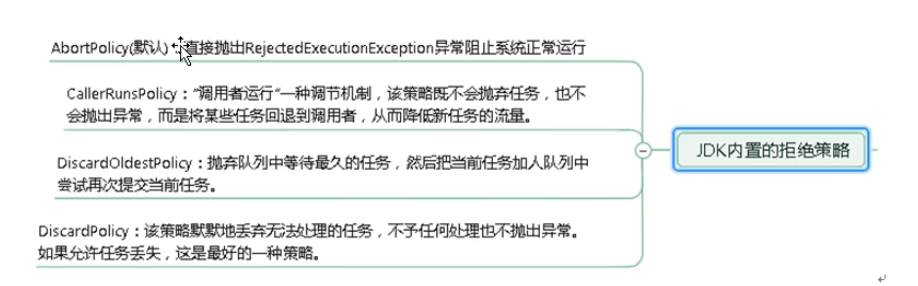
- 如果当前运行的线程数已经等同于最大线程数了,新建线程将会使当前运行的线程超出最大线程数,那么当前任务会被拒绝,拒绝策略会调用
RejectedExecutionHandler.rejectedExecution()方法。
自定义线程池
java
package com.example.juc.pool;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
// 自定义线程池
public class ThreadPoolDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2,
5,
2L,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3),
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
// 10 个顾客请求
try {
for (int i = 0; i <= 150; i++) {
// 执行
threadPool.execute(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 办理业务");
});
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}
}