You are given an integer array nums with no duplicates. A maximum binary tree can be built recursively from nums using the following algorithm:
- Create a root node whose value is the maximum value in
nums. - Recursively build the left subtree on the subarray prefix to the left of the maximum value.
- Recursively build the right subtree on the subarray suffix to the right of the maximum value.
Return the maximum binary tree built from nums.
Example 1:
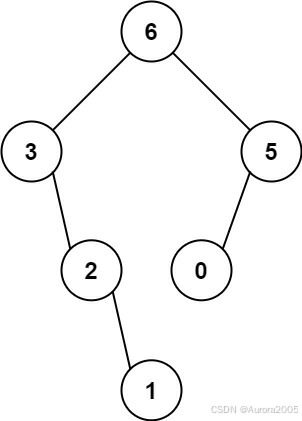
Input: nums = [3,2,1,6,0,5]
Output: [6,3,5,null,2,0,null,null,1]
Explanation: The recursive calls are as follow:
- The largest value in [3,2,1,6,0,5] is 6. Left prefix is [3,2,1] and right suffix is [0,5].
- The largest value in [3,2,1] is 3. Left prefix is [] and right suffix is [2,1].
- Empty array, so no child.
- The largest value in [2,1] is 2. Left prefix is [] and right suffix is [1].
- Empty array, so no child.
- Only one element, so child is a node with value 1.
- The largest value in [0,5] is 5. Left prefix is [0] and right suffix is [].
- Only one element, so child is a node with value 0.
- Empty array, so no child.Example 2:
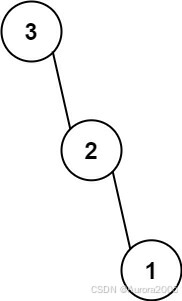
Input: nums = [3,2,1]
Output: [3,null,2,null,1]Constraints:
-
1 <= nums.length <= 1000 -
0 <= nums[i] <= 1000 -
All integers in
numsare unique.class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* constructMaximumBinaryTree(vector<int>& nums) {
TreeNode*node=new TreeNode(0);
//是否叶节点
if(nums.size()==1){
node->val=nums[0];
return node;
}
//找到数组最大值及其下标
int maxValue=0;//因为数组元素大于等于1
int maxValueIndex=0;
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){
if(maxValue<nums[i]){
maxValue=nums[i];
maxValueIndex=i;
}
}
node->val=maxValue;
//最大值所在的下标左区间,构造左子树
if(maxValueIndex>0){
vector<int>newVec(nums.begin(),nums.begin()+maxValueIndex);
node->left=constructMaximumBinaryTree(newVec);
}
//最大值所在的下标右区间,构造右子树
if(maxValueIndex<nums.size()-1){
vector<int>newVec(nums.begin()+maxValueIndex+1,nums.end());
node->right=constructMaximumBinaryTree(newVec);
}return node; }};
注意:
1,前提条件
1)二叉树
2,解题流程
PS :这里的代码及其流程存在缺陷,与 106/105 题一样,重复定义过多 vector ,浪费空间,后续熟练之后再进行优化,这个版本代码比较利于理解
1)先做,后做
- 第一步,梳理题意,这道题本身不是很难,主要的难点就是如何判断哪一部分构造左子树,哪一部分构造右子树。
- 第二步,new一个node存储数组最大值为根节点
- 第三步,判断叶节点
- 也就是nums的size==1
- 不要忘记给node赋值和return
- 第四步,找到数组的最大值及其下标
- 把maxValue的初始值设为0(原因:数组元素大于等于1),maxValueIndex也为0
- for循环找到maxValue和MaxValueIndex
- 给node赋值
- 第五步,根据最大值左区间,构造左子树
- 条件:MaxValue>0
- 新数组,newVec(begin,begin+MaxValueIndex)
- 递归
- 第六步,根据最大值右区间,构造右子树
- 条件:MaxValue<nums.size()-1
- 新数组,newVec(begin+MaxValueIndex+1,end)
- 递归
- 第七步,return node
2)知识点套路
- 递归
- 判断叶节点
- 判断左右子树及其范围
3)前提
4)注意点
- 判断完叶节点后不要忘记给node赋值
- for循环找到MaxValue和MaxValueIndex之后也要赋值