最近翻看了这篇翻译的文章详解卡尔曼滤波原理-CSDN博客
萌发了找个简单例子帮助自己理解的想法, 卡尔曼的作用在于可以在任何含有不确定信息 的动态系统中使用滤波,对系统下一步的走向做出有根据的预测,即使伴随着各种干扰,卡尔曼滤波总是能指出真实发生的情况。
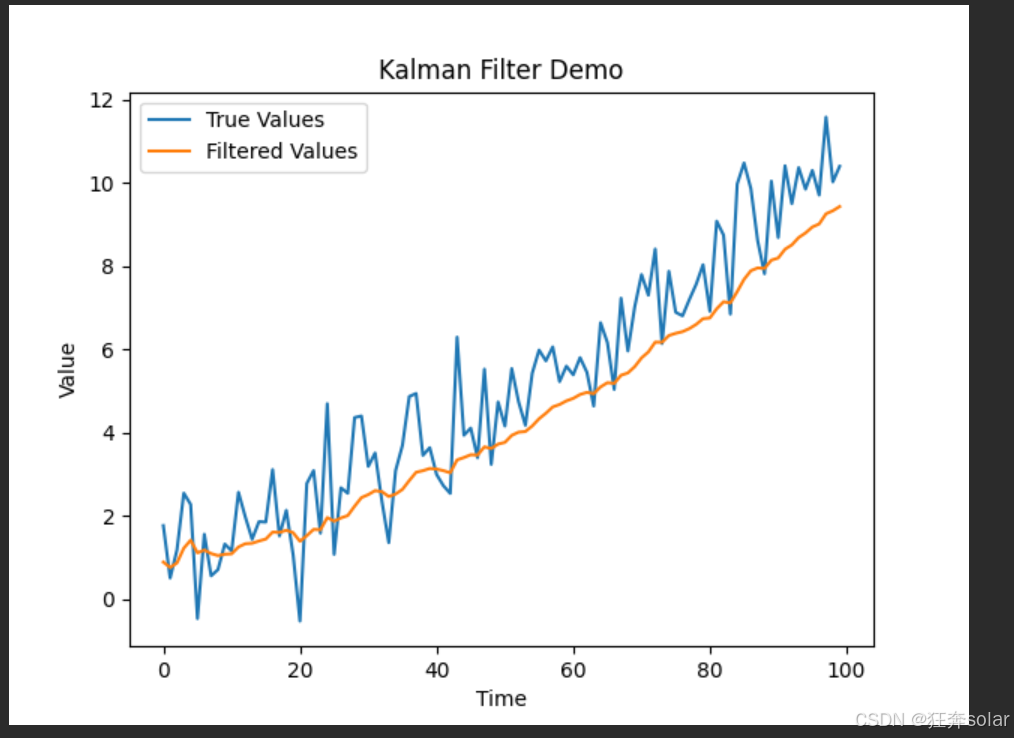
用一个线性随机波动的真实序列做卡尔曼滤波测试
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 定义卡尔曼滤波器
class KalmanFilter:
def __init__(self, process_variance, measurement_variance, estimated_measurement_variance):
self.process_variance = process_variance
self.measurement_variance = measurement_variance
self.estimated_measurement_variance = estimated_measurement_variance
self.posteri_estimate = 0.0
self.posteri_error_estimate = 1.0
def update(self, measurement):
# 预测步骤
priori_estimate = self.posteri_estimate
priori_error_estimate = self.posteri_error_estimate + self.process_variance
# 更新步骤
blending_factor = priori_error_estimate / (priori_error_estimate + self.measurement_variance)
self.posteri_estimate = priori_estimate + blending_factor * (measurement - priori_estimate)
self.posteri_error_estimate = (1 - blending_factor) * priori_error_estimate
return self.posteri_estimate
# 模拟观测数据
np.random.seed(0)
true_values = np.linspace(0, 10, 100) + np.random.normal(0, 1, 100)
# 初始化滤波器
kf = KalmanFilter(process_variance=0.01, measurement_variance=1, estimated_measurement_variance=0.01)
# 对观测数据进行滤波
filtered_values = []
for measurement in true_values:
filtered_values.append(kf.update(measurement))
# 绘制结果
plt.plot(range(100), true_values, label='True Values')
plt.plot(range(100), filtered_values, label='Filtered Values')
plt.xlabel('Time')
plt.ylabel('Value')
plt.title('Kalman Filter Demo')
plt.legend()
plt.show()类的构造函数,用于初始化卡尔曼滤波器的参数。
process_variance:过程噪声的方差,表示系统自身的变化不确定性。measurement_variance:测量噪声的方差,表示测量值的不确定性。estimated_measurement_variance:预估的测量方差(在这个代码中未使用)。posteri_estimate:后验估计值,初始化为 0.0,表示当前对系统状态的估计。posteri_error_estimate:后验误差估计,初始化为 1.0,表示当前估计的误差。
update 方法:用于更新卡尔曼滤波器的状态。
measurement:当前测量值。- 预测步骤 :
priori_estimate:当前的后验估计值,即上一次更新后的估计。priori_error_estimate:预测的误差估计,通过将后验误差加上过程噪声来获得。
更新步骤:
blending_factor:混合因子,决定了预测值和测量值在最终估计中的权重。它的值在 0 到 1 之间,越接近 1 表示测量值越可信,越接近 0 表示预测值越可信。self.posteri_estimate:更新后的后验估计值,通过将预测值与当前测量值结合来计算。self.posteri_error_estimate:更新后的后验误差估计,反映了新的误差情况。
最后,该方法返回更新后的后验估计值,表示当前对系统状态的最新估计。
整体来说,KalmanFilter 类实现了卡尔曼滤波的基本逻辑,能够根据不断更新的测量值来优化对系统状态的估计。通过预测和更新步骤,它有效地结合了测量噪声和过程噪声,从而提供一个更准确的状态估计。
测试结果