文章目录
LRUCache
LRU是Least Recently Used的缩写,即最近最少使用,是一种常用的页面置换算法,选择最近最久未使用的页面予以淘汰。该算法赋予每个页面一个访问字段,用来记录一个页面自上次被访问以来所经历的时间 t,当须淘汰一个页面时,选择现有页面中其 t 值最大的,即最近最少使用的页面予以淘汰。
Cache的容量有限,因此当Cache的容量用完后,而又有新的内容需要添加进来时, 就需要挑选并舍弃原有的部分内容,从而腾出空间来放新内容。LRU Cache 的替换原则就是将最近最少使用的内容替换掉。其实,LRU译成最久未使用会更形象, 因为该算法每次替换掉的就是一段时间内最久没有使用过的内容。

list::splice
cpp
void splice (iterator position, list& x);
void splice (const_iterator position, list& x);
void splice (const_iterator position, list&& x);
void splice (iterator position, list& x, iterator i);
void splice (const_iterator position, list& x, const_iterator i);
void splice (const_iterator position, list&& x, const_iterator i);
void splice (iterator position, list& x, iterator first, iterator last);
void splice (const_iterator position, list& x, const_iterator first, const_iterator last);
void splice (const_iterator position, list&& x, const_iterator first, const_iterator last);在C++的std::list容器中,splice函数用于将一个列表(list)中的元素移动到另一个列表的指定位置,而不复制它们。这是通过调整内部指针(或节点链接)来实现的,因此是一个高效的操作。以下是您提到的三个splice函数重载的简要说明:
-
void splice (iterator position, list& x);此函数将整个列表
x中的所有元素移动到当前列表的position位置。移动后,列表x将变为空,而当前列表将在position处包含原列表x的所有元素。如果position是当前列表的end()迭代器,则x的元素将被添加到当前列表的末尾。 -
void splice (iterator position, list& x, iterator i);此函数将单个元素从列表
x移动到当前列表的position位置。元素是由迭代器i指定的,它必须指向列表x中的一个有效元素。移动后,迭代器i将不再指向列表x中的任何元素(因为它现在属于当前列表)。 -
void splice (iterator position, list& x, iterator first, iterator last);此函数将列表
x中由迭代器范围[first, last)指定的元素移动到当前列表的position位置。这个范围包括first指向的元素,但不包括last指向的元素。移动后,这个范围内的元素将不再属于列表x,而是成为当前列表的一部分。如果first和last相等,则不移动任何元素。
需要注意的是,在所有这些情况下,splice操作都不会复制元素,而是通过重新链接节点来移动它们。因此,这是一个常数时间操作(O(1)),尽管遍历列表以找到迭代器所指向的元素可能需要线性时间(O(n)),但这与splice函数本身的效率无关。此外,splice函数要求所有涉及的迭代器都是有效的,并且属于指定的列表(在调用splice之前)。
cpp
/**
* Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such: // 实例化和调用
* LRUCache* obj = new LRUCache(capacity);
* int param_1 = obj->get(key);
* obj->put(key,value);
*/
class LRUCache {
typedef list<pair<int, int>>::iterator ListIt;
int _capacity;
unordered_map<int, ListIt> _hashmap;
list<pair<int, int>> _LRUlist;
public:
LRUCache(int capacity) : _capacity(capacity) {}
int get(int key) {
auto it = _hashmap.find(key);
if (it != _hashmap.end()) {
// 将该关键字移动到LRU队列头
ListIt listit = it->second;
_LRUlist.splice(_LRUlist.begin(), _LRUlist, listit);
return listit->second;
} else
return -1;
}
void put(int key, int value) {
auto it = _hashmap.find(key);
if (it == _hashmap.end()) {
// 判满,如果满了逐出最久未使用的关键字
if (_hashmap.size() == _capacity) {
pair<int, int> back = _LRUlist.back();
_hashmap.erase(back.first);
_LRUlist.pop_back();
}
// 将关键字插入到LRU队列头
_LRUlist.push_front(make_pair(key, value));
_hashmap.insert(make_pair(key, _LRUlist.begin()));
} else {
// 找到了更新其value值,并将该关键字移动到LRU队列头
ListIt listit = it->second;
listit->second = value;
_LRUlist.splice(_LRUlist.begin(), _LRUlist, listit);
}
}
};SkipList
Redis的内部数据结构------skiplist;skiplist,首先它是一个list。实际上,它是在有序链表的基础上发展起来的。如果是一个有序的链表,查找数据的时间复杂度是O(N)。
skiplist本质上也是一种查找结构,用于解决算法中的查找问题(Searching),即根据给定的key,快速查到它所在的位置(或者对应的value)。
一般查找问题的解法分为两个大类:一个是基于各种平衡树,一个是基于哈希表。但skiplist却比较特殊,它没法归属到这两大类里面。
William Pugh开始的优化思路:
-
假如我们每相邻两个节点升高一层,增加一个指针,让指针指向下下个节点,如下图b所示。这样所有新增加的指针连成了一个新的链表,但它包含的节点个数只有原来的一半。由于新增加的指针,我们不再需要与链表中每个节点逐个进行比较了,需要比较的节点数大概只有原来的一半。
-
以此类推,我们可以在第二层新产生的链表上,继续为每相邻的两个节点升高一层,增加一个指针,从而产生第三层链表。如下图c,这样搜索效率就进一步提高了。
-
skiplist正是受这种多层链表的想法的启发而设计出来的。实际上,按照上面生成链表的方式,上面每一层链表的节点个数,是下面一层的节点个数的一半,这样查找过程就非常类似二分查找,使得查找的时间复杂度可以降低到O(log n)。
-
但是这个结构在插入删除数据的时候有很大的问题,插入或者删除一个节点之后,就会打乱上下相邻两层链表上节点个数严格的2:1的对应关系。如果要维持这种对应关系,就必须把新插入的节点后面的所有节点(也包括新插入的节点)重新进行调整,这会让时间复杂度重新蜕化成O(n)。
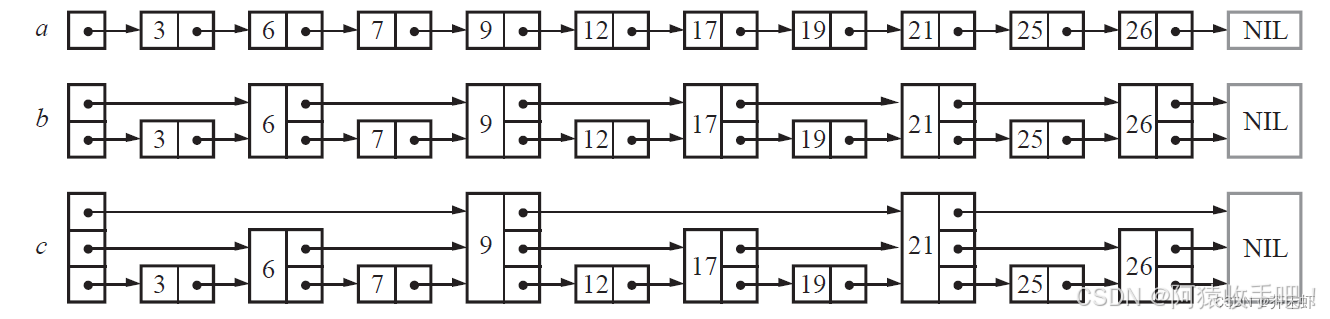
插入与删除的处理
- skiplist的设计为了避免这种问题,做了一个大胆的处理,不再严格要求对应比例关系,而是插入一个节点的时候随机出一个层数 。这样每次插入和删除都不需要考虑其他节点的层数,这样就好处理多了。

cpp
struct SkiplistNode
{
int _val;
vector<SkiplistNode *> _nextArr;
SkiplistNode(int val, int level)
: _val(val), _nextArr(level, nullptr)
{
}
};
class Skiplist
{
typedef SkiplistNode Node;
private:
Node *_head;
size_t _maxLevel = 32;
double _p = 0.25;
public:
Skiplist()
{
srand(time(0));
// 头节点,层数是1
_head = new Node(-1, 1);
}
bool search(int target)
{
Node *cur = _head;
int level = _head->_nextArr.size() - 1;
while (level >= 0)
{
// 目标值比下一个节点值要大,向右走
// 下一个节点是空(尾),目标值比下一个节点值要小,向下走
if (cur->_nextArr[level] && cur->_nextArr[level]->_val < target)
{
// 向右走
cur = cur->_nextArr[level];
}
else if (cur->_nextArr[level] == nullptr || cur->_nextArr[level]->_val > target)
{
// 向下走
--level;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
vector<Node *> FindPrevNode(int num)
{
Node *cur = _head;
int level = _head->_nextArr.size() - 1;
// 插入位置每一层前一个节点指针
vector<Node *> prevV(level + 1, _head);
while (level >= 0)
{
// 目标值比下一个节点值要大,向右走
// 下一个节点是空(尾),目标值比下一个节点值要小,向下走
if (cur->_nextArr[level] && cur->_nextArr[level]->_val < num)
{
// 向右走
cur = cur->_nextArr[level];
}
else if (cur->_nextArr[level] == nullptr || cur->_nextArr[level]->_val >= num)
{
// 更新level层前一个
prevV[level] = cur;
// 向下走
--level;
}
}
return prevV;
}
void add(int num)
{
vector<Node *> prevArr = FindPrevNode(num);
int n = RandomLevel();
Node *newnode = new Node(num, n);
// 如果n超过当前最大的层数,那就升高一下_head的层数
if (n > _head->_nextArr.size())
{
_head->_nextArr.resize(n, nullptr);
prevArr.resize(n, _head);
}
// 链接前后节点
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
newnode->_nextArr[i] = prevArr[i]->_nextArr[i];
prevArr[i]->_nextArr[i] = newnode;
}
}
bool erase(int num)
{
vector<Node *> prevV = FindPrevNode(num);
// 第一层下一个不是val,val不在表中
if (prevV[0]->_nextArr[0] == nullptr || prevV[0]->_nextArr[0]->_val != num)
{
return false;
}
else
{
Node *del = prevV[0]->_nextArr[0];
// del节点每一层的前后指针链接起来
for (size_t i = 0; i < del->_nextArr.size(); i++)
{
prevV[i]->_nextArr[i] = del->_nextArr[i];
}
delete del;
// 如果删除最高层节点,把头节点的层数也降一下
int i = _head->_nextArr.size() - 1;
while (i >= 0)
{
if (_head->_nextArr[i] == nullptr)
--i;
else
break;
}
_head->_nextArr.resize(i + 1);
return true;
}
}
int RandomLevel()
{
size_t level = 1;
// rand() ->[0, RAND_MAX]之间
while (rand() <= RAND_MAX * _p && level < _maxLevel)
{
++level;
}
return level;
}
int RandomLevel2()
{
// 静态随机数生成器 只会在第一次调用该函数时被初始化
// 生成器的种子是当前时间自纪元(1970年1月1日)以来的纳秒数
static std::default_random_engine generator(std::chrono::system_clock::now().time_since_epoch().count());
// 静态均匀分布对象 用于生成 [0.0, 1.0) 范围内的双精度浮点数
static std::uniform_real_distribution<double> distribution(0.0, 1.0);
size_t level = 1;
while (distribution(generator) <= _p && level < _maxLevel)
{
++level;
}
return level;
}
void Print()
{
printf("--------------------------------------------------------\n");
Node *cur = _head;
while (cur)
{
printf("%d\n", cur->_val);
// 打印每个每个cur节点
for (auto e : cur->_nextArr)
{
printf("%2s ", "↓");
}
printf("\n");
cur = cur->_nextArr[0];
}
printf("--------------------------------------------------------\n");
}
};模拟实现跳表 + 测试
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <ctime>
#include <random>
#include <chrono>
using namespace std;
struct SkiplistNode
{
int _val;
vector<SkiplistNode *> _nextArr;
SkiplistNode(int val, int level)
: _val(val), _nextArr(level, nullptr)
{
}
};
class Skiplist
{
typedef SkiplistNode Node;
private:
Node *_head;
size_t _maxLevel = 32;
double _p = 0.25;
public:
Skiplist()
{
srand(time(0));
// 头节点,层数是1
_head = new Node(-1, 1);
}
bool search(int target)
{
Node *cur = _head;
int level = _head->_nextArr.size() - 1;
while (level >= 0)
{
// 目标值比下一个节点值要大,向右走
// 下一个节点是空(尾),目标值比下一个节点值要小,向下走
if (cur->_nextArr[level] && cur->_nextArr[level]->_val < target)
{
// 向右走
cur = cur->_nextArr[level];
}
else if (cur->_nextArr[level] == nullptr || cur->_nextArr[level]->_val > target)
{
// 向下走
--level;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
vector<Node *> FindPrevNode(int num)
{
Node *cur = _head;
int level = _head->_nextArr.size() - 1;
// 插入位置每一层前一个节点指针
vector<Node *> prevV(level + 1, _head);
while (level >= 0)
{
// 目标值比下一个节点值要大,向右走
// 下一个节点是空(尾),目标值比下一个节点值要小,向下走
if (cur->_nextArr[level] && cur->_nextArr[level]->_val < num)
{
// 向右走
cur = cur->_nextArr[level];
}
else if (cur->_nextArr[level] == nullptr || cur->_nextArr[level]->_val >= num)
{
// 更新level层前一个
prevV[level] = cur;
// 向下走
--level;
}
}
return prevV;
}
void add(int num)
{
vector<Node *> prevArr = FindPrevNode(num);
int n = RandomLevel();
Node *newnode = new Node(num, n);
// 如果n超过当前最大的层数,那就升高一下_head的层数
if (n > _head->_nextArr.size())
{
_head->_nextArr.resize(n, nullptr);
prevArr.resize(n, _head);
}
// 链接前后节点
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
newnode->_nextArr[i] = prevArr[i]->_nextArr[i];
prevArr[i]->_nextArr[i] = newnode;
}
}
bool erase(int num)
{
vector<Node *> prevV = FindPrevNode(num);
// 第一层下一个不是val,val不在表中
if (prevV[0]->_nextArr[0] == nullptr || prevV[0]->_nextArr[0]->_val != num)
{
return false;
}
else
{
Node *del = prevV[0]->_nextArr[0];
// del节点每一层的前后指针链接起来
for (size_t i = 0; i < del->_nextArr.size(); i++)
{
prevV[i]->_nextArr[i] = del->_nextArr[i];
}
delete del;
// 如果删除最高层节点,把头节点的层数也降一下
int i = _head->_nextArr.size() - 1;
while (i >= 0)
{
if (_head->_nextArr[i] == nullptr)
--i;
else
break;
}
_head->_nextArr.resize(i + 1);
return true;
}
}
int RandomLevel()
{
size_t level = 1;
// rand() ->[0, RAND_MAX]之间
while (rand() <= RAND_MAX * _p && level < _maxLevel)
{
++level;
}
return level;
}
int RandomLevel2()
{
// 静态随机数生成器 只会在第一次调用该函数时被初始化
// 生成器的种子是当前时间自纪元(1970年1月1日)以来的纳秒数
static std::default_random_engine generator(std::chrono::system_clock::now().time_since_epoch().count());
// 静态均匀分布对象 用于生成 [0.0, 1.0) 范围内的双精度浮点数
static std::uniform_real_distribution<double> distribution(0.0, 1.0);
size_t level = 1;
while (distribution(generator) <= _p && level < _maxLevel)
{
++level;
}
return level;
}
void Print()
{
printf("--------------------------------------------------------\n");
Node *cur = _head;
while (cur)
{
printf("%d\n", cur->_val);
// 打印每个每个cur节点
for (auto e : cur->_nextArr)
{
printf("%2s ", "↓");
}
printf("\n");
cur = cur->_nextArr[0];
}
printf("--------------------------------------------------------\n");
}
};
// 随即层数最大值 经测试是16
// int main()
// {
// Skiplist sl;
// int max = 0;
// for (size_t i = 0; i < 1000000000; ++i)
// {
// //cout << sl.RandomLevel() <<" ";
// int r = sl.RandomLevel();
// if (r > max)
// max = r;
// }
// cout << max << endl;
// return 0;
// }
// 测试std随机数生成器
// int main()
// {
// unsigned seed = std::chrono::system_clock::now().time_since_epoch().count();
// std::default_random_engine generator(seed);
// std::uniform_real_distribution<double> distribution(0.0, 1.0);
// size_t count = 0;
// for (int i = 0; i < 100; ++i)
// {
// if (distribution(generator) <= 0.25)
// ++count;
// }
// cout << count << endl;// 100次有17次生成的数小于等于0.25
// return 0;
// }
// 测试跳表
int main()
{
Skiplist slist;
// int a[] = { 5, 2, 3, 8, 9, 6, 5, 2, 3, 8, 9, 6, 5, 2, 3, 8, 9, 6 };
int a[] = {3, 7, 11, 19, 22, 26, 37};
for (auto e : a)
{
slist.add(e);
}
slist.Print();
int x;
cout << "请输入要删除的元素:";
cin >> x;
slist.erase(x);
slist.Print();
cout << "请输入要查找的元素:";
cin >> x;
if (slist.search(x))
cout << "找到了" << endl;
else
cout << "没找到" << endl;
cout << "请输入要查找的元素:";
cin >> x;
if (slist.search(x))
cout << "找到了" << endl;
else
cout << "没找到" << endl;
return 0;
}