
文章目录
1、功能描述
找出图片中的轮廓,拟合轮廓外接椭圆和外接矩阵
2、代码实现
导入必要的库,固定好随机种子
python
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
import argparse
import random as rng
rng.seed(12345)读取输入图片,判定图片是否读入成功
python
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
description='Code for Creating Bounding rotated boxes and ellipses for contours tutorial.')
parser.add_argument('--input', help='Path to input image.', default='1.png')
args = parser.parse_args()
src = cv.imread(cv.samples.findFile(args.input))
if src is None:
print('Could not open or find the image:', args.input)
exit(0)灰度化图片,并平滑
python
# Convert image to gray and blur it
src_gray = cv.cvtColor(src, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
src_gray = cv.blur(src_gray, (3, 3))
source_window = 'Source'
cv.namedWindow(source_window)
cv.imshow(source_window, src)创建滚动条,动态配置参数,随着滑动条的滑动实现不同的算法效果
python
max_thresh = 255
thresh = 100 # initial threshold
cv.createTrackbar('Canny Thresh:', source_window, thresh, max_thresh, thresh_callback)
thresh_callback(thresh)
cv.waitKey()算法核心函数 thresh_callback,下面具体看看细节
python
def thresh_callback(val):
global src_gray
threshold = val
src_gray = cv.GaussianBlur(src_gray, (3, 3), 0.1)
canny_output = cv.Canny(src_gray, threshold, threshold * 2)高斯模糊,canny 算子
python
contours, _ = cv.findContours(canny_output, cv.RETR_TREE, cv.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
# Find the rotated rectangles and ellipses for each contour
minRect = [None] * len(contours)
minEllipse = [None] * len(contours)
for i, c in enumerate(contours):
minRect[i] = cv.minAreaRect(c)
if c.shape[0] > 5:
minEllipse[i] = cv.fitEllipse(c)
# Draw contours + rotated rects + ellipses找出轮廓,遍历轮廓,最小外接矩形框直接调用 cv2.minAreaRect 即可
如果轮廓多于 5 个点,cv2.fiEllipse 找椭圆
python
# Draw contours + rotated rects + ellipses
drawing = np.zeros((canny_output.shape[0], canny_output.shape[1], 3), dtype=np.uint8)
for i, c in enumerate(contours):
color = (rng.randint(0, 256), rng.randint(0, 256), rng.randint(0, 256))
# contour
cv.drawContours(drawing, contours, i, color)
# ellipse
if c.shape[0] > 5:
cv.ellipse(drawing, minEllipse[i], color, 2)
# rotated rectangle
box = cv.boxPoints(minEllipse[i])
# box = cv.boxPoints(minRect[i])
box = np.intp(box) # np.intp: Integer used for indexing (same as C ssize_t; normally either int32 or int64)
# box = np.int0(box) # normally either int32 or int64)
cv.drawContours(drawing, [box], 0, color)
cv.imshow('Contours', drawing)
cv.imshow("Canny", canny_output)绘制轮廓,轮廓外接矩阵,轮廓拟合出来的椭圆,随机颜色
注意 box = cv.boxPoints(minEllipse[i]) 绘制的是椭圆的外接矩阵,而 box = cv.boxPoints(minRect[i]) 绘制轮廓的外接矩阵被注释掉了
3、完整代码
python
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
import argparse
import random as rng
rng.seed(12345)
def thresh_callback(val):
global src_gray
threshold = val
src_gray = cv.GaussianBlur(src_gray, (3, 3), 0.1)
canny_output = cv.Canny(src_gray, threshold, threshold * 2)
contours, _ = cv.findContours(canny_output, cv.RETR_TREE, cv.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
# Find the rotated rectangles and ellipses for each contour
minRect = [None] * len(contours)
minEllipse = [None] * len(contours)
for i, c in enumerate(contours):
minRect[i] = cv.minAreaRect(c)
if c.shape[0] > 5:
minEllipse[i] = cv.fitEllipse(c)
# Draw contours + rotated rects + ellipses
drawing = np.zeros((canny_output.shape[0], canny_output.shape[1], 3), dtype=np.uint8)
for i, c in enumerate(contours):
color = (rng.randint(0, 256), rng.randint(0, 256), rng.randint(0, 256))
# contour
cv.drawContours(drawing, contours, i, color)
# ellipse
if c.shape[0] > 5:
cv.ellipse(drawing, minEllipse[i], color, 2)
# rotated rectangle
box = cv.boxPoints(minEllipse[i])
# box = cv.boxPoints(minRect[i])
box = np.intp(box) # np.intp: Integer used for indexing (same as C ssize_t; normally either int32 or int64)
# box = np.int0(box) # normally either int32 or int64)
cv.drawContours(drawing, [box], 0, color)
cv.imshow('Contours', drawing)
cv.imshow("Canny", canny_output)
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
description='Code for Creating Bounding rotated boxes and ellipses for contours tutorial.')
parser.add_argument('--input', help='Path to input image.', default='1.png')
args = parser.parse_args()
src = cv.imread(cv.samples.findFile(args.input))
if src is None:
print('Could not open or find the image:', args.input)
exit(0)
# Convert image to gray and blur it
src_gray = cv.cvtColor(src, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
src_gray = cv.blur(src_gray, (3, 3))
source_window = 'Source'
cv.namedWindow(source_window)
cv.imshow(source_window, src)
max_thresh = 255
thresh = 100 # initial threshold
cv.createTrackbar('Canny Thresh:', source_window, thresh, max_thresh, thresh_callback)
thresh_callback(thresh)
cv.waitKey()4、结果展示
Canny Thresh:0
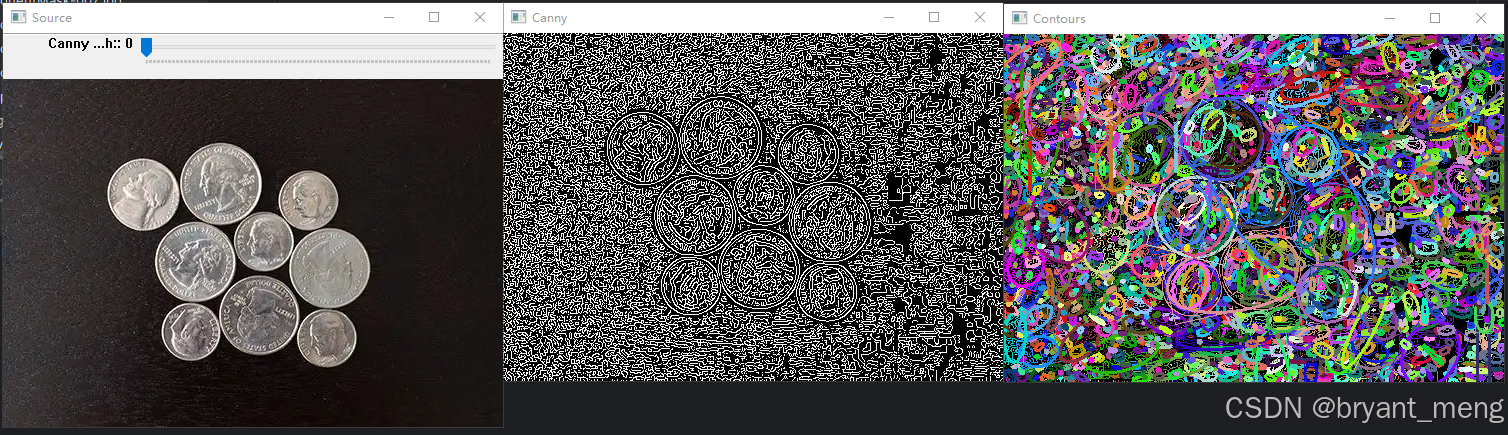
Canny Thresh:5

Canny Thresh:15

Canny Thresh:25

Canny Thresh:35
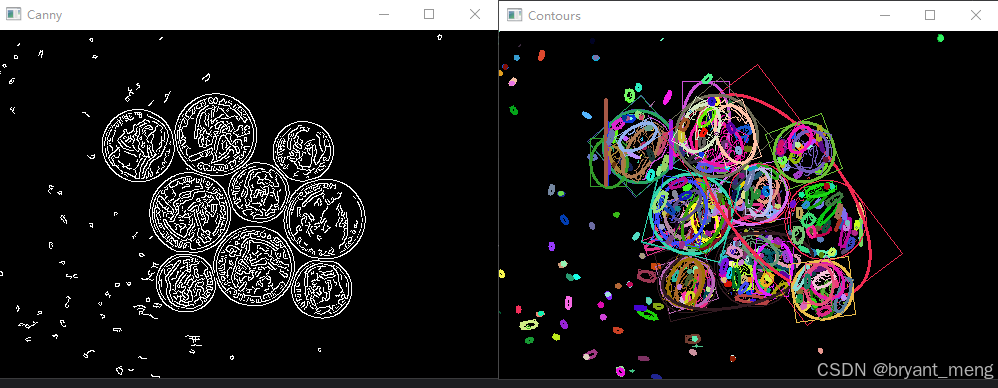
Canny Thresh:45

Canny Thresh:100
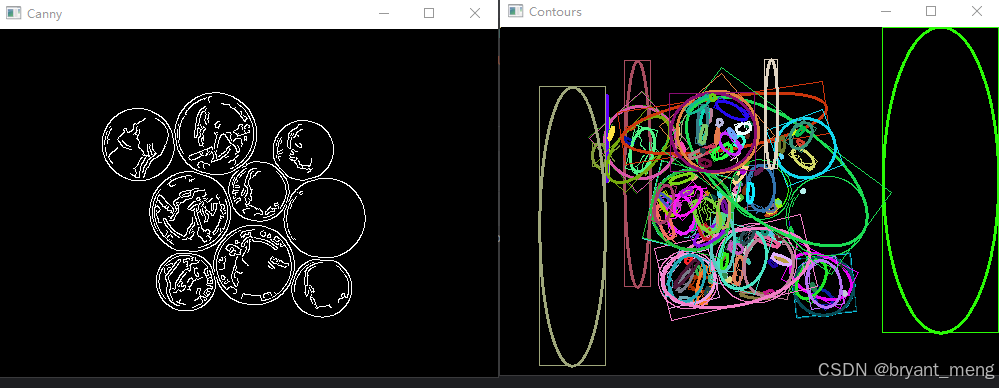
Canny Thresh:150
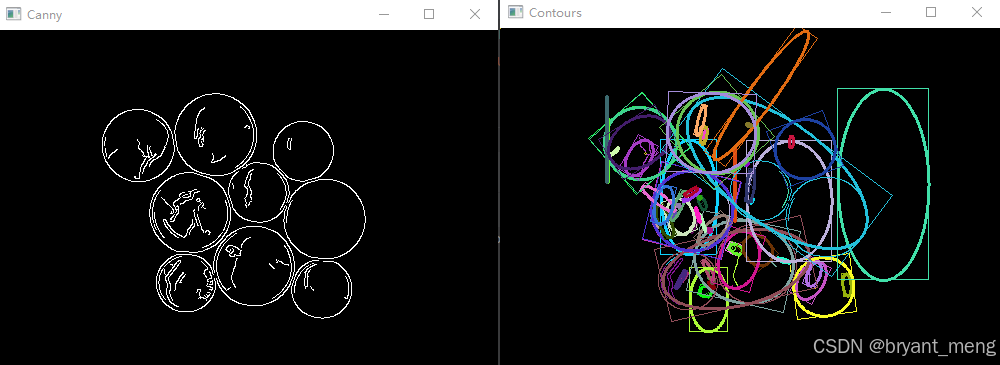
Canny Thresh:200
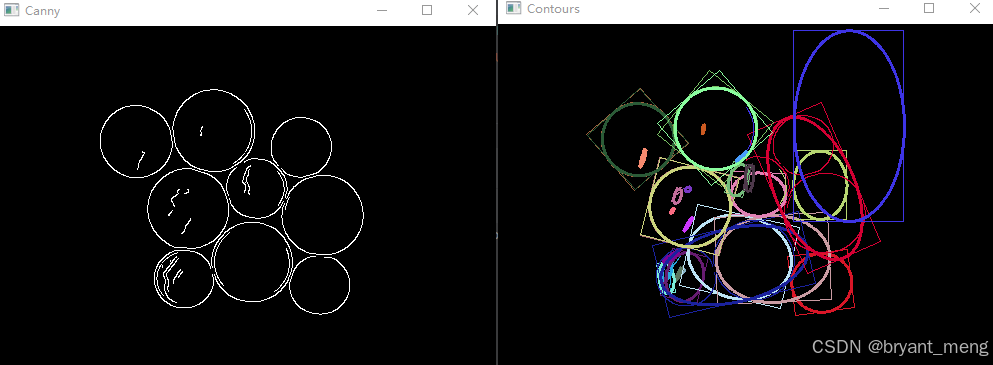
Canny Thresh:255

5、涉及到的库函数
5.1、cv2.Canny
cv2.Canny 是 OpenCV 库中用于边缘检测的一个函数,它实现了 Canny 边缘检测算法。Canny 边缘检测是一种非常流行的边缘检测算法,由 John F. Canny 在 1986 年提出。这个算法旨在寻找图像中的最优边缘,它通过应用多尺度高斯滤波来减少噪声,然后计算图像梯度,接着通过非极大值抑制和滞后阈值化来检测边缘。
python
edges = cv2.Canny(image, threshold1, threshold2[, edges[, apertureSize[, L2gradient]]])- image:输入的灰度图像。在进行 Canny 边缘检测之前,通常需要先将图像转换为灰度图像。
- threshold1:第一个阈值,用于滞后阈值化中的低阈值。
- threshold2:第二个阈值,用于滞后阈值化中的高阈值。只有那些梯度值高于 threshold2 的像素才会被当作边缘,而梯度值位于 threshold1 和 threshold2 之间的像素只有在它们连接到高阈值边缘时才会被接受。
- edges:输出参数,用于存储检测到的边缘。如果不指定,则会自动创建一个同大小的输出图像。
- apertureSize:Sobel 算子的大小,默认为 3。这个参数影响梯度计算的精度,但增加大小也会增加计算时间。
- L2gradient:一个布尔值,指示是否使用更精确的 L2 范数来计算图像梯度幅值。默认值为 False,即使用 L1 范数(即简单地将梯度在 x 和 y 方向的分量相加)。
返回值:
- edges:一个二值图像,其中检测到的边缘像素被设置为白色(255),其他像素被设置为黑色(0)。
Canny 边缘检测的优点在于它能够有效地抑制噪声,并且检测到的边缘通常是连续的。然而,它的效果也依赖于所选的阈值,因此在实际应用中,可能需要根据具体情况调整 threshold1 和 threshold2 的值。
5.2 cv2.boxPoints
cv2.boxPoints 用于计算给定矩形旋转后的顶点坐标。这个函数在需要处理旋转矩形时非常有用,比如在图像中绘制旋转的边界框时。
python
points = cv2.boxPoints(box[, rotMat])参数解释:
- box:表示矩形的参数。这可以是一个包含四个元素的元组或列表 (center_x, center_y, width, height),其中 (center_x, center_y) 是矩形中心的坐标,width 和 height 分别是矩形的宽度和高度(注意:这里的宽度和高度是按照矩形的原始大小,不考虑旋转)。在某些版本的 OpenCV 中,box 也可能是一个 cv2.RotatedRect 对象。
- rotMat:可选参数,表示旋转矩阵。这是一个 2x3 的浮点数数组,用于指定对矩形进行额外旋转的角度。如果未提供此参数,则矩形不会被额外旋转,只返回根据 box 参数计算出的四个顶点坐标。
返回值:
- points:一个包含四个点的 NumPy 数组,每个点都是一个包含两个元素的元组或列表 (x, y),表示旋转后矩形的顶点坐标。
需要注意的是,如果 box 是一个 cv2.RotatedRect 对象,那么它本身就包含了旋转信息(即旋转角度和中心点),此时 rotMat 参数将被忽略,因为 cv2.RotatedRect 已经定义了矩形的旋转状态。
示例代码:
python
import cv2
import numpy as np
# 定义一个中心点、宽度、高度的矩形
center = (100, 100)
width = 200
height = 100
angle = 45 # 旋转角度(以度为单位)
# 创建一个旋转矩形对象
rect = cv2.RotatedRect(center, (width, height), angle)
# 获取旋转矩形的顶点
points = cv2.boxPoints(rect)
points = np.intp(points) # 将坐标转换为整数类型,以便在图像上绘制
# 创建一个黑色图像
image = np.zeros((256, 256, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
# 在图像上绘制旋转矩形的边
for i in range(4):
cv2.line(image, tuple(points[i]), tuple(points[(i+1)%4]), (255, 0, 0), 2)
# 显示图像
cv2.imshow('Rotated Rectangle', image)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()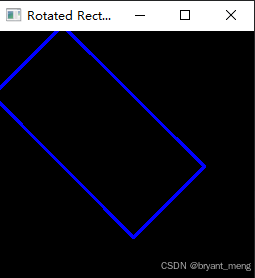
在这个示例中,我们首先定义了一个矩形的中心点、宽度、高度和旋转角度,然后创建了一个 cv2.RotatedRect 对象来表示这个旋转矩形。接着,我们使用 cv2.boxPoints 函数来获取旋转矩形的顶点坐标,并在一个黑色图像上绘制了这个矩形的边。最后,我们显示了包含旋转矩形的图像。