这篇博客是关于队列+宽搜的几道题,主要包括N叉树的层序遍历、二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历、二叉树最大宽度、在每个数行中找最大值。

cpp
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(Node* root)
{
vector<vector<int>> ret;
if(!root) return ret;
queue<Node*> q;
q.push(root);
while(q.size())
{
int num = q.size(); //先求出本层的元素个数
vector<int> tmp; //统计本层的节点
while(num--)
{
Node* top = q.front();
q.pop();
tmp.push_back(top->val);
for(auto e : top->children)
{
if(e != nullptr)
q.push(e);
}
}
ret.push_back(tmp);
}
return ret;
}
};题目分析:这道题我们需要层序遍历,需要借助一个队列实现,首先将第一层节点放进队列,然后出队列,在出队列后,把它的孩子节点都push到队列中,再依次把这几个孩子节点出队列,每一个节点出队列后,都要马上把它的孩子节点push到队列。为了知道每层有几个节点,在每一层出队列前,需要统计队列里的元素个数。

cpp
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode* root)
{
vector<vector<int>> ret;
if(!root) return ret;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
int flag = 1;
while(q.size())
{
int sz = q.size();
vector<int> tmp;
for(int i = 0 ; i < sz ; i++)
{
TreeNode* top = q.front();
q.pop();
tmp.push_back(top->val);
if(top->left) q.push(top->left);
if(top->right) q.push(top->right);
}
if(flag % 2 == 0)
{
reverse(tmp.begin(), tmp.end());
}
ret.push_back(tmp);
flag++;
}
return ret;
}
};题目分析:仍然是使用队列来存放节点,和上一题不同的是,在得到偶数层的队列后,需要将其逆序一下,可以通过创建一个变量来判断奇偶层。

cpp
class Solution {
public:
int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode* root)
{
vector<pair<TreeNode*,unsigned int>> queue;
unsigned int ret = 0;
queue.push_back({root, 1});
while(queue.size())
{
auto& [x1, y1] = queue[0];
auto& [x2, y2] = queue.back();
ret = max(ret, y2 - y1 + 1);
vector<pair<TreeNode*,unsigned int>> tmp;
for(auto& [x, y] : queue)
{
if(x->left) tmp.push_back({x->left, 2*y});
if(x->right) tmp.push_back({x->right, 2*y + 1});
}
queue = tmp;
}
return ret;
}
};题目分析:这道题我们可以使用数组存储二叉树的方式,给节点编号,数组的类型为pair<TreeNode*,int>,int为这个节点的编号,一层的两端节点编号相减+1就是这层的宽度。
需要注意的是,下标可能溢出,所以不能用int存储节点编号,而是用unsigned int 存储。
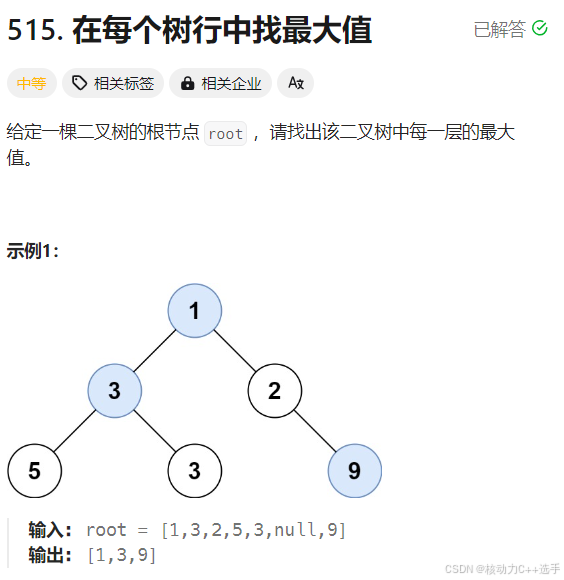
cpp
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> largestValues(TreeNode* root)
{
queue<TreeNode*> q;
vector<int> ret;
if(!root) return ret;
q.push(root);
// ret.push_back(root->val);
while(q.size())
{
int size = q.size();
int m = INT_MIN;
while(size--)
{
TreeNode* top = q.front();
q.pop();
m = max(m, top->val);
if(top->left) q.push(top->left);
if(top->right) q.push(top->right);
}
ret.push_back(m);
}
return ret;
}
};题目分析:很简单,利用层序遍历,统计每一层的最大值。