UICollectionView的学习
文章目录
前言
UICollectionVIew和我们之前的UITableView比较类似,但是UICollectionView可以实现布局的效果,比如说瀑布流布局抑或者是圆环布局,这也是UICollectionView比UITableView强大的地方,这里笔者简单学习了有关于UICollectionView的一些用法,下文笔者来简单介绍一下有关于UICollectionView的一个使用的内容。
简单使用UICollectionView
简单使用UICollectionView主要需要一下几个步骤:
- 创建一个布局类(这个布局类决定了我们最后的UICollectionView的样式,也可以说是UICollecitonVIew的一个核心内容)。
- 初始化我的一个UICollecitonView,这里也就是给我们的UICollecitonView设置布局的内容,相当于设置了他的一个布局内容。
- 实现相关的协议函数。
objc
//View层中的一个内容
UICollectionViewFlowLayout * myLayout = [[UICollectionViewFlowLayout alloc]init];
//设置垂直流布局
myLayout.scrollDirection = UICollectionViewScrollDirectionVertical;
myLayout.itemSize = CGSizeMake(100, 100);
self.collectionView = [[UICollectionView alloc] initWithFrame:self.bounds collectionViewLayout:myLayout];
[self addSubview:self.collectionView];
//控制器中的内容
self.iView.collectionView.delegate = self;
self.iView.collectionView.dataSource = self;
[self.iView.collectionView registerClass:[UICollectionViewCell class] forCellWithReuseIdentifier:@"UICollectionViewCell"];注意这里一定要进行一个注册cell的内容,否则就会出现问题,这里引用一篇博客的解释:
所以我们可以知道因为UITableView引入的版本较早,当时还未引入注册机制,在那时只需在cellForRowAtIndexPath方法中创建或者重用cell即可,而UICollectionView是在iOS
6.0引入的,相对较新。为了支持更灵活的布局和更复杂的cell类型,Apple在引入时就采用了注册机制。UICollectionView
然后我们就只用执行最后一个步骤,也就是一个实现它要求的一个协议函数,在ViewController层中实现
objc
- (NSInteger)collectionView:(UICollectionView *)collectionView numberOfItemsInSection:(NSInteger)section {
return 20;
}
- (__kindof UICollectionViewCell *)collectionView:(UICollectionView *)collectionView cellForItemAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {
UICollectionViewCell* cell = [collectionView dequeueReusableCellWithReuseIdentifier: @"UICollectionViewCell" forIndexPath: indexPath];
cell.backgroundColor = [UIColor colorWithRed:arc4random() % 255 / 255.0 green:arc4random() % 255 / 255.0 blue:arc4random() % 250 / 250.0 alpha:1];
return cell;
}这里简单解释一下__kindof这个关键字的内容:
__kindof通常用于泛型(generics)声明,表示该类型是某个类的具体类型或其子类的实例。它在提高代码的灵活性和类型安全方面起到了重要作用,尤其是在使用泛型和集合类时。他保留编译器检查类型的一个能力。
这样我们就初步完成了一个UICollecitonView的使用:

这里在讲解一下原生的垂直布局和水平布局的区别:
这是一个垂直流布局的格式:
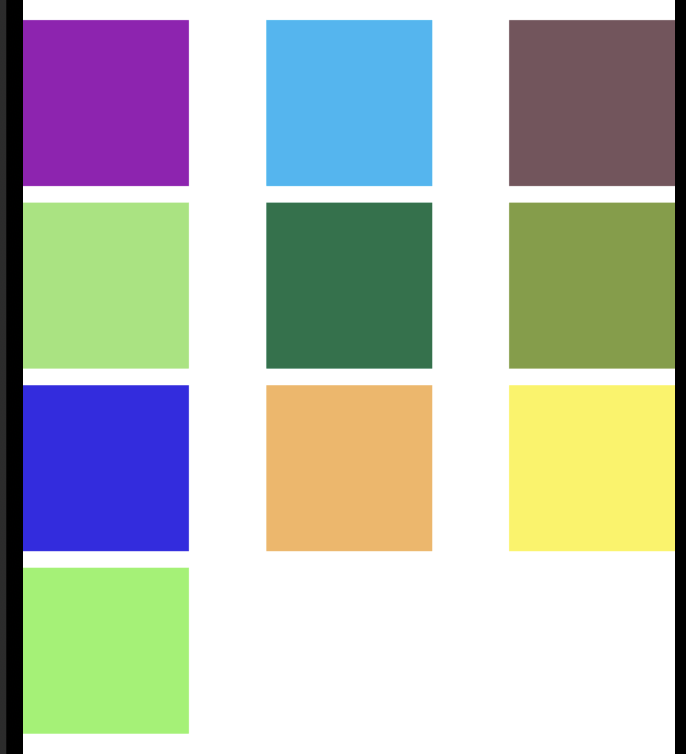

下面是水平流布局的一个形式:
两者的区别就在于一个按行填充,一个按列填充。
相关的代理方法
处理用户交互行为的协议,所有方法都是可选的。
-
collectionView:didSelectItemAtIndexPath:触发选择单元格的操作。
objc- (void)collectionView:(UICollectionView *)collectionView didSelectItemAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath { NSLog(@"选择了分区 %ld 的第 %ld 项", indexPath.section, indexPath.row); } -
collectionView:didDeselectItemAtIndexPath:触发取消选择的操作(多选模式下有效)。
- 高亮效果 :
collectionView:shouldHighlightItemAtIndexPath:
决定是否允许高亮指定单元格(默认返回 YES)。collectionView:didHighlightItemAtIndexPath:
用户触摸单元格时调用。
- 显示和隐藏 :
collectionView:willDisplayCell:forItemAtIndexPath:
将要显示某个单元格时调用,可以在这里进行内容更新或动画设置。collectionView:didEndDisplayingCell:forItemAtIndexPath:
单元格离开屏幕后触发。
Layout中常用的一些属性
主要属性:
itemSize:每个单元格的大小。sectionInset:分区的边距。minimumLineSpacing:行间距。minimumInteritemSpacing:列间距。scrollDirection:滚动方向(水平或垂直)。
其他效果实现
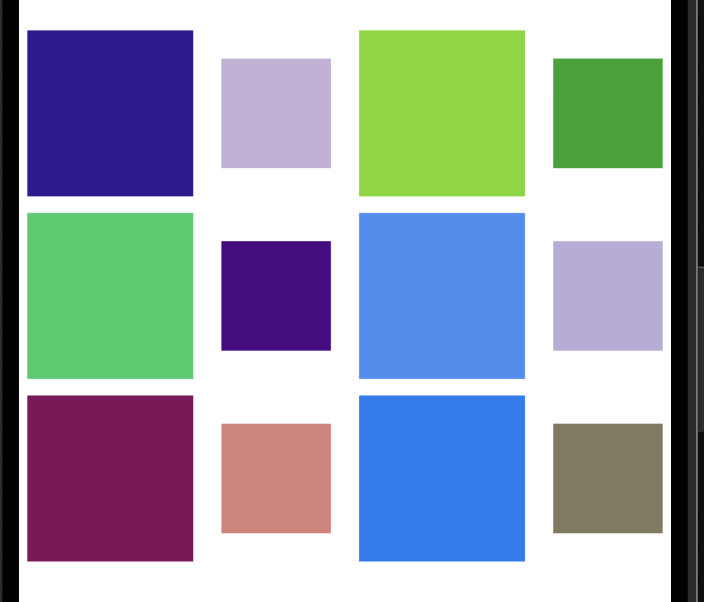
有些时候普通的九宫格也不能满足我们的一个需求,我们可以实现一些别的效果:
objc
//设置每个item的大小,双数的为50*50 单数的为100*100
-(CGSize)collectionView:(UICollectionView *)collectionView layout:(UICollectionViewLayout *)collectionViewLayout sizeForItemAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath{
if (indexPath.row % 2 != 0) {
return CGSizeMake(66, 66);
} else {
return CGSizeMake(100, 100);
}
}
瀑布流布局的一个实现
首先,要实现一个瀑布流的布局我们需要了解UICollectionView的一个布局的一个过程:
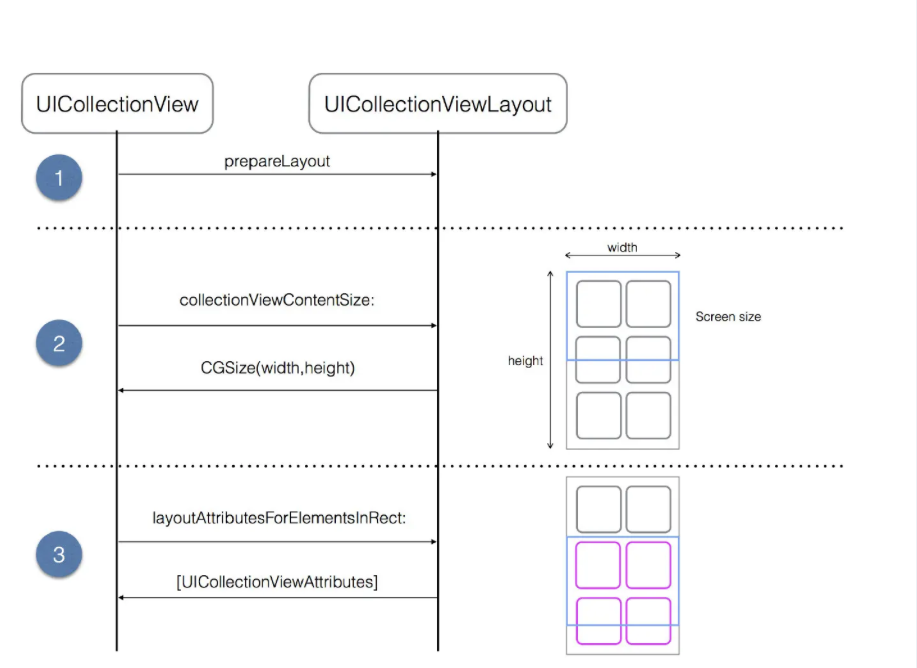
从上面这个图中可以看出一个点,也就是我们如果想实现一个瀑布流,应该是我们设计一个自己的layout,然后就可以让我的cell按照我们想要的效果呈现在我们的手机上。
自定义UICollectionViewFlowLayout
首先我们先要自定义一个Layout。
objc
NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_BEGIN
@interface MainPageFlowLayout : UICollectionViewFlowLayout
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSMutableArray* array;
@property (nonatomic, assign) NSInteger itemCount;
@property (nonatomic, assign) NSInteger sectionCount;
@end
NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_END返回一个瀑布流的效果,其实是主要是重写下面这两个函数
objc
- (void)prepareLayout {
}//只会调用一次这个方法在一开始布局的时候,我们在这个函数把我们的布局设计好,然后将数组元素填充好就可以了。
- (NSArray<__kindof UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes *> *)layoutAttributesForElementsInRect:(CGRect)rect {
return [NSArray arrayWithArray:self.array];
}//用于返回我们的一个布局数组,我们的cell按照这个要求布局这里笔者引用一段博客,简单介绍一下perpareLayout中可以做到的一些事情
其中我们在prepareLayout方法进行布局前的准备,其主要有两个作用:
初始化布局参数: 在 prepareLayout 中,你可以进行一些初始化工作,例如计算和缓存用于布局的参数。这可能包括计算每个单元格的大小、计算行列的数量、初始化用于存储布局属性的数据结构等。
计算并缓存布局属性: 你可以在 prepareLayout 中计算并缓存集合视图中所有单元格的布局属性(UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes)。这样,当集合视图需要显示或进行交互时,可以直接访问缓存的布局属性,而不需要在运行时动态计算。UICollectionView
下面来介绍一下实现瀑布流的一个函数:
objc
- (void)prepareLayout {
self.array = [NSMutableArray array];
[super prepareLayout];
//sectionInset是一个UIEdgeInset的类型,主要返回的是组之间的一个间隙
CGFloat width = ([UIScreen mainScreen].bounds.size.width - self.sectionInset.left - self.sectionInset.right - self.minimumInteritemSpacing) / 2;//计算每个cell的一个宽度
CGFloat colHeight[2] = {self.sectionInset.top, self.sectionInset.bottom};//定义一个浮点型的数组
for (int i = 0; i < self.itemCount; i++) { //遍历每一个cell
NSIndexPath* indexPath = [NSIndexPath indexPathForItem:i inSection:0];//获取对应的一个indexPath
UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes* attributes = [UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes layoutAttributesForCellWithIndexPath:indexPath];//设置一个对应的布局
CGFloat height = arc4random() % 123 + 77;//设置高度
int indexCol = 0; //标记短的列
if (colHeight[0] < colHeight[1]) {
colHeight[0] = colHeight[0] + height + self.minimumLineSpacing;//计算高度的位置
indexCol = 0;
} else {
colHeight[1] = colHeight[1] + height + self.minimumLineSpacing;
indexCol = 1;
}
attributes.frame = CGRectMake(self.sectionInset.left + (self.minimumInteritemSpacing + width) * indexCol, colHeight[indexCol] - height - self.minimumLineSpacing, width, height);//设置布局的一个位置
[self.array addObject:attributes];
if (colHeight[0] > colHeight[1]) {//找出高度最大的列
self.itemSize = CGSizeMake(width, (colHeight[0] - self.sectionInset.top) * 2 / self.itemCount - self.minimumLineSpacing);//计算对应的一个高度的同时取出一个平均值防止数据偏差太大,动态调整大小,同时通过itemSize来决定我们的一个CotentSize的大小,避免这里的滑动问题
} else {
self.itemSize = CGSizeMake(width, (colHeight[1] - self.sectionInset.top) * 2 / self.itemCount - self.minimumLineSpacing);
}
}
}
- (NSArray<__kindof UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes *> *)layoutAttributesForElementsInRect:(CGRect)rect {
return [NSArray arrayWithArray:self.array];
}这里简单解释一下我们的一个sectionInset的内容这里笔者给出一张图来帮助理解这个属性的内容:
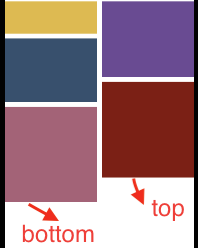
这里我们就实现了一个让瀑布流的一个布局,然后我们在View层中使用这个我们设计的自定义类
objc
- (void)setUI {
MainPageFlowLayout* layout = [[MainPageFlowLayout alloc] init];
layout.itemCount = 20;
layout.sectionInset = UIEdgeInsetsMake(5, 5, 5, 5);
self.collectionView = [[UICollectionView alloc] initWithFrame:self.bounds collectionViewLayout:layout];
[self addSubview:self.collectionView];
}然后就实现了我们的一个瀑布流的一个效果:
 **
**
实现一个圆环布局
在上面的参差瀑布流布局的案例中,我们发现如果想要实现一个自定义的一个布局,我们需要创建一个自定义的layout来实现一个布局数组,然后我们的一个cell就会按照上面的内容进行一个布局,所以如果我们想实现一个更高级的布局的话,同样也是采用这个思路。
objc
- (void)prepareLayout {
[super prepareLayout];
self.itemCount = (NSInteger)[self.collectionView numberOfItemsInSection:0];
_attributeArray = [NSMutableArray array];
CGFloat radius = MIN(self.collectionView.frame.size.width, self.collectionView.frame.size.height) / 2;
CGPoint center = CGPointMake(self.collectionView.frame.size.width / 2, self.collectionView.frame.size.height / 2);
for (int i = 0; i < self.itemCount; i++) {
NSIndexPath* indexPath = [NSIndexPath indexPathForItem:i inSection:0];
UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes* attris = [UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes layoutAttributesForCellWithIndexPath:indexPath];
attris.size = CGSizeMake(50, 50);
CGFloat x = center.x + cosf(2 * M_PI / self.itemCount * i) * (radius - 25);//计算x轴坐标
CGFloat y = center.y + sinf(2 * M_PI / self.itemCount * i) * (radius - 25);//计算y轴坐标
attris.center = CGPointMake(x, y);
[_attributeArray addObject:attris];
}
}
-(CGSize)collectionViewContentSize {
return self.collectionView.frame.size;
}
- (NSArray<__kindof UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes *> *)layoutAttributesForElementsInRect:(CGRect)rect {
return [NSArray arrayWithArray:_attributeArray];
}VC层中
objc
#import "MainPageViewController.h"
@interface MainPageViewController ()
@end
@implementation MainPageViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
self.iView = [[MainPageView alloc] initWithFrame:self.view.bounds];
[self.view addSubview:self.iView];
self.iView.collectionView.delegate = self;
self.iView.collectionView.dataSource = self;
[self.iView.collectionView registerClass:[UICollectionViewCell class] forCellWithReuseIdentifier:@"UICollectionViewCell"];
// Do any additional setup after loading the view.
}
- (NSInteger)collectionView:(UICollectionView *)collectionView numberOfItemsInSection:(NSInteger)section {
return 11;
}
- (__kindof UICollectionViewCell *)collectionView:(UICollectionView *)collectionView cellForItemAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {
UICollectionViewCell* cell = [collectionView dequeueReusableCellWithReuseIdentifier: @"UICollectionViewCell" forIndexPath: indexPath];
cell.layer.masksToBounds = YES;
cell.layer.cornerRadius = 25;
cell.backgroundColor = [UIColor colorWithRed:arc4random() % 255 / 255.0 green:arc4random() % 255 / 255.0 blue:arc4random() % 250 / 250.0 alpha:1];
return cell;
}
- (NSInteger)numberOfSectionsInCollectionView:(UICollectionView *)collectionView {
return 1;
}
/*
#pragma mark - Navigation
// In a storyboard-based application, you will often want to do a little preparation before navigation
- (void)prepareForSegue:(UIStoryboardSegue *)segue sender:(id)sender {
// Get the new view controller using [segue destinationViewController].
// Pass the selected object to the new view controller.
}
*/
@end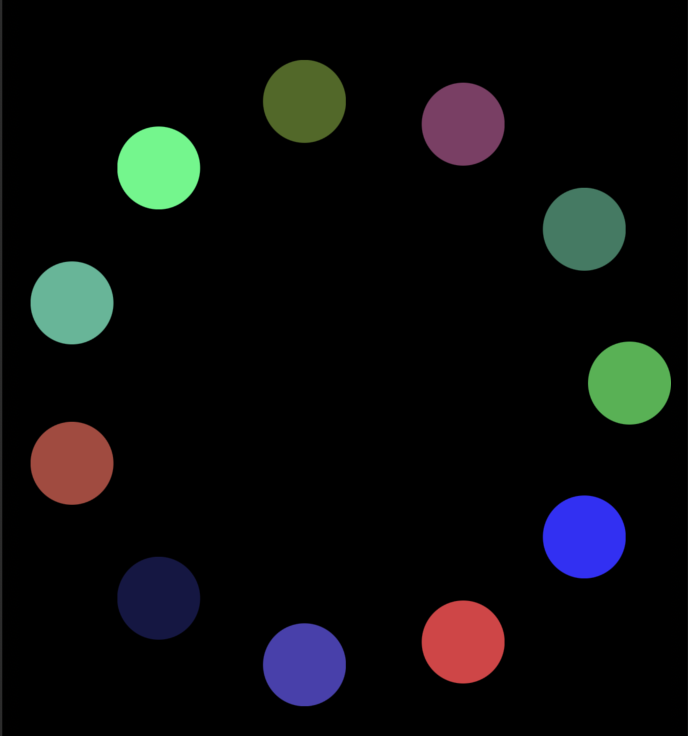
这样就实现了一个圆环形式的一个布局。
小结
笔者简单学习了UICollecitonView这个控件,学习了自定义布局的内容,笔者认为实现瀑布流的核心还是在自定义布局中,笔者也是初次学习UICollecitonVIew这个类如果有什么问题还请不吝指出。
参考博客: