背景:因为最近经常用到es,但是测试环境没有es,自己本地也没安装,为了方便测试,然后安装一下,但是刚开始安装就报错,记录一下,安装的版本为8.16.1
第一步:去官网下载macos版本的es

解决方案:
javascript
在终端中输入:sudo spctl --master-disable然后再启动,显示如下

第二步:上一步中没有配置es默认这些用不的账户、密码,这一步中配置es的账户、密码,(我修改用户的密码没用这个命令,用的是./elasticsearch-reset-password -u elastic -i命令)
执行命令:
javascript
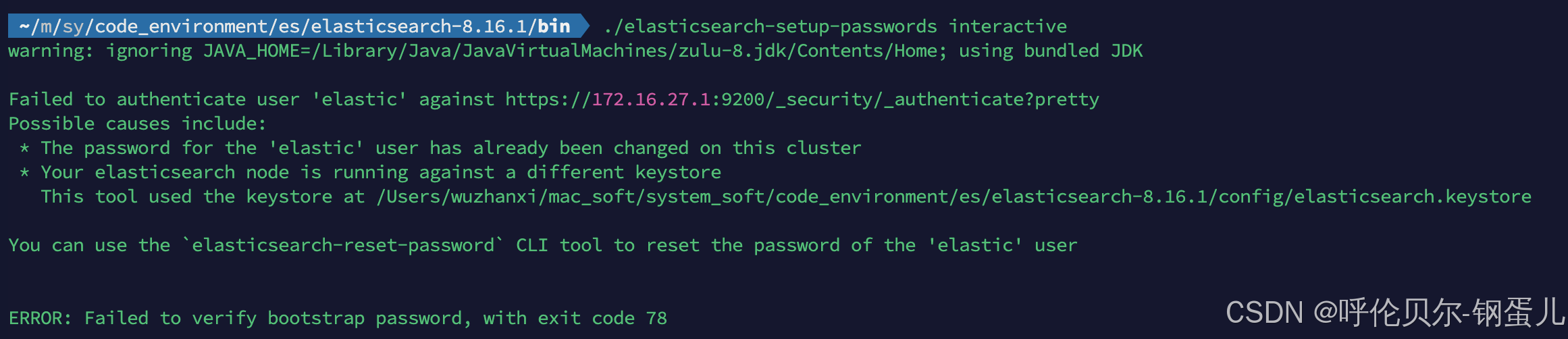
./elasticsearch-setup-passwords interactive报错如下;
javascript
warning: ignoring JAVA_HOME=/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/zulu-8.jdk/Contents/Home; using bundled JDK
Failed to authenticate user 'elastic' against https://172.16.27.1:9200/_security/_authenticate?pretty
Possible causes include:
* The password for the 'elastic' user has already been changed on this cluster
* Your elasticsearch node is running against a different keystore
This tool used the keystore at /Users/wuzhanxi/mac_soft/system_soft/code_environment/es/elasticsearch-8.16.1/config/elasticsearch.keystore
You can use the `elasticsearch-reset-password` CLI tool to reset the password of the 'elastic' user
ERROR: Failed to verify bootstrap password, with exit code 78图片截图:
解决方案:
执行修改用户的命令
javascript
./elasticsearch-reset-password -u elastic -i执行成功返回如下;
javascript
~/m/sy/c/es/elasticsearch-8.16.1/bin ./elasticsearch-reset-password -u elastic -i ✔ took 14s base Py at 10:14:23
warning: ignoring JAVA_HOME=/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/zulu-8.jdk/Contents/Home; using bundled JDK
This tool will reset the password of the [elastic] user.
You will be prompted to enter the password.
Please confirm that you would like to continue [y/N]y
Enter password for [elastic]:
Re-enter password for [elastic]:
Password for the [elastic] user successfully reset.我elasticsearch的配置文件如下;
javascript
# ======================== Elasticsearch Configuration =========================
#
# NOTE: Elasticsearch comes with reasonable defaults for most settings.
# Before you set out to tweak and tune the configuration, make sure you
# understand what are you trying to accomplish and the consequences.
#
# The primary way of configuring a node is via this file. This template lists
# the most important settings you may want to configure for a production cluster.
#
# Please consult the documentation for further information on configuration options:
# https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/index.html
#
# ---------------------------------- Cluster -----------------------------------
#
# Use a descriptive name for your cluster:
#
cluster.name: wzx-es-cluster
#
# ------------------------------------ Node ------------------------------------
#
# Use a descriptive name for the node:
#
node.name: wzx-node
#
# Add custom attributes to the node:
#
#node.attr.rack: r1
#
# ----------------------------------- Paths ------------------------------------
#
# Path to directory where to store the data (separate multiple locations by comma):
#
#path.data: /path/to/data
#
# Path to log files:
#
#path.logs: /path/to/logs
#
# ----------------------------------- Memory -----------------------------------
#
# Lock the memory on startup:
#
#bootstrap.memory_lock: true
#
# Make sure that the heap size is set to about half the memory available
# on the system and that the owner of the process is allowed to use this
# limit.
#
# Elasticsearch performs poorly when the system is swapping the memory.
#
# ---------------------------------- Network -----------------------------------
#
# By default Elasticsearch is only accessible on localhost. Set a different
# address here to expose this node on the network:
#
#network.host: 192.168.0.1
network.host: localhost
#
# By default Elasticsearch listens for HTTP traffic on the first free port it
# finds starting at 9200. Set a specific HTTP port here:
#
http.port: 9200
#
# For more information, consult the network module documentation.
#
# --------------------------------- Discovery ----------------------------------
#
# Pass an initial list of hosts to perform discovery when this node is started:
# The default list of hosts is ["127.0.0.1", "[::1]"]
#
discovery.seed_hosts: ["localhost"]
#
# Bootstrap the cluster using an initial set of master-eligible nodes:
#
cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["wzx-node-1"]
#
# For more information, consult the discovery and cluster formation module documentation.
#
# ---------------------------------- Various -----------------------------------
#
# Allow wildcard deletion of indices:
#
#action.destructive_requires_name: false
#----------------------- BEGIN SECURITY AUTO CONFIGURATION -----------------------
#
# The following settings, TLS certificates, and keys have been automatically
# generated to configure Elasticsearch security features on 28-11-2024 09:11:45
#
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Enable security features
xpack.security.enabled: true
xpack.security.enrollment.enabled: true
# Enable encryption for HTTP API client connections, such as Kibana, Logstash, and Agents
xpack.security.http.ssl:
enabled: false
keystore.path: certs/http.p12
# Enable encryption and mutual authentication between cluster nodes
xpack.security.transport.ssl:
enabled: false
verification_mode: certificate
keystore.path: certs/transport.p12
truststore.path: certs/transport.p12
# Create a new cluster with the current node only
# Additional nodes can still join the cluster later
#cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["wuzhanxideMBP-2"]
# Allow HTTP API connections from anywhere
# Connections are encrypted and require user authentication
http.host: 0.0.0.0
# Allow other nodes to join the cluster from anywhere
# Connections are encrypted and mutually authenticated
#transport.host: 0.0.0.0
#----------------------- END SECURITY AUTO CONFIGURATION -------------------------配置kibana连接elasticsearch的配置文件如下;
javascript
# For more configuration options see the configuration guide for Kibana in
# https://www.elastic.co/guide/index.html
# =================== System: Kibana Server ===================
# Kibana is served by a back end server. This setting specifies the port to use.
server.port: 5601
# Specifies the address to which the Kibana server will bind. IP addresses and host names are both valid values.
# The default is 'localhost', which usually means remote machines will not be able to connect.
# To allow connections from remote users, set this parameter to a non-loopback address.
server.host: "localhost"
# Enables you to specify a path to mount Kibana at if you are running behind a proxy.
# Use the `server.rewriteBasePath` setting to tell Kibana if it should remove the basePath
# from requests it receives, and to prevent a deprecation warning at startup.
# This setting cannot end in a slash.
#server.basePath: ""
# Specifies whether Kibana should rewrite requests that are prefixed with
# `server.basePath` or require that they are rewritten by your reverse proxy.
# Defaults to `false`.
#server.rewriteBasePath: false
# Specifies the public URL at which Kibana is available for end users. If
# `server.basePath` is configured this URL should end with the same basePath.
#server.publicBaseUrl: ""
# The maximum payload size in bytes for incoming server requests.
#server.maxPayload: 1048576
# The Kibana server's name. This is used for display purposes.
#server.name: "your-hostname"
# =================== System: Kibana Server (Optional) ===================
# Enables SSL and paths to the PEM-format SSL certificate and SSL key files, respectively.
# These settings enable SSL for outgoing requests from the Kibana server to the browser.
#server.ssl.enabled: false
#server.ssl.certificate: /path/to/your/server.crt
#server.ssl.key: /path/to/your/server.key
# =================== System: Elasticsearch ===================
# The URLs of the Elasticsearch instances to use for all your queries.
elasticsearch.hosts: ["http://localhost:9200"]
# If your Elasticsearch is protected with basic authentication, these settings provide
# the username and password that the Kibana server uses to perform maintenance on the Kibana
# index at startup. Your Kibana users still need to authenticate with Elasticsearch, which
# is proxied through the Kibana server.
elasticsearch.username: "kibana_system"
#elasticsearch.username: "elastic"
elasticsearch.password: "es123!@#"
#elasticsearch.password: "pass"
# Kibana can also authenticate to Elasticsearch via "service account tokens".
# Service account tokens are Bearer style tokens that replace the traditional username/password based configuration.
# Use this token instead of a username/password.
# elasticsearch.serviceAccountToken: "my_token"
# Time in milliseconds to wait for Elasticsearch to respond to pings. Defaults to the value of
# the elasticsearch.requestTimeout setting.
#elasticsearch.pingTimeout: 1500
# Time in milliseconds to wait for responses from the back end or Elasticsearch. This value
# must be a positive integer.
#elasticsearch.requestTimeout: 30000
# The maximum number of sockets that can be used for communications with elasticsearch.
# Defaults to `Infinity`.
#elasticsearch.maxSockets: 1024
# Specifies whether Kibana should use compression for communications with elasticsearch
# Defaults to `false`.
#elasticsearch.compression: false
# List of Kibana client-side headers to send to Elasticsearch. To send *no* client-side
# headers, set this value to [] (an empty list).
#elasticsearch.requestHeadersWhitelist: [ authorization ]
# Header names and values that are sent to Elasticsearch. Any custom headers cannot be overwritten
# by client-side headers, regardless of the elasticsearch.requestHeadersWhitelist configuration.
#elasticsearch.customHeaders: {}
# Time in milliseconds for Elasticsearch to wait for responses from shards. Set to 0 to disable.
#elasticsearch.shardTimeout: 30000
# =================== System: Elasticsearch (Optional) ===================
# These files are used to verify the identity of Kibana to Elasticsearch and are required when
# xpack.security.http.ssl.client_authentication in Elasticsearch is set to required.
#elasticsearch.ssl.certificate: /path/to/your/client.crt
#elasticsearch.ssl.key: /path/to/your/client.key
# Enables you to specify a path to the PEM file for the certificate
# authority for your Elasticsearch instance.
#elasticsearch.ssl.certificateAuthorities: [ "/path/to/your/CA.pem" ]
# To disregard the validity of SSL certificates, change this setting's value to 'none'.
#elasticsearch.ssl.verificationMode: full
# =================== System: Logging ===================
# Set the value of this setting to off to suppress all logging output, or to debug to log everything. Defaults to 'info'
#logging.root.level: debug
# Enables you to specify a file where Kibana stores log output.
#logging.appenders.default:
# type: file
# fileName: /var/logs/kibana.log
# layout:
# type: json
# Example with size based log rotation
#logging.appenders.default:
# type: rolling-file
# fileName: /var/logs/kibana.log
# policy:
# type: size-limit
# size: 256mb
# strategy:
# type: numeric
# max: 10
# layout:
# type: json
# Logs queries sent to Elasticsearch.
#logging.loggers:
# - name: elasticsearch.query
# level: debug
# Logs http responses.
#logging.loggers:
# - name: http.server.response
# level: debug
# Logs system usage information.
#logging.loggers:
# - name: metrics.ops
# level: debug
# Enables debug logging on the browser (dev console)
#logging.browser.root:
# level: debug
# =================== System: Other ===================
# The path where Kibana stores persistent data not saved in Elasticsearch. Defaults to data
#path.data: data
# Specifies the path where Kibana creates the process ID file.
#pid.file: /run/kibana/kibana.pid
# Set the interval in milliseconds to sample system and process performance
# metrics. Minimum is 100ms. Defaults to 5000ms.
#ops.interval: 5000
# Specifies locale to be used for all localizable strings, dates and number formats.
# Supported languages are the following: English (default) "en", Chinese "zh-CN", Japanese "ja-JP", French "fr-FR".
#i18n.locale: "en"
# =================== Frequently used (Optional)===================
# =================== Saved Objects: Migrations ===================
# Saved object migrations run at startup. If you run into migration-related issues, you might need to adjust these settings.
# The number of documents migrated at a time.
# If Kibana can't start up or upgrade due to an Elasticsearch `circuit_breaking_exception`,
# use a smaller batchSize value to reduce the memory pressure. Defaults to 1000 objects per batch.
#migrations.batchSize: 1000
# The maximum payload size for indexing batches of upgraded saved objects.
# To avoid migrations failing due to a 413 Request Entity Too Large response from Elasticsearch.
# This value should be lower than or equal to your Elasticsearch cluster's `http.max_content_length`
# configuration option. Default: 100mb
#migrations.maxBatchSizeBytes: 100mb
# The number of times to retry temporary migration failures. Increase the setting
# if migrations fail frequently with a message such as `Unable to complete the [...] step after
# 15 attempts, terminating`. Defaults to 15
#migrations.retryAttempts: 15
# =================== Search Autocomplete ===================
# Time in milliseconds to wait for autocomplete suggestions from Elasticsearch.
# This value must be a whole number greater than zero. Defaults to 1000ms
#unifiedSearch.autocomplete.valueSuggestions.timeout: 1000
# Maximum number of documents loaded by each shard to generate autocomplete suggestions.
# This value must be a whole number greater than zero. Defaults to 100_000
#unifiedSearch.autocomplete.valueSuggestions.terminateAfter: 100000启动kibana时,需要登录用户名、密码,但是用kibana_system用户登录时权限不够,需要用elastic用户登录才可以