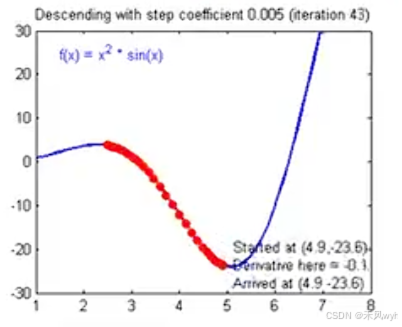
梯度下降法是优化算法中一种常用的技术,用于通过最小化损失函数来求解模型的最优参数。在线性回归中,目标是通过拟合数据来找到一条最适合的直线。梯度下降法通过迭代地调整模型参数,使得损失函数(通常是均方误差)最小化,从而找到最优的参数。
线性回归的目标是根据输入特征 x 预测输出 y。假设我们有一个输入特征 x 和对应的输出标签 y,线性回归模型可以用以下公式表示:
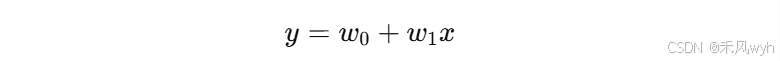
给定一组数据集, 我们的目标是通过调整权重
和
,使得模型的预测值与真实值之间的误差最小。首先对参数进行求梯度:
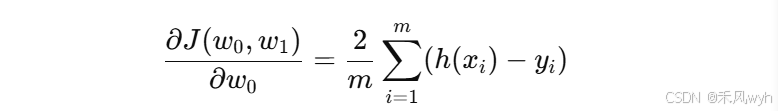
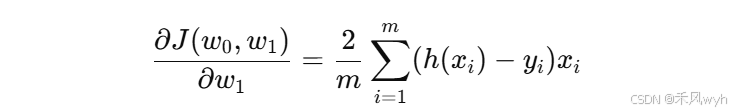
通过计算梯度,我们知道了损失函数在每个参数方向上的变化趋势。为了最小化损失函数,我们沿着梯度的反方向更新参数。参数更新的公式为:
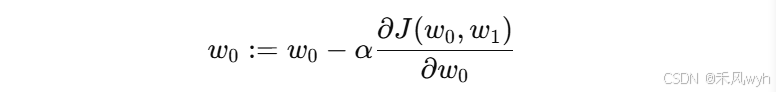
采用MSE计算损失函数,损失函数为 ,那么更新后的参数为
,其中
,
计算损失函数:
python
def compute_error_for_line_given_points(b,w,points):
totalError = 0
for i in range(0, len(points)):
x = points[i,0]
y = points[i,1]
totalError += (y-(w*x+b))**2
return totalError/float(len(points))计算梯度值:
python
def step_grdient(b_current, w_current, points, learningRate):
b_gradient = 0
w_gradient = 0
N = float(len(points))
for i in range(0, len(points)):
x = points[i, 0]
y = points[i, 1]
b_gradient += -(2/N) * (y - ((w_current * x) + b_current))
# 梯度信息多了一个x
w_gradient += -(2/N) * x * (y - ((w_current * x) + b_current))
new_b = b_current - (learningRate * b_gradient)
new_w = w_current - (learningRate * w_gradient)
return [new_b, new_w]循环计算梯度:
python
def gradient_descent_runner(points, starting_b, starting_m, learning_rate, num_iterations):
b = starting_b
w = starting_w
for i in range(num_iterations):
b, w = step_gradient(b, w, np.array(points), learning_rate)
return [b, w]进行运行:
python
def run():
points = np.genfromtext("data.csv", delimiter=",")
learining_rate = 0.0001
initial_b = 0
initial_w = 0
num_iterations = 100
print("Starting gradient descent at b={0}, w={1},error={2}".format(initial_b, initial_m, compute_errror_for_line_given_points(initial_b, initial_w, points)))
print("Running......")
[b, w] = gradient_descent_runner(points, initial_b, initial_w, learning_rate, num_iterations)
print("After {0} iterations b = {1}, w = {2}, error = {3}".format(num_iterations, b, m))