import sys
import pytest
class TestDemo:
def test_demo1(self):
x = "hello world"
print(f"{x} python")
assert 'h' in x
def test_demo3(self):
x = "hello world"
print(f"{x} python")
assert 'h' in x
def test_demo2(self):
x = 'hello'
assert hasattr(x,"check")
if __name__ == "__main__":
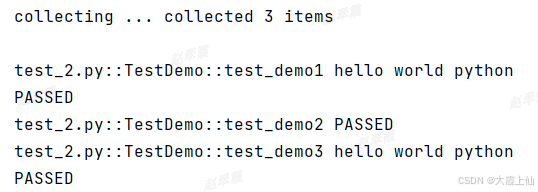
pytest.main(['-v', '-s','test_2.py'])看着默认执行顺序是代码中函数的顺序
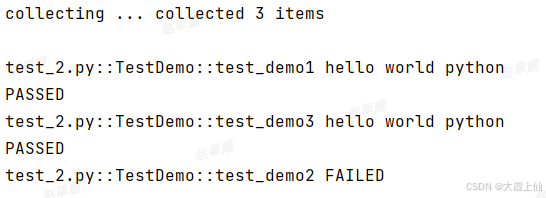
更改用例的执行顺序,可以安装包 pip install pytest-ordering
按序执行@pytest.mark.run(order=x)
import sys
import pytest
class TestDemo:
@pytest.mark.run(order=1)
def test_demo1(self):
x = "hello world"
print(f"{x} python")
assert 'h' in x
@pytest.mark.run(order=3)
def test_demo3(self):
x = "hello world"
print(f"{x} python")
assert 'h' in x
@pytest.mark.run(order=2)
def test_demo2(self):
x = 'hello'
assert hasattr(x,"check")
if __name__ == "__main__":
pytest.main(['-v', '-s','test_2.py'])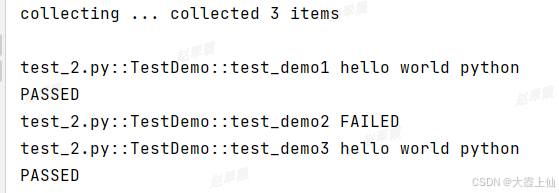
依赖执行
pip install pytest-dependency
用例默认执行顺序是test1-->test2-->test3,test2依赖test1,test3依赖test2。
test1通过才会执行test2,test2通过才会执行test3,如果test1失败,则后续依赖的用例跳过,
如果依赖的用例还未执行,也会跳过
import sys
import pytest
class TestDemo:
@pytest.mark.dependency(name="test1")
def test_demo1(self):
x = "hello world"
print(f"{x} python")
assert 'h' in x
@pytest.mark.dependency(name="test3",depends=['test2'])
def test_demo3(self):
x = "hello world"
print(f"{x} python")
assert 'h' in x
@pytest.mark.dependency(name="test2",depends=['test1'])
def test_demo2(self):
x = 'hello'
assert hasattr(x,"check")
if __name__ == "__main__":
pytest.main(['-v', '-s','test_2.py'])test_demo2未执行,test_demo3跳过
import sys
import pytest
class TestDemo:
@pytest.mark.dependency(name="test1")
@pytest.mark.run(order=1)
def test_demo1(self):
x = "hello world"
print(f"{x} python")
assert 'h' in x
@pytest.mark.dependency(name="test3",depends=['test2'])
@pytest.mark.run(order=3)
def test_demo3(self):
x = "hello world"
print(f"{x} python")
assert 'h' in x
@pytest.mark.dependency(name="test2",depends=['test1'])
@pytest.mark.run(order=2)
def test_demo2(self):
x = 'hello'
assert hasattr(x,"check")
if __name__ == "__main__":
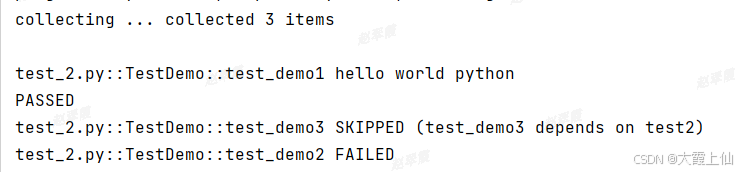
pytest.main(['-v', '-s','test_2.py'])顺序对了,但是test_demo2失败,test_demo3跳过
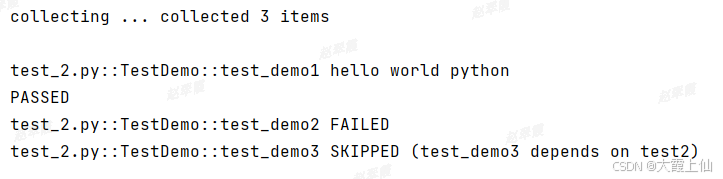
import sys
import pytest
class TestDemo:
@pytest.mark.dependency(name="test1")
@pytest.mark.run(order=1)
def test_demo1(self):
x = "hello world"
print(f"{x} python")
assert 'h' in x
@pytest.mark.dependency(name="test3",depends=['test2'])
@pytest.mark.run(order=3)
def test_demo3(self):
x = "hello world"
print(f"{x} python")
assert 'h' in x
@pytest.mark.dependency(name="test2",depends=['test1'])
@pytest.mark.run(order=2)
def test_demo2(self):
x = 'hello'
assert hasattr(x,"replace")
if __name__ == "__main__":
pytest.main(['-v', '-s','test_2.py'])顺序对,依赖对