1. 查找的基本概念

2. 静态查找
2.1 顺序查找
c
typedef int KeyType;
typedef int InfoType;
typedef struct
{
KeyType key;
InfoType otherdata;
}SeqList; // 顺序表类型
// 顺序查找
c
int SeqSearch(SeqList R[], int n, int k)
{
int i = n;
R[0].key = k; // R[0].key为查找不成功的监视哨
while (R[i].key != k)
i--;
return i; // 查找成功返回所找元素的索引,否则返回0;
}2.2 有序表的查找
二分查找
c
int BinarySearch(SeqList R[], int n, int k)
{
int left = 0, right = n - 1;
int mid = 0;
while (left <= right)
{
mid = (left + right) / 2;
if (R[mid].key > k)
right = mid - 1;
else if (R[mid].key < k)
left = mid + 1;
else
return mid;
}
return 0;// 没有找到
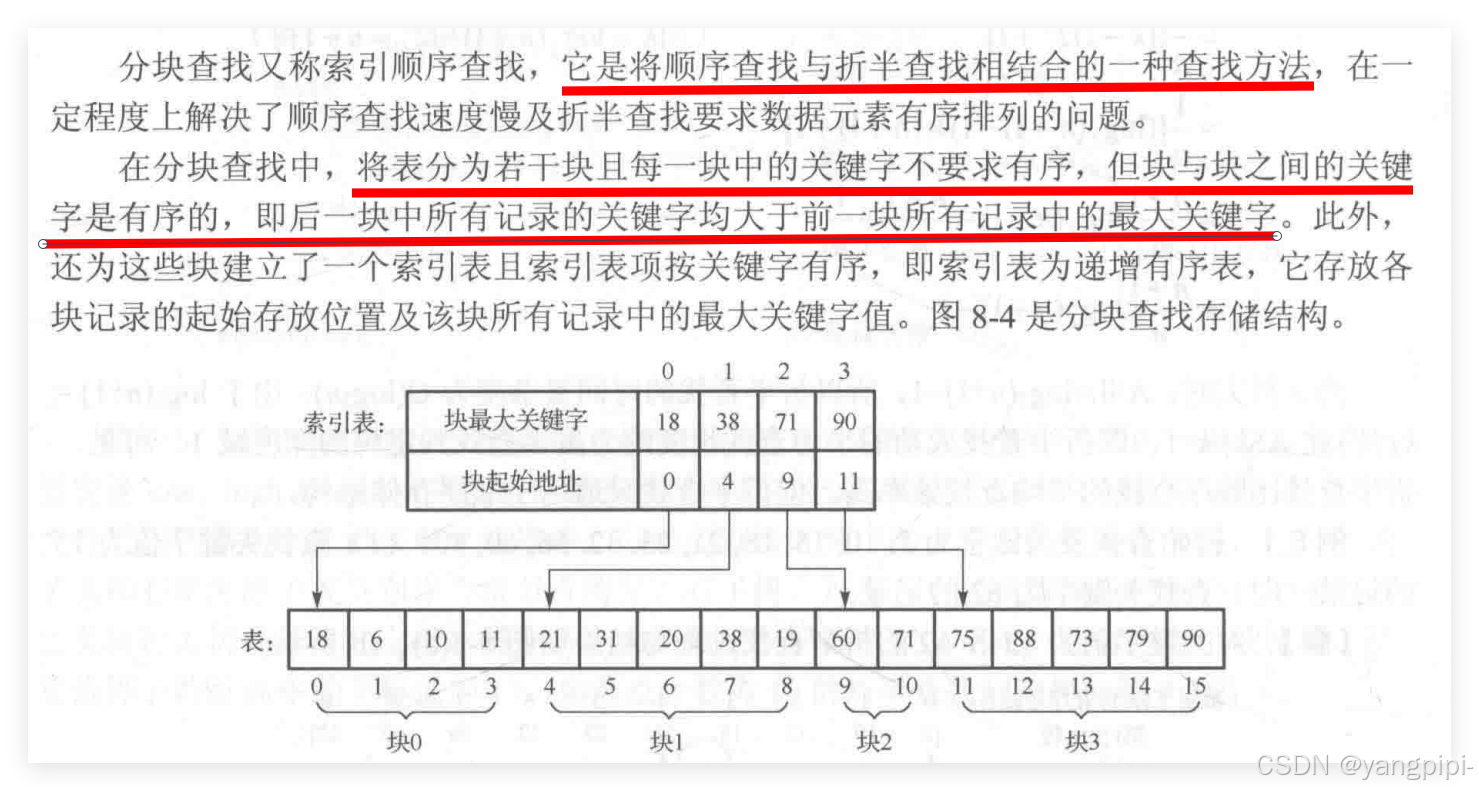
}分块查找(索引顺序查找)
3. 树表形式的动态查找表

3.1 二叉排序树
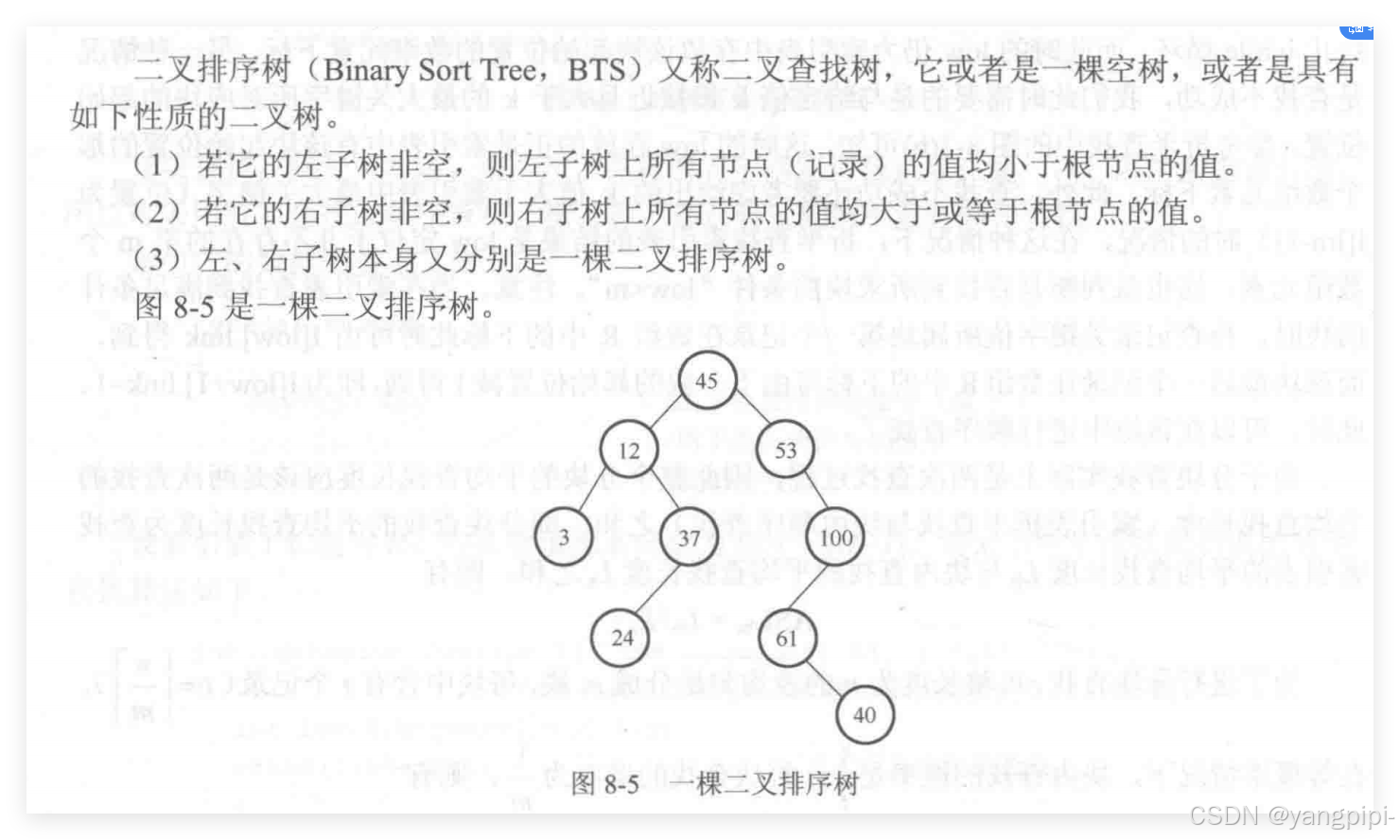
二叉排序树的查找操作
c
// 二叉排序树的查找操作
BSTree* BSTSearch(BSTree* t, int k)
{
while (t != NULL)
{
if (t->key > k)
t = t->lchild;
else if (t->key < k)
t = t->rchild;
else
return t;
}
return NULL;
}二叉排序树的插入操作和二叉树排序树的构造
- 愚蠢的bug,直接拿着main函数传入的指针遍历二叉排序树,导致每次插入节点时都会丢失二叉排序树的根
c
void BSTCreate(BSTree** t, int k)
{
BSTree* pre = NULL;
while ((*t) != NULL)
{
if ((*t)->key > k) {
pre = *t;
*t = (*t)->lchild;
}
else if ((*t)->key < k) {
printf("______________,右子树\n");
pre = *t;
*t = (*t)->rchild;
}
else // 所查节点已经存在
break;
}
//当所查节点不存在时
if (*t == NULL)
{
BSTree* tmp = (BSTree*)malloc(sizeof(BSTree));
tmp->lchild = NULL;
tmp->rchild = NULL;
tmp->key = k;
if (pre != NULL) {
if (pre->key > k) { // 应该插入pre的左孩子
pre->lchild = tmp;
}
else { // 应该插入pre的右孩子
printf("应该插入pre的右孩子\n");
pre->rchild = tmp;
}
}
else { // 二叉排序树还未建立
printf("建立二叉排序树\n");
*t = tmp;
}
}
}- 正确的方式
c
void BSTCreate(BSTree** t, int k)
{
BSTree* pre = NULL,*current = *t;
while (current != NULL)
{
if (current->key > k) {
pre = current;
current = current->lchild;
}
else if (current->key < k) {
/* printf("______________,右子树\n");*/
pre = current;
current = current->rchild;
}
else // 所查节点已经存在
return;
}
BSTree* tmp = (BSTree*)malloc(sizeof(BSTree));
tmp->lchild = NULL;
tmp->rchild = NULL;
tmp->key = k;
if (pre != NULL) {
if (pre->key > k) { // 应该插入pre的左孩子
pre->lchild = tmp;
}
else { // 应该插入pre的右孩子
//printf("应该插入pre的右孩子\n");
pre->rchild = tmp;
}
}
// 二叉排序树还未建立
else {
printf("建立二叉排序树\n");
*t = tmp;
}
}

删除二叉排序树中的节点


c
void BSTDeleteLeafChild(BSTree* pre, BSTree* current)
{
if (pre->lchild == current) // 待删除节点为pre的左孩子
{
pre->lchild = NULL;
}
else if (pre->rchild == current) {
pre->rchild = NULL;
}
free(current);
current = NULL;
}
void BSTDeleteRightChild(BSTree* pre, BSTree* current)
{
// 待删除节点current只有右孩子,直接将该有孩子替换到待删除节点位置即可
if (pre->lchild == current) // 待删除节点为pre的左孩子
{
pre->lchild = current->rchild;
free(current);
current = NULL;
}
else if (pre->rchild == current) {
pre->rchild = current->rchild;
free(current);
current = NULL;
}
else {
printf("BSTDeleteRightChild:pre和current没有父子关系!!!\n");
}
}
void BSTDeleteLeftChild(BSTree* pre, BSTree* current)
{
// 待删除节点current只有左孩子,直接将该左孩子替换到待删除节点位置即可
if (pre->lchild == current) // 待删除节点为pre的左孩子
{
pre->lchild = current->lchild;
free(current);
current = NULL;
}
else if (pre->rchild == current) {
pre->rchild = current->lchild;
free(current);
current = NULL;
}
else {
printf("BSTDeleteRightChild:pre和current没有父子关系!!!\n");
}
}
// 在二叉排序树种删除某个节点
void BSTDelete(BSTree** t, int k)
{
/*
会出现四种情况
1. 待删除的节点为叶子
2. 待删除的节点只有左孩子
3. 待删除节点只有右孩子
4. 待删除节点左右孩子都有
*/
BSTree* pre = NULL, * current = *t;
while (current != NULL)
{
if (current->key > k) {
pre = current;
current = current->lchild;
}
else if (current->key < k) {
pre = current;
current = current->rchild;
}
else // 节点找到
break;
}
if (current == NULL)
{
printf("该节点没有找到\n");
return;
}
//1. 待删除的节点为叶子
if (current->lchild == NULL && current->rchild == NULL)
{
BSTDeleteLeafChild(pre, current);
}
//2. 待删除的节点只有左孩子
else if (current->lchild != NULL && current->rchild == NULL)
{
BSTDeleteLeftChild(pre, current);
}
//3. 待删除节点只有右孩子
else if (current->lchild == NULL && current->rchild != NULL)
{
BSTDeleteRightChild(pre,current);
}
//4. 待删除节点左右孩子都有
else
{
// 1. 首先找到以待删除节点为根的最左节点
BSTree* t1 = current,*t2 = current;
while (t2->lchild != NULL)
{
t1 = t2;
t2 = t2->lchild;
}
current->key = t2->key;
2. 删除最左节点
if(t2->rchild!=NULL)
BSTDeleteRightChild(t1, t2);
else {
t1->lchild = NULL;
free(t2);
t2 = NULL;
}
}
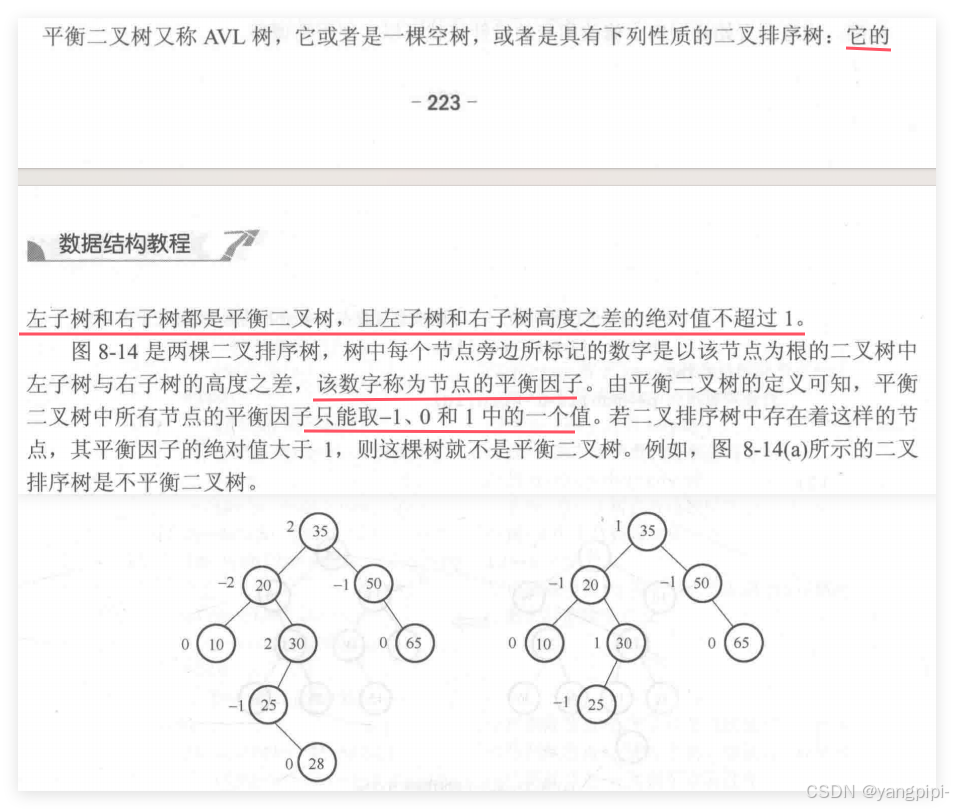
}3.2 平衡二叉树(AVL)




红黑树





3.3 B树和B+树





B树



B树的插入


- 例子





- 例子

- 插入15

- 插入35

- 插入95

B树的删除
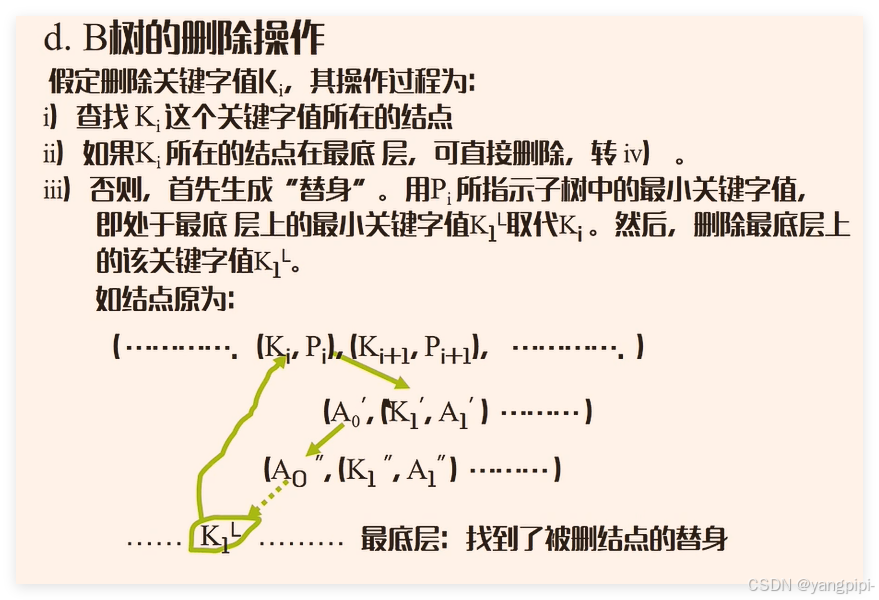


-
例子



-
删除92


-
删除80

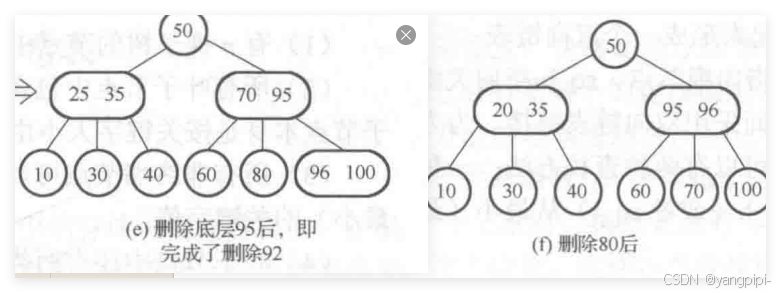
-
- 删除70


- 删除70

B+树





两者的区别
4. 哈希
4.1 哈希表与哈希方法

4.2 哈希函数
直接定址法

除留余数法

数字分析法

平方取中法

折叠法

4.3 处理冲突的方法


闭散列表
开放地址法

再散列法

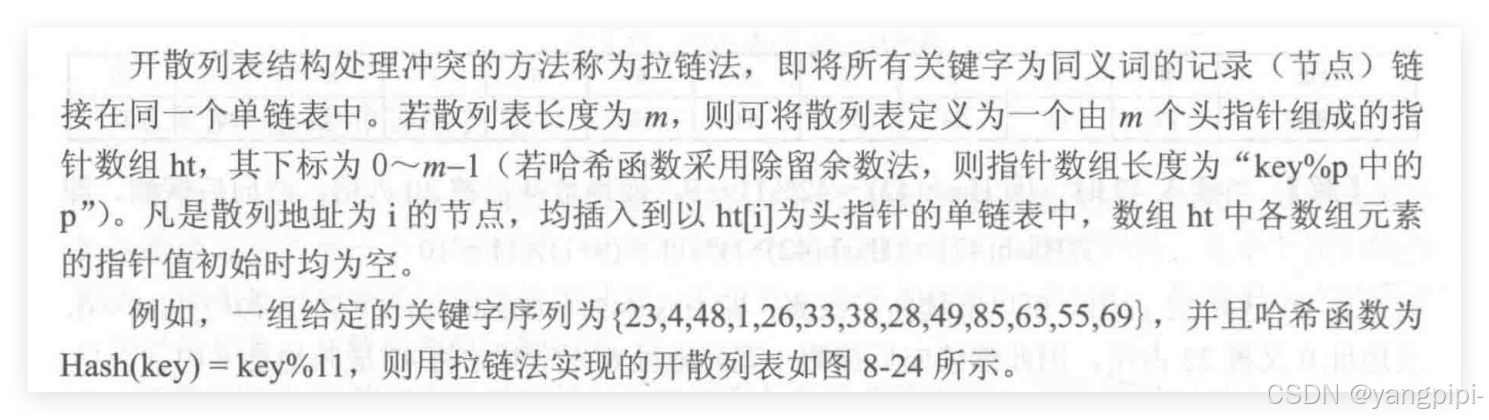
开散列表