一、引言
随着人工智能技术的不断进步,传统的教学方式已经逐渐向智能化、互动化转变。在众多英语测试题型中,选择题作为一种高效的方式被广泛应用于各类培训与考试中。为了帮助学生高效学习与自测,本篇文章将采用Python编写一款基于 Python 开发的选择题训练工具。该工具不仅支持加载 Excel 文件中的题库,还具备题干和选项展示、答题记录、音频朗读等多种功能,旨在为用户提供便捷、高效的学习体验。
二、开发背景
在日常教学过程中,老师往往需要准备大量的选择题作为测试题目。我们可以把这些题目存储在 Excel 文件中,如果手动处理和展示题目会非常繁琐。为了提高教学效率,选用一种自动化展示工具成为一种迫切的需求。本项目通过 Python 和 Tkinter 库实现了一个图形化界面应用,可以自动加载并展示选择题,记录用户答题情况,同时通过音频朗读题目,进一步增强互动性。软件的示意图如下:
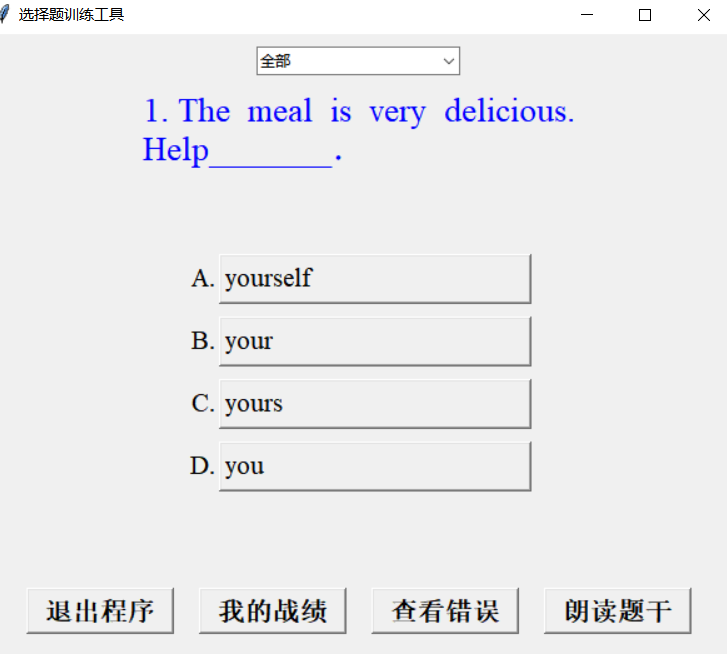
软件展示
三、软件特点
- 题库加载与展示:支持从 Excel 文件中加载选择题,并且可以根据课程单元名称筛选题目。
- 音频朗读功能:使用 Python 的 Pygame 库播放题目音频,即朗读题干,帮助用户通过听力巩固已学单词。
- 答题记录与统计:软件会自动记录用户的答题情况,并在决定答题结束时,提供正确率和错误题目的回顾功能。
- 多线程支持:使用线程处理音频播放等耗时操作,避免界面卡顿,提升用户体验。同时,当完成一道题时,会自动转到下一道,并给出正确或错误的提示。正确就是显示绿色button选项,错误就显示红色button选项。
- 图形化界面:基于 Tkinter 实现的 GUI 界面,简单直观,易于操作。
四、使用方法
1. 安装依赖
在运行程序之前,需要安装一些 Python 库,依赖包括 openpyxl, pygame 和 requests。可以使用以下命令安装所需的库:
python
pip install openpyxl pygame requests 2. 准备题库
本程序需要一个 Excel 文件,并命名为【选择题.xlsx】作为题库,Excel 文件应包括如下列:
- 单元:课程名称或章节
- 序号:题目的编号
- 题干:选择题的内容
- 选项A、B、C、D:四个选择项
- 正确答案:正确的答案选项
Excel表的内容如下:
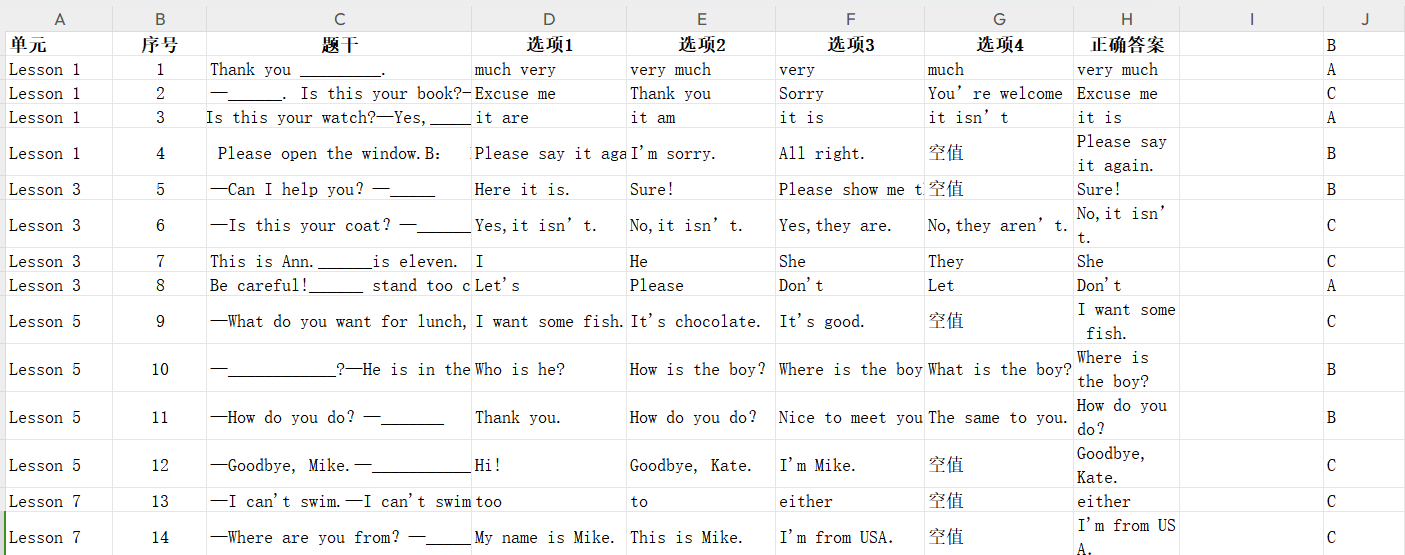
Excel表内容
3. 运行程序
运行 Python 程序,tkinter GUI界面会自动加载,用户可以在顶部下拉框选择不同的课程,然后开始答题,结束前查看战绩,回顾错误题目,还可以点朗读通过音频功能听题干。
4. 功能概览
- 选择题显示:在每道题目显示时,用户可以选择答案。程序会自动判断正确与否,并高亮显示选择的答案。
- 战绩统计:用户答题完成后,可以查看自己的正确率统计。
- 错误回顾:用户可以查看答错的题目,并且看到正确答案与自己的选择。
- 朗读功能:用户可以点击按钮让程序朗读题干。
五、源码展示
以下是该程序的主要代码:
python
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk, messagebox
from openpyxl import load_workbook
import random
import os,re
import pygame,requests
from io import BytesIO
from threading import Lock, Thread, Timer
def load_excel_data(filename):
workbook = load_workbook(filename)
sheet = workbook.active
questions = []
lessons = set() # 用于存储所有课程名,避免重复
for row in sheet.iter_rows(min_row=2, values_only=True):
lesson = row[0]
lessons.add(lesson)
question = {
'单元': lesson,
'序号': row[1],
'题干': row[2],
'选项': [row[3], row[4], row[5], row[6]],
'正确答案': row[7]
}
questions.append(question)
return list(lessons), questions
lessons, questions = load_excel_data('选择题.xlsx')
random.shuffle(questions)
# 使用正则表达式从课程名中提取数字,并按数字排序课程名
sorted_lessons = sorted(lessons, key=lambda x: (lambda m: int(m.group(0)) if m else 0)(re.search(r'\d+', x)))
class QuizApp:
def __init__(self, root):
self.root = root
# 设置窗口大小
self.root.geometry("600x500")
#self.root.resizable(False, False)
pygame.init()
self.all_questions = questions
self.questions = questions # 当前显示的问题列表
self.current_question_index = 0
self.correct_answers = 0
self.wrong_answers = 0
self.error_questions = []
self.setup_ui()
self.load_question()
def thread_it(self,func):
self.thread1=Thread(target=func)
self.thread1.setDaemon(True)
self.thread1.start()
def setup_ui(self):
self.root.title("选择题训练工具")
self.lesson_combobox = ttk.Combobox(self.root, values=['全部'] + sorted_lessons, state="readonly")
self.lesson_combobox.pack(pady=(10, 0))
self.lesson_combobox.set('全部')
self.lesson_combobox.bind('<<ComboboxSelected>>', self.on_combobox_change)
self.question_label = tk.Label(self.root, text="", font=("Times New Roman", 20), fg="blue", wraplength=520, justify=tk.LEFT) #设置文本长度,并且文本左对齐
self.question_label.pack(pady=(10, 40))
self.options_frame = tk.Frame(self.root)
self.options_frame.pack(pady=20)
option_labels = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'] # 选项标签
self.option_buttons = [] # 存储选项按钮
self.option_labels = [] # 存储选项标签控件
for i in range(4):
# 创建选项标签控件并放置
label = tk.Label(self.options_frame, text=f"{option_labels[i]}.", font=("Times New Roman", 16))
label.grid(row=i, column=0, pady=5, sticky="e")
self.option_labels.append(label)
# 创建选项按钮并放置
btn = tk.Button(self.options_frame, text="", font=("Times New Roman", 16), width=20,
command=lambda b=i: self.check_answer(b), # type: ignore
anchor="w")
btn.grid(row=i, column=1, pady=5)
self.option_buttons.append(btn)
self.action_frame = tk.Frame(self.root)
self.action_frame.pack(side=tk.BOTTOM, pady=20)
tk.Button(self.action_frame, text="退出程序", font=("宋体", 16, "bold"), width=9, command=self.ui_quit).pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=10)
tk.Button(self.action_frame, text="我的战绩", font=("宋体", 16, "bold"), width=9, command=self.show_score).pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=10)
tk.Button(self.action_frame, text="查看错误", font=("宋体", 16, "bold"), width=9, command=self.show_errors).pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=10)
tk.Button(self.action_frame, text="朗读题干", font=("宋体", 16, "bold"), width=9, command=self.show_sound).pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=10)# 其余UI代码与原来相同...
def on_combobox_change(self, event):
selected_lesson = self.lesson_combobox.get()
if selected_lesson == '全部':
self.questions = self.all_questions
else:
self.questions = [q for q in self.all_questions if q['单元'] == selected_lesson]
self.current_question_index = 0
self.correct_answers = 0
self.wrong_answers = 0
self.error_questions = []
self.load_question()
def load_question(self):
if self.current_question_index < len(self.questions):
question = self.questions[self.current_question_index]
self.question_label.config(text=str(self.current_question_index+1)+". "+question['题干'],anchor='w')
correct_answer = question['正确答案']
options = question['选项']
self.correct_option_index = options.index(correct_answer)
random.shuffle(options)
for i, option in enumerate(options):
self.option_buttons[i].config(text=option, bg='SystemButtonFace')
def check_answer(self, button_index):
question = self.questions[self.current_question_index]
selected_option = self.option_buttons[button_index].cget('text')
correct_option = question['正确答案']
# 确定正确答案按钮的索引
correct_option_index = None
for i, btn in enumerate(self.option_buttons):
if btn.cget('text') == correct_option:
correct_option_index = i
break
if selected_option == correct_option:
# 用户选择了正确的答案
self.option_buttons[button_index].config(bg='light green')
self.correct_answers += 1
else:
# 用户选择了错误的答案
self.option_buttons[button_index].config(bg='red')
if correct_option_index is not None:
self.option_buttons[correct_option_index].config(bg='light green')
self.wrong_answers += 1
self.error_questions.append((question['题干'], selected_option, question['正确答案']))
# 准备间隔1秒显示下一个问题
self.root.after(1000, self.next_question)
def next_question(self):
self.current_question_index += 1
if self.current_question_index < len(self.questions):
self.load_question()
else:
messagebox.showinfo("结束", "所有问题都已回答完毕!")
def ui_quit(self):
self.root.destroy()
def show_score(self):
messagebox.showinfo("战绩", f"正确: {self.correct_answers}\n错误: {self.wrong_answers}\n总计: {len(self.questions)}\n正确率:{self.correct_answers/len(self.questions)*100}%")
def show_sound(self):
self.thread_it(self.show_sound2)
def show_errors(self):
error_messages = "\n".join([f"题干: {q[0]},正确答案是:{q[2]}, 您的选择: {q[1]}" for q in self.error_questions])
messagebox.showinfo("错误回顾", error_messages if error_messages else "完美!没有任何错误。")
def show_sound2(self):
self.current_name = self.question_label.cget("text")
audio_path = f"https://dict.youdao.com/dictvoice?audio={self.current_name}&type=1"
resp = requests.get(audio_path)
audio_data = BytesIO(resp.content)
pygame.mixer.music.load(audio_data)
pygame.mixer.music.play()
while pygame.mixer.music.get_busy():
continue
# 退出pygame
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = tk.Tk()
app = QuizApp(root)
root.mainloop()六、注意事项
- Excel 文件格式 :确保题库文件【
选择题.xlsx】的格式正确,每个问题必须包含单元、序号、题干、选项和正确答案等字段。 - 音频播放:程序中使用了 Pygame 库进行音频播放,因此需要安装相应的音频库,并且程序会访问在线字典接口生成题目音频。
- 线程管理:为了避免界面卡顿,音频播放等操作被放置在单独的线程中处理,保证主界面的流畅性。
- 数据存储:答题结果和错误回顾会暂时保存在程序内存中,但如果需要长期保存数据,可以考虑添加导出功能。
七、总结
这款选择题训练工具通过 Python 实现了一个简单易用的答题系统,利用 Tkinter 提供了良好的用户界面,结合 Pygame 和音频播放技术,增强了选择题问答的互动性。它可以帮助学生提高学习效率,帮助教师管理题库,并提供了直观的成绩统计与错误回顾功能,是一款非常实用的教学辅助工具。