1. 集成学习的基本概念
集成学习是通过构建并结合多个学习器来完成学习任务,通常比单一学习器有更好的泛化性能。
个体与集成
- 个体学习器:是指集成中每个单独的学习器,通常可以是决策树、神经网络等。
- 集成学习器:将多个个体学习器的结果结合起来得到最终结果。
2. Boosting
Boosting 是一种串行的集成学习方法,通过不断调整训练样本的分布,使得后续的学习器更加关注之前学习器分错的样本。
AdaBoost 算法
- 数学公式:
- 初始化样本权重

是样本数量。 - 对于

- 初始化样本权重
((T) 是迭代次数):
- 训练一个弱学习器 (h_t) ,使用加权样本集

-
计算弱学习器的错误率

-
计算弱学习器的权重

-
更新样本权重

,(Z_t) 是归一化因子。
3. Bagging 与随机森林
Bagging 是一种并行的集成学习方法,通过自助采样(Bootstrap Sampling)生成多个训练集,训练多个学习器,然后结合它们的结果。
随机森林
- 是一种基于决策树的 Bagging 方法,在构建决策树时,每个节点的划分特征是从所有特征中随机选择一个子集。
4. 结合策略
常见的结合策略有:
-
平均法:
-
对于回归问题

-
对于分类问题,投票法:

-
-
加权平均法:
- 对于回归问题,

是学习器的权重。 - 对于分类问题,在这里插入图片描述
- 对于回归问题,
5. 多样性
多样性是集成学习的关键,衡量多样性的方法有:
- 分歧 :

(D) 是差异度量函数。 - 相关系数:

可视化代码示例
1. 使用 Python 和 scikit-learn 实现 AdaBoost 和可视化
python
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostClassifier
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
# 加载数据集
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data[:, :2]
y = iris.target
# 划分训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=42)
# 创建 AdaBoost 分类器
ada_clf = AdaBoostClassifier(
DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=1),
n_estimators=50,
algorithm="SAMME",
learning_rate=0.5
)
ada_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 预测
y_pred = ada_clf.predict(X_test)
print("Accuracy:", accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred))
# 可视化决策边界
def plot_decision_boundary(clf, X, y, ax=None):
if ax is None:
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
h = 0.02
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(
np.arange(x_min, x_max, h),
np.arange(y_min, y_max, h)
)
Z = clf.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
ax.contourf(xx, yy, Z, alpha=0.8, cmap=plt.cm.RdYlBu)
ax.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, edgecolors='k', cmap=plt.cm.RdYlBu)
ax.set_xlim(xx.min(), xx.max())
ax.set_ylim(yy.min(), yy.max())
# 可视化单个决策树的决策边界
fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 3, figsize=(12, 8))
for i, ax in enumerate(axs.flat):
if i < len(ada_clf.estimators_):
plot_decision_boundary(ada_clf.estimators_[i], X, y, ax)
ax.set_title(f"Estimator {i + 1}")
else:
ax.axis('off')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# 可视化 AdaBoost 的决策边界
plot_decision_boundary(ada_clf, X, y)
plt.title("AdaBoost Decision Boundary")
plt.show()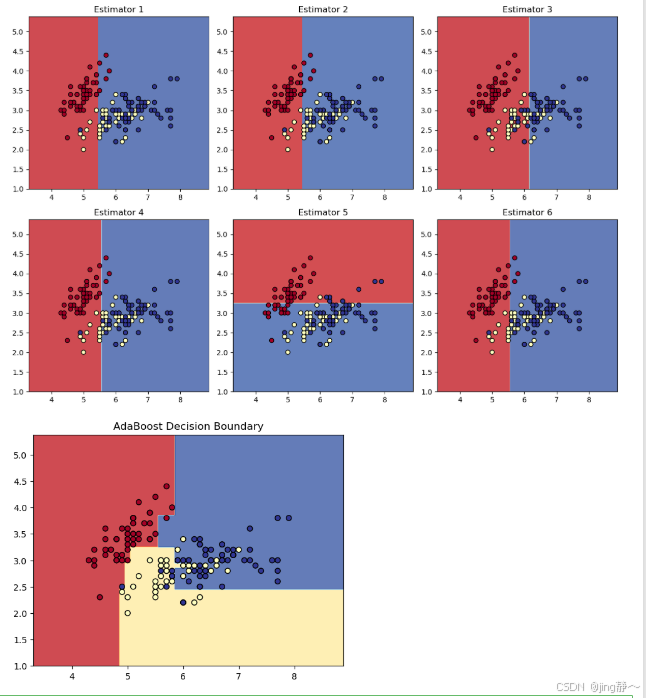
代码解释:
datasets.load_iris():加载鸢尾花数据集并选取前两个特征进行二维可视化。AdaBoostClassifier:创建 AdaBoost 分类器,使用决策树作为基学习器。plot_decision_boundary函数:绘制决策边界,通过meshgrid生成网格点,预测网格点的类别,然后使用contourf绘制等高线图。
2. 使用 Python 和 scikit-learn 实现随机森林和可视化
python
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
# 加载数据集
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data[:, :2]
y = iris.target
# 划分训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=42)
# 创建随机森林分类器
rf_clf = RandomForestClassifier(
n_estimators=100,
max_depth=2,
random_state=42
)
rf_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 预测
y_pred = rf_clf.predict(X_test)
print("Accuracy:", accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred))
# 可视化决策边界
def plot_decision_boundary(clf, X, y, ax=None):
if ax is None:
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
h = 0.02
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(
np.arange(x_min, x_max, h),
np.arange(y_min, y_max, h)
)
Z = clf.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
ax.contourf(xx, yy, Z, alpha=0.8, cmap=plt.cm.RdYlBu)
ax.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, edgecolors='k', cmap=plt.cm.RdYlBu)
ax.set_xlim(xx.min(), xx.max())
ax.set_ylim(yy.min(), y_max)
# 可视化单个决策树的决策边界
fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 3, figsize=(12, 8))
estimators = rf_clf.estimators_[:6]
for i, ax in enumerate(axs.flat):
if i < len(estimators):
plot_decision_boundary(estimators[i], X, y, ax)
ax.set_title(f"Estimator {i + 1}")
else:
ax.axis('off')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# 可视化随机森林的决策边界
plot_decision_boundary(rf_clf, X, y)
plt.title("Random Forest Decision Boundary")
plt.show()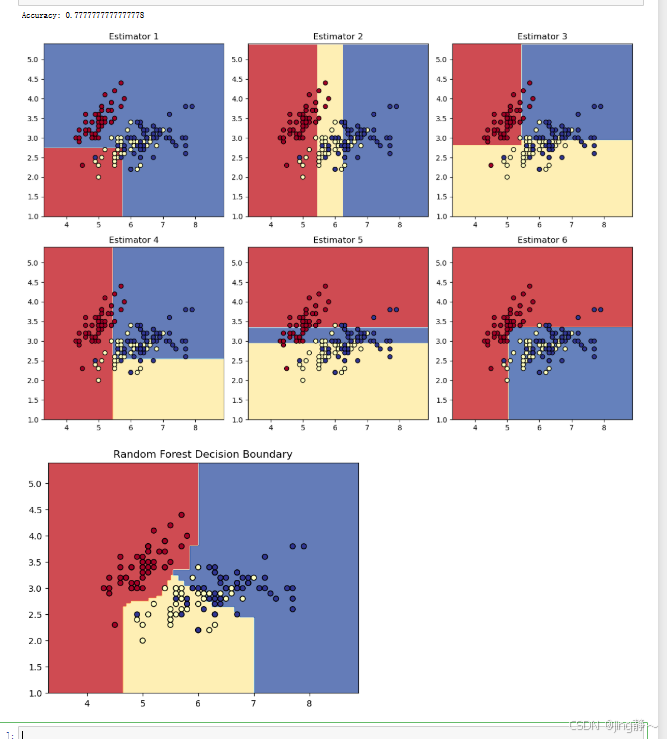
代码解释:
RandomForestClassifier:创建随机森林分类器。- 其他部分与 AdaBoost 的可视化类似,通过
plot_decision_boundary函数绘制决策边界,展示单个决策树和随机森林的分类边界。
3. 多样性可视化
python
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import BaggingClassifier
# 生成数据集
X, y = make_classification(n_samples=300, n_features=2, n_informative=2, n_redundant=0, random_state=42)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=42)
# 创建多个决策树
tree1 = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=5, random_state=42).fit(X_train, y_train)
tree2 = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=5, random_state=123).fit(X_train, y_train)
def disagreement_measure(h1, h2, X):
y1 = h1.predict(X)
y2 = h2.predict(X)
return np.mean(y1!= y2)
def correlation_measure(h1, h2, X):
y1 = h1.predict(X)
y2 = h2.predict(X)
mean_h1 = np.mean(y1)
mean_h2 = np.mean(y2)
numerator = np.mean((y1 - mean_h1) * (y2 - mean_h2))
denominator = np.sqrt(np.mean((y1 - mean_h1) ** 2) * np.mean((y2 - mean_h2) ** 2))
return numerator / denominator
print("Disagreement:", disagreement_measure(tree1, tree2, X_test))
print("Correlation:", correlation_measure(tree1, tree2, X_test))
# 可视化决策边界
def plot_decision_boundary(clf, X, y, ax=None, title=None):
if ax is None:
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
h = 0.02
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(
np.arange(x_min, x_max, h),
np.arange(y_min, y_max, h)
)
Z = clf.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
ax.contourf(xx, yy, Z, alpha=0.8, cmap=plt.cm.RdYlBu)
ax.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, edgecolors='k', cmap=plt.cm.RdYlBu)
ax.set_xlim(xx.min(), xx.max())
ax.set_ylim(yy.min(), y_max)
if title:
ax.set_title(title)
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(12, 6))
plot_decision_boundary(tree1, X, y, ax1, "Decision Tree 1")
plot_decision_boundary(tree2, X, y, ax2, "Decision Tree 2")
plt.show()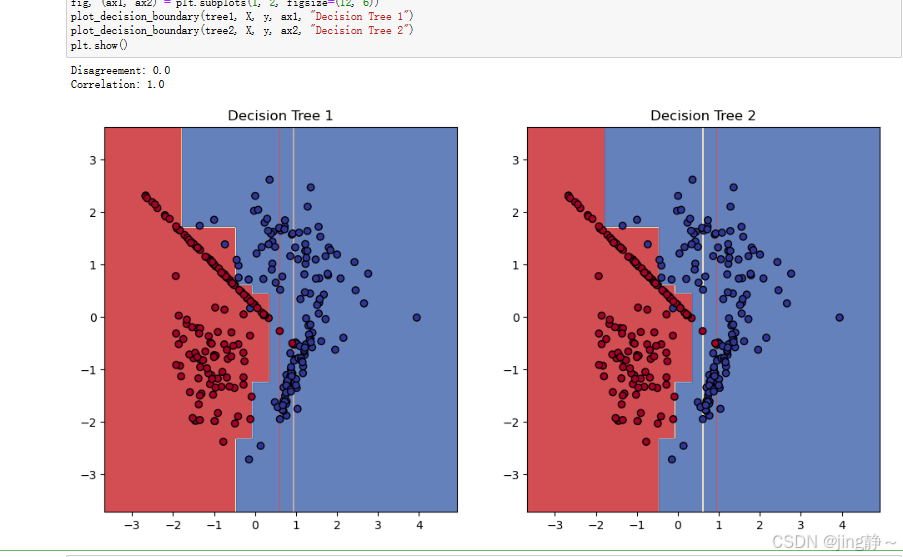
代码解释:
make_classification:生成一个分类数据集。disagreement_measure函数:计算两个学习器的分歧。correlation_measure函数:计算两个学习器的相关系数。plot_decision_boundary函数:绘制决策边界,对比两个不同决策树的决策边界。
