进程间通信

进程间通信介绍
进程间通信⽬的
数据传输:⼀个进程需要将它的数据发送给另⼀个进程
资源共享:多个进程之间共享同样的资源。
通知事件:⼀个进程需要向另⼀个或⼀组进程发送消息,通知它(它们)发⽣了某种事件(如进程终⽌时要通知⽗进程)。
进程控制:有些进程希望完全控制另⼀个进程的执⾏(如Debug进程),此时控制进程希望能够拦截另⼀个进程的所有陷⼊和异常,并能够及时知道它的状态改变。
管道
什么是管道
管道是Unix中最古⽼的进程间通信的形式。
我们把从⼀个进程连接到另⼀个进程的⼀个数据流称为⼀个"管道"
匿名管道
C++
#include <unistd.h>
功能:创建⼀⽆名管道
原型
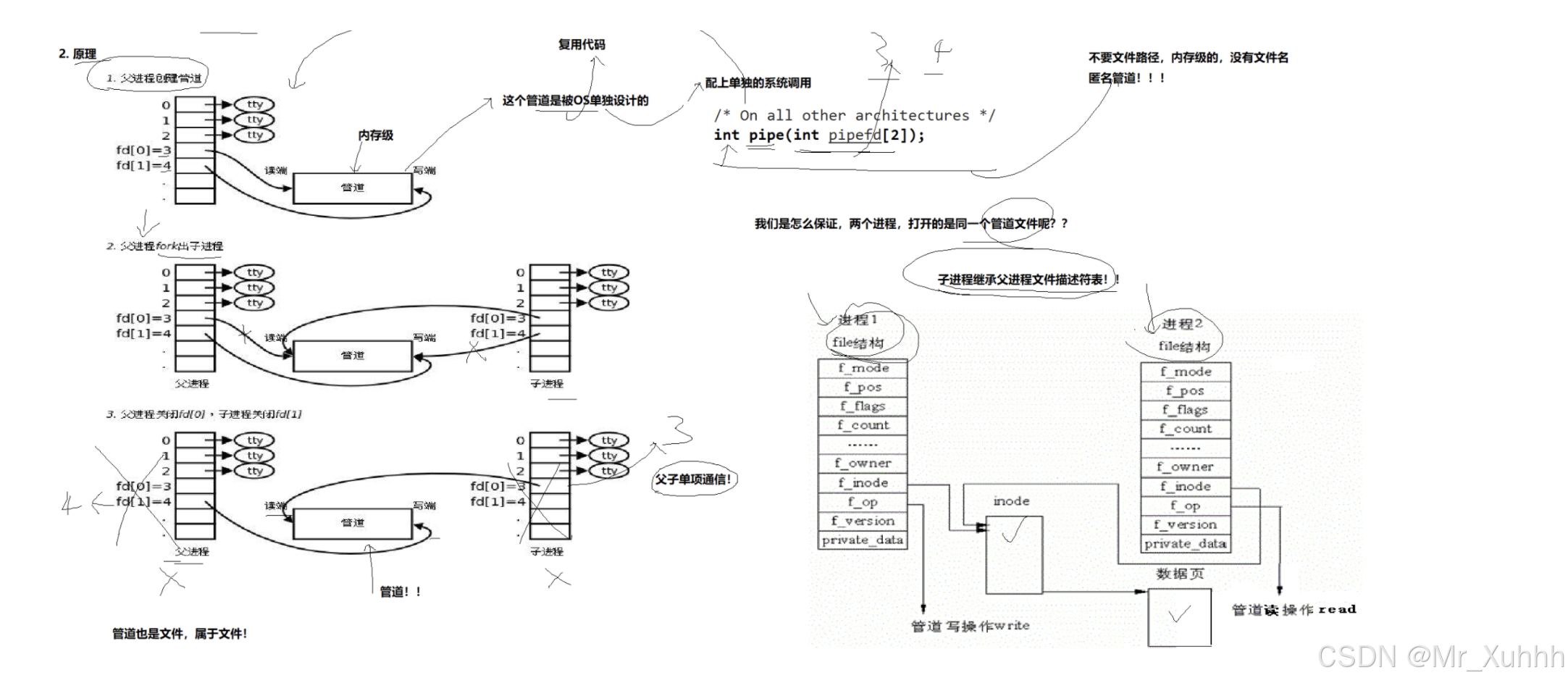
int pipe(int fd[2]);
参数
fd:⽂件描述符数组,其中fd[0]表⽰读端, fd[1]表⽰写端
返回值:成功返回0,失败返回错误代码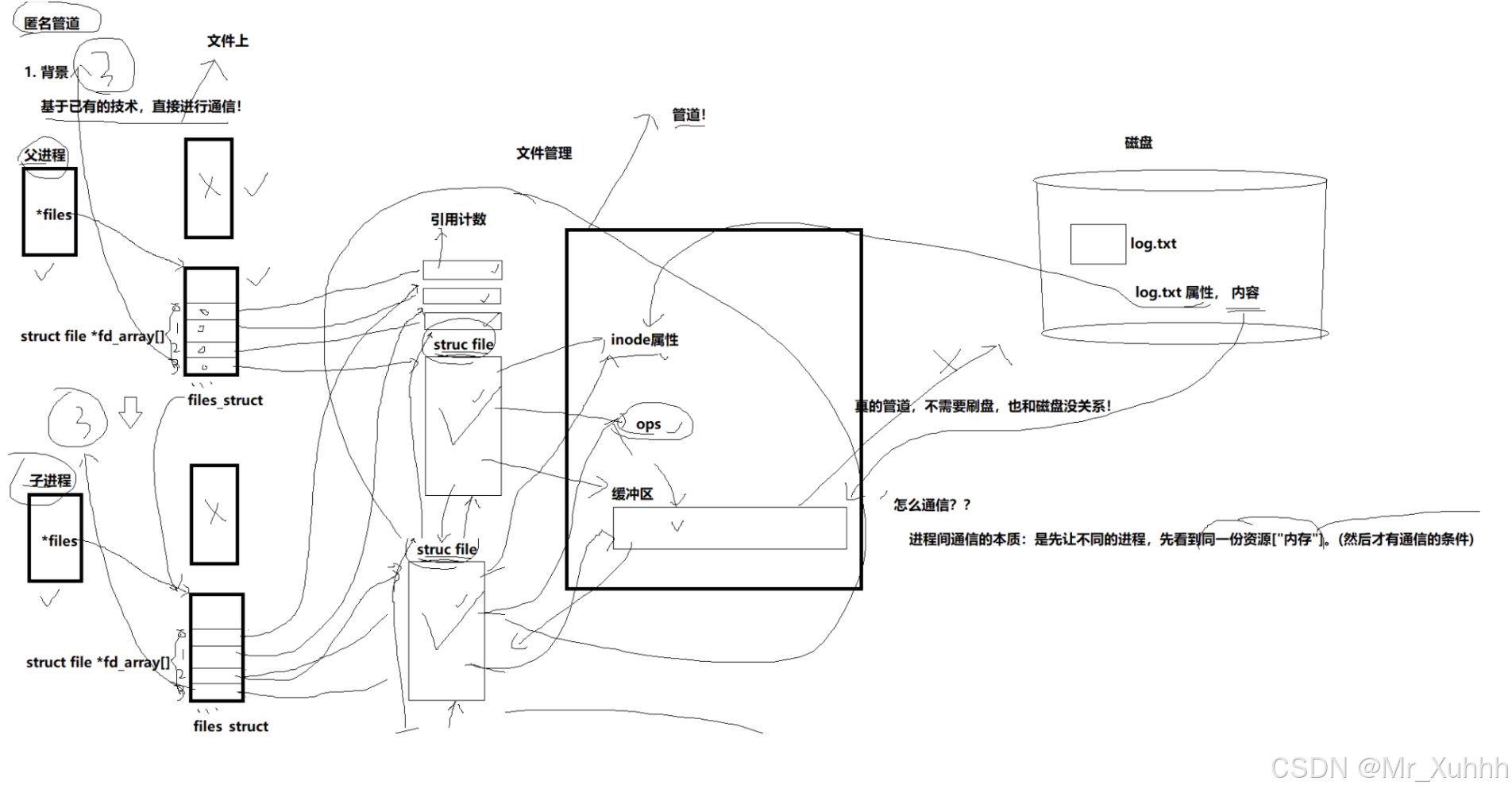
所以,看待管道,就如同看待⽂件⼀样!管道的使⽤和⽂件⼀致,迎合了"Linux⼀切皆⽂件思想"。
管道读写规则
• 当没有数据可读时
◦ O_NONBLOCK disable:read调⽤阻塞,即进程暂停执⾏,⼀直等到有数据来到为⽌。
◦ O_NONBLOCK enable:read调⽤返回-1,errno值为EAGAIN。
• 当管道满的时候
◦ O_NONBLOCK disable: write调⽤阻塞,直到有进程读⾛数据
◦ O_NONBLOCK enable:调⽤返回-1,errno值为EAGAIN
• 如果所有管道写端对应的⽂件描述符被关闭,则read返回0
• 如果所有管道读端对应的⽂件描述符被关闭,则write操作会产⽣信号SIGPIPE,进⽽可能导致write进程退出
• 当要写⼊的数据量不⼤于PIPE_BUF时,linux将保证写⼊的原⼦性。
• 当要写⼊的数据量⼤于PIPE_BUF时,linux将不再保证写⼊的原⼦性。
管道特点
只能⽤于具有共同祖先的进程(具有亲缘关系的进程)之间进⾏通信;通常,⼀个管道由⼀个进程创建,然后该进程调⽤fork,此后⽗、⼦进程之间就可应⽤该管道。
• 管道提供流式服务
• ⼀般⽽⾔,进程退出,管道释放,所以管道的⽣命周期随进程
• ⼀般⽽⾔,内核会对管道操作进⾏同步与互斥
• 管道是半双⼯的,数据只能向⼀个⽅向流动;需要双⽅通信时,需要建⽴起两个管道
验证管道通信的4种情况
读正常&&写满
写正常&&读空
写关闭&&读正常
读关闭&&写正常



创建进程池处理任务
Channel.hpp
C++
#ifndef __CHANNEL_HPP__
#define __CHANNEL_HPP__
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
// 先描述
class Channel
{
public:
Channel(int wfd, pid_t who) : _wfd(wfd), _who(who)
{
// Channel-3-1234
_name = "Channel-" + std::to_string(wfd) + "-" + std::to_string(who);
}
std::string Name()
{
return _name;
}
void Send(int cmd)
{
::write(_wfd, &cmd, sizeof(cmd));
}
void Close()
{
::close(_wfd);
}
pid_t Id()
{
return _who;
}
int wFd()
{
return _wfd;
}
~Channel()
{
}
private:
int _wfd;
std::string _name;
pid_t _who;
};
#endifProcessPool.hpp
C++
#ifndef __PROCESS_POOL_HPP__
#define __PROCESS_POOL_HPP__
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib> // stdlib.h stdio.h -> cstdlib cstdio
#include <vector>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include "Task.hpp"
// 先描述
class Channel
{
public:
Channel(int fd, pid_t id) : _wfd(fd), _subid(id)
{
_name = "channel-" + std::to_string(_wfd) + "-" + std::to_string(_subid);
}
~Channel()
{
}
void Send(int code)
{
int n = write(_wfd, &code, sizeof(code));
(void)n; // ?
}
void Close()
{
close(_wfd);
}
void Wait()
{
pid_t rid = waitpid(_subid, nullptr, 0);
(void)rid;
}
int Fd() { return _wfd; }
pid_t SubId() { return _subid; }
std::string Name() { return _name; }
private:
int _wfd;
pid_t _subid;
std::string _name;
// int _loadnum;
};
// 在组织
class ChannelManager
{
public:
ChannelManager() : _next(0)
{
}
void Insert(int wfd, pid_t subid)
{
_channels.emplace_back(wfd, subid);
// Channel c(wfd, subid);
// _channels.push_back(std::move(c));
}
Channel &Select()
{
auto &c = _channels[_next];
_next++;
_next %= _channels.size();
return c;
}
void PrintChannel()
{
for (auto &channel : _channels)
{
std::cout << channel.Name() << std::endl;
}
}
void StopSubProcess()
{
for (auto &channel : _channels)
{
channel.Close();
std::cout << "关闭: " << channel.Name() << std::endl;
}
}
void WaitSubProcess()
{
for (auto &channel : _channels)
{
channel.Wait();
std::cout << "回收: " << channel.Name() << std::endl;
}
}
~ChannelManager() {}
private:
std::vector<Channel> _channels;
int _next;
};
const int gdefaultnum = 5;
class ProcessPool
{
public:
ProcessPool(int num) : _process_num(num)
{
_tm.Register(PrintLog);
_tm.Register(Download);
_tm.Register(Upload);
}
void Work(int rfd)
{
while (true)
{
int code = 0;
ssize_t n = read(rfd, &code, sizeof(code));
if (n > 0)
{
if (n != sizeof(code))
{
continue;
}
std::cout << "子进程[" << getpid() << "]收到一个任务码: " << code << std::endl;
_tm.Execute(code);
}
else if (n == 0)
{
std::cout << "子进程退出" << std::endl;
break;
}
else
{
std::cout << "读取错误" << std::endl;
break;
}
}
}
bool Start()
{
for (int i = 0; i < _process_num; i++)
{
// 1. 创建管道
int pipefd[2] = {0};
int n = pipe(pipefd);
if (n < 0)
return false;
// 2. 创建子进程
pid_t subid = fork();
if (subid < 0)
return false;
else if (subid == 0)
{
// 子进程
// 3. 关闭不需要的文件描述符
close(pipefd[1]);
Work(pipefd[0]); //??
close(pipefd[0]);
exit(0);
}
else
{
// 父进程
// 3. 关闭不需要的文件描述符
close(pipefd[0]); // 写端:pipefd[1];
_cm.Insert(pipefd[1], subid);
// wfd, subid
}
}
return true;
}
void Debug()
{
_cm.PrintChannel();
}
void Run()
{
// 1. 选择一个任务
int taskcode = _tm.Code();
// 2. 选择一个信道[子进程],负载均衡的选择一个子进程,完成任务
auto &c = _cm.Select();
std::cout << "选择了一个子进程: " << c.Name() << std::endl;
// 2. 发送任务
c.Send(taskcode);
std::cout << "发送了一个任务码: " << taskcode << std::endl;
}
void Stop()
{
// 关闭父进程所有的wfd即可
_cm.StopSubProcess();
// 回收所有子进程
_cm.WaitSubProcess();
}
~ProcessPool()
{
}
private:
ChannelManager _cm;
int _process_num;
TaskManager _tm;
};
#endifTask.hpp
C++
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <ctime>
typedef void (*task_t)();
debug/
void PrintLog()
{
std::cout << "我是一个打印日志的任务" << std::endl;
}
void Download()
{
std::cout << "我是一个下载的任务" << std::endl;
}
void Upload()
{
std::cout << "我是一个上传的任务" << std::endl;
}
//
class TaskManager
{
public:
TaskManager()
{
srand(time(nullptr));
}
void Register(task_t t)
{
_tasks.push_back(t);
}
int Code()
{
return rand() % _tasks.size();
}
void Execute(int code)
{
if(code >= 0 && code < _tasks.size())
{
_tasks[code]();
}
}
~TaskManager()
{}
private:
std::vector<task_t> _tasks;
};
C++
#include "ProcessPool.hpp"
int main()
{
// 这个代码,有一个藏得比较深的bug --- TODO
// 创建进程池对象
ProcessPool pp(gdefaultnum);
// 启动进程池
pp.Start();
// 自动派发任务
int cnt = 10;
while(cnt--)
{
pp.Run();
sleep(1);
}
// 回收,结束进程池
pp.Stop();
return 0;
}Makefile
test Pipe:testPipe.cc
g++ -0 ^@^$ -std=C++11
.PHONY: clean
clean:
rm -f testPipe
process_pool:Main.cc
g++ -o $@ $^ -std=c++11
.PHONY:clean
clean:
rm -f process_pool
// 创建进程池对象
ProcessPool pp(gdefaultnum);
// 启动进程池
pp.Start();
// 自动派发任务
int cnt = 10;
while(cnt--)
{
pp.Run();
sleep(1);
}
// 回收,结束进程池
pp.Stop();
return 0;}
Makefiletest Pipe:testPipe.cc
g++ -0 @$ -std=C++11
.PHONY: clean
clean:
rm -f testPipe
process_pool:Main.cc
g++ -o @ ^ -std=c++11
.PHONY:clean
clean:
rm -f process_pool