人工智能例子汇总:AI常见的算法和例子-CSDN博客
LSTM 通过 记忆单元(cell) 和 三个门控机制(遗忘门、输入门、输出门)来控制信息流:
记忆单元(Cell State)
- 负责存储长期信息,并通过门控机制决定保留或丢弃信息。
遗忘门(Forget Gate, ftf_tft)

输入门(Input Gate, iti_tit)

输出门(Output Gate, oto_tot)
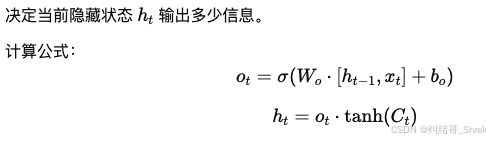
| 特性 | 传统 RNN | LSTM |
|---|---|---|
| 记忆能力 | 短期记忆 | 长短期记忆 |
| 计算复杂度 | 低 | 高 |
| 解决梯度消失 | 否 | 是 |
| 适用场景 | 短序列数据 | 长序列数据 |
LSTM 应用场景
- 自然语言处理(NLP):文本生成、情感分析、机器翻译
- 时间序列预测:股票预测、天气预报、传感器数据分析
- 语音识别:自动字幕生成、语音转文字(ASR)
- 机器人与控制系统:智能体决策、自动驾驶
例子:
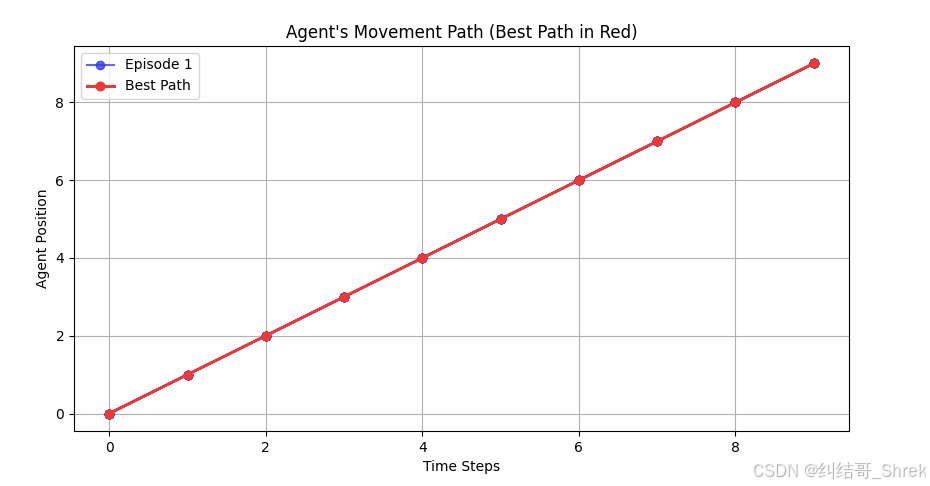
下面例子实现了一个 基于 LSTM 的强化学习智能体 ,在 1D 网格环境 里移动,并找到最优路径。
最终,我们 绘制 5 条测试路径,并高亮显示最佳路径(红色)
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# ========== 1. 定义 LSTM 策略网络 ==========
class LSTMPolicy(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, output_size, num_layers=1):
super(LSTMPolicy, self).__init__()
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.lstm = nn.LSTM(input_size, hidden_size, num_layers, batch_first=True)
self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size)
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)
def forward(self, x, hidden_state):
batch_size = x.size(0)
# 确保 hidden_state 维度正确
if hidden_state[0].dim() == 2:
hidden_state = (hidden_state[0].unsqueeze(1).repeat(1, batch_size, 1),
hidden_state[1].unsqueeze(1).repeat(1, batch_size, 1))
out, hidden_state = self.lstm(x, hidden_state)
out = self.fc(out[:, -1, :]) # 取最后时间步的输出
action_prob = self.softmax(out) # 归一化输出,作为策略
return action_prob, hidden_state
def init_hidden(self, batch_size=1):
return (torch.zeros(self.num_layers, batch_size, self.hidden_size),
torch.zeros(self.num_layers, batch_size, self.hidden_size))
# ========== 2. 创建网格环境 ==========
class GridWorld:
def __init__(self, grid_size=10, goal_position=9):
self.grid_size = grid_size
self.goal_position = goal_position
self.reset()
def reset(self):
self.position = 0
return self.position
def step(self, action):
if action == 0:
self.position = max(0, self.position - 1)
elif action == 1:
self.position = min(self.grid_size - 1, self.position + 1)
reward = 1 if self.position == self.goal_position else -0.1
done = self.position == self.goal_position
return self.position, reward, done
# ========== 3. 训练智能体 ==========
def train(num_episodes=500, max_steps=50):
env = GridWorld()
input_size = 1
hidden_size = 64
output_size = 2
num_layers = 1
policy = LSTMPolicy(input_size, hidden_size, output_size, num_layers)
optimizer = optim.Adam(policy.parameters(), lr=0.01)
gamma = 0.99
for episode in range(num_episodes):
state = torch.tensor([[env.reset()]], dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(0) # (1, 1, input_size)
hidden_state = policy.init_hidden(batch_size=1)
log_probs = []
rewards = []
for step in range(max_steps):
action_probs, hidden_state = policy(state, hidden_state)
action = torch.multinomial(action_probs, 1).item()
log_prob = torch.log(action_probs.squeeze(0)[action])
log_probs.append(log_prob)
next_state, reward, done = env.step(action)
rewards.append(reward)
if done:
break
state = torch.tensor([[next_state]], dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(0)
# 计算回报并更新策略
returns = []
R = 0
for r in reversed(rewards):
R = r + gamma * R
returns.insert(0, R)
returns = torch.tensor(returns, dtype=torch.float32)
returns = (returns - returns.mean()) / (returns.std() + 1e-9)
loss = sum([-log_prob * R for log_prob, R in zip(log_probs, returns)])
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if (episode + 1) % 50 == 0:
print(f"Episode {episode + 1}/{num_episodes}, Total Reward: {sum(rewards)}")
torch.save(policy.state_dict(), "policy.pth")
# 训练智能体
train(500)
# ========== 4. 测试智能体并绘制最佳路径 ==========
def test(num_episodes=5):
env = GridWorld()
input_size = 1
hidden_size = 64
output_size = 2
num_layers = 1
policy = LSTMPolicy(input_size, hidden_size, output_size, num_layers)
policy.load_state_dict(torch.load("policy.pth"))
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))
best_path = None
best_steps = float('inf')
for episode in range(num_episodes):
state = torch.tensor([[env.reset()]], dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(0) # (1, 1, input_size)
hidden_state = policy.init_hidden(batch_size=1)
positions = [env.position] # 记录位置变化
while True:
action_probs, hidden_state = policy(state, hidden_state)
action = torch.argmax(action_probs, dim=-1).item()
next_state, reward, done = env.step(action)
positions.append(next_state)
if done:
break
state = torch.tensor([[next_state]], dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(0)
# 记录最佳路径(最短步数)
if len(positions) < best_steps:
best_steps = len(positions)
best_path = positions
# 绘制普通路径(蓝色)
plt.plot(range(len(positions)), positions, marker='o', linestyle='-', color='blue', alpha=0.6,
label=f'Episode {episode + 1}' if episode == 0 else "")
# 绘制最佳路径(红色)
if best_path:
plt.plot(range(len(best_path)), best_path, marker='o', linestyle='-', color='red', linewidth=2,
label="Best Path")
# 打印最佳路径
print(f"Best Path (steps={best_steps}): {best_path}")
plt.xlabel("Time Steps")
plt.ylabel("Agent Position")
plt.title("Agent's Movement Path (Best Path in Red)")
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
# 测试并绘制智能体移动路径
test(5)