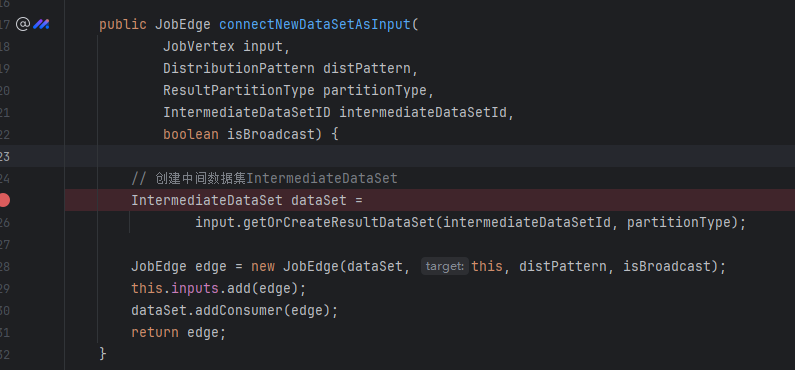
JobGraph组成
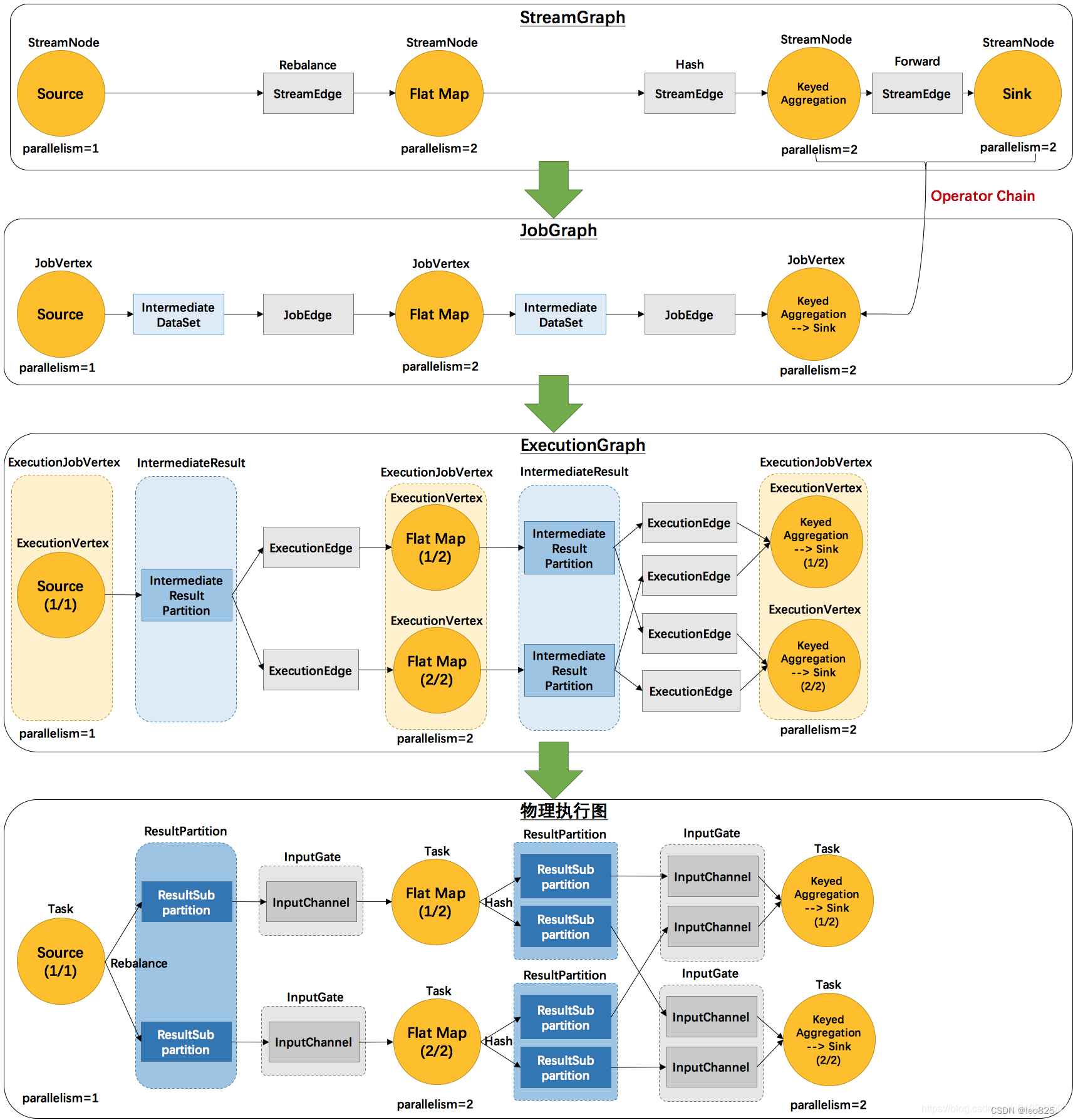
JobGraph主要是StreamGraph经过优化后生成的,主要优化的就是对符合条件节点进行chain,这样可以减少数据流动的序列化和传输。
JobGraph主要由三部分组成。
- JobVertex:图的顶点。输入是一个JobEdge,输出是IntermediateDataSet。它可以对应多个StreamNode,将多个operator合并到一起。
- IntermediateDataSet:中间结果集。是JobVertex处理后生成的结果集,为了方便下游复用,producer 是 JobVertex ,consumer 是 JobEdge。
- JobEdge:边。JobGraph的传输管道。source 是 IntermediateDataSet,target 是 JobVertex。即数据通过 JobEdge 由 IntermediateDataSet 传递给目标 JobVertex 。
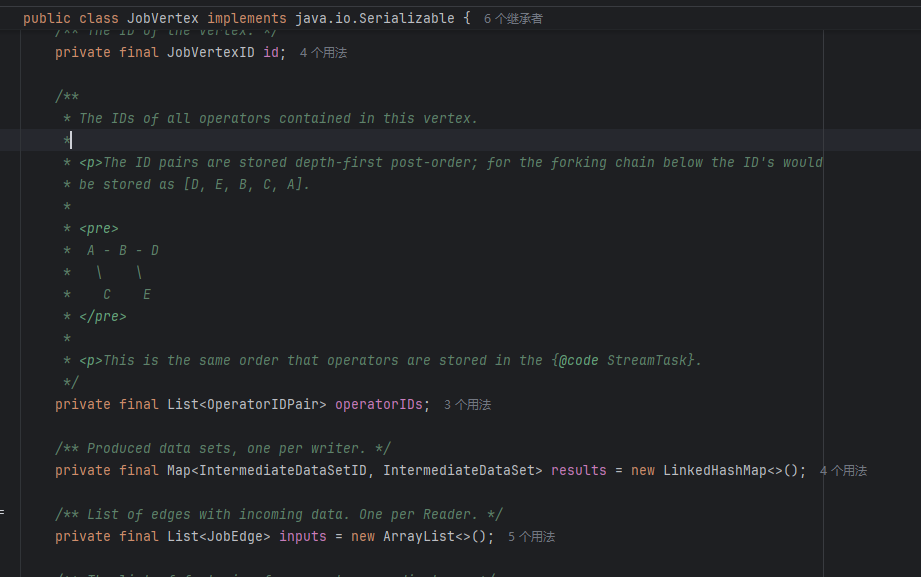
JobVertex
- operatorIDs:该 job 节点包含的所有 operator ids,以深度优先方式存储 ids
- results:job 节点计算出的中间结果
- inputs:输入数据的边列表
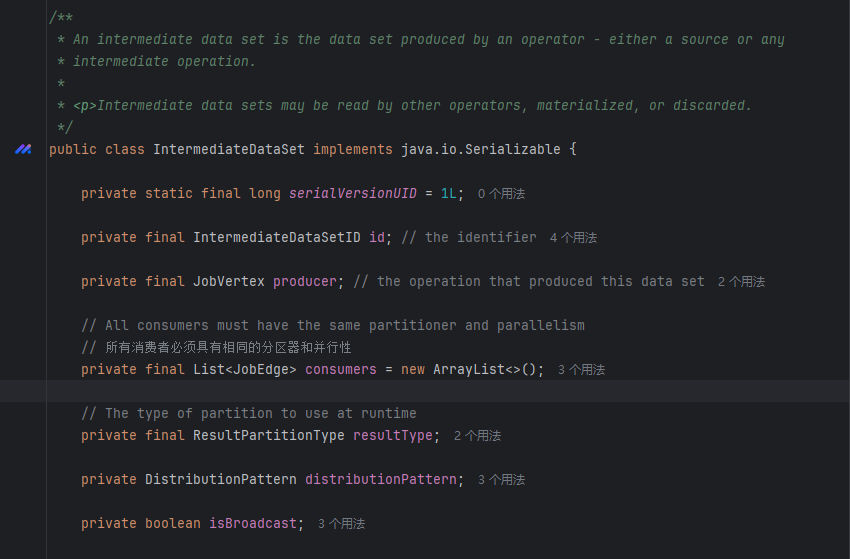
IntermediateDataSet
- producer:生产者,JobVertex
- consumers:消费边,可以对应多个,但是必须具有相同的分区器和并行性
- resultType:运行时使用的分区类型
- BLOCKING 阻塞,批处理模式
- PIPELINED 管道非阻塞,流处理模式
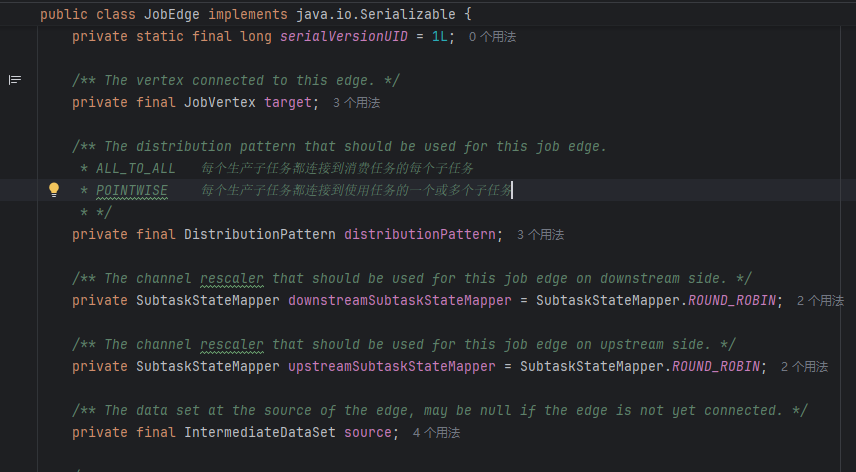
JobEdge
- target:edge的输出,JobVertex
- source:edge的源,IntermediateDataSet
- distributionPattern:决定了在上游节点(生产者)的子任务和下游节点(消费者)之间的连接模式
- ALL_TO_ALL:每个生产子任务都连接到消费任务的每个子任务
- POINTWISE:每个生产子任务都连接到使用任务的一个或多个子任务
JobGraph生成
入口是在StreamingJobGraphGenerator的createJobGraph方法
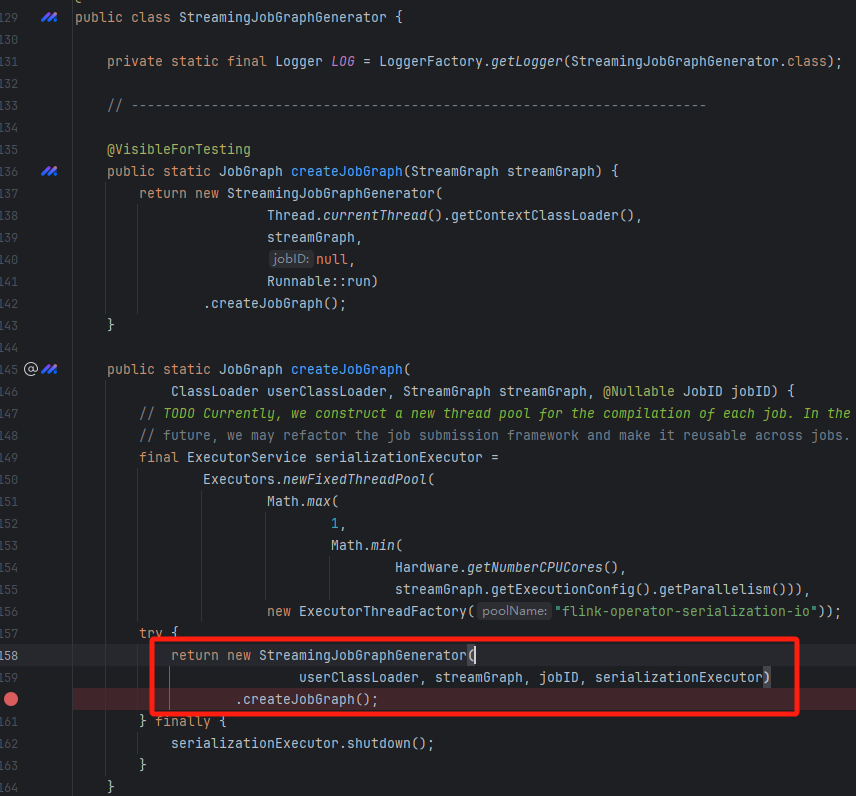
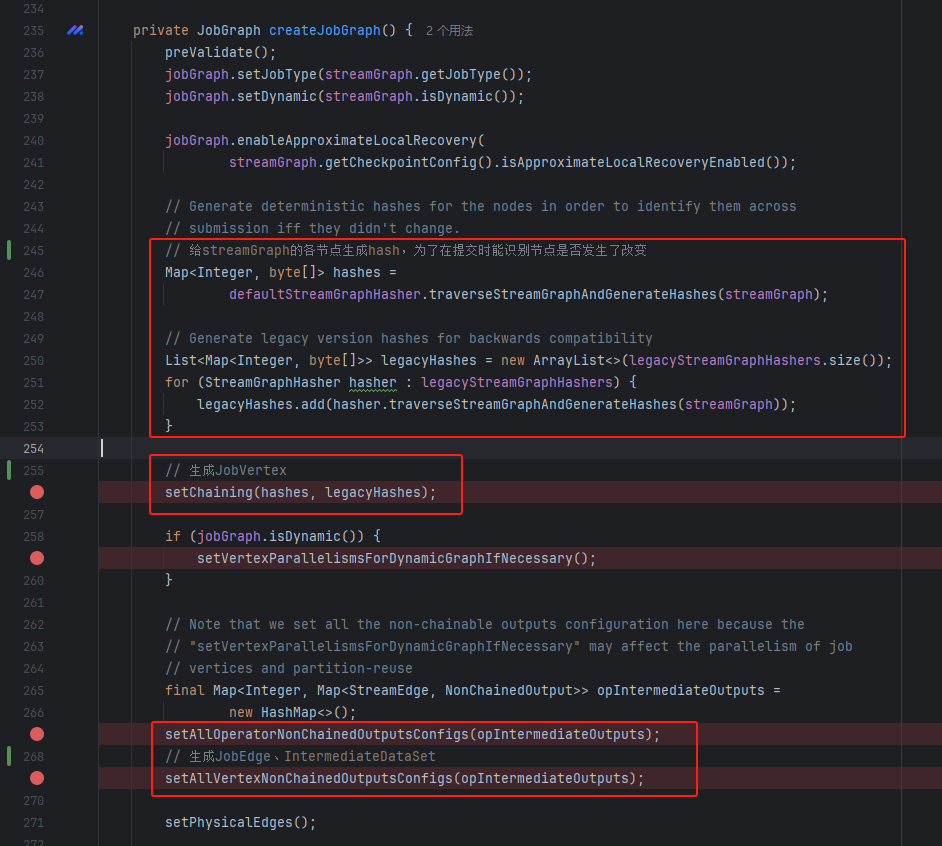
createJobGraph过程比较多,重点是三步:
- 为各个StreamNode生成hash值,这样在故障恢复的时候可以识别
- 生成JobVertex
- 生成JobEdge、IntermediateDataSet
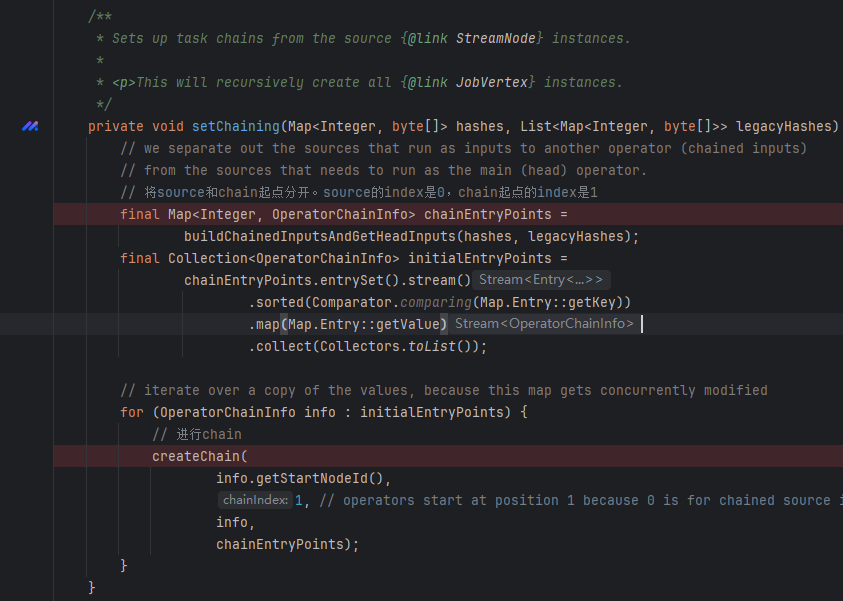
生成JobVertex(setChaining)
从 Source StreamNode 实例开始设置 task chain,它将会递归地创建所有的 JobVertex 实例。
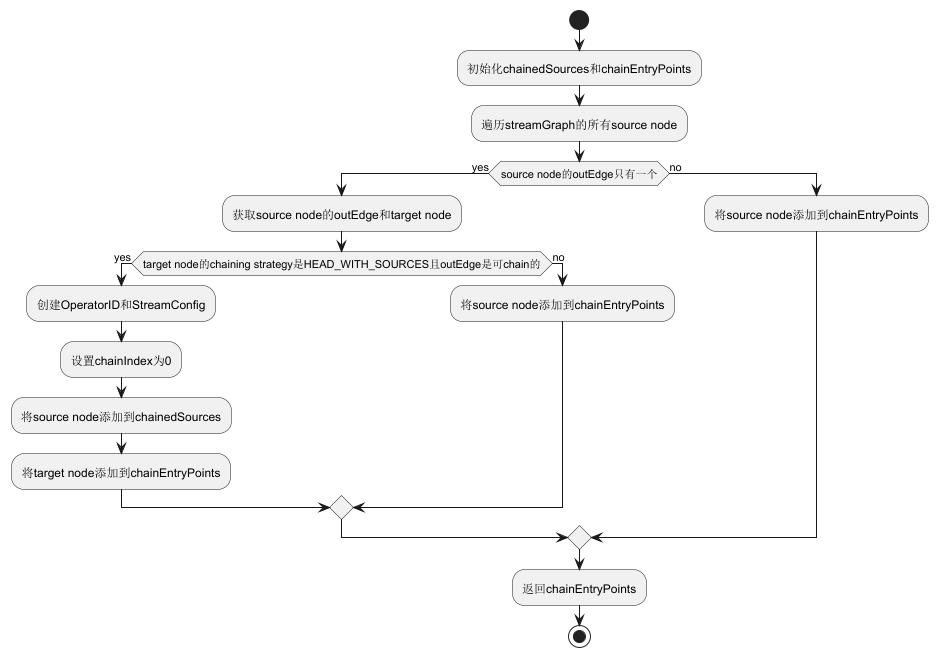
buildChainedInputsAndGetHeadInputs会得到chain的起点集合,然后遍历进行createChain
buildChainedInputsAndGetHeadInputs
java
private Map<Integer, OperatorChainInfo> buildChainedInputsAndGetHeadInputs(
final Map<Integer, byte[]> hashes, final List<Map<Integer, byte[]>> legacyHashes) {
// 可以chain的source,单独处理这种节点
final Map<Integer, ChainedSourceInfo> chainedSources = new HashMap<>();
// chain的起点(不能chain的souce节点、可以chain的souce节点的下一个节点)
final Map<Integer, OperatorChainInfo> chainEntryPoints = new HashMap<>();
// 遍历streamGraph的所有source node
for (Integer sourceNodeId : streamGraph.getSourceIDs()) {
final StreamNode sourceNode = streamGraph.getStreamNode(sourceNodeId);
if (sourceNode.getOperatorFactory() instanceof SourceOperatorFactory
&& sourceNode.getOutEdges().size() == 1) {
// 要求source node的outEdge只有一个。有多个出边的source不能chain
// as long as only NAry ops support this chaining, we need to skip the other parts
final StreamEdge sourceOutEdge = sourceNode.getOutEdges().get(0);
final StreamNode target = streamGraph.getStreamNode(sourceOutEdge.getTargetId());
final ChainingStrategy targetChainingStrategy =
target.getOperatorFactory().getChainingStrategy();
if (targetChainingStrategy == ChainingStrategy.HEAD_WITH_SOURCES
&& isChainableInput(sourceOutEdge, streamGraph)) {
final OperatorID opId = new OperatorID(hashes.get(sourceNodeId));
final StreamConfig.SourceInputConfig inputConfig =
new StreamConfig.SourceInputConfig(sourceOutEdge);
final StreamConfig operatorConfig = new StreamConfig(new Configuration());
setOperatorConfig(sourceNodeId, operatorConfig, Collections.emptyMap());
setOperatorChainedOutputsConfig(operatorConfig, Collections.emptyList());
// we cache the non-chainable outputs here, and set the non-chained config later
opNonChainableOutputsCache.put(sourceNodeId, Collections.emptyList());
// sources的index都是0
operatorConfig.setChainIndex(0); // sources are always first
operatorConfig.setOperatorID(opId);
operatorConfig.setOperatorName(sourceNode.getOperatorName());
chainedSources.put(
sourceNodeId, new ChainedSourceInfo(operatorConfig, inputConfig));
final SourceOperatorFactory<?> sourceOpFact =
(SourceOperatorFactory<?>) sourceNode.getOperatorFactory();
final OperatorCoordinator.Provider coord =
sourceOpFact.getCoordinatorProvider(sourceNode.getOperatorName(), opId);
// chainEntryPoints中添加(targetNodeId, chainInfo)
final OperatorChainInfo chainInfo =
chainEntryPoints.computeIfAbsent(
sourceOutEdge.getTargetId(),
(k) ->
new OperatorChainInfo(
sourceOutEdge.getTargetId(),
hashes,
legacyHashes,
chainedSources,
streamGraph));
chainInfo.addCoordinatorProvider(coord);
chainInfo.recordChainedNode(sourceNodeId);
continue;
}
}
chainEntryPoints.put(
sourceNodeId,
new OperatorChainInfo(
sourceNodeId, hashes, legacyHashes, chainedSources, streamGraph));
}
return chainEntryPoints;
}
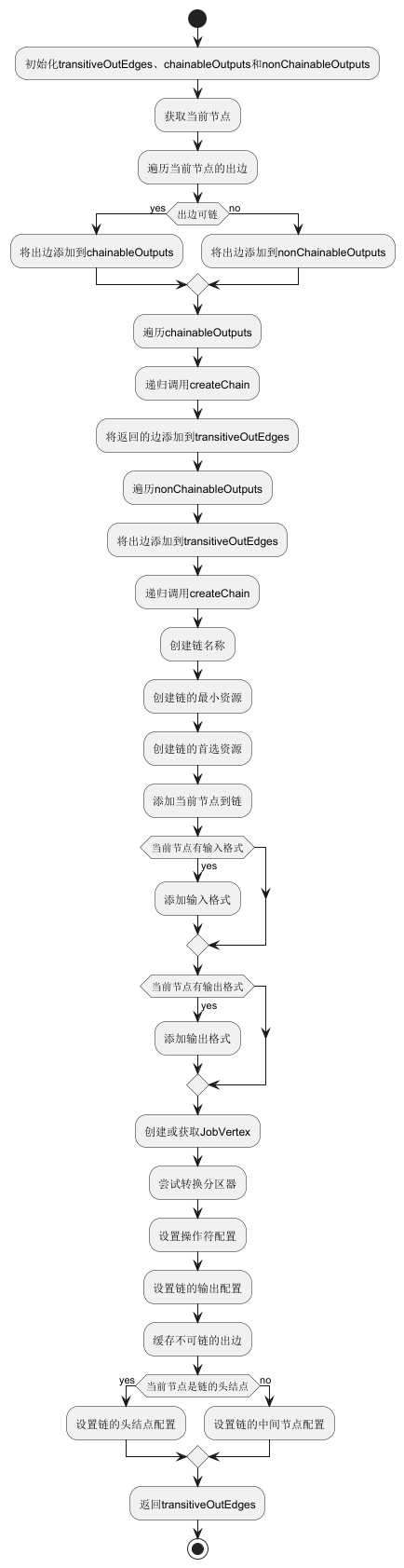
createChain
在创建chain的过程中,一个chain完成后,在头结点创建一个JobVertex。
java
private List<StreamEdge> createChain(
final Integer currentNodeId,
final int chainIndex,
final OperatorChainInfo chainInfo,
final Map<Integer, OperatorChainInfo> chainEntryPoints) {
Integer startNodeId = chainInfo.getStartNodeId();
if (!builtVertices.contains(startNodeId)) {
// transitiveOutEdges 过渡的出边集合,就是两个StreamNode不能再进行chain的那条边,用于生成JobEdge
List<StreamEdge> transitiveOutEdges = new ArrayList<StreamEdge>();
// chainableOutputs 两个StreamNode可以进行chain的出边集合
// nonChainableOutputs 两个StreamNode不能进行chain的出边
List<StreamEdge> chainableOutputs = new ArrayList<StreamEdge>();
List<StreamEdge> nonChainableOutputs = new ArrayList<StreamEdge>();
StreamNode currentNode = streamGraph.getStreamNode(currentNodeId);
for (StreamEdge outEdge : currentNode.getOutEdges()) {
if (isChainable(outEdge, streamGraph)) {
chainableOutputs.add(outEdge);
} else {
nonChainableOutputs.add(outEdge);
}
}
for (StreamEdge chainable : chainableOutputs) {
// 如果存在可以chain的边,那么就继续往这条边的target operator进行chain。
// transitiveOutEdges最终返回给首次调用栈的是不能再继续chain的那条边
transitiveOutEdges.addAll(
createChain(
chainable.getTargetId(),
chainIndex + 1,
chainInfo,
chainEntryPoints));
}
for (StreamEdge nonChainable : nonChainableOutputs) {
//如果存在了不可chain的边,说明该边就是StreamNode chain之间的过渡边,添加到transitiveOutEdges中,
//继续对该边的target StreamNode进行新的createChain操作,意味着一个新的chain
transitiveOutEdges.add(nonChainable);
createChain(
nonChainable.getTargetId(),
1, // operators start at position 1 because 0 is for chained source inputs
chainEntryPoints.computeIfAbsent(
nonChainable.getTargetId(),
(k) -> chainInfo.newChain(nonChainable.getTargetId())),
chainEntryPoints);
}
chainedNames.put(
currentNodeId,
createChainedName(
currentNodeId,
chainableOutputs,
Optional.ofNullable(chainEntryPoints.get(currentNodeId))));
chainedMinResources.put(
currentNodeId, createChainedMinResources(currentNodeId, chainableOutputs));
chainedPreferredResources.put(
currentNodeId,
createChainedPreferredResources(currentNodeId, chainableOutputs));
// 添加当前的StreamNode到chain中
OperatorID currentOperatorId =
chainInfo.addNodeToChain(
currentNodeId,
streamGraph.getStreamNode(currentNodeId).getOperatorName());
if (currentNode.getInputFormat() != null) {
getOrCreateFormatContainer(startNodeId)
.addInputFormat(currentOperatorId, currentNode.getInputFormat());
}
if (currentNode.getOutputFormat() != null) {
getOrCreateFormatContainer(startNodeId)
.addOutputFormat(currentOperatorId, currentNode.getOutputFormat());
}
// chain的头结点创建JobVertex
StreamConfig config =
currentNodeId.equals(startNodeId)
? createJobVertex(startNodeId, chainInfo)
: new StreamConfig(new Configuration());
tryConvertPartitionerForDynamicGraph(chainableOutputs, nonChainableOutputs);
setOperatorConfig(currentNodeId, config, chainInfo.getChainedSources());
setOperatorChainedOutputsConfig(config, chainableOutputs);
// we cache the non-chainable outputs here, and set the non-chained config later
// 缓存不能chain的出边集合
opNonChainableOutputsCache.put(currentNodeId, nonChainableOutputs);
if (currentNodeId.equals(startNodeId)) {
// 头结点
chainInfo.setTransitiveOutEdges(transitiveOutEdges);
chainInfos.put(startNodeId, chainInfo);
config.setChainStart();
config.setChainIndex(chainIndex);
config.setOperatorName(streamGraph.getStreamNode(currentNodeId).getOperatorName());
config.setTransitiveChainedTaskConfigs(chainedConfigs.get(startNodeId));
} else {
chainedConfigs.computeIfAbsent(
startNodeId, k -> new HashMap<Integer, StreamConfig>());
config.setChainIndex(chainIndex);
StreamNode node = streamGraph.getStreamNode(currentNodeId);
config.setOperatorName(node.getOperatorName());
chainedConfigs.get(startNodeId).put(currentNodeId, config);
}
config.setOperatorID(currentOperatorId);
if (chainableOutputs.isEmpty()) {
// chain尾节点
config.setChainEnd();
}
return transitiveOutEdges;
} else {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
}
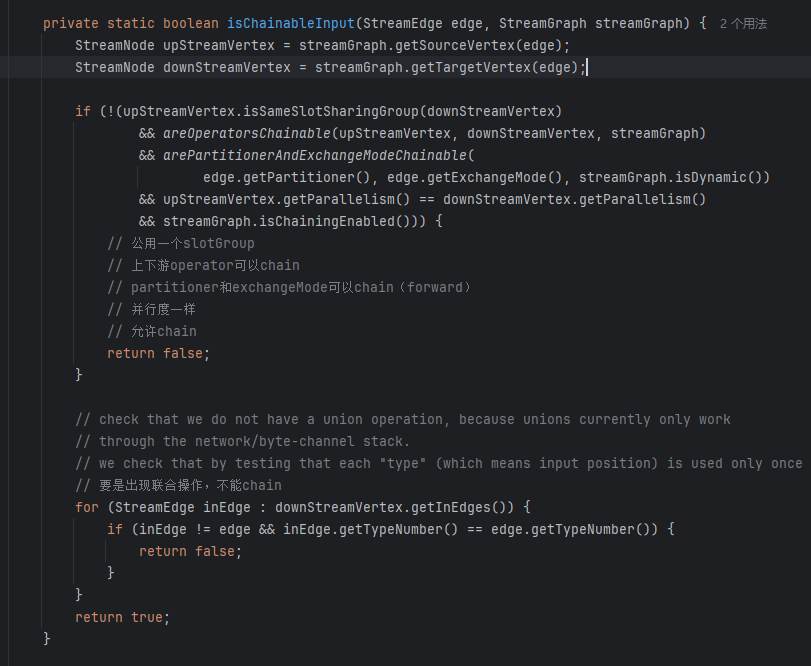
判断是否chainable
- 公用一个slotGroup
- 上下游operator可以chain
- partitioner和exchangeMode可以chain(forward)
- 并行度一样
- 允许chain
- 不能是联合操作
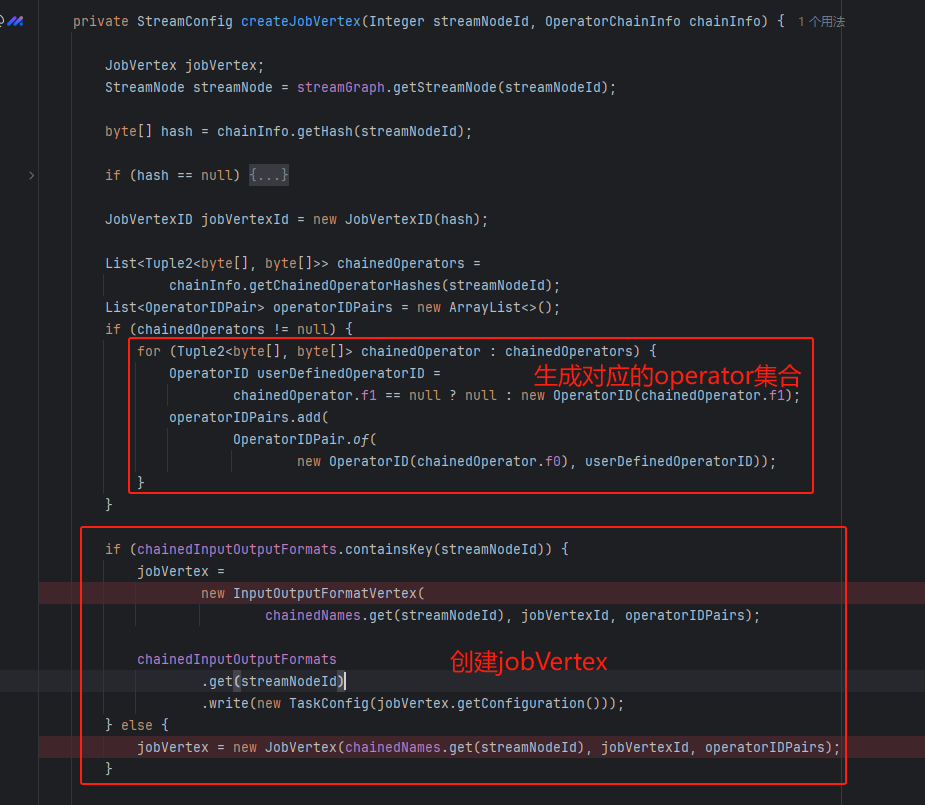
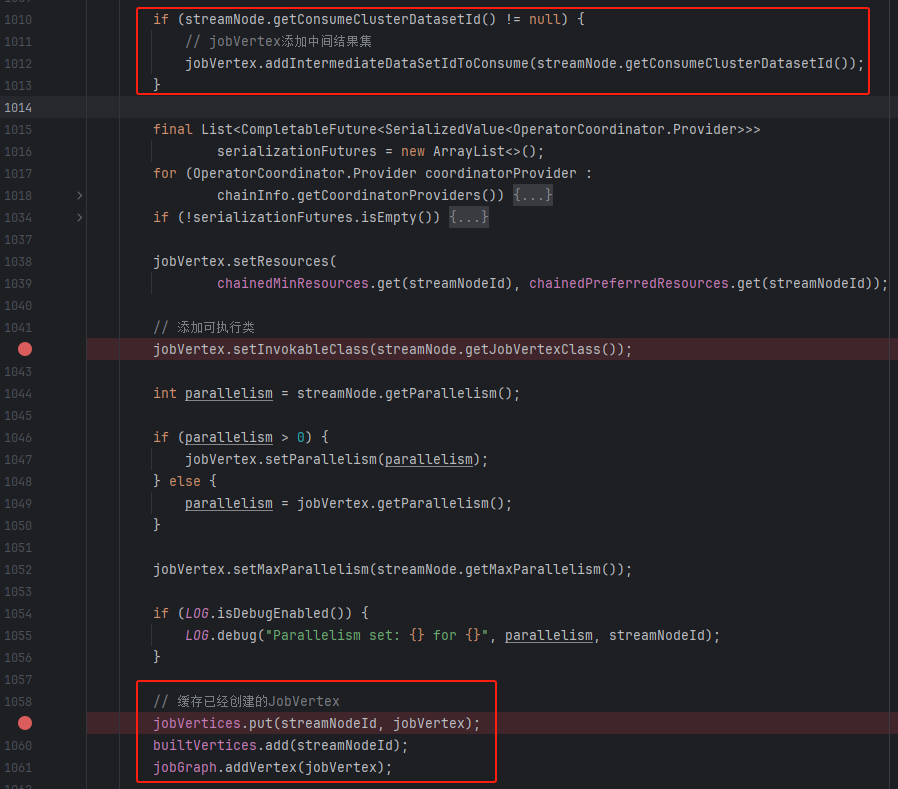
createJobVertex
- 创建对应的operator集合
- 创建JobVertex(InputOutputFormatVertex是一种特殊的 JobVertex,它用于处理输入输出格式相关的任务,例如读取和写入文件、数据库等)
- 添加对应的上游数据集
- 缓存JobVertex相关信息
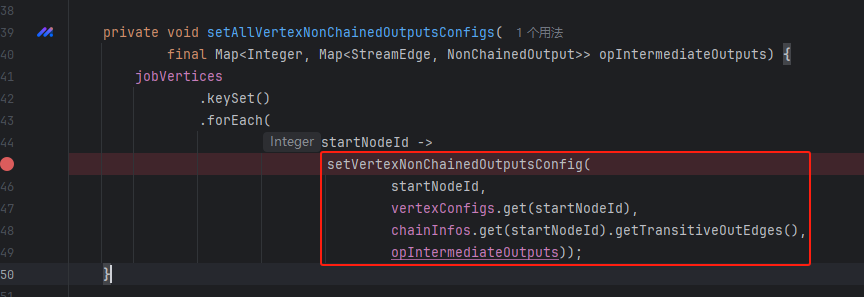
生成JobEdge、IntermediateDataSet(setAllVertexNonChainedOutputsConfigs)
遍历jobVertices,调用connect连接起来。
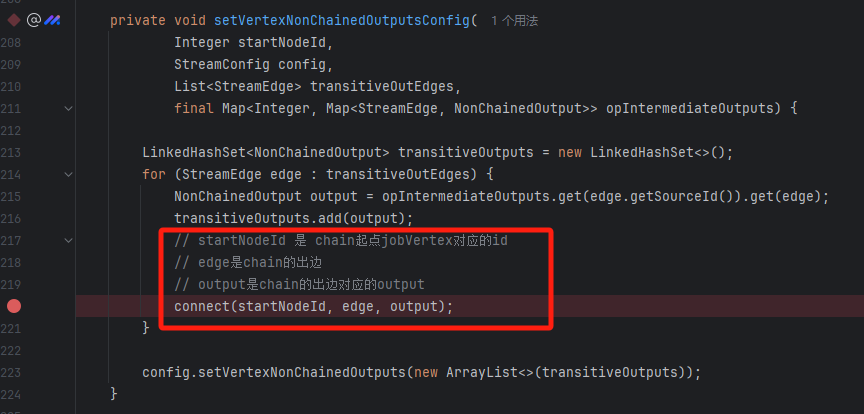
connect
将两个JobVertex(headVertex、downStreamVertex)连接起来。关键方法是downStreamVertex.connectNewDataSetAsInput
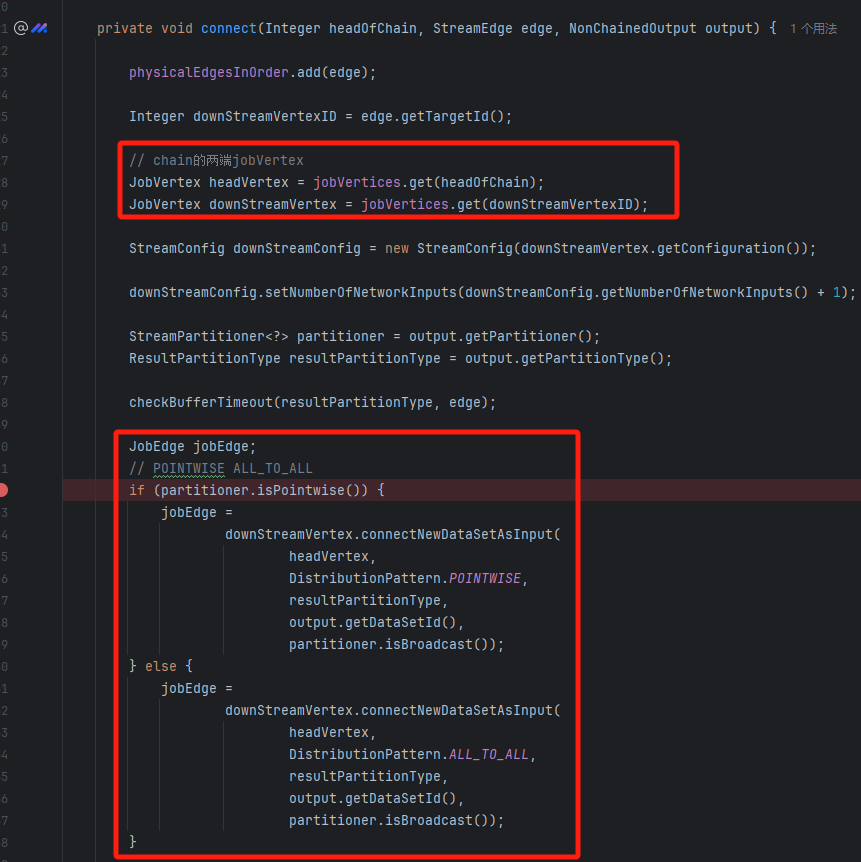
connectNewDataSetAsInput
创建IntermediateDataSet和JobEdge,形成JobVertex->IntermediateDataSet->JobEdge->JobVertex