各位看官早安午安晚安呀
如果您觉得这篇文章对您有帮助的话
欢迎您一键三连,小编尽全力做到更好
欢迎您分享给更多人哦
大家好,我们今天来学习java数据结构的二叉树
递归很重要的一些注意事项:
- 1:递归你能不能掌握在于:你能不能想清楚第一层非递归 以及 递归结束的条件(也就是最后一层递归,有时候递归结束的条件可能有好几个这很常见)(结束的条件仔细想一下是否能够合并呢?return root,return null,下一层root啥也没干,root == null,是否能够合并呢?这个其实无伤大雅,但是能合并尽量还是合并一下)(这两个场景你能够想清楚,你基本思路就没什么问题)
- 2:递归有返回值的
- 2.1:如果有返回值,你大概率是要接收你下一层递归的返回值 ()(然后你进行整理完之后继续向上返回)
- 2.2:递归如果返回值是要叠加的,譬如求二叉树的高度的,这个返回值一定要接收。
1.1.判断两个二叉树是否相等
java
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(p == null && q != null || p != null && q == null){ //结构不一样不相等
return false;
}
if(p == null && q == null){ // 看你俩只要同时为空就相等
return true;
}
return p.val == q.val && isSameTree(p.left,q.left) && isSameTree(p.right,q.right);
}1.2.相同的二叉树
java
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(p == null && q != null || p != null && q == null){
return false;
}
if(p == null && q == null){
return true;
}
return p.val == q.val && isSameTree(p.left,q.left) && isSameTree(p.right,q.right);
}
public boolean isSubtree(TreeNode root, TreeNode subRoot) {
if(isSameTree(root,subRoot)){ //判断一开始就是否相等
return true;
}
if(root == null){
return false;
}
if(isSubtree(root.left,subRoot) || isSubtree(root.right,subRoot)){ //左边和右边一个相等就行
//其实这个就是前序遍历,利用返回值
return true;
}
return false;
}1.3.翻转二叉树
java
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return null;
}
//交换节点
TreeNode tmp = root.left;
root.left = root.right;
root.right = tmp;
//翻转
invertTree(root.left);
invertTree(root.right);
return root;
}
1.4.平衡二叉树
补充知识点:
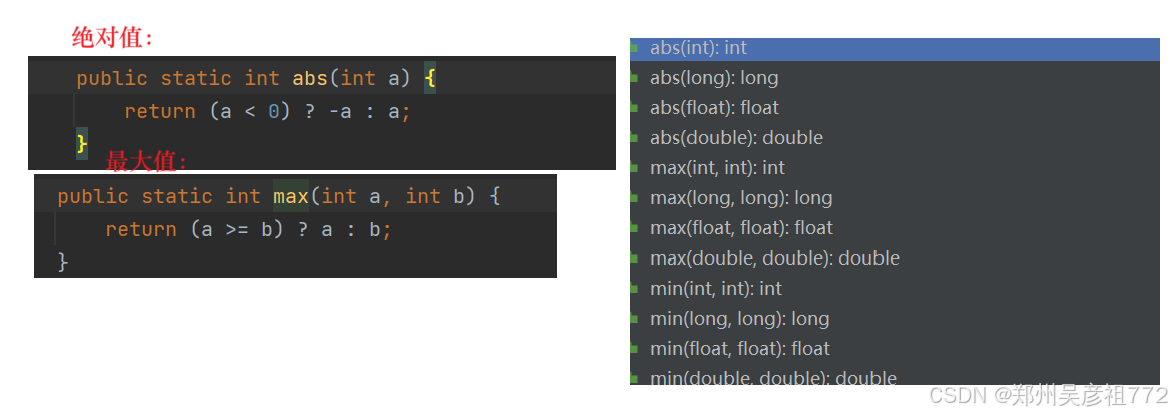
java
//更改的平衡二叉树,因为我们在算高度的时候每一颗子树的高度我们都算过,我们完全可以算整个树的高度
//然后进行顺带算两边的高度差是否 <= 1,一次性算完
int getHeight2(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
//左树高度和右树高度
int leftHeight = getHeight2(root.left);
int rightHeight = getHeight2(root.right);
//两边高度差<= 1并且都大于0(任何一个高度为-1的时候,整个树的返回值就为-1(-1代表不平衡))
// 只要有一个-1返回,那么之后都是返回-1,不平衡
if(Math.abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) <= 1 && leftHeight >= 0 && rightHeight >= 0){
return Math.max(leftHeight,rightHeight)+1;
}
return -1;
}
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return true;
}
return getHeight2(root) >= 0;
}1.5.对称二叉树
java
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return true;
}
//我要看是否对称,肯定要两个节点进行比较,要两个变量
return isSample(root.left,root.right);
}
public boolean isSample(TreeNode p , TreeNode q){
//两边都是空的,就一个根,直接返回true
if( p == null && q == null){
return true;
}
//一个为空另一个不为空,直接返回false
if( p == null || q == null){
return false;
}
if(p.val != q.val){
return false;
}
return isSample(p.left,q.right) && isSample(p.right,q.left);
}
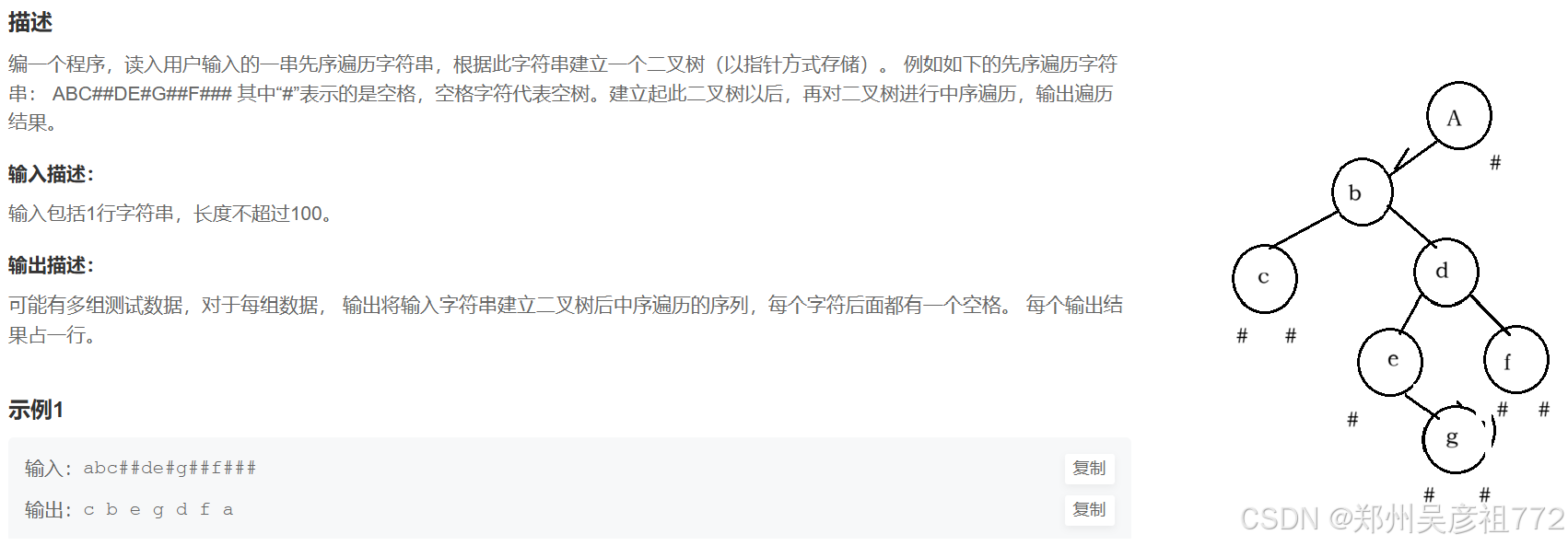
1.6.通过字符串构建二叉树
java
import java.util.Scanner;
class TreeNode{
char val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(){
}
public TreeNode(char val){
this.val = val;
}
}
// 注意类名必须为 Main, 不要有任何 package xxx 信息
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
// 注意 hasNext 和 hasNextLine 的区别
while (in.hasNextLine()) { // 注意 while 处理多个 case
String str = in.nextLine();
//创建二叉树
TreeNode root = create(str);
//中序遍历
inorder(root);
}
}
public static int i = 0;
public static TreeNode create(String str){ //递归的第一层要素就是要知道什么时候结束
// 首先我们遇到 "#" 就要返回 ,但是我们的i还是要先++ 后返回
if(str.charAt(i) == '#'){//但是我们要考虑的是,我们就算是返回了,我们的遍历str的i还是要往前走
i++;
return null;
}else{
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(str.charAt(i));
i++;
root.left = create(str);
root.right = create(str);
return root;
}
//最后你会发现其实这两个返回值可以合并成一个,//其实每次递归题大家都可以看一下
}
//中序遍历
public static void inorder(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return;
}
inorder(root.left);
System.out.print(root.val +" ");
inorder(root.right);
}
}
1.7.二叉树分层遍历:
java
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();//别问 问就是OJ的测试用例让我这么干的
// root = [] 预期结果[],所以下面返回的也是List而不是null
if(root == null){ //如果根节点都是null,就不用遍历了
return list;
}
// 先把 根节点add进去队列里面
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
//tmp.add(root);//这里不对呀,最后一倍一倍的增长。这个size也不对,看我下面如何修改
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
//int size = tmp.size();
List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();//这个可不敢放在一开始呀,不然又叠加了(ArrayList好一点)
int size = queue.size();//计算上一次add进来的总和, 下面直接就是 size!=0,这完全就是要把上一次的全poll出去
while (size != 0) { //和上一个的区别就在于,上一个层序遍历是一个一个出队列的,这个是一次性把上一次add进来的全部poll出去
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
tmp.add(cur.val);
// System.out.println(cur.val + " ");
size--;//记得--;
if (cur.left != null) {
queue.offer(cur.left);
}
if (cur.right != null) {
queue.offer(cur.right);
}
}
list.add(tmp);
}
return list;
}
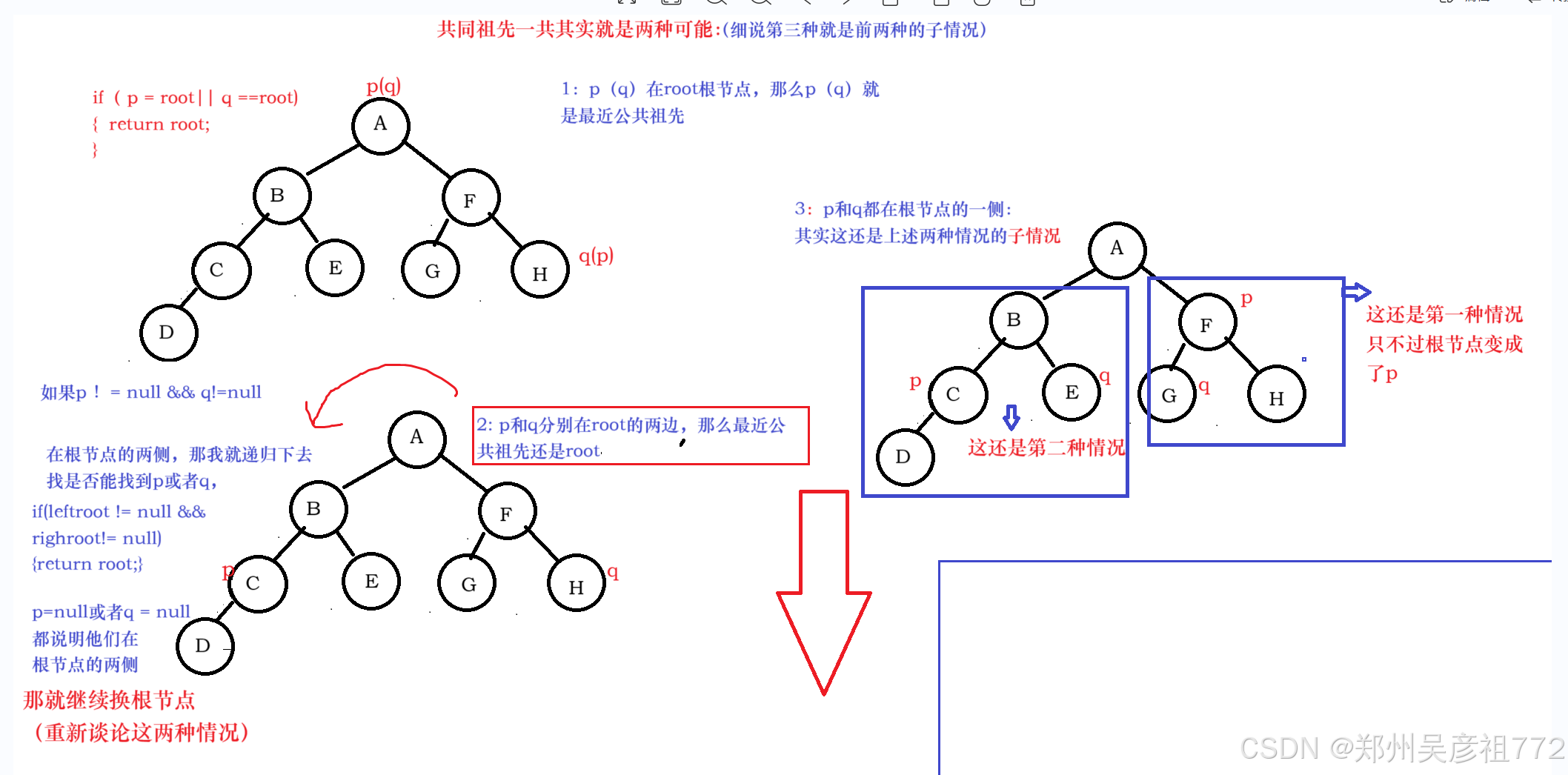
1.8.二叉树的最近公共祖先
java
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(p == root || q == root){
return root;
}
if(root == null){
return null;
}
TreeNode leftRoot = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
TreeNode rightRoot = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
if(leftRoot != null && rightRoot != null){
return root;
} else if (leftRoot != null) {
return leftRoot;
}else{
return rightRoot;
}
}
解法二:看成两个链表相交,找相交点
java
private boolean getPath(TreeNode root,TreeNode node,Stack<TreeNode>stack){
// 判断这个节点是不是这个路径上的节点(如果不是,看看它的左子树和右子树是不是这个路径上的节点如果都不是)
//就返回false,把这个节点pop出来
if(root == null || node == null){
return false;
}
stack.push(root);
//一定要压进去,不然root == node 导致这个栈里面没有了元素
if(root == node){
return true;
}
boolean flg1 = getPath(root.left,node,stack);
//看看左节点有没有
if(flg1){
return true;
}
boolean flg2 = getPath(root.right,node,stack);
//看看右节点有没有
if(flg2){
return true;
}
//都没有就return false
stack.pop();
return false;
}
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
Stack<TreeNode>stack1 = new Stack<>();
Stack<TreeNode>stack2 = new Stack<>();
//利用getPath初始化这两个栈
getPath(root,p,stack1);
getPath(root,q,stack2);
//初始化之后,进行比较,让长栈先走size步
int size = stack1.size() -stack2.size();
if(size > 0){
while(size != 0){
stack1.pop();
size--;
}
}else{
while(size != 0){
stack2.pop();
size++;
}
}
while(!stack1.isEmpty() && ! stack2.isEmpty()){ //&&后面的写不写都行
if(stack1.peek().equals(stack2.peek())){
return stack1.peek();
}
stack1.pop();
stack2.pop();
}
return null;
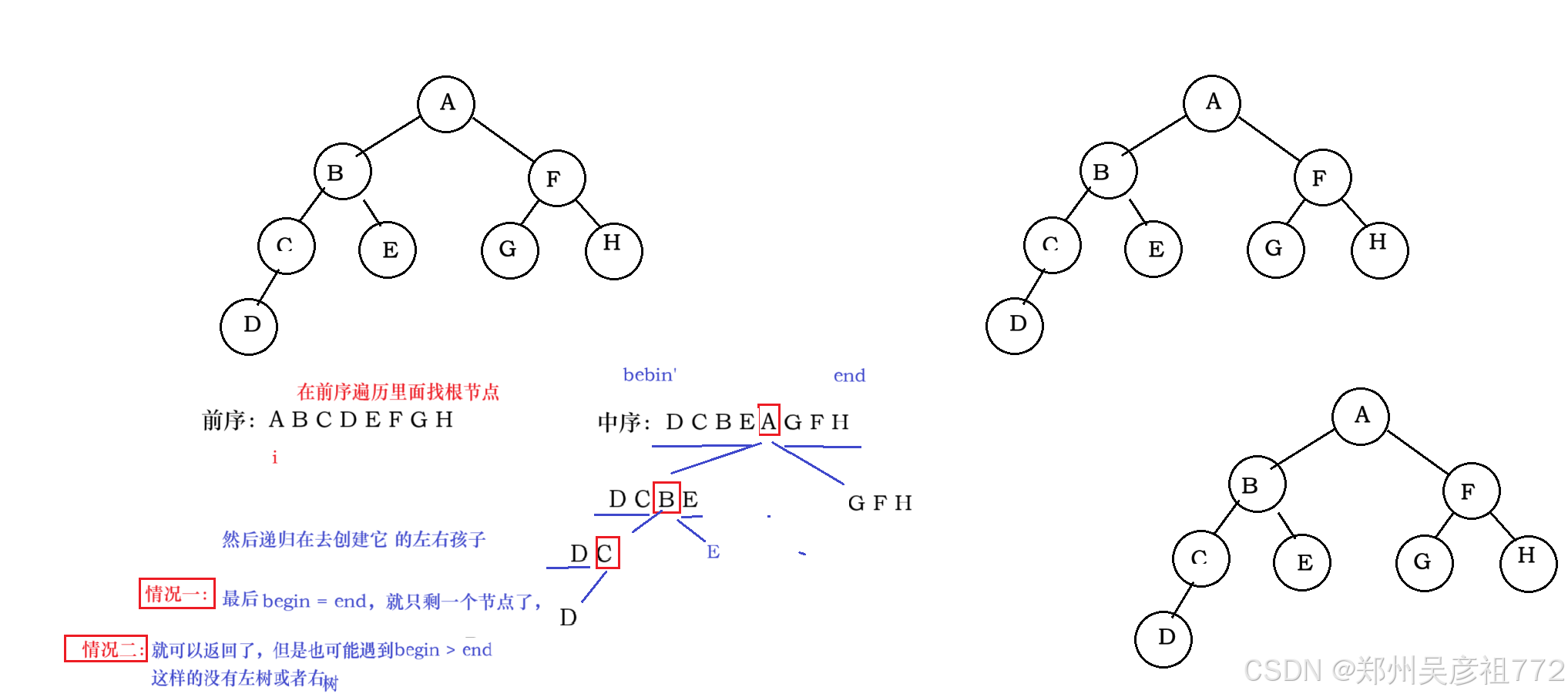
}1.9. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
java
class Solution {
public int preIndex;//一定要设置成成员变量(全局效果),局部变量的话放方法参数里,每次都是传值调用
//不能保证preIndex一直往前走
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
return buildTreeChild(preorder,inorder,0,inorder.length -1);
}
private TreeNode buildTreeChild(int[] preorder,int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend){
if(inbegin > inend ){ //其实这里的结束有两次,inbegin = inend 也应该结束(但是合并成一种情况了)
return null;
}
if(inbegin == inend){
int pre = preIndex;
preIndex++;
return new TreeNode(preorder[pre]);
}
//先看这个(前序遍历的)节点是否在中序遍历的这个范围内,在的话我再把这个根节点给创建出来
int rootIndex = findIndex(inorder,inbegin,inend,preorder[preIndex]);
if(rootIndex == -1){
return null;
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[preIndex]);
preIndex++;
root.left = buildTreeChild(preorder,inorder,inbegin,rootIndex-1);
root.right = buildTreeChild(preorder,inorder,rootIndex + 1,inend);
return root;
}
private int findIndex(int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend,int key){
for(int i = inbegin; i<= inend ; i++){
if(inorder[i] == key){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
}

1.10.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
如果后序:是先递归右树,再左树,再根(此刻的后序的字符串就是前序的逆转)
java
class Solution {
public int postIndex ;//一定要设置成成员变量(全局效果),局部变量的话放方法参数里,每次都是传值调用
//不能保证preIndex一直往前走
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
postIndex = postorder.length -1;
return buildTreeChild(postorder,inorder,0,inorder.length -1);
}
private TreeNode buildTreeChild(int[] postorder,int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend){
if(inbegin > inend ){ //其实这里的结束有两次,inbegin = inend 也应该结束(但是合并成一种情况了)
return null;
}
//先看这个(前序遍历的)节点是否在中序遍历的这个范围内,在的话我再把这个根节点给创建出来
int rootIndex = findIndex(inorder,inbegin,inend,postorder[postIndex]);
if(rootIndex == -1){
return null;
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(postorder[postIndex]);
postIndex--;
root.right = buildTreeChild(postorder,inorder,rootIndex + 1,inend);
root.left = buildTreeChild(postorder,inorder,inbegin,rootIndex-1);
return root;
}
private int findIndex(int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend,int key){
for(int i = inbegin; i<= inend ; i++){
if(inorder[i] == key){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
}1.11.前序遍历二叉树(迭代实现)
java
public static void preOrder1(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
//本质上这还是递归的思想(stack还是往回走,不然你路上的节点,没办法遍历他的右边;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {// 加个cur !=null,纯粹是因为,第一次stack是空的
while (cur != null) {//一直往
System.out.print(cur.val);
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
//其实一开始我是这么想的
/*if(cur == null){
cur = stack.pop();
cur = cur.right;
//但是这样就废了呀,右边为空就完蛋了,循环结束,gameOver
}*/
}
//左边为空,直接就拿回我上一个根,然后打印右边
cur = stack.pop();
cur = cur.right;
}
}1.11.中序遍历二叉树(迭代实现)
javapublic static void inOrder1(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return; } //本质上这还是递归的思想(stack还是往回走,不然你路上的节点,没办法遍历他的右边; Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>(); TreeNode cur = root; while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {// 加个cur !=null,纯粹是因为,第一次stack是空的 while (cur != null) {//一直往 stack.push(cur); cur = cur.left; } //左边为空,直接就拿回我上一个根,然后打印右边 cur = stack.pop(); System.out.print(cur.val); cur = cur.right; } }
1.11.后序遍历二叉树(迭代实现)
java
//根据字符串循环进行后序遍历
public static void postOrder1(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
//本质上这还是递归的思想(stack还是往回走,不然你路上的节点,没办法遍历他的右边;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
TreeNode prev = null;
TreeNode top = null;
while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {// 加个cur !=null,纯粹是因为,第一次stack是空的
while (cur != null) {//一直往
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}
//左边为空,直接就拿回我上一个根,然后打印右边
top = stack.peek();
if(top .right == null || top.right == prev){
stack.pop();
System.out.print(top.val + " ");
prev = top;
}else {
// 右边不为空不能pop
cur = top.right;
}
}
}上述就是二叉树习题讲解的全部内容了,能看到这里相信您一定对小编的文章有了一定的认可,二叉树的出现让我们对于数据的组织的利用有了更加方便的使用~~
有什么问题欢迎各位大佬指出
欢迎各位大佬评论区留言修正

您的支持就是我最大的动力!!!!

