1、开发c代码
引用的库
/usr/include
c代码
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/un.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define SOCKET_PATH "/tmp/my_socket"
int main() {
int server_fd, new_socket;
struct sockaddr_un address;
int opt = 1;
int addrlen = sizeof(address);
char buffer[1024] = { 0 };
const char *hello = "Hello from C server!";
// 创建套接字文件描述符
if ((server_fd = socket(AF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM, 0)) == 0) {
perror("socket failed");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
// 设置套接字地址结构
address.sun_family = AF_UNIX;
strcpy(address.sun_path, SOCKET_PATH);
// 绑定套接字到指定路径
if (bind(server_fd, (struct sockaddr *)&address, sizeof(address)) < 0) {
perror("bind failed");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
// 监听连接
if (listen(server_fd, 3) < 0) {
perror("listen");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("Server listening on %s...\n", SOCKET_PATH);
// 接受客户端连接
if ((new_socket = accept(server_fd, (struct sockaddr *)&address, (socklen_t*)&addrlen)) < 0) {
perror("accept");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
// 读取客户端发送的数据
int valread = read(new_socket, buffer, 1024);
if (valread < 0) {
perror("read");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("Received from client: %s\n", buffer);
// 发送响应给客户端
send(new_socket, hello, strlen(hello), 0);
printf("Message sent to client\n");
// 关闭套接字
close(new_socket);
close(server_fd);
unlink(SOCKET_PATH);
return 0;
}编译
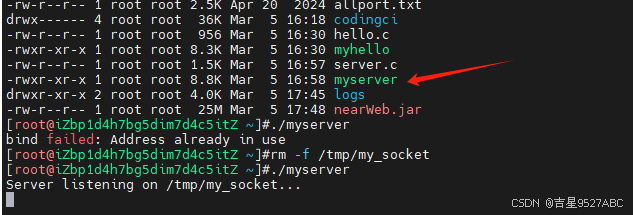
gcc -o myserver server.c
执行
2、开发java代码
引入第三方库junixsocket ,注意这里的type是pom
https://gitcode.com/gh_mirrors/ju/junixsocket/blob/main/junixsocket-demo/src/main/java/org/newsclub/net/unix/demo/SimpleTestClient.java
XML
<dependency>
<groupId>com.kohlschutter.junixsocket</groupId>
<artifactId>junixsocket-core</artifactId>
<version>2.10.1</version>
<type>pom</type>
</dependency>代码
java
package com.example.service;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.SocketException;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import org.newsclub.net.unix.AFUNIXSocket;
import org.newsclub.net.unix.AFUNIXSocketAddress;
public class SimpleTestClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// final File socketFile = new File(new File(System.getProperty("java.io.tmpdir")),
// "junixsocket-test.sock");
final File socketFile = new File("/tmp/my_socket");
boolean connected = false;
try (AFUNIXSocket sock = AFUNIXSocket.connectTo(AFUNIXSocketAddress.of(socketFile));
InputStream is = sock.getInputStream(); //
OutputStream os = sock.getOutputStream();
DataInputStream din = new DataInputStream(is);
DataOutputStream dout = new DataOutputStream(os);) {
System.out.println("Connected");
connected = true;
byte[] buf = new byte[128];
int read = is.read(buf);
System.out.println("Server says: " + new String(buf, 0, read, StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
System.out.println("Replying to server...");
os.write("Hello Server".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
os.flush();
System.out.println("Now reading numbers from the server...");
while (!Thread.interrupted()) {
int number = din.readInt();
if (number == -123) {
// by convention of this demo, if the number is -123, we stop.
// If we don't do this, we'll get an EOFException upon the next unsuccessful read.
break;
}
System.out.println(number);
int ourNumber = number * 2;
System.out.println("Sending back " + ourNumber);
dout.writeInt(ourNumber);
}
} catch (SocketException e) {
if (!connected) {
System.out.println("Cannot connect to server. Have you started it?");
System.out.println();
}
throw e;
}
System.out.println("End of communication.");
}
}打包
利用idea,创建Artifacts
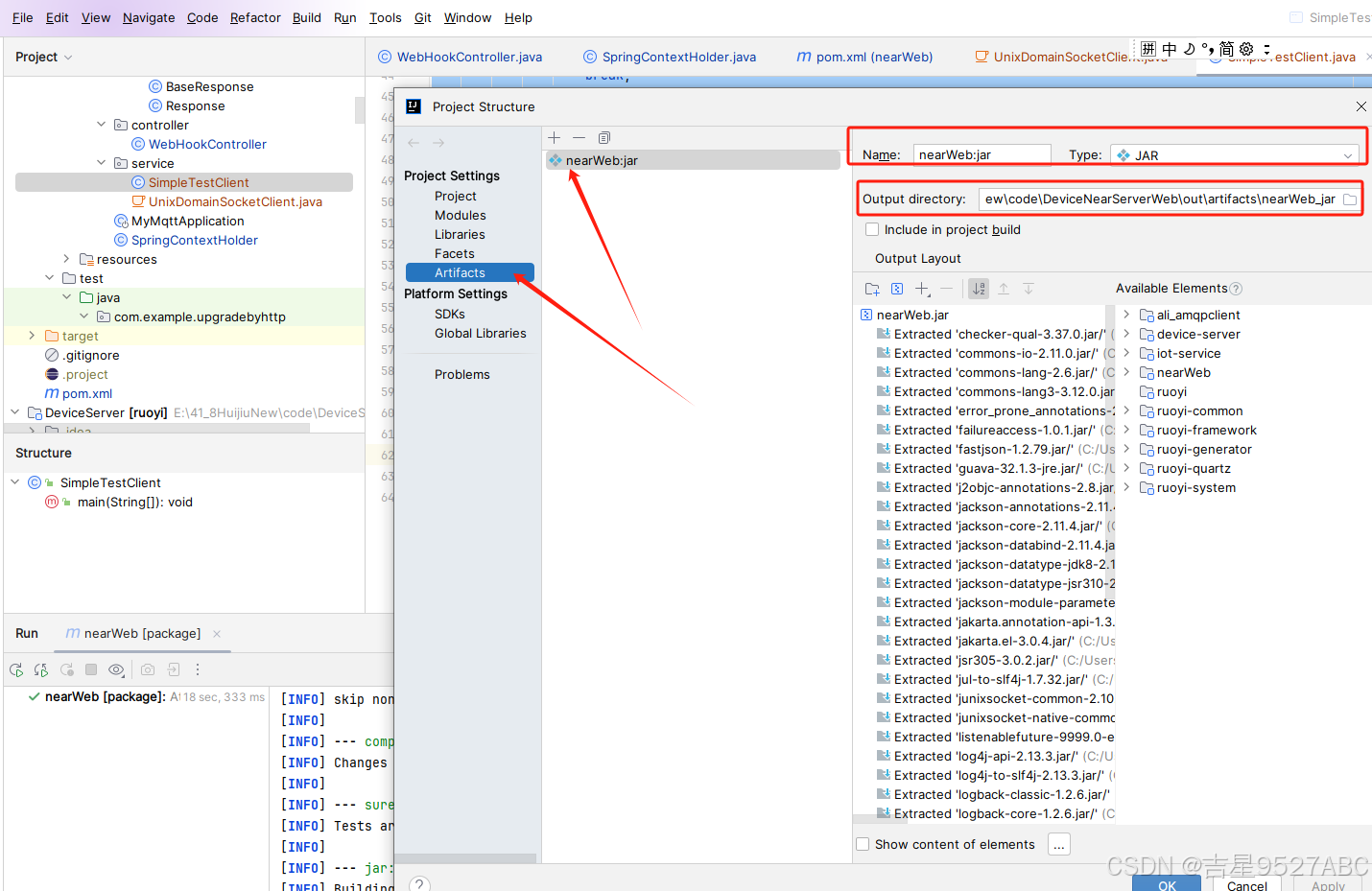
Build Artifacts
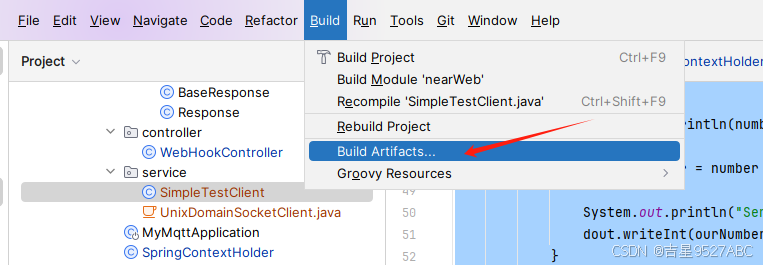
执行
java -jar nearWeb.jar