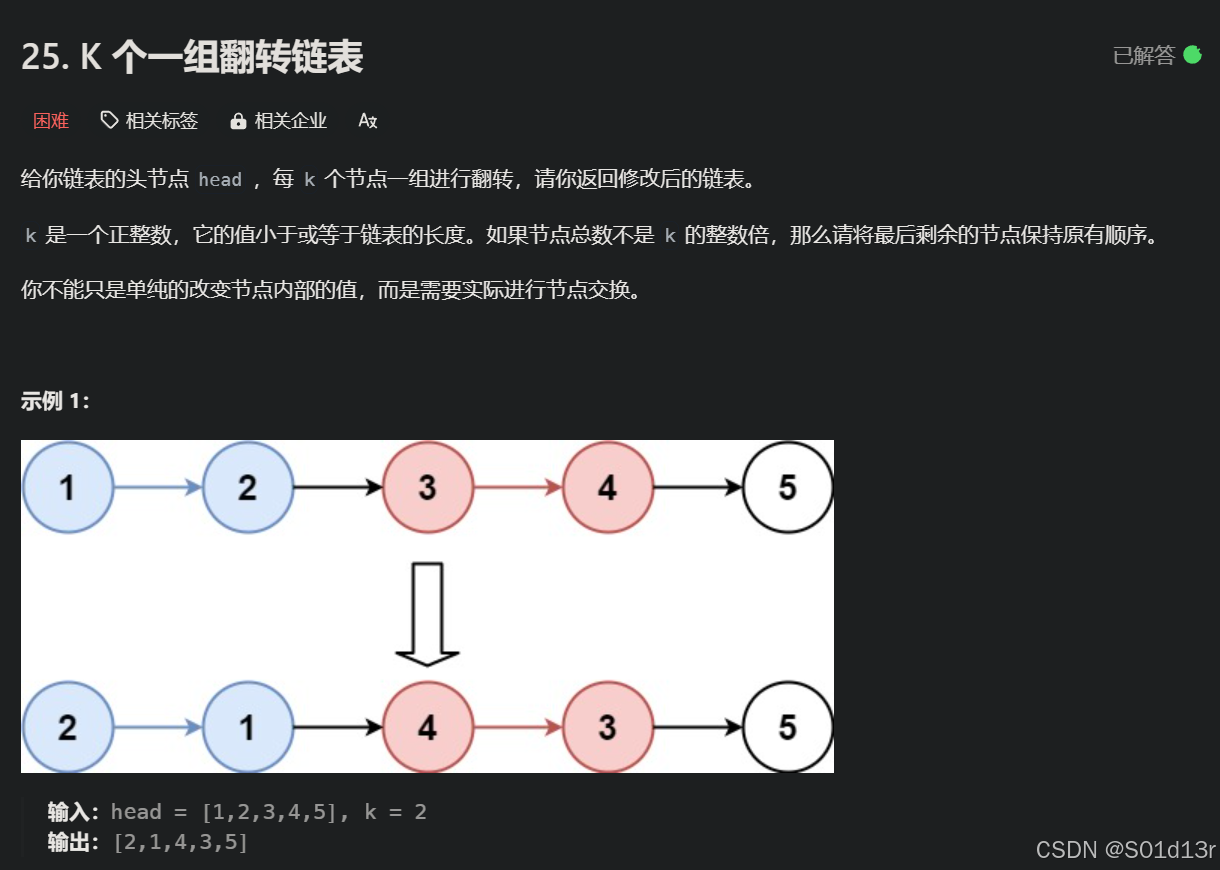
解题思路:
- 初始化辅助节点:
- dummy:哑节点。
- pre:当前链表的前一个节点。
- start:当前链表的第一个节点。
- end:当前链表的最后一个节点。
- nextStart:end.next,下组链表的第一个节点,用于连接当前链表尾部。
- 翻转当前的链表:
- 断开当前链表与剩余链表组,end.next = null。
- 通过 start 翻转链表并得到翻转后的头节点 newHead = reverse(start)。
- 连接翻转后链表:
- 头部:pre.next = newHead;
- 尾部:start.next = nextStart;
- 更新状态: pre = start。
Java代码:
java
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
if (head.next == null || k == 1) return head;
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode pre = dummy;
while (true) {
ListNode start = pre.next;
ListNode end = pre;
for(int i = 0; i < k && end != null; i++){
end = end.next;
}
if (end == null) break;
ListNode nextStart = end.next;
end.next = null;
ListNode newHead = reverse(start);
pre.next = newHead;
start.next = nextStart;
pre = start;
}
return dummy.next;
}
public ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {
ListNode current = head;
ListNode pre = null;
while (current != null) {
ListNode temp = current.next;
current.next = pre;
pre = current;
current = temp;
}
return pre;
}
}复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(n)。
- 空间复杂度: O(1),无额外空间占用。
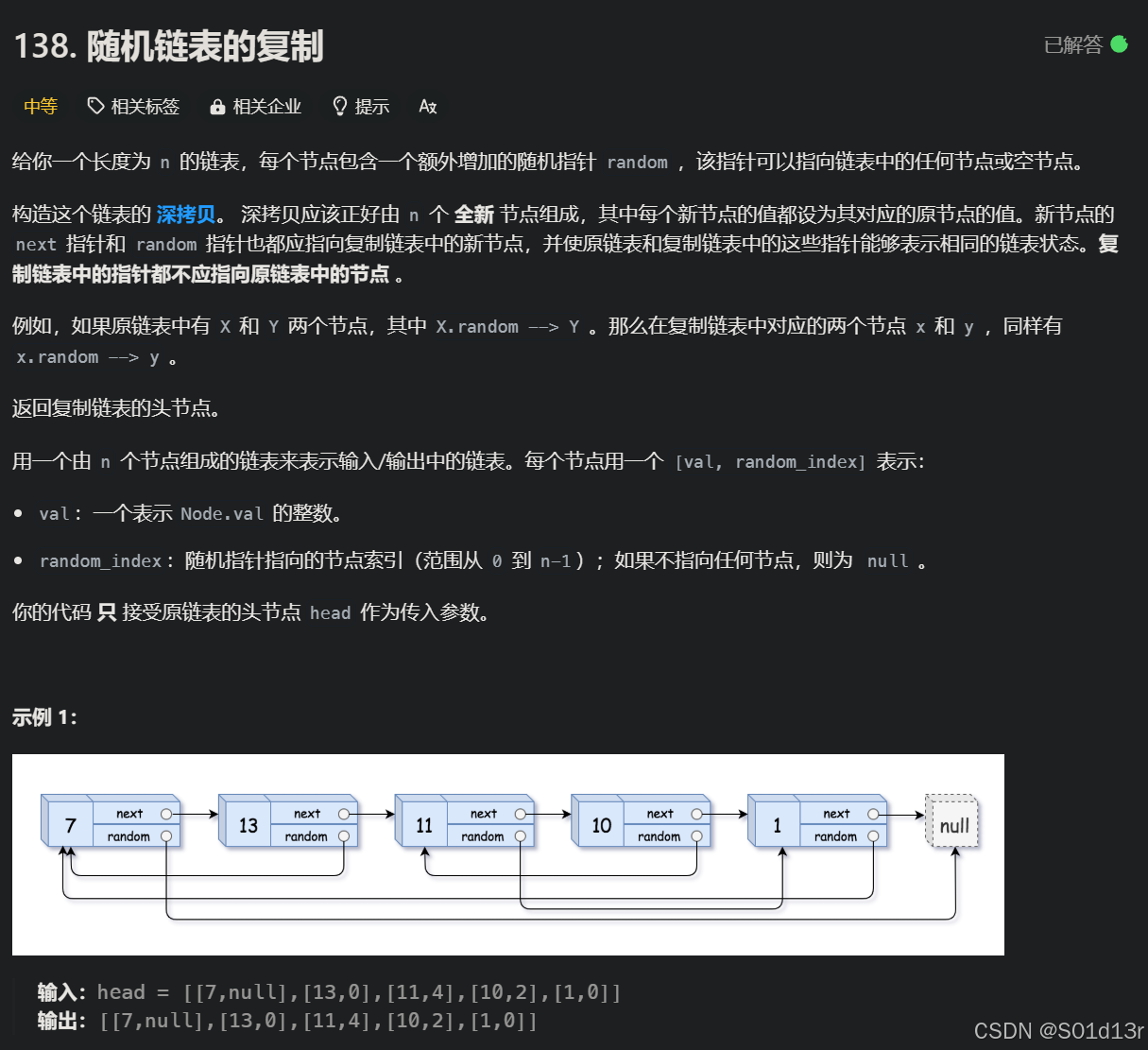
解题思路:
- 第一次遍历: 创建复制节点并建立映射。
- 第二次遍历: 设置next和random指针。
Java代码:
java
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if (head == null) return null;
Map<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<>();
Node pre = head;
while (pre != null) {
map.put(pre, new Node(pre.val));
pre = pre.next;
}
pre = head;
while (pre != null) {
Node copy = map.get(pre);
copy.next = map.get(pre.next);
copy.random = map.get(pre.random);
pre = pre.next;
}
return map.get(head);
}
}复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(n),需要两次遍历链表,每次遍历时间为 O(n),总时间为 O(2n) = O(n)。
- 空间复杂度: O(n),哈希表存储所有原节点到复制节点的映射,占用 O(n) 空间。