文章目录
[1. 安装Chrome和Chrome Driver](#1. 安装Chrome和Chrome Driver)
[2. 安装Python库](#2. 安装Python库)
[1. init_driver 函数](#1. init_driver 函数)
[2. play_2048 函数](#2. play_2048 函数)
[1. 棋盘状态获取](#1. 棋盘状态获取)
[2. 位置权重系统](#2. 位置权重系统)
[3. 连续性评估](#3. 连续性评估)
[4. 单调性评估](#4. 单调性评估)
[5. 移动模拟系统](#5. 移动模拟系统)
[1. 评估标准](#1. 评估标准)
[2. 决策机制](#2. 决策机制)
[1. 延迟控制](#1. 延迟控制)
[2. 错误处理](#2. 错误处理)
一、创作背景
厌倦了手动滑动方块,在2048的海洋中挣扎?是时候让AI接管了!这是一个基于Python和Selenium的2048游戏AI程序,通过模拟浏览器操作实现自动玩游戏。下面我们一起构建游戏环境、设计AI算法,并最终见证AI如何以惊人的策略和速度,突破2048!
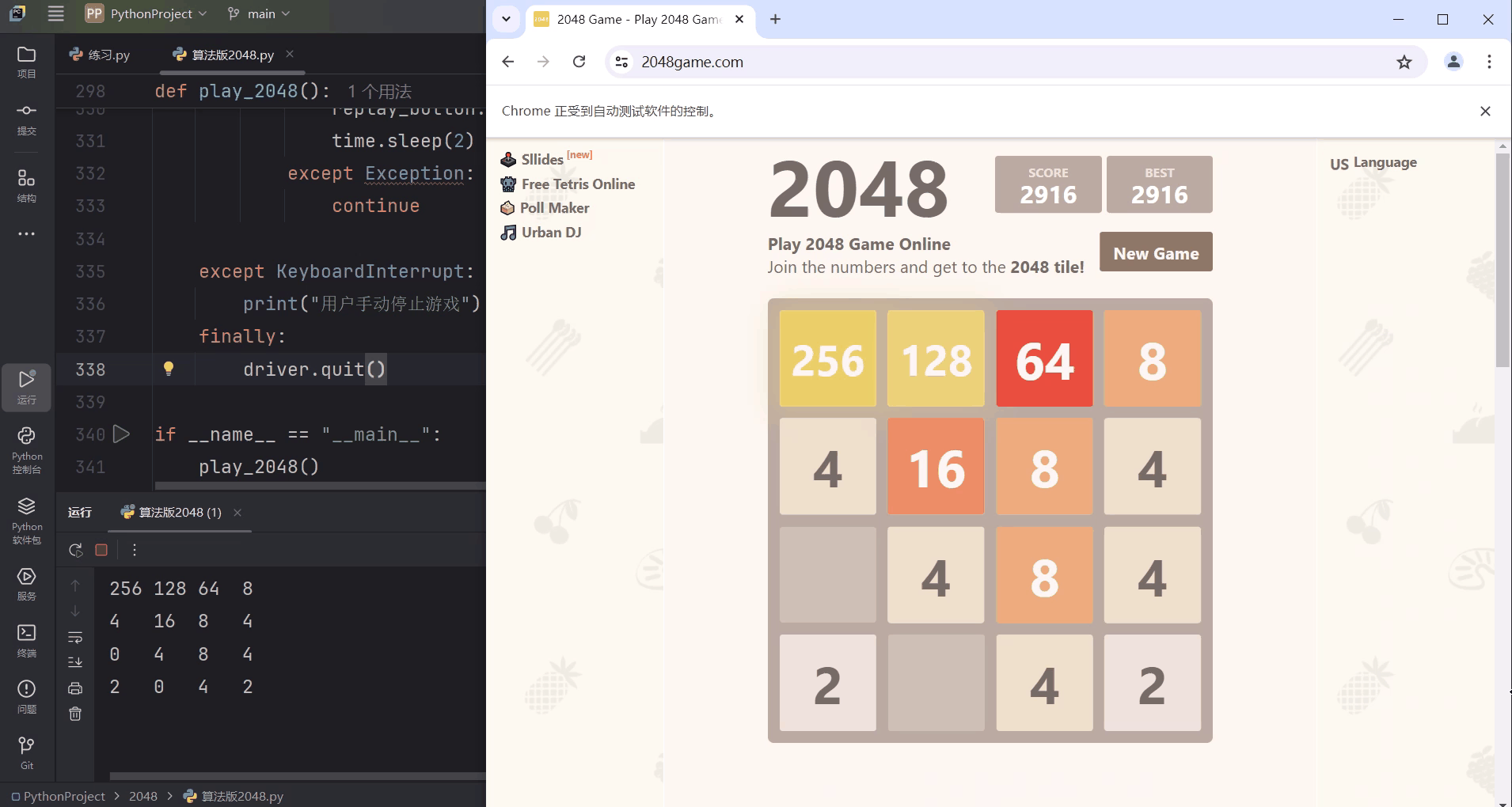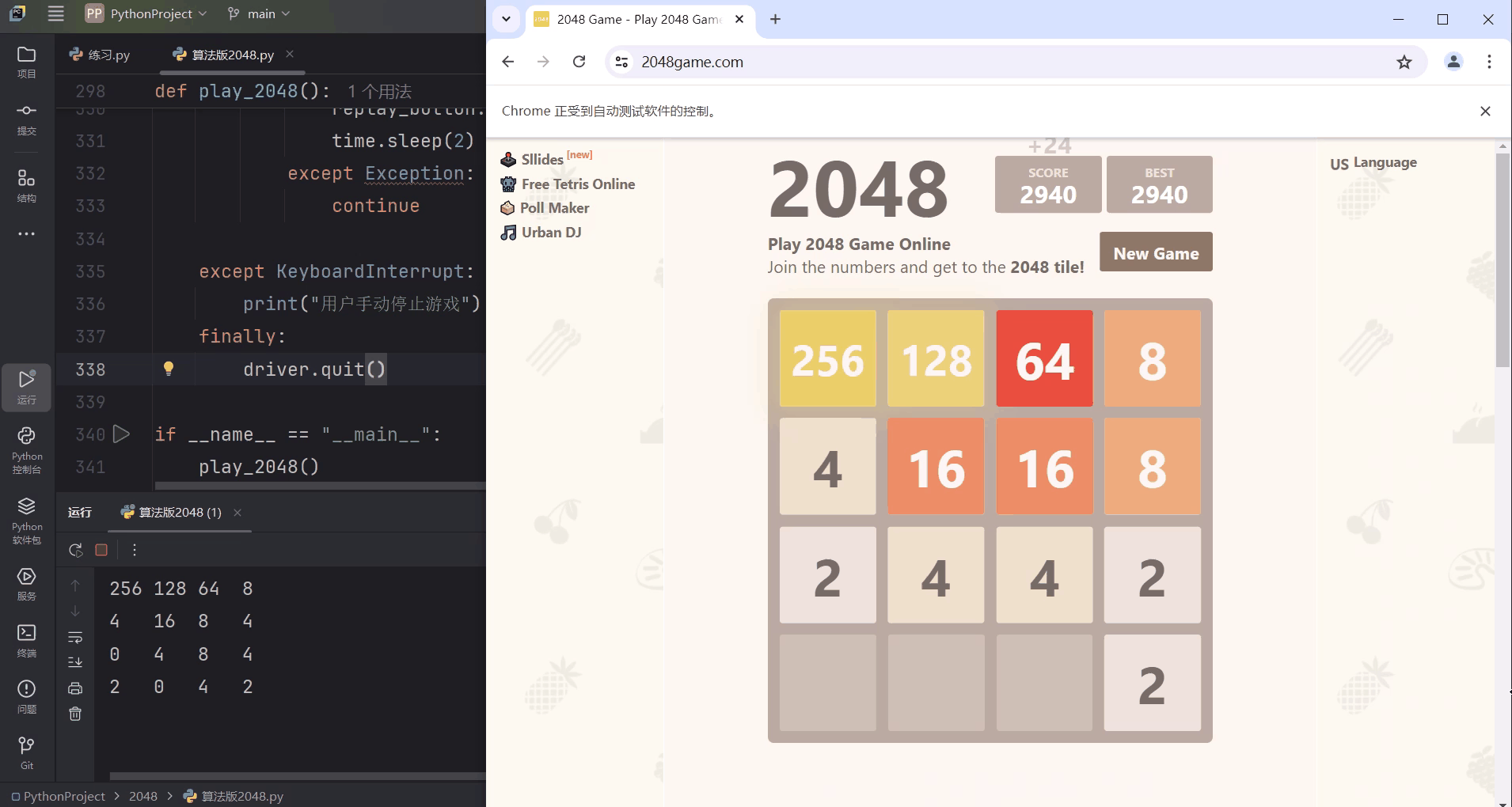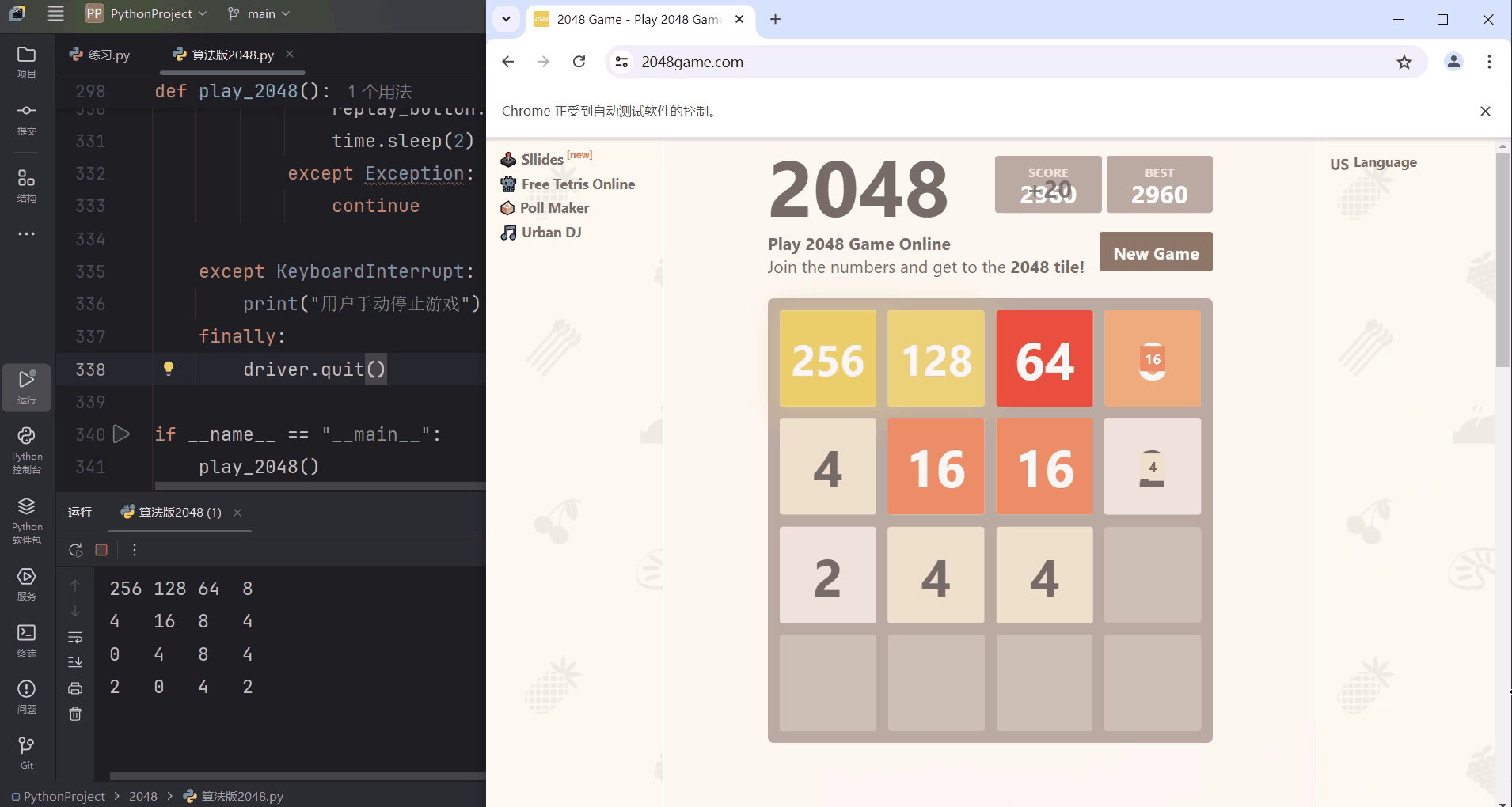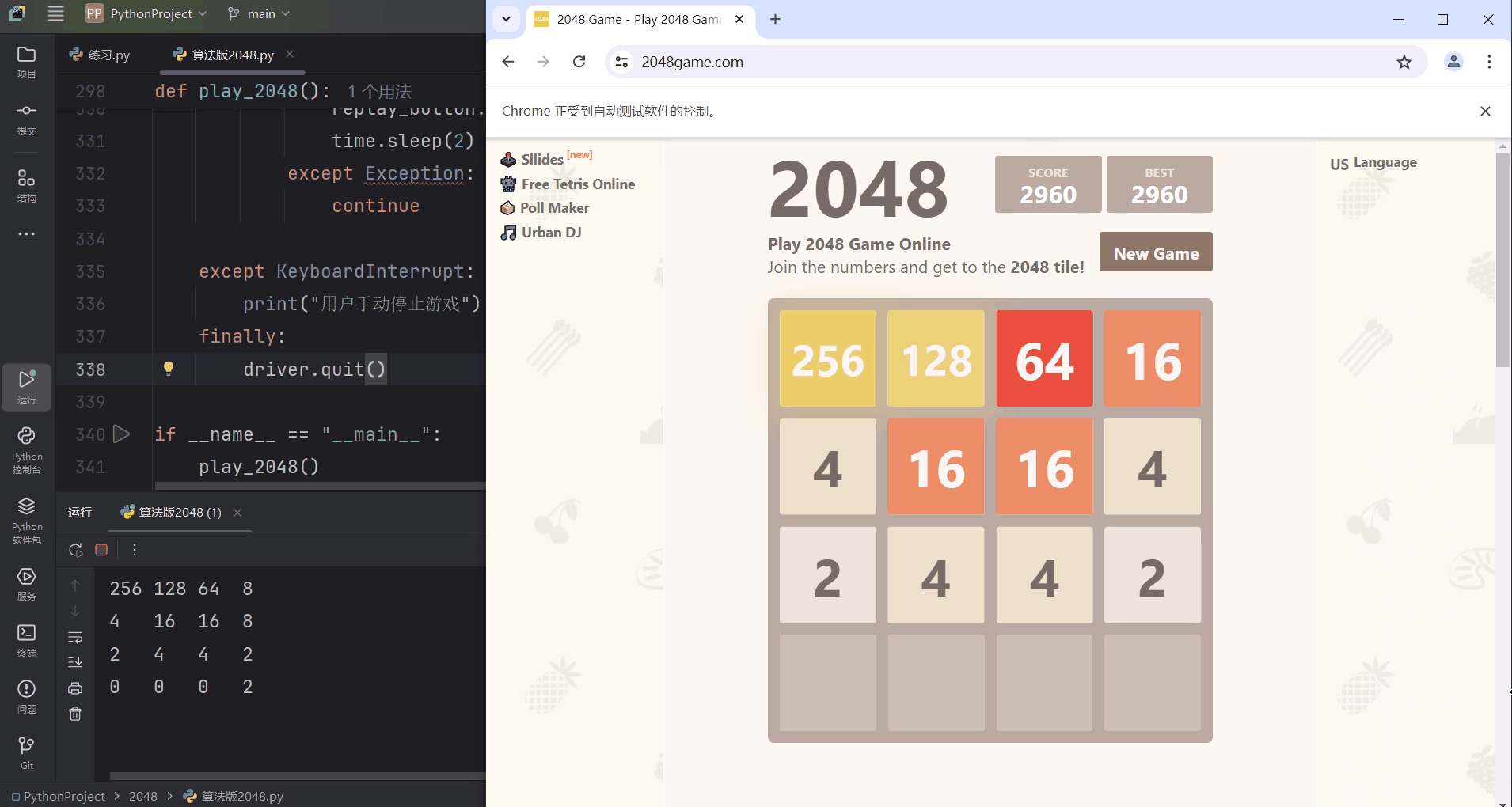
二、效果图
说明:模拟Chrome浏览器登入2048小游戏网站,AI将自动开始游戏,Pycharm终端输出实时棋盘
三、准备工作
1. 安装Chrome和Chrome Driver
下载与 Chrome 浏览器和与之版本匹配的 ChromeDriver,并将其路径添加到系统 PATH 中,或在代码中指定路径。
具体细节可参考这两篇文章:彻底解决 Selenium ChromeDriver 不匹配问题:Selenium ChromeDriver 最新版本下载安装教程_driver = webdriver.chrome-CSDN博客
ChromeDriver下载安装 - chenhongl - 博客园
2. 安装Python库
pip install selenium四、代码说明
1. init_driver 函数
初始化 Chrome WebDriver
2. play_2048 函数
使用 driver.get(GAME_URL) 打开 2048 游戏网页。
等待游戏加载完成(这里使用简单的 time.sleep(2),可根据实际情况调整)。
通过 driver.find_element_by_tag_name('body') 获取游戏主体元素,用于发送键盘指令。
在无限循环中,随机选择一个移动方向,并发送键盘指令。
使用 time.sleep(random.uniform(*DELAY_RANGE)) 实现随机延迟,模拟人类操作。
检查游戏是否结束,这里通过尝试点击"重玩"按钮来判断。如果找到"重玩"按钮,则打印最终得分并点击按钮开始新游戏;如果找不到,则继续游戏循环。
捕获 KeyboardInterrupt 异常,允许用户通过 Ctrl+C 手动停止游戏。
在 finally 块中确保 WebDriver 正常关闭。
五、完整代码
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
from selenium.webdriver.common.keys import Keys
import time
import random
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.service import Service
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.options import Options
# 游戏网址
GAME_URL = 'https://2048game.com/'
# 指定 Chrome以及Chrome Driver可执行文件路径
chrome_path = {"Windows": r"你自己电脑上chrome可执行文件的绝对路径",}
options = Options()
options.binary_location = chrome_path["Windows"]
driver_path = r'你自己电脑上chrome Driver所在目录'
service = Service(executable_path=driver_path)
# 定义移动方向
MOVES = [Keys.ARROW_UP, Keys.ARROW_RIGHT, Keys.ARROW_DOWN, Keys.ARROW_LEFT]
# 随机延迟时间范围(秒)
DELAY_RANGE = (0.5, 1.5)
def init_driver():
driver = webdriver.Chrome(service=service, options=options)
return driver
def play_2048():
driver = init_driver()
try:
driver.get(GAME_URL)
# 等待游戏加载完成(可根据实际情况调整等待时间)
time.sleep(2)
game_board = driver.find_element(By.TAG_NAME, 'body')
while True:
# 随机选择一个移动方向
move = random.choice(MOVES)
game_board.send_keys(move)
# 随机延迟
time.sleep(random.uniform(*DELAY_RANGE))
# 检查游戏是否结束(可根据页面元素调整检查逻辑)
# 这里简单通过尝试点击"重玩"按钮来判断游戏是否结束,如果不存在则继续游戏
try:
replay_button = driver.find_element(By.CLASS_NAME, 'replay-button')
print("游戏结束!最终得分:", driver.find_element(By.CLASS_NAME, 'score-board').text.split()[-1])
replay_button.click()
# 等待新游戏开始
time.sleep(2)
except Exception:
# 如果找不到"重玩"按钮,则继续游戏循环
continue
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("用户手动停止游戏")
finally:
driver.quit()
if __name__ == "__main__":
play_2048()六、改进版本
由于采用的策略是随机移动,因此游戏表现性能不稳定,得分不高。下面将介绍一种更智能的移动策略来提高游戏成绩。
主要特点包括:
-
采用启发式评估系统进行决策
-
实现了基于位置的权重系统
-
考虑了数字的连续性和单调性
-
具有完善的错误处理机制
七、主要模块
- 浏览器控制模块
-
初始化WebDriver
-
页面元素定位
-
键盘事件模拟
- 游戏状态获取模块
-
棋盘状态解析
-
数据转换和存储
- 决策系统模块
-
移动模拟
-
状态评估
-
最优移动选择
- 评估系统模块
-
位置权重计算
-
连续性评估
-
单调性评估
八、核心算法分析
1. 棋盘状态获取
实现细节:
1)使用Selenium的find_elements方法获取所有tile元素
2)通过class属性解析每个tile的位置信息
3)使用try-except处理空值情况
4)返回4x4的二维数组表示棋盘状态
def get_board_state(driver):
tiles = driver.find_elements(By.CLASS_NAME, 'tile')
board = [[0] * 4 for _ in range(4)]
for tile in tiles:
classes = tile.get_attribute('class').split()
for cls in classes:
if cls.startswith('tile-position-'):
position = cls.split('-')
x = int(position[2]) - 1
y = int(position[3]) - 1
try:
value = int(tile.text) if tile.text else 0
except ValueError:
value = 0
board[y][x] = value
return board2. 位置权重系统
POSITION_WEIGHTS = [
4, 3, 2, 1\], \[3, 2, 1, 1\], \[2, 1, 1, 1\], \[1, 1, 1, 1
]
实现细节:
-
定义4x4的权重矩阵,角落权重最高
-
遍历棋盘计算加权得分
-
大数字在角落获得更高分数
def calculate_position_score(board):
score = 0
for i in range(4):
for j in range(4):
if board[i][j] != 0:
score += board[i][j] * POSITION_WEIGHTS[i][j]
return score
3. 连续性评估
实现细节:
-
分别评估水平和垂直方向的连续性
-
相同数字相邻获得双倍分数
-
数字相差1获得额外奖励
def calculate_continuity(board):
score = 0
# 水平连续性
for i in range(4):
for j in range(3):
if board[i][j] != 0 and board[i][j+1] != 0:
if board[i][j] == board[i][j+1]:
score += board[i][j] * 2
elif abs(board[i][j] - board[i][j+1]) == 1:
score += min(board[i][j], board[i][j+1])
return score
4. 单调性评估
实现细节:
-
评估数字是否按顺序排列
-
计算符合单调性的相邻数字对
-
鼓励数字的有序排列
def calculate_monotonicity(board):
score = 0
for i in range(4):
for j in range(3):
if board[i][j] >= board[i][j+1]:
score += 1
return score
5. 移动模拟系统
实现细节:
-
深拷贝当前棋盘状态
-
使用merged数组防止重复合并
-
分别处理四个方向的移动
-
实现数字的移动和合并逻辑
def simulate_move(board, move):
new_board = [row[:] for row in board]
merged = [[False] * 4 for _ in range(4)]
# ... 移动逻辑实现
九、评估系统
1. 评估标准
def evaluate_move(board, move):
score = (empty_cells * 200 + # 空格权重
max_tile * 100 + # 最大数字权重
position_score * 50 + # 位置权重
continuity_score * 30 + # 连续性权重
monotonicity_score * 20) # 单调性权重权重分配说明:
- 空格数量:200
保持棋盘有足够空间
避免过早填满
- 最大数字:100
鼓励产生更大的数字
提高游戏得分
- 位置权重:50
优化数字分布
保持大数字在角落
- 连续性:30
提高合并效率
保持数字相邻
- 单调性:20
保持数字有序
便于后续合并
2. 决策机制
实现细节:
-
遍历所有可能的移动方向
-
评估每个移动的得分
-
选择得分最高的移动
-
默认返回向下移动
def get_best_move(board):
best_score = float('-inf')
best_move = None
for move in MOVES:
score = evaluate_move(board, move)
if score > best_score:
best_score = score
best_move = move
十、性能优化
1. 延迟控制
说明:
1)使用随机延迟避免固定模式
2)延迟范围0.5-1.5秒
3)模拟人类操作特征
DELAY_RANGE = (0.5, 1.5)
time.sleep(random.uniform(*DELAY_RANGE))2. 错误处理
实现细节:
-
处理空值情况
-
处理数值转换异常
-
确保程序稳定运行
try:
value = int(tile.text) if tile.text else 0
except ValueError:
value = 0
十一、完整代码
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
from selenium.webdriver.common.keys import Keys
import time
import random
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.service import Service
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.options import Options
import numpy as np
# 游戏网址
GAME_URL = 'https://2048game.com/'
# 指定 Chrome以及Chrome Driver可执行文件路径
chrome_path = {"Windows": r"你自己电脑上chrome可执行文件的绝对路径",}
options = Options()
options.binary_location = chrome_path["Windows"]
driver_path = r'你自己电脑上chrome Driver所在目录'
service = Service(executable_path=driver_path)
# 定义移动方向
MOVES = [Keys.ARROW_UP, Keys.ARROW_RIGHT, Keys.ARROW_DOWN, Keys.ARROW_LEFT]
# 随机延迟时间范围(秒)
DELAY_RANGE = (0.5, 1.5)
# 位置权重矩阵(角落和边缘权重更高)
POSITION_WEIGHTS = [
[4, 3, 2, 1],
[3, 2, 1, 1],
[2, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1]
]
def init_driver():
driver = webdriver.Chrome(service=service, options=options)
return driver
def get_board_state(driver):
tiles = driver.find_elements(By.CLASS_NAME, 'tile')
board = [[0] * 4 for _ in range(4)]
for tile in tiles:
classes = tile.get_attribute('class').split()
for cls in classes:
if cls.startswith('tile-position-'):
position = cls.split('-')
x = int(position[2]) - 1
y = int(position[3]) - 1
try:
value = int(tile.text) if tile.text else 0
except ValueError:
value = 0
board[y][x] = value
return board
def print_board(board):
for row in board:
print('\t'.join(map(str, row)))
print()
def calculate_position_score(board):
"""计算基于位置的得分"""
score = 0
for i in range(4):
for j in range(4):
if board[i][j] != 0:
score += board[i][j] * POSITION_WEIGHTS[i][j]
return score
def calculate_continuity(board):
"""计算数字的连续性"""
score = 0
# 水平连续性
for i in range(4):
for j in range(3):
if board[i][j] != 0 and board[i][j + 1] != 0:
if board[i][j] == board[i][j + 1]:
score += board[i][j] * 2
elif abs(board[i][j] - board[i][j + 1]) == 1:
score += min(board[i][j], board[i][j + 1])
# 垂直连续性
for i in range(3):
for j in range(4):
if board[i][j] != 0 and board[i + 1][j] != 0:
if board[i][j] == board[i + 1][j]:
score += board[i][j] * 2
elif abs(board[i][j] - board[i + 1][j]) == 1:
score += min(board[i][j], board[i + 1][j])
return score
def calculate_monotonicity(board):
"""计算单调性(数字是否按顺序排列)"""
score = 0
# 水平单调性
for i in range(4):
for j in range(3):
if board[i][j] >= board[i][j + 1]:
score += 1
# 垂直单调性
for i in range(3):
for j in range(4):
if board[i][j] >= board[i + 1][j]:
score += 1
return score
def evaluate_move(board, move):
"""评估移动后的棋盘状态"""
new_board = simulate_move(board, move)
if new_board == board: # 如果移动没有改变棋盘,返回负无穷
return float('-inf')
score = 0
empty_cells = 0
max_tile = 0
# 计算空格数量
for row in new_board:
empty_cells += row.count(0)
# 找出最大数字
for row in new_board:
max_tile = max(max_tile, max(row))
# 计算位置得分
position_score = calculate_position_score(new_board)
# 计算连续性得分
continuity_score = calculate_continuity(new_board)
# 计算单调性得分
monotonicity_score = calculate_monotonicity(new_board)
# 计算总分(调整权重)
score = (empty_cells * 200 + # 空格权重增加
max_tile * 100 + # 最大数字权重增加
position_score * 50 + # 位置权重
continuity_score * 30 + # 连续性权重
monotonicity_score * 20) # 单调性权重
return score
def simulate_move(board, move):
"""模拟移动并返回新的棋盘状态"""
new_board = [row[:] for row in board]
merged = [[False] * 4 for _ in range(4)]
if move == Keys.ARROW_DOWN:
# 向下移动
for j in range(4):
for i in range(2, -1, -1):
if new_board[i][j] != 0:
row = i
while row < 3 and (new_board[row + 1][j] == 0 or
(new_board[row + 1][j] == new_board[row][j] and
not merged[row + 1][j])):
if new_board[row + 1][j] == 0:
new_board[row + 1][j] = new_board[row][j]
new_board[row][j] = 0
else:
new_board[row + 1][j] *= 2
new_board[row][j] = 0
merged[row + 1][j] = True
row += 1
elif move == Keys.ARROW_LEFT:
# 向左移动
for i in range(4):
for j in range(1, 4):
if new_board[i][j] != 0:
col = j
while col > 0 and (new_board[i][col - 1] == 0 or
(new_board[i][col - 1] == new_board[i][col] and
not merged[i][col - 1])):
if new_board[i][col - 1] == 0:
new_board[i][col - 1] = new_board[i][col]
new_board[i][col] = 0
else:
new_board[i][col - 1] *= 2
new_board[i][col] = 0
merged[i][col - 1] = True
col -= 1
elif move == Keys.ARROW_RIGHT:
# 向右移动
for i in range(4):
for j in range(2, -1, -1):
if new_board[i][j] != 0:
col = j
while col < 3 and (new_board[i][col + 1] == 0 or
(new_board[i][col + 1] == new_board[i][col] and
not merged[i][col + 1])):
if new_board[i][col + 1] == 0:
new_board[i][col + 1] = new_board[i][col]
new_board[i][col] = 0
else:
new_board[i][col + 1] *= 2
new_board[i][col] = 0
merged[i][col + 1] = True
col += 1
elif move == Keys.ARROW_UP:
# 向上移动
for j in range(4):
for i in range(1, 4):
if new_board[i][j] != 0:
row = i
while row > 0 and (new_board[row - 1][j] == 0 or
(new_board[row - 1][j] == new_board[row][j] and
not merged[row - 1][j])):
if new_board[row - 1][j] == 0:
new_board[row - 1][j] = new_board[row][j]
new_board[row][j] = 0
else:
new_board[row - 1][j] *= 2
new_board[row][j] = 0
merged[row - 1][j] = True
row -= 1
return new_board
def get_best_move(board):
"""获取最佳移动方向"""
best_score = float('-inf')
best_move = None
# 评估每个可能的移动
for move in MOVES:
score = evaluate_move(board, move)
if score > best_score:
best_score = score
best_move = move
# 如果没有找到有效的移动,返回默认移动
if best_move is None:
return Keys.ARROW_DOWN
return best_move
def play_2048():
driver = init_driver()
try:
driver.get(GAME_URL)
time.sleep(2)
game_board = driver.find_element(By.TAG_NAME, 'body')
while True:
board = get_board_state(driver)
print_board(board)
# 获取最佳移动方向
best_move = get_best_move(board)
game_board.send_keys(best_move)
time.sleep(random.uniform(*DELAY_RANGE))
try:
replay_button = driver.find_element(By.CLASS_NAME, 'replay-button')
print("游戏结束!最终得分:", driver.find_element(By.CLASS_NAME, 'score-board').text.split()[-1])
replay_button.click()
time.sleep(2)
except Exception:
continue
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("用户手动停止游戏")
finally:
driver.quit()
if __name__ == "__main__":
play_2048()十二、总结
程序能够实现基本的游戏功能,在复杂局面下的表现还有提升空间,只玩到1024,离2048还差一些,读者可以通过进一步优化算法和评估系统,提高游戏表现,自己试试吧。
喜欢这篇文章的话记得点赞收藏加关注哦!!
