抓住那头牛
农夫知道一头牛的位置,想要抓住它。农夫和牛都位于数轴上 ,农夫起始位于点N(0<=N<=100000),牛位于点 K(0<=K<=100000)。农夫有两种移动方式:
1、从X移动到X-1或X+1,每次移动花费一分钟
2、从X移动到2*X,每次移动花费一分钟 假设牛没有意识到农夫的行动,站在原地不动。农夫最少要 花多少时间才能抓住牛?
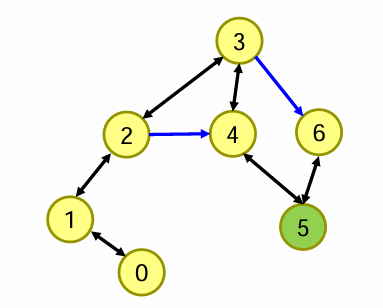
策略1
深度优先搜索:从起 点出发,随机挑一个方向,能 往前走就往前走(扩展),走 不动了则回溯。不能走已经走 过的点(要判重)。
运气好的话: 3->4->5 或 3->6->5 问题解决!
运气不太好的话: 3->2->4->5 运气最坏的话: 3->2->1->0->4->5
要想求最优(短)解,则要遍历所有走法。可以用 各种手段优化,比如,若已经找到路径长度为n 的解,则所有长度大于n的走法就不必尝试。 运算过程中需要存储路径上的节点,数量较少。 用栈存节点。
策略2
广度优先搜索: 给节点分层。起点是第0层。从起 点最少需n步就能到达的点属于第n 层。
第1层:2,4,6
第2层:1,5
第3层:0
依层次顺序,从小到大扩展节点。 把层次低的点全部扩展出来后,才 会扩展层次高的点。
扩展时,不能扩展出已经走过的节 点(要判重)。
可确保找到最优解,但是因扩展出 来的节点较多,且多数节点都需要 保存,因此需要的存储空间较大。 用队列存节点。
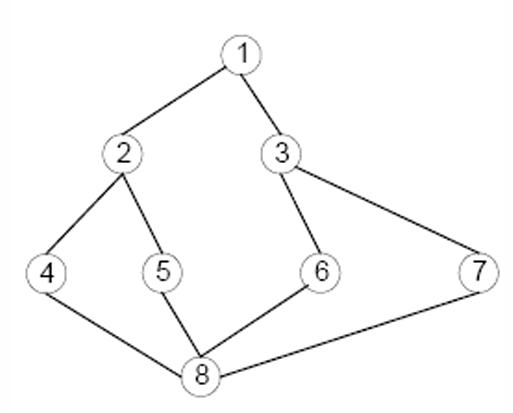
若要遍历所有节点: 深搜 1-2-4-8-5-6-3-7 广搜 1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8
广搜算法
广度优先搜索算法如下:(用QUEUE)
(1) 把初始节点S0放入Open表中;
(2) 如果Open表为空,则问题无解,失败 退出;
(3) 把Open表的第一个节点取出放入 Closed表,并记该节点为n;
(4) 考察节点n是否为目标节点。若是,则 得到问题的解,成功退出;
(5) 若节点n不可扩展,则转第(2)步;
(6) 扩展节点n,将其不在Closed表和 Open表中的子节点(判重)放入Open表的尾 部,并为每一个子节点设置指向父节点的指针 (或记录节点的层次),然后转第(2)步。
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int N,K;
const int MAXN = 100000;
int visited[MAXN+10]; //判重标记,visited[i] = true表示i已经扩展过
struct Step{
int x; //位置
int steps; //到达x所需的步数
Step(int xx,int s):x(xx),steps(s) { }
};
queue<Step> q; //队列,即Open表
int main() {
cin >> N >> K;
memset(visited,0,sizeof(visited));
q.push(Step(N,0));
visited[N] = 1;
while(!q.empty()) {
Step s = q.front();
if( s.x == K ) { //找到目标
cout << s.steps <<endl;
return 0;
}
else {
if( s.x- 1 >= 0 && !visited[s.x-1] ) {
q.push(Step(s.x-1,s.steps+1));
visited[s.x-1] = 1;
}
if( s.x + 1 <= MAXN && !visited[s.x+1] ) {
q.push(Step(s.x+1,s.steps+1));
visited[s.x+1] = 1;
}
if( s.x * 2 <= MAXN &&!visited[s.x*2] ) {
q.push(Step(s.x*2,s.steps+1));
visited[s.x*2] = 1;
}
q.pop();
}
}
return 0;
}输入2 7
输出3
迷宫问题
定义一个矩阵:
0 1 0 0 0
0 1 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 1 1 1 0
0 0 0 1 0
它表示一个迷宫,其中的1表示墙壁,0表示可以走的路, 只能横着走或竖着走,不能斜着走,要求编程序找出从 左上角到右下角的最短路线。
基础广搜。先将起始位置入队列 每次从队列拿出一个元素,扩展其相邻的4个元素入队列(要判重), 直到队头元素为终点为止。队列里的元素记录了指向父节点(上一步)的指针 队列元素:
cpp
struct {
int r,c;
int f; //父节点在队列中的下标
};
cpp
//BFS第二次编写
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
struct Node
{
int x,y;
int pre;
}q[5*5 + 10];//使用数组创建的队列,出栈的时候不会真正的删除元素
int map[5][5];//输入矩阵,判断是否可达
int vis[5][5];//判断是否已经访问
//维护队列的指针,并且相当于完成初始化,直接存放第一个元素
//出队和入队千万不要忘记这两个指针的维护
int qhead = 0;//指向第一个元素
int qtail = 1;//指向最后一个元素的下一个元素
int X[4] = {1,-1,0,0};
int Y[4] = {0,0,-1,1};
int test(int x,int y)
{
if(x<0 || x>=5 || y<0 || y>=5) return 0;
if(map[x][y] == 1) return 0;
if(vis[x][y] == 1) return 0;
return 1;
}
void BFS()
{
//第一个节点入队
q[qhead].x = 0;
q[qhead].y = 0;
q[qhead].pre = -1;
vis[0][0] = 1;
while(qhead<qtail)
{
Node temp_head = q[qhead];//访问队首元素
//qhead++;此处编写错误,会影响下面的q[qtail].pre = head;
if(temp_head.x == 4 &&temp_head.y == 4)
return;
for(int i = 0;i<4;i++)
{
int newX = temp_head.x + X[i];
int newY = temp_head.y + Y[i];
if(test(newX,newY))
{
//入队
q[qtail].x = newX;
q[qtail].y = newY;
q[qtail].pre = qhead;
vis[newX][newY] = 1;
qtail++;
}
}
qhead++;//出队,注意只有这个位置正确
}
}
void print(int head)
{
if(head == 0)
printf("(0, 0)\n");
else
{
if(q[head].pre != -1)
{
print(q[head].pre);
printf("(%d, %d)\n",q[head].x,q[head].y);
}
}
}
int main()
{
int i,j;
for(i = 0;i<5;i++)
{
for(j = 0;j<5;j++)
{
scanf("%d",&map[i][j]);//输入数据
}
}
BFS();
print(qhead);
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));//初始化vis数组
return 0;
}输入
0 1 0 0 0
0 1 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 1 1 1 0
0 0 0 1 0
输出
(0, 0)
(1, 0)
(2, 0)
(2, 1)
(2, 2)
(2, 3)
(2, 4)
(3, 4)
(4, 4)
鸣人和佐助
已知一张地图(以二维矩阵的形式表示)以及佐助和鸣人的 位置。地图上的每个位置都可以走到,只不过有些位置上有 大蛇丸的手下(#),需要先打败大蛇丸的手下才能到这些位 置。
鸣人有一定数量的查克拉,每一个单位的查克拉可以打败一 个大蛇丸的手下。假设鸣人可以往上下左右四个方向移动, 每移动一个距离需要花费1个单位时间,打败大蛇丸的手下 不需要时间。如果鸣人查克拉消耗完了,则只可以走到没有 大蛇丸手下的位置,不可以再移动到有大蛇丸手下的位置。 佐助在此期间不移动,大蛇丸的手下也不移动。
鸣人 要追上佐助最少需要花费多少时间?
状态定义为: (r,c,k) ,
鸣人所在的行,列和查克拉数量 如果队头节点扩展出来的节点是有大蛇手下的节点, 则其k 值比队头的k要减掉1。如果队头节点的查克 拉数量为0,则不能扩展出有大蛇手下的节点。
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
struct pos{
int x;
int y;
int k;//当前所剩下的查克拉
int t;//花费的时间
pos(int xx, int yy, int kk, int tt) : x(xx), y(yy), k(kk), t(tt) {}
};
char maze[206][206];
int ans, dir[4][2] = {{1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}};
int maxk[206][206];//到达当前格子时,所剩查克拉的最大值
int m, n, t;
queue<pos> q;
int judge(int xx,int yy)
{
if(xx < 0 || xx >= m || yy < 0 || yy >= n )
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
void bfs()
{
while (!q.empty())
{
pos now = q.front();
q.pop();
if (maze[now.x][now.y] == '+')
{
ans = now.t;
return;
}
else
{
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int xx = now.x + dir[i][0];
int yy = now.y + dir[i][1];
if (judge(xx,yy)|| maxk[xx][yy] >= now.k)
continue;
if (maze[xx][yy] == '#')//碰到大蛇丸手下
{
if (now.k > 0)//查克拉充足
{
q.push(pos(xx, yy, now.k - 1, now.t + 1));
maxk[xx][yy] = now.k;
}
}
else
{
q.push(pos(xx, yy, now.k, now.t + 1));
maxk[xx][yy] = now.k;
}
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> m >> n >> t;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
cin >> maze[i][j];
maxk[i][j] = -1;//为零的时候也是可以走的,所以初始化为-1
if (maze[i][j] == '@')//找到鸣人的位置
{
q.push(pos(i, j, t, 0));
maxk[i][j] = t;
}
}
}
ans = inf;
bfs ();
if (ans == inf)
{
cout << -1 << endl;
}
else
{
cout << ans << endl;
}
return 0;
}八数码问题
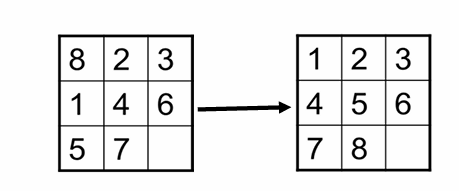
有一个3*3的棋盘,其中有0-8共9个数字,0表示空格, 其他的数字可以和0交换位置。求由初始状态 到达目标状态
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 0 的步数最少的解。
用队列保存待扩展的节点
从队首队取出节点,扩展出的新节点放入队尾, 直到队首出现目标节点(问题的解)
如果问题无解,输出"unsolvable"。如果有解,则输出空格的移动序列。"u"表示将空格向上移,"d"表示将空格向下移,"1"表示左移,"r"表示右移。
cpp
//广度优先搜索--标志位采用set二分查找
//内存:10752kB 时间:533ms
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>//sprintf()头文件
#include<cstdlib>//atoi()头文件
#include<set>//STL容器
using namespace std;
int goalStatus;
const int MAXS=400000;
char result[MAXS];
struct Node
{
int status;
int father;
char move;
Node(int s,int f,char m):status(s),father(f),move(m){}
Node(){}
};
Node myQueue[MAXS];
int qhead=0;
int qtail=1;
char moves[]="udrl";
void IntStatusToStrStatus(int n,char*strStatus)
{//字符串格式化命令,按十进制转换成9位的字符串,可在前面添加0凑足
sprintf(strStatus,"%09d",n);//需要保留前导0
}
int NewStatus(int status,char cMove)
{//求从状态status经过cMove移动后的新状态;若不可行则返回-1
char tmp[20];
int zeroPos;
IntStatusToStrStatus(status,tmp);//转换成字符串形式进行移动
for(int i=0;i<9;++i)
if(tmp[i]=='0'){zeroPos=i;break;}
switch(cMove)
{
case'u':
if(zeroPos-3<0)return -1;
else {tmp[zeroPos]=tmp[zeroPos-3];
tmp[zeroPos-3]='0';}
break;
case'd':
if(zeroPos+3>8)return -1;
else {tmp[zeroPos]=tmp[zeroPos+3];
tmp[zeroPos+3]='0';}
break;
case'l':
if(zeroPos%3==0)return -1;
else {tmp[zeroPos]=tmp[zeroPos-1];
tmp[zeroPos-1]='0';}
break;
case'r':
if(zeroPos%3==2)return -1;
else {tmp[zeroPos]=tmp[zeroPos+1];
tmp[zeroPos+1]='0';}
break;
}
return atoi(tmp);//再将字符串还原为整数状态返回
}
bool Bfs(int status)
{//从初始状态status到目标的路径,找不到则返回false
int newStatus;
set<int>expanded;//存放标记位
expanded.insert(status);
myQueue[qhead]=Node(status,-1,0);//初始化队列头节点(起始节点)
while(qhead!=qtail)//队列不为空
{
status=myQueue[qhead].status;
if(status==goalStatus)return true;
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
{
newStatus=NewStatus(status,moves[i]);
if(newStatus==-1)continue;
if(expanded.find(newStatus)!=expanded.end())continue;//set中若没找到则返回end
expanded.insert(newStatus);
myQueue[qtail++]=Node(newStatus,qhead,moves[i]);
}
qhead++;
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
goalStatus=atoi("123456780");
char line1[50]; char line2[20];
while(cin.getline(line1,48))
{
int i,j;
//将原始输入转变成数字字符串
for(i=0,j=0;line1[i];i++)
{
if(line1[i]!=' '){
if(line1[i]=='x')line2[j++]='0';
else line2[j++]=line1[i];
}
}
line2[j]=0;
if(Bfs(atoi(line2)))
{
int moves=0;
int pos=qhead;
do{
result[moves++]=myQueue[pos].move;
pos=myQueue[pos].father;
}while(pos);//pos=0说明已经退回初始状态
for(int i=moves-1;i>=0;i--)cout<<result[i];
}
else cout<<"unsolvable"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}2 3 4 1 5 x 7 6 8
ullddrurdllurdruldr