文章目录
不用框架实现web接口
go
复制代码
// blog main.go 文件
package main
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
fmt.Println("Hello World!")
// 注册 HTTP 路由 /hello
http.HandleFunc("/hello", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "Hello Go!")
})
// 启动 HTTP 服务器
err := http.ListenAndServe("8111", nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}
http.HandleFunc 注册一个路由 /hello 并绑定处理函数。- 当用户访问
http://localhost:8111/hello 时,执行匿名函数:
w http.ResponseWriter:用于向客户端发送 HTTP 响应。r *http.Request:包含客户端发来的请求信息(如 URL、Headers 等)。
fmt.Fprintf(w, "Hello Go!"):
- 向 HTTP 响应写入
"Hello Go!"(相当于 w.Write([]byte("Hello Go!")))。
- 默认状态码是
200 OK。
http.ListenAndServe(":8111", nil):
- 启动 HTTP 服务器,监听
8111 端口(: 表示监听所有网络接口)。
nil 表示使用默认的 DefaultServeMux 路由器(即之前用 http.HandleFunc 注册的路由)。
if err != nil { log.Fatal(err) }:如果服务器启动失败(如端口被占用),打印错误并终止程序。fmt.Fprintf 是 Go 语言 fmt 包提供的一个格式化输出函数,用于将格式化后的字符串写入指定的 io.Writer 接口(如文件、HTTP 响应、标准输出等)。它的作用类似于 fmt.Printf,但不是输出到终端,而是写入到任意实现了 io.Writer 的对象。
go
复制代码
func Fprintf(w io.Writer, format string, a ...interface{}) (n int, err error)
w io.Writer:目标写入器(如 http.ResponseWriter、文件、缓冲区等)。format string:格式化字符串(包含占位符,如 %s, %d, %v 等)。a ...interface{}:可变参数,用于填充格式化字符串中的占位符。- 返回值:
n int:成功写入的字节数。err error:写入过程中遇到的错误(如写入失败)。
实现简单的路由
go
复制代码
// zjgo ms.go 文件
package zjgo
import (
"log"
"net/http"
)
type Engine struct {
}
func New() *Engine {
return &Engine{}
}
func (e *Engine) Run() {
err := http.ListenAndServe("8111", nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}
- 经过封装之后,原来的
main 函数可以简洁为如下:
go
复制代码
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/ErizJ/ZJGo/zjgo"
)
func main() {
fmt.Println("Hello World!")
// // 注册 HTTP 路由 /hello
// http.HandleFunc("/hello", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// fmt.Fprintf(w, "Hello Go!")
// })
// // 启动 HTTP 服务器
// err := http.ListenAndServe("8111", nil)
// if err != nil {
// log.Fatal(err)
// }
engine := zjgo.New()
engine.Run()
}
- 注意这里服务启动后会
404 Not Found,因为我们没有实现对应的响应函数 Handler。
go
复制代码
package zjgo
import (
"log"
"net/http"
)
// 定义处理响应函数
type HandleFunc func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request)
// 定义路由结构体
type router struct {
handleFuncMap map[string]HandleFunc
}
// 给路由结构体添加一个添加路由功能的函数
func (r *router) Add(name string, handleFunc HandleFunc) {
r.handleFuncMap[name] = handleFunc
}
// 定义一个引擎结构体
type Engine struct {
router
}
// 引擎结构体的初始化方法
func New() *Engine {
return &Engine{
router: router{
handleFuncMap: make(map[string]HandleFunc),
},
}
}
// 引擎的启动方法
func (e *Engine) Run() {
for key, value := range e.handleFuncMap {
http.HandleFunc(key, value)
}
err := http.ListenAndServe("8111", nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}
- 在 Go 语言中,当你将一个类型(如
router)嵌入到另一个结构体(如 Engine)中时,这被称为类型嵌入(Embedded Type)。这是一种组合的方式,它允许 Engine 直接访问 router 的字段和方法,而不需要显式地通过一个字段名来访问。
go
复制代码
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
"github.com/ErizJ/ZJGo/zjgo"
)
func main() {
fmt.Println("Hello World!")
// // 注册 HTTP 路由 /hello
// http.HandleFunc("/hello", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// fmt.Fprintf(w, "Hello Go!")
// })
// // 启动 HTTP 服务器
// err := http.ListenAndServe("8111", nil)
// if err != nil {
// log.Fatal(err)
// }
engine := zjgo.New()
engine.Add("/hello", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "Hello Go!")
})
engine.Run()
}
- 这样我们就实现了一个简单的路由功能,下面进行进一步完善。
实现分组路由
- 大多数情况下我们希望写的接口归属于某一个模块,这样便于管理以及维护,代码也会更为清晰。
- 例如:
/user/getUser 和 /user/createUser 都同属于 user 模块。
go
复制代码
// zj.go
package zjgo
import (
"log"
"net/http"
)
// 定义处理响应函数
type HandleFunc func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request)
// 抽象出路由的概念
type routerGroup struct {
name string // 组名
handleFuncMap map[string]HandleFunc // 映射关系应该由每个路由组去维护
}
// 定义路由结构体
type router struct {
routerGroups []*routerGroup // 路由下面应该维护着不同的组
}
// 添加路由组
func (r *router) Group(name string) *routerGroup {
routerGroup := &routerGroup{
name: name,
handleFuncMap: make(map[string]HandleFunc),
}
r.routerGroups = append(r.routerGroups, routerGroup)
return routerGroup
}
// 给路由结构体添加一个添加路由功能的函数
func (routerGroup *routerGroup) Add(name string, handleFunc HandleFunc) {
routerGroup.handleFuncMap[name] = handleFunc
}
// 定义一个引擎结构体
type Engine struct {
router
}
// 引擎结构体的初始化方法
func New() *Engine {
return &Engine{
router: router{},
}
}
// 引擎的启动方法
func (e *Engine) Run() {
for _, group := range e.routerGroups {
for name, value := range group.handleFuncMap {
http.HandleFunc("/"+group.name+name, value)
}
}
err := http.ListenAndServe(":3986", nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}
go
复制代码
// main.go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
"github.com/ErizJ/ZJGo/zjgo"
)
func main() {
fmt.Println("Hello World!")
// // 注册 HTTP 路由 /hello
// http.HandleFunc("/hello", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// fmt.Fprintf(w, "Hello Go!")
// })
// // 启动 HTTP 服务器
// err := http.ListenAndServe("8111", nil)
// if err != nil {
// log.Fatal(err)
// }
engine := zjgo.New()
g1 := engine.Group("user")
g1.Add("/hello", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "Hello Go!------user/hello")
})
g1.Add("/info", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "Hello Go!------user/info")
})
g2 := engine.Group("order")
g2.Add("/hello", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "Hello Go!------order/hello")
})
g2.Add("/info", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "Hello Go!------order/info")
})
fmt.Println("Starting...")
engine.Run()
}
支持不同的请求方式
net / http下的路由,只要路径匹配,就可以进入处理方法。- 但是在我们实际应用之中,比如我们使用 Restful 风格的接口在同一路径下,会使用
GET、POST、DELETE、PUT来代替增删改查,所以我们要对不同的请求方式做相应的支持。
go
复制代码
// zj.go
package zjgo
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"net/http"
)
// 定义处理响应函数
type HandleFunc func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request)
// 抽象出路由的概念
type routerGroup struct {
name string // 组名
handleFuncMap map[string]HandleFunc // 映射关系应该由每个路由组去维护
handlerMethodMap map[string][]string // 记录GET,POST等请求方式所记录的路由,实现对同一路由不同请求方式的支持
}
// 定义路由结构体
type router struct {
routerGroups []*routerGroup // 路由下面应该维护着不同的组
}
// 添加路由组
func (r *router) Group(name string) *routerGroup {
routerGroup := &routerGroup{
name: name,
handleFuncMap: make(map[string]HandleFunc),
handlerMethodMap: make(map[string][]string),
}
r.routerGroups = append(r.routerGroups, routerGroup)
return routerGroup
}
// 给路由结构体添加一个添加路由功能的函数
// func (routerGroup *routerGroup) Add(name string, handleFunc HandleFunc) {
// routerGroup.handleFuncMap[name] = handleFunc
// }
// Any代表支持任意的请求方式
func (routerGroup *routerGroup) Any(name string, handleFunc HandleFunc) {
routerGroup.handleFuncMap[name] = handleFunc
routerGroup.handlerMethodMap["ANY"] = append(routerGroup.handlerMethodMap["ANY"], name)
}
// POST代表支持POST请求方式
func (routerGroup *routerGroup) Post(name string, handleFunc HandleFunc) {
routerGroup.handleFuncMap[name] = handleFunc
routerGroup.handlerMethodMap[http.MethodPost] = append(routerGroup.handlerMethodMap[http.MethodPost], name)
}
// GET代表支持GET请求方式
func (routerGroup *routerGroup) Get(name string, handleFunc HandleFunc) {
routerGroup.handleFuncMap[name] = handleFunc
routerGroup.handlerMethodMap[http.MethodGet] = append(routerGroup.handlerMethodMap[http.MethodGet], name)
}
// 只要实现 ServeHTTP 这个方法,就相当于实现了对应的 HTTP 处理器
// 结构体 Engine 实现了 ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) 方法
// 所以它就自动实现了 http.Handler 接口,因此可以直接被用于 http.ListenAndServe
// Engine 实现了 ServeHTTP,它就是一个合法的 http.Handler,可以用 http.Handle 来绑定它到某个具体的路由路径上!
func (e *Engine) ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// 在 Go 的 net/http 包中,r *http.Request 代表了客户端发来的 HTTP 请求对象。
// 可以通过 r.Method 来获取这次请求使用的是什么方法(Method),例如:GET、POST、PUT、DELETE 等。
if r.Method == http.MethodGet {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "这是一个 GET 请求")
} else if r.Method == http.MethodPost {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "这是一个 POST 请求")
} else {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "这是一个其他类型的请求:%s", r.Method)
}
for _, group := range e.routerGroups {
for name, methodHandle := range group.handleFuncMap {
url := "/" + group.name + name
//判断一下当前的url是否等于请求的url,即路由匹配
if r.RequestURI == url {
// 先判断当前请求路由是否在支持任意请求方式的 Any map里面
if routers, exist := group.handlerMethodMap["ANY"]; exist {
for _, routerName := range routers {
// 确实支持 Any 请求方式
if routerName == name {
methodHandle(w, r)
return
}
}
}
// 不支持 Any,去该请求所对应的请求方式对应的 Map 里面去找是否有对应的路由
if routers, exist := group.handlerMethodMap[r.Method]; exist {
for _, routerName := range routers {
// 确实支持对应请求方式
if routerName == name {
methodHandle(w, r)
return
}
}
}
// 没找到对应的路由,说明该请求方式不允许
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusMethodNotAllowed)
fmt.Fprintf(w, "%s %s not allowed!!!\n", r.Method, r.RequestURI)
return
}
}
}
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusNotFound)
fmt.Fprintf(w, "%s %s not found!!!\n", r.Method, r.RequestURI)
return
}
// 定义一个引擎结构体
type Engine struct {
router
}
// 引擎结构体的初始化方法
func New() *Engine {
return &Engine{
router: router{},
}
}
// 引擎的启动方法
func (e *Engine) Run() {
// for _, group := range e.routerGroups {
// for name, value := range group.handleFuncMap {
// http.HandleFunc("/"+group.name+name, value)
// }
// }
// 把 e 这个http处理器绑定到对应路由下
http.Handle("/", e)
err := http.ListenAndServe(":3986", nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}
go
复制代码
// main.go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
"github.com/ErizJ/ZJGo/zjgo"
)
func main() {
fmt.Println("Hello World!")
// // 注册 HTTP 路由 /hello
// http.HandleFunc("/hello", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// fmt.Fprintf(w, "Hello Go!")
// })
// // 启动 HTTP 服务器
// err := http.ListenAndServe("8111", nil)
// if err != nil {
// log.Fatal(err)
// }
engine := zjgo.New()
g1 := engine.Group("user")
g1.Get("/hello", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
fmt.Fprintf(w, http.MethodGet+" Hello Go!------user/hello")
})
// 浏览器地址栏输入的都是 GET 请求
// 需要用 curl 或 Postman 来发一个真正的 POST 请求,才会命中 Post handler
g1.Post("/info", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
fmt.Fprintf(w, http.MethodPost+" Hello Go!------user/info")
})
// 只要路由匹配,就会执行对应的处理函数
g1.Any("/any", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
fmt.Fprintf(w, " Hello Go!------user/any")
})
// g2 := engine.Group("order")
// g2.Add("/hello", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// fmt.Fprintf(w, "Hello Go!------order/hello")
// })
// g2.Add("/info", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// fmt.Fprintf(w, "Hello Go!------order/info")
// })
fmt.Println("Starting...")
engine.Run()
}
- 但是目前还是存在一些问题的,目前不支持同一个路由进行
GET 和 POST,因为在 map 里面会被覆盖。
routerGroup.handleFuncMap[name] = handleFunc,在 Post 和 Get 方法下都有这段代码,这就会造成方法的覆盖。
支持同一个路径的不同请求方式
- 标准库 net/http 本身只提供了最基础的路由匹配机制,也就是通过:
http.HandleFunc("/path", handler),它的匹配机制非常简单:只根据请求路径匹配,不区分请求方法(GET/POST)。
- 如果在方法中这样写,是手动在
handler 里面区分请求方法,net/http 本身并不会替你区分。
go
复制代码
http.HandleFunc("/info", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
if r.Method == http.MethodPost {
// 处理 POST
} else if r.Method == http.MethodGet {
// 处理 GET
} else {
http.Error(w, "Method not allowed", http.StatusMethodNotAllowed)
}
})
- 要限制不同请求方法(
GET、POST 分别调用不同的 handler),就得框架(或者你自己)在 ServeHTTP 里手动实现。
- 像 Gin、Echo、Fiber 等这些 Web 框架,都是在它们内部封装了:
- 请求方法和路径的双重匹配机制
- 路由注册表,支持多种请求方式绑定不同
handler
- 匹配失败时返回
405 Method Not Allowed 或 404 Not Found
- 考虑在每个路由组
routerGroup 的 handleFuncMap 上做文章,原先是 map[name]HandleFunc,现在可以加入 map 中 map,也即 map[name]map[method]HandleFunc。
go
复制代码
// context.go
package zjgo
import "net/http"
// context 用于保存上下文的信息,用于传递信息
type Context struct {
W http.ResponseWriter
R *http.Request
}
go
复制代码
// zj.go
package zjgo
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"net/http"
)
const ANY = "ANY"
// 定义处理响应函数
type HandleFunc func(ctx *Context)
// 抽象出路由的概念
type routerGroup struct {
name string // 组名
handleFuncMap map[string]map[string]HandleFunc // 映射关系应该由每个路由组去维护
handlerMethodMap map[string][]string // 记录GET,POST等请求方式所记录的路由,实现对同一路由不同请求方式的支持
}
// 定义路由结构体
type router struct {
routerGroups []*routerGroup // 路由下面应该维护着不同的组
}
// 添加路由组
func (r *router) Group(name string) *routerGroup {
routerGroup := &routerGroup{
name: name,
handleFuncMap: make(map[string]map[string]HandleFunc),
handlerMethodMap: make(map[string][]string),
}
r.routerGroups = append(r.routerGroups, routerGroup)
return routerGroup
}
// 给路由结构体添加一个添加路由功能的函数
// func (routerGroup *routerGroup) Add(name string, handleFunc HandleFunc) {
// routerGroup.handleFuncMap[name] = handleFunc
// }
// 由于 ANY POST GET 都需要重复相同的逻辑代码,所以做一个提取操作
func (routerGroup *routerGroup) handleRequest(name string, method string, handleFunc HandleFunc) {
if _, exist := routerGroup.handleFuncMap[name]; !exist {
routerGroup.handleFuncMap[name] = make(map[string]HandleFunc)
}
if _, exist := routerGroup.handleFuncMap[name][method]; !exist {
routerGroup.handleFuncMap[name][method] = handleFunc
routerGroup.handlerMethodMap[method] = append(routerGroup.handlerMethodMap[method], name)
} else {
panic("Under the same route, duplication is not allowed!!!")
}
}
// Any代表支持任意的请求方式
func (routerGroup *routerGroup) Any(name string, handleFunc HandleFunc) {
routerGroup.handleRequest(name, ANY, handleFunc)
}
// POST代表支持POST请求方式
func (routerGroup *routerGroup) Post(name string, handleFunc HandleFunc) {
routerGroup.handleRequest(name, http.MethodPost, handleFunc)
}
// GET代表支持GET请求方式
func (routerGroup *routerGroup) Get(name string, handleFunc HandleFunc) {
routerGroup.handleRequest(name, http.MethodGet, handleFunc)
}
// 只要实现 ServeHTTP 这个方法,就相当于实现了对应的 HTTP 处理器
// 结构体 Engine 实现了 ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) 方法
// 所以它就自动实现了 http.Handler 接口,因此可以直接被用于 http.ListenAndServe
// Engine 实现了 ServeHTTP,它就是一个合法的 http.Handler,可以用 http.Handle 来绑定它到某个具体的路由路径上!
func (e *Engine) ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// 在 Go 的 net/http 包中,r *http.Request 代表了客户端发来的 HTTP 请求对象。
// 可以通过 r.Method 来获取这次请求使用的是什么方法(Method),例如:GET、POST、PUT、DELETE 等。
if r.Method == http.MethodGet {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "这是一个 GET 请求!!!")
} else if r.Method == http.MethodPost {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "这是一个 POST 请求!!!")
} else {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "这是一个其他类型的请求:%s", r.Method)
}
for _, group := range e.routerGroups {
for name, methodHandleMap := range group.handleFuncMap {
url := "/" + group.name + name
//判断一下当前的url是否等于请求的url,即路由匹配
if r.RequestURI == url {
ctx := &Context{W: w, R: r}
// 先判断当前请求路由是否支持任意请求方式的Any
if handle, exist := methodHandleMap[ANY]; exist {
handle(ctx)
return
}
// 不支持 Any,去该请求所对应的请求方式对应的 Map 里面去找是否有对应的路由
if handle, exist := methodHandleMap[r.Method]; exist {
handle(ctx)
return
}
// 没找到对应的路由,说明该请求方式不允许
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusMethodNotAllowed)
fmt.Fprintf(w, "%s %s not allowed!!!\n", r.Method, r.RequestURI)
return
}
}
}
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusNotFound)
fmt.Fprintf(w, "%s %s not found!!!\n", r.Method, r.RequestURI)
return
}
// 定义一个引擎结构体
type Engine struct {
router
}
// 引擎结构体的初始化方法
func New() *Engine {
return &Engine{
router: router{},
}
}
// 引擎的启动方法
func (e *Engine) Run() {
// for _, group := range e.routerGroups {
// for name, value := range group.handleFuncMap {
// http.HandleFunc("/"+group.name+name, value)
// }
// }
// 把 e 这个http处理器绑定到对应路由下
http.Handle("/", e)
err := http.ListenAndServe(":3986", nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}
go
复制代码
// main.go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
"github.com/ErizJ/ZJGo/zjgo"
)
func main() {
fmt.Println("Hello World!")
// // 注册 HTTP 路由 /hello
// http.HandleFunc("/hello", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// fmt.Fprintf(w, "Hello Go!")
// })
// // 启动 HTTP 服务器
// err := http.ListenAndServe("8111", nil)
// if err != nil {
// log.Fatal(err)
// }
engine := zjgo.New()
g1 := engine.Group("user")
g1.Get("/hello", func(ctx *zjgo.Context) {
fmt.Fprintf(ctx.W, http.MethodGet+" Hello Go!------user/hello")
})
// 浏览器地址栏输入的都是 GET 请求
// 需要用 curl 或 Postman 来发一个真正的 POST 请求,才会命中 Post handler
g1.Post("/info", func(ctx *zjgo.Context) {
fmt.Fprintf(ctx.W, http.MethodPost+" Hello Go!------user/info------POST")
})
g1.Get("/info", func(ctx *zjgo.Context) {
fmt.Fprintf(ctx.W, http.MethodGet+" Hello Go!------user/info------GET")
})
// 只要路由匹配,就会执行对应的处理函数
g1.Any("/any", func(ctx *zjgo.Context) {
fmt.Fprintf(ctx.W, " Hello Go!------user/any")
})
// g2 := engine.Group("order")
// g2.Add("/hello", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// fmt.Fprintf(w, "Hello Go!------order/hello")
// })
// g2.Add("/info", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// fmt.Fprintf(w, "Hello Go!------order/info")
// })
fmt.Println("Starting...")
engine.Run()
}
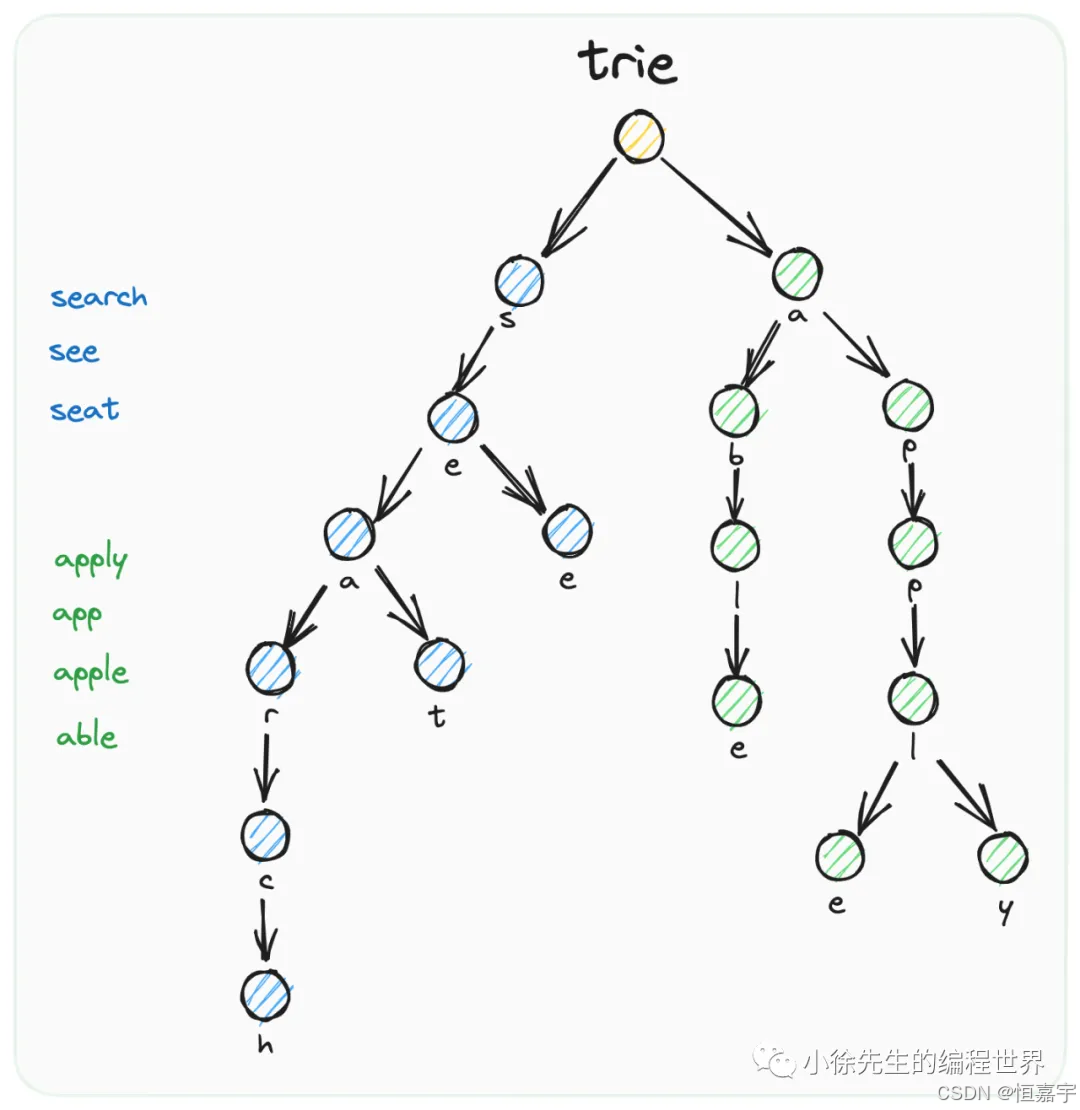
前缀树
- 前面的实现,我们只是实现了静态路由,不能实现更为复杂的需求,比如
/user/get/:id 这种才有参数的。
- 带有参数的路由路径,成为动态路由。
- 除了带有参数的,一般情况下我们还希望有更多支持,比如希望支持通配符
**,比如 /static/**,可以匹配 /static/vue.js,/static/css/index.css 这些。
go
复制代码
// 简单的前缀树实现代码思路
type Trie struct {
next [26]*Trie
end bool
}
func Constructor() Trie {
myTrie := Trie{}
return myTrie
}
func (this *Trie) Insert(word string) {
if this.Search(word) {
return
}
node := this
for _, ch := range word {
if node.next[ch-'a'] == nil {
node.next[ch-'a'] = &Trie{}
}
node = node.next[ch-'a']
}
node.end = true
}
func (this *Trie) Search(word string) bool {
node := this.search(word)
return node != nil && (*node).end
}
func (this *Trie) search(word string) *Trie {
node := this
for _, ch := range word {
if node.next[ch-'a'] == nil {
return nil
}
node = node.next[ch-'a']
}
return node
}
func (this *Trie) StartsWith(prefix string) bool {
node := this.search(prefix)
return node != nil
}
go
复制代码
// tree.go
package zjgo
import "strings"
type TreeNode struct {
name string // 用 '/' 分割路径后的每个路由名称
children []*TreeNode // 子节点
}
// Put path --> /user/get/:id
// PUT 一般用于"更新"
// :id 是一种路由参数(Path Parameter)占位符
// /user/get/123 会匹配 /user/get/:id,并提取出 id = 123
// /user/get/abc 会匹配 /user/get/:id,提取出 id = abc
func (t *TreeNode) Put(path string) {
root := t
strs := strings.Split(path, "/")
for index, name := range strs {
// 忽略第一个斜杠前的那个空格
if index == 0 {
continue
}
isMatch := false
for _, node := range t.children {
if node.name == name {
isMatch = true
t = node
break
}
}
if !isMatch {
node := &TreeNode{
name: name,
children: make([]*TreeNode, 0),
}
t.children = append(t.children, node)
t = node
}
}
t = root
}
// Get path --> /user/get/1
// GET 一般用于"查"
func (t *TreeNode) Get(path string) *TreeNode {
strs := strings.Split(path, "/")
for index, name := range strs {
// 忽略第一个斜杠前的那个空格
if index == 0 {
continue
}
isMatch := false
for _, node := range t.children {
if node.name == name || node.name == "*" || strings.Contains(node.name, ":") {
isMatch = true
t = node
if index == len(strs)-1 {
return node
}
break
}
}
if !isMatch {
for _, node := range t.children {
// /user/**
// /user/get/userInfo
// /user/aa/bb
if node.name == "**" {
// only one
return node
}
}
}
}
return nil
}
// test_tree.go
package zjgo
import (
"fmt"
"testing"
)
func TestTreeNode(t *testing.T) {
root := &TreeNode{name: "/", children: make([]*TreeNode, 0)}
root.Put("/user/get/:id")
root.Put("/user/info/hello")
root.Put("/user/create/aaa")
root.Put("/order/get/aaa")
node := root.Get("/user/get/1")
fmt.Println(node)
node = root.Get("/user/info/hello")
fmt.Println(node)
node = root.Get("/user/create/aaa")
fmt.Println(node)
node = root.Get("/order/get/aaa")
fmt.Println(node)
}
=== RUN TestTreeNode
&{:id []}
&{hello []}
&{aaa []}
&{aaa []}
--- PASS: TestTreeNode (0.00s)
PASS
ok github.com/ErizJ/ZJGo/zjgo (cached)
应用前缀树
go
复制代码
// utils.go
package zjgo
import "strings"
// 分割字符串,只留下去掉了路由组名字后的字路由的路径
func SubStringLast(name string, groupName string) string {
if index := strings.Index(name, groupName); index < 0 {
return ""
} else {
return name[index+len(groupName):]
}
}
go
复制代码
// tree.go
package zjgo
import "strings"
type TreeNode struct {
name string // 用 '/' 分割路径后的每个路由名称
children []*TreeNode // 子节点
routerName string // 前缀树到当前节点所走过的路径
isEnd bool // 对bug的修正,防止 /user/hello/xx 这样的路由 /user/hello 访问这个路径也一样能从前缀树查找出来,并不会报404
}
// Put path --> /user/get/:id
// PUT 一般用于"更新"
// :id 是一种路由参数(Path Parameter)占位符
// /user/get/123 会匹配 /user/get/:id,并提取出 id = 123
// /user/get/abc 会匹配 /user/get/:id,提取出 id = abc
func (t *TreeNode) Put(path string) {
strs := strings.Split(path, "/")
for index, name := range strs {
// 忽略第一个斜杠前的那个空格
if index == 0 {
continue
}
isMatch := false
for _, node := range t.children {
if node.name == name {
isMatch = true
t = node
break
}
}
if !isMatch {
node := &TreeNode{
name: name,
children: make([]*TreeNode, 0),
isEnd: index == len(strs)-1,
}
t.children = append(t.children, node)
t = node
}
}
t.isEnd = true
}
// Get path --> /user/get/1
// GET 一般用于"查"
func (t *TreeNode) Get(path string) *TreeNode {
strs := strings.Split(path, "/")
routerName := ""
for index, name := range strs {
// 忽略第一个斜杠前的那个空格
if index == 0 {
continue
}
isMatch := false
for _, node := range t.children {
if node.name == name || node.name == "*" || strings.Contains(node.name, ":") {
isMatch = true
routerName += "/" + node.name
node.routerName = routerName
t = node
if index == len(strs)-1 {
return node
}
break
}
}
if !isMatch {
for _, node := range t.children {
// /user/**
// /user/get/userInfo
// /user/aa/bb
if node.name == "**" {
// only one
routerName += "/" + node.name
node.routerName = routerName
return node
}
}
}
}
return nil
}
go
复制代码
// zj.go
package zjgo
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"net/http"
)
const ANY = "ANY"
// 定义处理响应函数
type HandleFunc func(ctx *Context)
// 抽象出路由的概念
type routerGroup struct {
name string // 组名
handleFuncMap map[string]map[string]HandleFunc // 映射关系应该由每个路由组去维护
handlerMethodMap map[string][]string // 记录GET,POST等请求方式所记录的路由,实现对同一路由不同请求方式的支持
TreeNode *TreeNode // 记录该路由组下的路由前缀树
}
// 定义路由结构体
type router struct {
routerGroups []*routerGroup // 路由下面应该维护着不同的组
}
// 添加路由组
func (r *router) Group(name string) *routerGroup {
routerGroup := &routerGroup{
name: name,
handleFuncMap: make(map[string]map[string]HandleFunc),
handlerMethodMap: make(map[string][]string),
TreeNode: &TreeNode{name: "/", children: make([]*TreeNode, 0)},
}
r.routerGroups = append(r.routerGroups, routerGroup)
return routerGroup
}
// 给路由结构体添加一个添加路由功能的函数
// func (routerGroup *routerGroup) Add(name string, handleFunc HandleFunc) {
// routerGroup.handleFuncMap[name] = handleFunc
// }
// 由于 ANY POST GET 都需要重复相同的逻辑代码,所以做一个提取操作
func (routerGroup *routerGroup) handleRequest(name string, method string, handleFunc HandleFunc) {
if _, exist := routerGroup.handleFuncMap[name]; !exist {
routerGroup.handleFuncMap[name] = make(map[string]HandleFunc)
}
if _, exist := routerGroup.handleFuncMap[name][method]; !exist {
routerGroup.handleFuncMap[name][method] = handleFunc
routerGroup.handlerMethodMap[method] = append(routerGroup.handlerMethodMap[method], name)
} else {
panic("Under the same route, duplication is not allowed!!!")
}
routerGroup.TreeNode.Put(name)
}
// Any代表支持任意的请求方式
func (routerGroup *routerGroup) Any(name string, handleFunc HandleFunc) {
routerGroup.handleRequest(name, ANY, handleFunc)
}
// POST代表支持POST请求方式
func (routerGroup *routerGroup) Post(name string, handleFunc HandleFunc) {
routerGroup.handleRequest(name, http.MethodPost, handleFunc)
}
// GET代表支持GET请求方式
func (routerGroup *routerGroup) Get(name string, handleFunc HandleFunc) {
routerGroup.handleRequest(name, http.MethodGet, handleFunc)
}
// 只要实现 ServeHTTP 这个方法,就相当于实现了对应的 HTTP 处理器
// 结构体 Engine 实现了 ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) 方法
// 所以它就自动实现了 http.Handler 接口,因此可以直接被用于 http.ListenAndServe
// Engine 实现了 ServeHTTP,它就是一个合法的 http.Handler,可以用 http.Handle 来绑定它到某个具体的路由路径上!
func (e *Engine) ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// 在 Go 的 net/http 包中,r *http.Request 代表了客户端发来的 HTTP 请求对象。
// 可以通过 r.Method 来获取这次请求使用的是什么方法(Method),例如:GET、POST、PUT、DELETE 等。
if r.Method == http.MethodGet {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "这是一个 GET 请求!!! ")
} else if r.Method == http.MethodPost {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "这是一个 POST 请求!!! ")
} else {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "这是一个其他类型的请求:%s!!! ", r.Method)
}
for _, group := range e.routerGroups {
routerName := SubStringLast(r.RequestURI, "/"+group.name)
if node := group.TreeNode.Get(routerName); node != nil && node.isEnd {
// 路由匹配上了
ctx := &Context{W: w, R: r}
// 先判断当前请求路由是否支持任意请求方式的Any
if handle, exist := group.handleFuncMap[node.routerName][ANY]; exist {
handle(ctx)
return
}
// 不支持 Any,去该请求所对应的请求方式对应的 Map 里面去找是否有对应的路由
if handle, exist := group.handleFuncMap[node.routerName][r.Method]; exist {
handle(ctx)
return
}
// 没找到对应的路由,说明该请求方式不允许
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusMethodNotAllowed)
fmt.Fprintf(w, "%s %s not allowed!!!\n", r.Method, r.RequestURI)
return
}
// for name, methodHandleMap := range group.handleFuncMap {
// url := "/" + group.name + name
// //判断一下当前的url是否等于请求的url,即路由匹配
// if r.RequestURI == url {
// }
// }
}
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusNotFound)
fmt.Fprintf(w, "%s %s not found!!!\n", r.Method, r.RequestURI)
return
}
// 定义一个引擎结构体
type Engine struct {
router
}
// 引擎结构体的初始化方法
func New() *Engine {
return &Engine{
router: router{},
}
}
// 引擎的启动方法
func (e *Engine) Run() {
// for _, group := range e.routerGroups {
// for name, value := range group.handleFuncMap {
// http.HandleFunc("/"+group.name+name, value)
// }
// }
// 把 e 这个http处理器绑定到对应路由下
http.Handle("/", e)
err := http.ListenAndServe(":3986", nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}
go
复制代码
// main.go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
"github.com/ErizJ/ZJGo/zjgo"
)
func main() {
fmt.Println("Hello World!")
// // 注册 HTTP 路由 /hello
// http.HandleFunc("/hello", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// fmt.Fprintf(w, "Hello Go!")
// })
// // 启动 HTTP 服务器
// err := http.ListenAndServe("8111", nil)
// if err != nil {
// log.Fatal(err)
// }
engine := zjgo.New()
g1 := engine.Group("user")
g1.Get("/hello", func(ctx *zjgo.Context) {
fmt.Fprintf(ctx.W, http.MethodGet+" Hello Go!------user/hello")
})
// 浏览器地址栏输入的都是 GET 请求
// 需要用 curl 或 Postman 来发一个真正的 POST 请求,才会命中 Post handler
g1.Post("/info", func(ctx *zjgo.Context) {
fmt.Fprintf(ctx.W, http.MethodPost+" Hello Go!------user/info------POST")
})
g1.Get("/info", func(ctx *zjgo.Context) {
fmt.Fprintf(ctx.W, http.MethodGet+" Hello Go!------user/info------GET")
})
g1.Get("/get/:id", func(ctx *zjgo.Context) {
fmt.Fprintf(ctx.W, http.MethodGet+" Hello Go!------user/get/:id------GET")
})
g1.Get("/isEnd/get", func(ctx *zjgo.Context) {
fmt.Fprintf(ctx.W, http.MethodGet+" Hello Go!------user/isEnd/get------GET")
})
// 只要路由匹配,就会执行对应的处理函数
g1.Any("/any", func(ctx *zjgo.Context) {
fmt.Fprintf(ctx.W, " Hello Go!------user/any")
})
// g2 := engine.Group("order")
// g2.Add("/hello", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// fmt.Fprintf(w, "Hello Go!------order/hello")
// })
// g2.Add("/info", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// fmt.Fprintf(w, "Hello Go!------order/info")
// })
fmt.Println("Starting...")
engine.Run()
}
完善路由代码
go
复制代码
// zj.go
package zjgo
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"net/http"
)
const ANY = "ANY"
// 定义处理响应函数
type HandleFunc func(ctx *Context)
// 抽象出路由的概念
type routerGroup struct {
name string // 组名
handleFuncMap map[string]map[string]HandleFunc // 映射关系应该由每个路由组去维护
handlerMethodMap map[string][]string // 记录GET,POST等请求方式所记录的路由,实现对同一路由不同请求方式的支持
TreeNode *TreeNode // 记录该路由组下的路由前缀树
}
// 定义路由结构体
type router struct {
routerGroups []*routerGroup // 路由下面应该维护着不同的组
}
// 添加路由组
func (r *router) Group(name string) *routerGroup {
routerGroup := &routerGroup{
name: name,
handleFuncMap: make(map[string]map[string]HandleFunc),
handlerMethodMap: make(map[string][]string),
TreeNode: &TreeNode{name: "/", children: make([]*TreeNode, 0)},
}
r.routerGroups = append(r.routerGroups, routerGroup)
return routerGroup
}
// 给路由结构体添加一个添加路由功能的函数
// func (routerGroup *routerGroup) Add(name string, handleFunc HandleFunc) {
// routerGroup.handleFuncMap[name] = handleFunc
// }
// 由于 ANY POST GET 都需要重复相同的逻辑代码,所以做一个提取操作
func (routerGroup *routerGroup) handleRequest(name string, method string, handleFunc HandleFunc) {
if _, exist := routerGroup.handleFuncMap[name]; !exist {
routerGroup.handleFuncMap[name] = make(map[string]HandleFunc)
}
if _, exist := routerGroup.handleFuncMap[name][method]; !exist {
routerGroup.handleFuncMap[name][method] = handleFunc
routerGroup.handlerMethodMap[method] = append(routerGroup.handlerMethodMap[method], name)
} else {
panic("Under the same route, duplication is not allowed!!!")
}
routerGroup.TreeNode.Put(name)
}
// Any代表支持任意的请求方式
func (routerGroup *routerGroup) Any(name string, handleFunc HandleFunc) {
routerGroup.handleRequest(name, ANY, handleFunc)
}
// POST代表支持POST请求方式
func (routerGroup *routerGroup) Post(name string, handleFunc HandleFunc) {
routerGroup.handleRequest(name, http.MethodPost, handleFunc)
}
// GET代表支持GET请求方式
func (routerGroup *routerGroup) Get(name string, handleFunc HandleFunc) {
routerGroup.handleRequest(name, http.MethodGet, handleFunc)
}
// DELETE代表支持DELETE请求方式
func (routerGroup *routerGroup) Delete(name string, handleFunc HandleFunc) {
routerGroup.handleRequest(name, http.MethodDelete, handleFunc)
}
// PUT代表支持PUT请求方式
func (routerGroup *routerGroup) Put(name string, handleFunc HandleFunc) {
routerGroup.handleRequest(name, http.MethodPut, handleFunc)
}
// PATCH代表支持PATCH请求方式
func (routerGroup *routerGroup) Patch(name string, handleFunc HandleFunc) {
routerGroup.handleRequest(name, http.MethodPatch, handleFunc)
}
// 只要实现 ServeHTTP 这个方法,就相当于实现了对应的 HTTP 处理器
// 结构体 Engine 实现了 ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) 方法
// 所以它就自动实现了 http.Handler 接口,因此可以直接被用于 http.ListenAndServe
// Engine 实现了 ServeHTTP,它就是一个合法的 http.Handler,可以用 http.Handle 来绑定它到某个具体的路由路径上!
func (e *Engine) ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// 在 Go 的 net/http 包中,r *http.Request 代表了客户端发来的 HTTP 请求对象。
// 可以通过 r.Method 来获取这次请求使用的是什么方法(Method),例如:GET、POST、PUT、DELETE 等。
if r.Method == http.MethodGet {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "这是一个 GET 请求!!! ")
} else if r.Method == http.MethodPost {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "这是一个 POST 请求!!! ")
} else {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "这是一个其他类型的请求:%s!!! ", r.Method)
}
for _, group := range e.routerGroups {
routerName := SubStringLast(r.RequestURI, "/"+group.name)
if node := group.TreeNode.Get(routerName); node != nil && node.isEnd {
// 路由匹配上了
ctx := &Context{W: w, R: r}
// 先判断当前请求路由是否支持任意请求方式的Any
if handle, exist := group.handleFuncMap[node.routerName][ANY]; exist {
handle(ctx)
return
}
// 不支持 Any,去该请求所对应的请求方式对应的 Map 里面去找是否有对应的路由
if handle, exist := group.handleFuncMap[node.routerName][r.Method]; exist {
handle(ctx)
return
}
// 没找到对应的路由,说明该请求方式不允许
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusMethodNotAllowed)
fmt.Fprintf(w, "%s %s not allowed!!!\n", r.Method, r.RequestURI)
return
}
// for name, methodHandleMap := range group.handleFuncMap {
// url := "/" + group.name + name
// //判断一下当前的url是否等于请求的url,即路由匹配
// if r.RequestURI == url {
// }
// }
}
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusNotFound)
fmt.Fprintf(w, "%s %s not found!!!\n", r.Method, r.RequestURI)
return
}
// 定义一个引擎结构体
type Engine struct {
router
}
// 引擎结构体的初始化方法
func New() *Engine {
return &Engine{
router: router{},
}
}
// 引擎的启动方法
func (e *Engine) Run() {
// for _, group := range e.routerGroups {
// for name, value := range group.handleFuncMap {
// http.HandleFunc("/"+group.name+name, value)
// }
// }
// 把 e 这个http处理器绑定到对应路由下
http.Handle("/", e)
err := http.ListenAndServe(":3986", nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}
