目录
3.容量:size,capacity,empty,resize,reserve
5.修改:push_back,operator+=,append,clear,swap,c_str
[(5) clear](#(5) clear)
一.string类的成员变量与成员函数
cpp
namespace my_string
{
class string
{
friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& _cout, const my_string::string& s);
friend std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& _cin, my_string::string& s);
public:
typedef char* iterator;
typedef const char* const_iterator;
string(const char* str = "")
:_size(strlen(str))
{
_str = new char[_size + 1];
_capacity = _size;
memcpy(_str, str, _size + 1);
}
string(const string& s)
{
_str = new char[s._capacity + 1];
memcpy(_str, s._str, s._size + 1);
_size = s._size;
_capacity = s._capacity;
}
string& operator=(const string& s)
{
char* tmp = new char[s._capacity + 1];
memcpy(tmp, s._str, s._size + 1);
delete[] _str;
_str = tmp;
_size = s._size;
_capacity = s._capacity;
return *this;
}
~string()
{
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
_size = _capacity = 0;
}
// iterator
iterator begin();
iterator end();
const_iterator begin() const;
const_iterator end() const;
// capacity
size_t size() const;
size_t capacity() const;
bool empty() const;
void resize(size_t n, char c = '\0');
void reserve(size_t n);
// access
char& operator[](size_t index);
const char& operator[](size_t index)const;
// relational operators
bool operator<(const string& s);
bool operator<=(const string& s);
bool operator>(const string& s);
bool operator>=(const string& s);
bool operator==(const string& s);
bool operator!=(const string& s);
// modify
void push_back(char c);
string& operator+=(char c);
void append(const char* str);
string& operator+=(const char* str);
void clear();
void swap(string& s);
const char* c_str() const;
// 返回c在string中第一次出现的位置
size_t find(char c, size_t pos = 0) const;
// 返回子串s在string中第一次出现的位置
size_t find(const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const;
// 在pos位置上插入字符c/字符串str,并返回该字符的位置
string& insert(size_t pos, char c);
string& insert(size_t pos, const char* str);
// 删除pos位置上的元素,并返回该元素的下一个位置
string& erase(size_t pos, size_t len);
private:
char* _str;
size_t _size;
size_t _capacity;
public:
static const size_t npos;
};
}二.string类的接口实现
1.构造函数,析构函数,拷贝构造函数,赋值重载
(1)构造函数
cpp
string(const char* str = "")
:_size(strlen(str))
{
_str = new char[_size + 1];
_capacity = _size;
memcpy(_str, str, _size + 1);
}_size在初始化列表中用给定的字符串的长度初始化,若没有给定字符串,则采用缺省值的空字符串。
在函数体内初始化_str,new一个size+1大小的连续空间,用来存放给定的字符串的'\0',申请完空间后,最后将给定字符串中的数据按字节拷贝给_str。
(2)析构函数
cpp
~string()
{
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
_size = _capacity = 0;
}(3)拷贝构造函数
cpp
string(const string& s)
{
_str = new char[s._capacity + 1];
memcpy(_str, s._str, s._size + 1);
_size = s._size;
_capacity = s._capacity;
}如果在这里不写拷贝构造,那么编译器则会调用默认的拷贝构造来进行浅拷贝,则会导致同一块空间被析构两次,所以这里需要手动写深拷贝,并将数据按字节转移到新对象中。
(4)赋值重载
cpp
string& operator=(const string& s)
{
char* tmp = new char[s._capacity + 1];
memcpy(tmp, s._str, s._size + 1);
delete[] _str;
_str = tmp;
_size = s._size;
_capacity = s._capacity;
return *this;
}赋值重载与拷贝构造的区别在于需要将被赋值对象所申请的资源释放,并返回被赋值的对象,实现连续赋值。
2.迭代器
string类的迭代器以指针为底层逻辑进行实现:
cpp
typedef char* iterator;
typedef const char* const_iterator;
cpp
string::iterator string::begin()
{
return _str;
}
string::iterator string::end()
{
return _str + _size;
}
string::const_iterator string::begin() const
{
return _str;
}
string::const_iterator string::end() const
{
return _str + _size;
}有了迭代器之后就可以实现范围for:
3.容量:size,capacity,empty,resize,reserve
(1)size
cpp
size_t string::size() const
{
return _size;
}(2)capacity
cpp
size_t string::capacity() const
{
return _capacity;
}(3)empty
cpp
bool string::empty() const
{
return _size == 0;
}(4)reserve
reserve所传的参数n一般分为两种情况:
 根据std中的reserve,我们在n<capacity的情况下,对容量不做处理。
根据std中的reserve,我们在n<capacity的情况下,对容量不做处理。
在n>capacity的情况下,进行异地扩容,并将原数据复制到新空间中,释放旧空间,更新capacity大小:
cpp
void string::reserve(size_t n)
{
if (n > _capacity)
{
char* tmp = new char[n + 1];
memcpy(tmp, _str, _size + 1);
delete[] _str;
_str = tmp;
_capacity = n;
}
}(5)resize
resize所传的参数n一般分为三种情况:
 当n<size,删除数据,不改变容量。
当n<size,删除数据,不改变容量。
当size<n<capacity,插入数据,不改变容量。
当n>capacity,先进行扩容,再插入数据。
由于resize如果不传用来插入的数据c,则直接用'\0'进行填充,所以缺省值采用'\0':
cpp
void resize(size_t n, char c = '\0')
{
if (n < _size)
{
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
else
{
if (n > _capacity)
{
reserve(n);
}
for (int i = _size; i < n; i++)
{
_str[i] = c;
}
}
_size = n;
}4.访问:operator[]
cpp
char& string::operator[](size_t index)
{
return _str[index];
}
const char& string::operator[](size_t index) const
{
return _str[index];
}5.修改:push_back,operator+=,append,clear,swap,c_str
(1)push_back
cpp
void string::push_back(char c)
{
if (_size == _capacity)
{
size_t newcapacity = _capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * _capacity;
reserve(newcapacity);
}
_str[_size++] = c;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}(2)operator[]
cpp
string& string::operator+=(char c)
{
push_back(c);
return *this;
}
string& string::operator+=(const char* str)
{
append(str);
return *this;
}(3)append
cpp
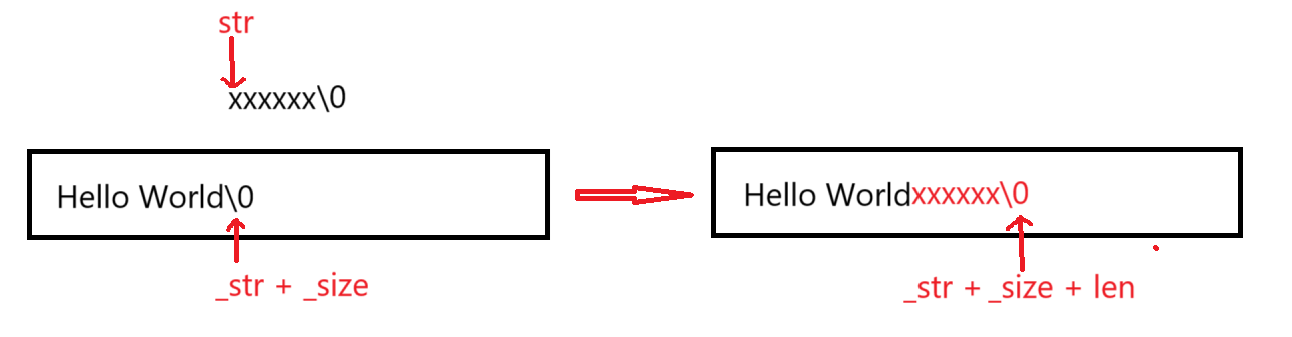
void string::append(const char* str)
{
size_t len = strlen(str);
if (_size + len > _capacity)
{
// 扩容
size_t newcapacity = _size + len > 2 * _capacity ? _size + len : 2 * _capacity;
reserve(newcapacity);
}
memcpy(_str + _size, str, len + 1);
_size += len;
}(4)operator+=
cpp
// += 单个字符
string& string::operator+=(char c)
{
push_back(c);
return *this;
}
// += 字符串
string& string::operator+=(const char* str)
{
append(str);
return *this;
}(5) clear
cpp
void string::clear()
{
_str[0] = '\0';
_size = 0;
}(6)swap
cpp
void string::swap(string& s)
{
std::swap(_str, s._str);
std::swap(_size, s._size);
std::swap(_capacity, s._capacity);
}(7)c_str
cpp
const char* string::c_str() const
{
return _str;
}6.逻辑运算符
对于比较运算符,字符的ASCII码相等,则继续比较,不相等,则根据实际情况返回比较结果,若到比较结束,并未返回,则根据字符串的长度来决定返回结果:
以operator<和operator==为例:
cpp
bool string::operator<(const string& s)
{
size_t end1 = _size - 1;
size_t end2 = s._size - 1;
size_t begin1 = 0;
size_t begin2 = 0;
while (begin1 != end1 && begin2 != end2)
{
if (_str[begin1] < s._str[begin2])
{
return true;
}
else if (_str[begin1] > s._str[begin2])
{
return false;
}
begin1++;
begin2++;
}
//if (begin1 == end1 && begin2 != end2)
//{
// return true;
//}
//else
//{
// return false;
//}
return begin1 == end1 && begin2 != end2;
}
bool string::operator==(const string& s)
{
size_t end1 = _size - 1;
size_t end2 = s._size - 1;
size_t begin1 = 0;
size_t begin2 = 0;
while (begin1 != end1 && begin2 != end2)
{
if (_str[begin1] != s._str[begin2])
{
return false;
}
begin1++;
begin2++;
}
return begin1 == end1 && begin2 == end2;
}这里的比较没有使用strcmp的原因是strcmp在遇到'\0'后则不再比较,无法解决字符串中包含'\0'的情况。
在实现了任一比较大小和相等后,剩余的比较运算符则可以直接进行复用:
cpp
bool string::operator<=(const string& s)
{
return *this < s || *this == s;
}
bool string::operator>(const string& s)
{
return !(*this <= s);
}
bool string::operator>=(const string& s)
{
return !(*this < s);
}
bool string::operator!=(const string& s)
{
return !(*this == s);
}7.查找:find
(1)从pos位置开始向后查找字符c,返回c在string中第一次出现的位置,没找到返回npos
cpp
size_t string::find(char c, size_t pos) const
{
assert(pos < _size);
for (int i = pos; i < _size; ++i)
{
if (_str[i] == c)
{
return i;
}
}
return npos;
}(2)从pos位置开始向后查找字符串s,返回s在string中第一次出现的位置,没找到返回npos
cpp
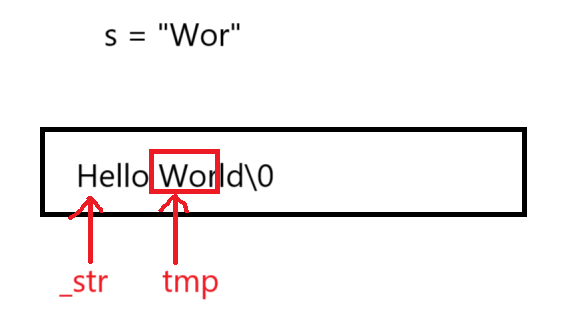
size_t string::find(const char* s, size_t pos) const
{
assert(pos < _size);
const char* tmp = strstr(_str + pos, s);
if (tmp == nullptr)
{
return npos;
}
return tmp - _str;
}8.在固定位置插入数据:insert
(1)在pos位置上插入字符c
cpp
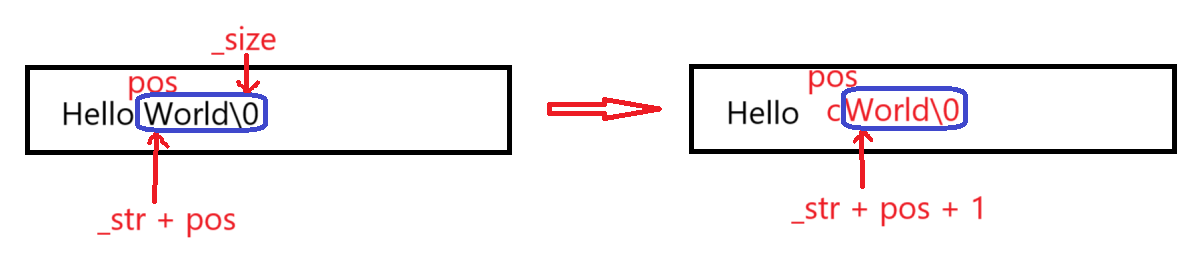
string& string::insert(size_t pos, char c)
{
assert(pos <= _size);
if (_size == _capacity)
{
// 扩容
size_t newcapacity = _capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * _capacity;
reserve(newcapacity);
}
//size_t end = _size + 1;
//while (end > pos)
//{
// _str[end] = _str[end - 1];
// end--;
//}
memmove(_str + pos + 1, _str + pos, _size - pos + 1);
_str[pos] = c;
_size++;
return *this;
}(2)在pos位置上插入字符串str
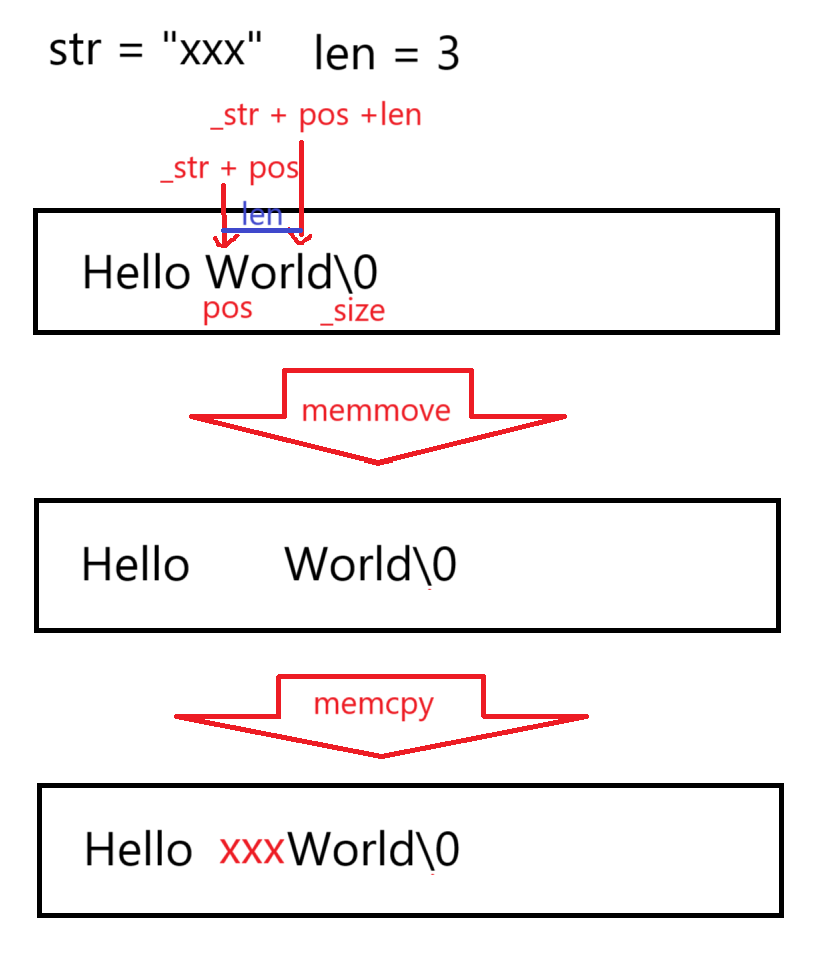
cpp
string& string::insert(size_t pos, const char* str)
{
size_t len = strlen(str);
if (_size + len > _capacity)
{
size_t newcapacity = _size + len > 2 * _capacity ? _size + len : 2 * _capacity;
reserve(newcapacity);
}
memmove(_str + pos + len, _str + pos, _size + 1 - pos);
memcpy(_str + pos, str, len);
_size += len;
return *this;
}9.删除固定位置的数据:erase
当从pos位置开始要删除元素的个数大于剩余元素个数或等于npos时,将pos为之后的字符全部删除。
当从pos位置开始要删除元素的个数小于剩余元素个数时,将要被删除的元素用后面的元素覆盖:
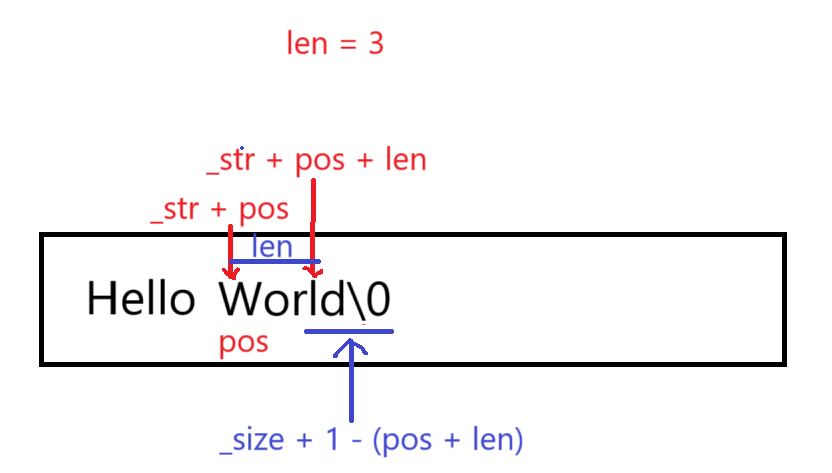
cpp
string& string::erase(size_t pos, size_t len)
{
assert(pos < _size);
if (len == npos || len >= _size - pos)
{
_str[pos] = '\0';
_size = pos;
return *this;
}
memmove(_str + pos, _str + pos + len, _size + 1 - (pos + len));
_size -= len;
return *this;
}10.流插入,流提取运算符重载:<<,>>
(1)流插入<<
cpp
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& _cout, const my_string::string& s)
{
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i)
{
_cout << s[i];
}
return _cout;
}(2)流提取>>
cpp
std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& _cin, my_string::string& s)
{
// 每次提取前需要将s中的数据清除
s.clear();
// 模拟string中的buff缓冲区,当所输入的字符串有效数据个数小于256时,存放到buff中
char buff[256];
// 使用get函数,能够输入空白字符和换行符
char ch = _cin.get();
size_t i = 0;
while (ch != ' ' && ch != '\n')
{
buff[i++] = ch;
ch = _cin.get();
if (i == 255)
{
s += buff;
// 重置buff
i = 0;
}
}
// buff中有剩余字符
if (i > 0)
{
buff[i] = '\0';
s += buff;
}
return _cin;
}三.现代版写法的string类
1.构造函数
用迭代器初始化string类:
cpp
template <class InputIterator>
string(InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
{
while (first != last)
{
push_back(*first);
++first;
}
}2.拷贝构造函数
cpp
// s2(s1)
string::string(const string& s)
{
//string tmp(s._str);
string tmp(s.begin(), s.end());
swap(tmp);
}这里用s1的成员变量_str构造tmp,再将tmp和s2交换swap,这样tmp中的成员变量就与s2中的成员变量交换,出函数体后tmp同时也会被析构。
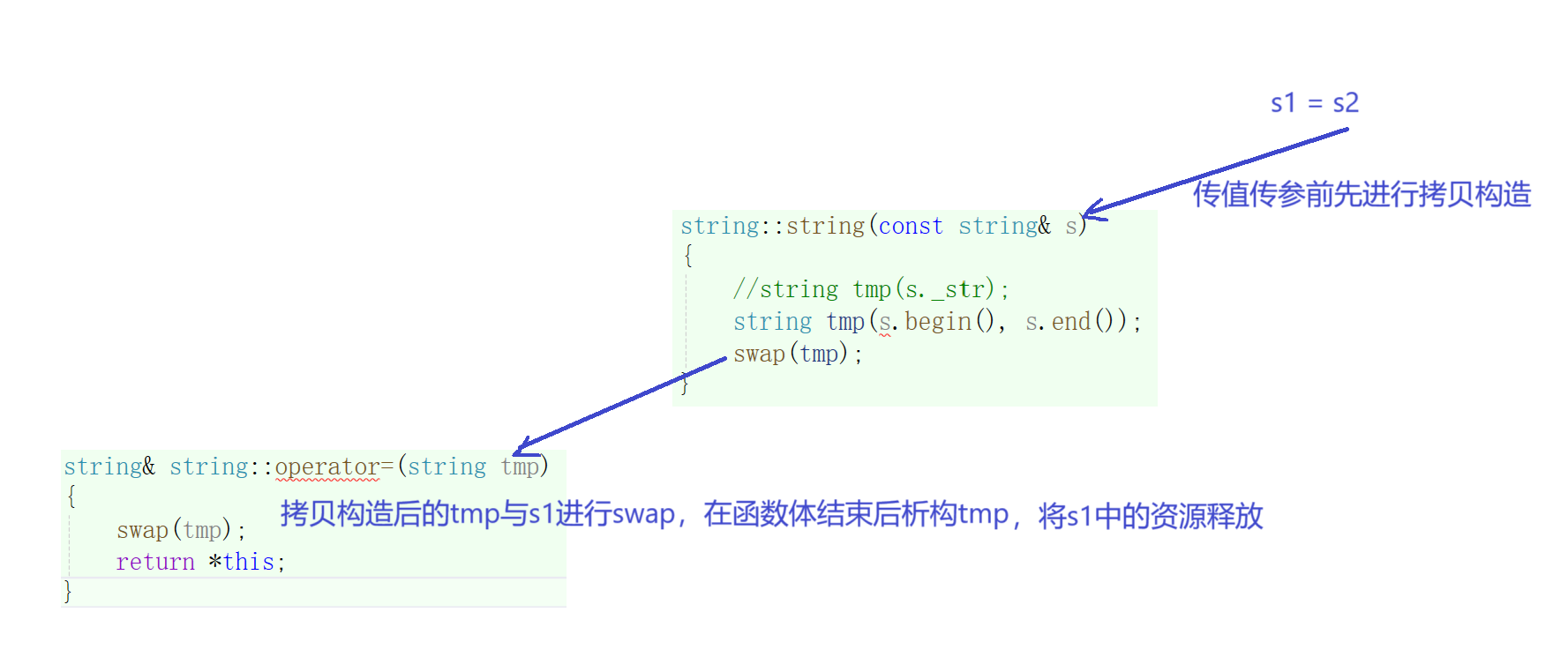
3.赋值重载
cpp
string& string::operator=(string tmp)
{
swap(tmp);
return *this;
}
四.代码总览
string.h
cpp
#pragma once
#include<string.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<iostream>
namespace my_string
{
class string
{
friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& _cout, const my_string::string& s);
friend std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& _cin, my_string::string& s);
public:
typedef char* iterator;
typedef const char* const_iterator;
string(const char* str = "")
:_size(strlen(str))
{
_str = new char[_size + 1];
_capacity = _size;
memcpy(_str, str, _size + 1);
}
string(const string& s)
{
_str = new char[s._capacity + 1];
memcpy(_str, s._str, s._size + 1);
_size = s._size;
_capacity = s._capacity;
}
string& operator=(const string& s)
{
char* tmp = new char[s._capacity + 1];
memcpy(tmp, s._str, s._size + 1);
delete[] _str;
_str = tmp;
_size = s._size;
_capacity = s._capacity;
return *this;
}
~string()
{
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
_size = _capacity = 0;
}
// iterator
iterator begin();
iterator end();
const_iterator begin() const;
const_iterator end() const;
// capacity
size_t size() const;
size_t capacity() const;
bool empty() const;
void resize(size_t n, char c = '\0');
void reserve(size_t n);
// access
char& operator[](size_t index);
const char& operator[](size_t index) const;
// relational operators
bool operator<(const string& s);
bool operator<=(const string& s);
bool operator>(const string& s);
bool operator>=(const string& s);
bool operator==(const string& s);
bool operator!=(const string& s);
// modify
void push_back(char c);
string& operator+=(char c);
void append(const char* str);
string& operator+=(const char* str);
void clear();
void swap(string& s);
const char* c_str() const;
// 返回c在string中第一次出现的位置
size_t find(char c, size_t pos = 0) const;
// 返回子串s在string中第一次出现的位置
size_t find(const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const;
// 在pos位置上插入字符c/字符串str,并返回该字符的位置
string& insert(size_t pos, char c);
string& insert(size_t pos, const char* str);
// 删除pos位置上的元素,并返回该元素的下一个位置
string& erase(size_t pos, size_t len);
private:
char* _str;
size_t _size;
size_t _capacity;
public:
static const size_t npos;
};
}string.cpp
cpp
#include"string.h"
namespace my_string
{
const size_t string::npos = -1;
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& _cout, const my_string::string& s)
{
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i)
{
_cout << s[i];
}
return _cout;
}
std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& _cin, my_string::string& s)
{
// 每次提取前需要将s中的数据清除
s.clear();
// 模拟string中的buff缓冲区,当所输入的字符串有效数据个数小于256时,存放到buff中
char buff[256];
// 使用get函数,能够输入空白字符和换行符
char ch = _cin.get();
size_t i = 0;
while (ch != ' ' && ch != '\n')
{
buff[i++] = ch;
ch = _cin.get();
if (i == 255)
{
s += buff;
// 重置buff
i = 0;
}
}
// buff中有剩余字符
if (i > 0)
{
buff[i] = '\0';
s += buff;
}
return _cin;
}
const char* string::c_str() const
{
return _str;
}
size_t string::size() const
{
return _size;
}
size_t string::capacity() const
{
return _capacity;
}
string::iterator string::begin()
{
return _str;
}
string::iterator string::end()
{
return _str + _size;
}
string::const_iterator string::begin() const
{
return _str;
}
string::const_iterator string::end() const
{
return _str + _size;
}
bool string::empty() const
{
return _size == 0;
}
void string::resize(size_t n, char c)
{
//if (n < _size)
//{
// _str[n] = '\0';
// _size = n;
//}
//if (n > _size && n < _capacity)
//{
// while (_size != n)
// {
// _str[_size++] = c;
// }
// _str[n] = '\0';
//}
//if (n > _capacity)
//{
// (*this).reserve(n);
//}
if (n > _size)
{
if (n > _capacity)
{
reserve(n);
}
memset(_str + _size, c, n - _size);
}
_str[n] = '\0';
_size = n;
}
void string::reserve(size_t n)
{
if (n > _capacity)
{
char* tmp = new char[n + 1];
memcpy(tmp, _str, _size + 1);
delete[] _str;
_str = tmp;
_capacity = n;
}
}
char& string::operator[](size_t index)
{
return _str[index];
}
const char& string::operator[](size_t index) const
{
return _str[index];
}
bool string::operator<(const string& s)
{
size_t end1 = _size - 1;
size_t end2 = s._size - 1;
size_t begin1 = 0;
size_t begin2 = 0;
while (begin1 != end1 && begin2 != end2)
{
if (_str[begin1] < s._str[begin2])
{
return true;
}
else if (_str[begin1] > s._str[begin2])
{
return false;
}
begin1++;
begin2++;
}
//if (begin1 == end1 && begin2 != end2)
//{
// return true;
//}
//else
//{
// return false;
//}
return begin1 == end1 && begin2 != end2;
}
bool string::operator==(const string& s)
{
size_t end1 = _size - 1;
size_t end2 = s._size - 1;
size_t begin1 = 0;
size_t begin2 = 0;
while (begin1 != end1 && begin2 != end2)
{
if (_str[begin1] != s._str[begin2])
{
return false;
}
begin1++;
begin2++;
}
return begin1 == end1 && begin2 == end2;
}
bool string::operator<=(const string& s)
{
return *this < s || *this == s;
}
bool string::operator>(const string& s)
{
return !(*this <= s);
}
bool string::operator>=(const string& s)
{
return !(*this < s);
}
bool string::operator!=(const string& s)
{
return !(*this == s);
}
void string::push_back(char c)
{
if (_size == _capacity)
{
size_t newcapacity = _capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * _capacity;
reserve(newcapacity);
}
_str[_size++] = c;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
void string::append(const char* str)
{
size_t len = strlen(str);
if (_size + len > _capacity)
{
size_t newcapacity = _size + len > 2 * _capacity ? _size + len : 2 * _capacity;
reserve(newcapacity);
}
memcpy(_str + _size, str, len + 1);
_size += len;
}
string& string::operator+=(char c)
{
push_back(c);
return *this;
}
string& string::operator+=(const char* str)
{
append(str);
return *this;
}
void string::clear()
{
_str[0] = '\0';
_size = 0;
}
void string::swap(string& s)
{
std::swap(_str, s._str);
std::swap(_size, s._size);
std::swap(_capacity, s._capacity);
}
size_t string::find(char c, size_t pos) const
{
assert(pos < _size);
for (int i = pos; i < _size; ++i)
{
if (_str[i] == c)
{
return i;
}
}
return npos;
}
size_t string::find(const char* s, size_t pos) const
{
assert(pos < _size);
const char* tmp = strstr(_str + pos, s);
if (tmp == nullptr)
{
return npos;
}
return tmp - _str;
}
string& string::insert(size_t pos, char c)
{
assert(pos <= _size);
if (_size == _capacity)
{
size_t newcapacity = _capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * _capacity;
reserve(newcapacity);
}
//size_t end = _size + 1;
//while (end > pos)
//{
// _str[end] = _str[end - 1];
// end--;
//}
memmove(_str + pos + 1, _str + pos, _size - pos + 1);
_str[pos] = c;
_size++;
return *this;
}
string& string::erase(size_t pos, size_t len)
{
assert(pos < _size);
if (len == npos || len >= _size - pos)
{
_str[pos] = '\0';
_size = pos;
return *this;
}
memmove(_str + pos, _str + pos + len, _size + 1 - (pos + len));
_size -= len;
return *this;
}
string& string::insert(size_t pos, const char* str)
{
size_t len = strlen(str);
if (_size + len > _capacity)
{
size_t newcapacity = _size + len > 2 * _capacity ? _size + len : 2 * _capacity;
reserve(newcapacity);
}
memmove(_str + pos + len, _str + pos, _size + 1 - pos);
memcpy(_str + pos, str, len);
_size += len;
return *this;
}
}test.cpp
cpp
#include"string.h"
using namespace std;
namespace my_string
{
void Test_String1()
{
string s1("Hello world");
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
cout << s1.size() << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
string s2 = "Hello";
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
cout << s2.size() << endl;
cout << s2.capacity() << endl;
string s3(s2);
cout << s3.c_str() << endl;
cout << s3.size() << endl;
cout << s3.capacity() << endl;
string s4 = s1;
cout << s4.c_str() << endl;
cout << s4.size() << endl;
cout << s4.capacity() << endl;
s4 = s2;
cout << s4.c_str() << endl;
cout << s4.size() << endl;
cout << s4.capacity() << endl;
}
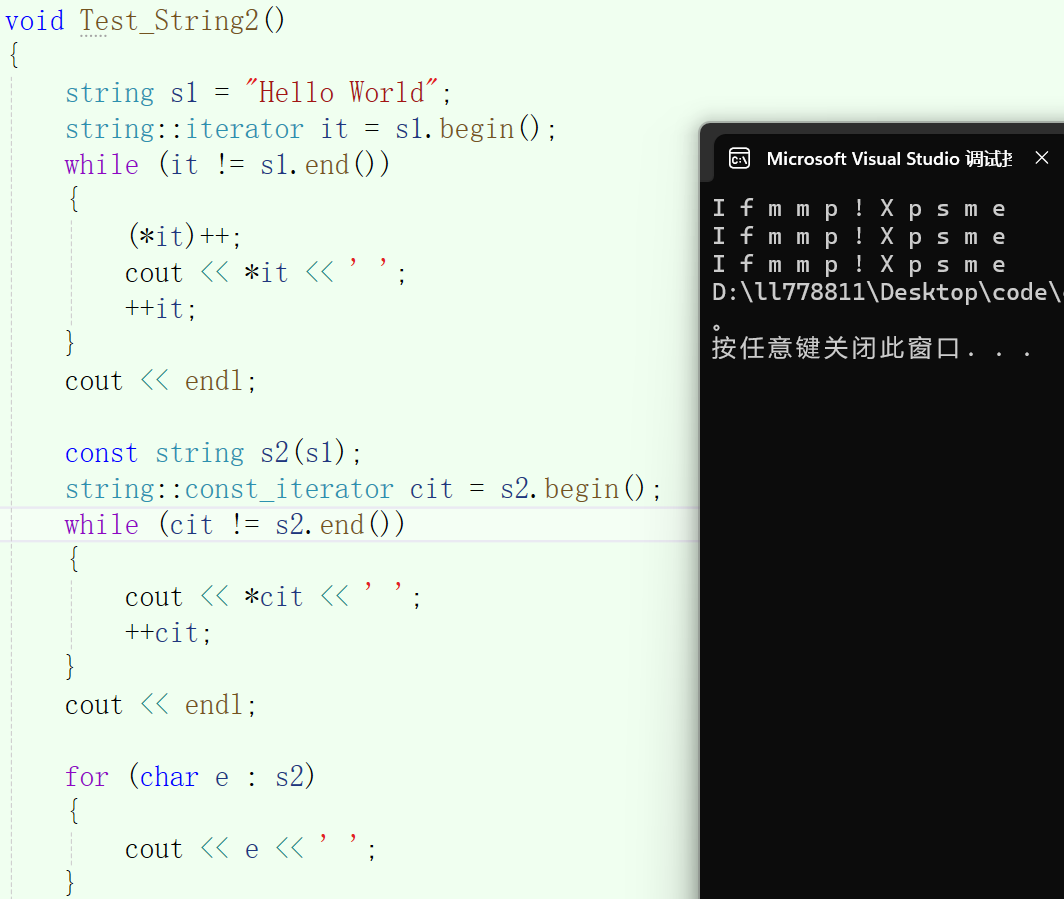
void Test_String2()
{
string s1 = "Hello World";
string::iterator it = s1.begin();
while (it != s1.end())
{
(*it)++;
cout << *it << ' ';
++it;
}
cout << endl;
const string s2(s1);
string::const_iterator cit = s2.begin();
while (cit != s2.end())
{
cout << *cit << ' ';
++cit;
}
cout << endl;
for (char e : s2)
{
cout << e << ' ';
}
}
void Test_String3()
{
string s1 = "Hello World";
s1.reserve(100);
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
cout << s1.size() << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
cout << s1[0] << endl;
++s1[0];
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
string s2 = "Hello";
s2.resize(2);
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
cout << s2.size() << endl;
cout << s2.capacity() << endl;
s2.resize(4);
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
cout << s2.size() << endl;
cout << s2.capacity() << endl;
s2.resize(10);
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
cout << s2.size() << endl;
cout << s2.capacity() << endl;
//std::string s2 = "Hello";
//s2.resize(2);
//cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
//cout << s2.size() << endl;
//cout << s2.capacity() << endl;
//s2.resize(4);
//cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
//cout << s2.size() << endl;
//cout << s2.capacity() << endl;
//s2.resize(10);
//cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
//cout << s2.size() << endl;
//cout << s2.capacity() << endl;
}
void Test_String4()
{
string s1 = "Hello World";
string s2 = "Hello";
cout << (s1 < s2) << endl;
cout << (s2 < s1) << endl;
string s3(s1);
cout << (s1 == s3) << endl;
cout << (s2 == s3) << endl;
cout << (s1 >= s2) << endl;
cout << (s1 != s2) << endl;
cout << (s2 <= s1) << endl;
}
void Test_String5()
{
string s1("Hello");
s1.push_back('x');
s1 += 'x';
s1 += "xxxxx";
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
cout << s1.size() << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
const char* p = "Worldxxxxxxx";
string s3 = "Hello ";
cout << s3.c_str() << endl;
cout << s3.size() << endl;
cout << s3.capacity() << endl;
s3.append(p);
cout << s3.c_str() << endl;
cout << s3.size() << endl;
cout << s3.capacity() << endl;
string s4 = "Hello";
string s5 = "Worldxxxxxxxx";
cout << s4.c_str() << endl;
cout << s4.size() << endl;
cout << s4.capacity() << endl;
cout << s5.c_str() << endl;
cout << s5.size() << endl;
cout << s5.capacity() << endl;
s4.swap(s5);
cout << s4.c_str() << endl;
cout << s4.size() << endl;
cout << s4.capacity() << endl;
cout << s5.c_str() << endl;
cout << s5.size() << endl;
cout << s5.capacity() << endl;
}
void Test_String6()
{
string s1 = "Hello ";
cout << s1.find('e') << endl;
s1 += "World";
cout << s1.find("Wor") << endl;
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
cout << s1.size() << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
// "Hello World"
s1.insert(0, 'x');
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
cout << s1.size() << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
string s2 = "Hello World";
//s2.erase(1, 2);
s2.insert(11, "xxx");
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
cout << s2.size() << endl;
cout << s2.capacity() << endl;
}
void Test_String7()
{
string s1 = "Hello World";
cout << s1 << endl;
cin >> s1;
cout << s1 << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
my_string::Test_String2();
return 0;
}