引言
还记得那些需要反复查阅API文档、手动输入长函数名的日子吗?如今,AI代码补全已经成为开发者日常编码中最强大的生产力工具之一。当你敲下几个字符时,它能神奇地预测出你接下来想要编写的整段代码。本文将深入探索AI代码补全的核心实现原理,揭开这项"魔法"背后的技术秘密。
无论你是对AI工具充满好奇的前端,还是想了解大型语言模型如何应用于开发工具的其他类型的工程师,这篇文章都将为你提供有价值的技术洞见。让我们一起揭开AI代码补全的神秘面纱,了解它是如何理解我们的代码意图并提供精准补全的。
传统vs人工智能:代码补全的革命性变化
在深入技术细节前,让我们先了解AI代码补全与传统方式的根本区别:
| 特性 | 传统代码补全 | AI驱动代码补全 |
|---|---|---|
| 补全来源 | 基于静态分析、符号表 | 基于大语言模型和上下文理解 |
| 补全长度 | 通常是单个符号或方法 | 可以是完整函数体、多行代码块 |
| 上下文理解 | 有限,主要基于当前文件 | 广泛,包含项目结构、导入、相关文件 |
| 实现复杂度 | 较低,规则驱动 | 较高,涉及模型调用、上下文处理 |
| 响应速度 | 毫秒级 | 百毫秒到秒级(有缓存可提速) |
想象一下:传统补全就像一本字典,只能按字母顺序查找单词;而AI补全则像一位了解你编码风格的搭档,能猜测你的下一步意图并提供完整解决方案。
系统架构
整个代码补全系统将采用分层架构设计,包括IDE集成层、核心处理层和AI交互层。
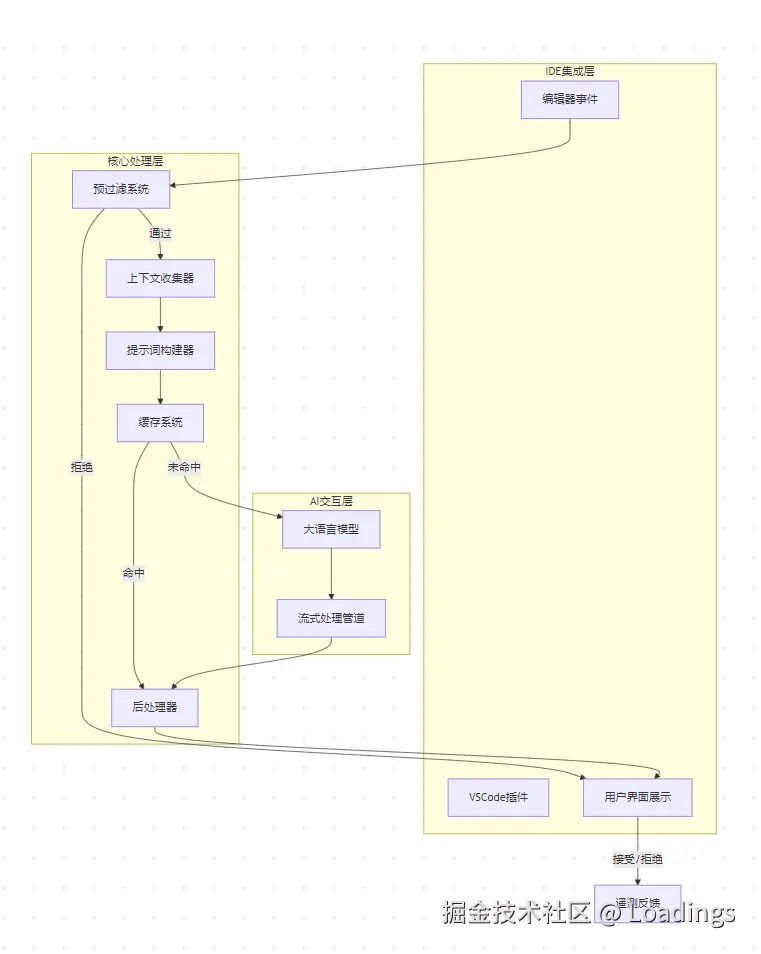
编辑器中的代码补全请求从触发到显示,经历以下详细流程:
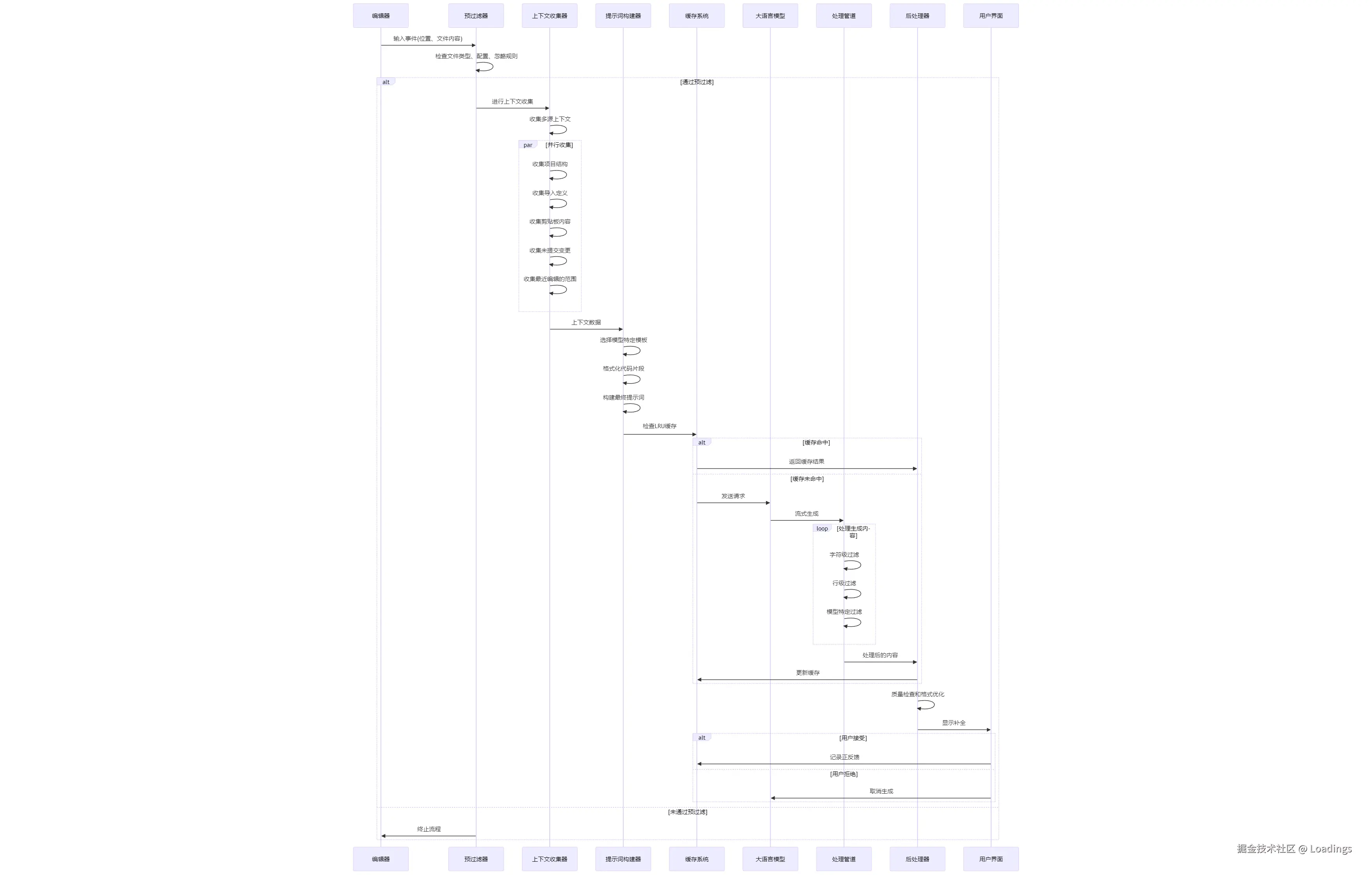
完整使用流程的序列图
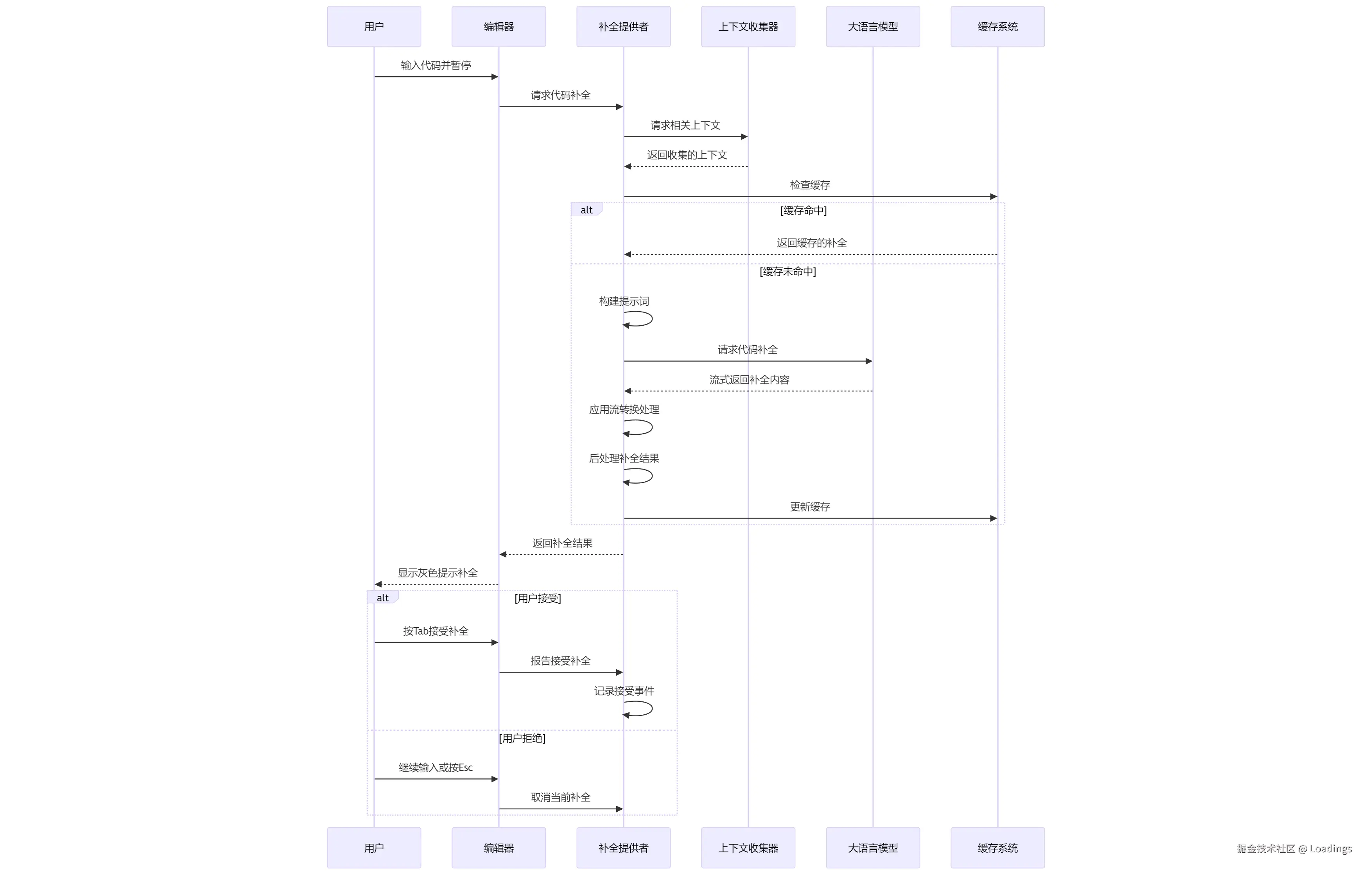
AST在AutoComplete中的作用
AST(抽象语法树)在自动完成中扮演关键角色:
-
上下文理解:通过AST分析光标所在的代码结构
typescript// 获取光标位置的AST路径 const treePath = await getTreePathAtCursor( documentText, cursorPosition, filepath, languageInfo ); -
过滤:基于AST结构决定是否触发补全
typescriptfunction shouldPrefilter(treePath) { // 在注释中不触发自动完成 if (isInComment(treePath)) { return true; } // 检查是否处于字符串内 if (isInString(treePath)) { return !options.completeInsideStrings; } return false; } -
多行补全判断:判断是否应该提供多行代码补全
typescriptfunction shouldCompleteMultiline(treePath) { // 在函数体内提供多行补全 if (isInFunctionBody(treePath)) { return true; } // 在代码块内提供多行补全 if (isInBlockStatement(treePath)) { return true; } return false; }
揭秘核心组件:补全引擎的"大脑"
补全提供者是整个系统的中枢,它负责整个自动补全过程的协调。流程主要分为以下几个阶段:
- 请求处理:接收编辑器中的当前位置和上下文
- 上下文收集:从多个源获取相关代码片段
- 提示词构建:基于收集的上下文和当前位置构建提示词
- 生成补全:调用LLM生成代码补全
- 过滤和后处理:处理和优化生成的补全结果显示和应用:将补全显示给用户并处理用户操作
这段代码展示了补全引擎的核心设计思想:采用模块化结构,各组件各司其职,通过精心的协调共同完成复杂的补全任务。就像一个精密的机器,每个齿轮都至关重要。
js
/**
* 智能代码补全系统的核心提供者类
* 负责协调整个补全过程的各个环节
*/
class CompletionProvider {
constructor(configHandler, ide, getLlmFunc, onErrorHandler, getDefinitionsFunc) {
// 初始化内部组件
this.autocompleteCache = new AutocompleteLruCache(); // 缓存管理
this.errorsShown = new Set(); // 已显示的错误
this.bracketMatchingService = new BracketMatchingService(); // 括号匹配服务
this.debouncer = new AutocompleteDebouncer(); // 延迟处理
this.completionStreamer = new CompletionStreamer(this.onError.bind(this)); // 流处理
this.loggingService = new AutocompleteLoggingService(); // 日志记录
this.contextRetrievalService = new ContextRetrievalService(ide); // 上下文收集
// 外部依赖
this.configHandler = configHandler;
this.ide = ide;
this._injectedGetLlm = getLlmFunc;
this._onError = onErrorHandler;
this.getDefinitionsFromLsp = getDefinitionsFunc;
}
/**
* 处理错误的方法
* 过滤常见错误,只显示重要错误给用户
*/
onError(e) {
// 忽略常见错误,如连接超时等
if (ERRORS_TO_IGNORE.some(err =>
typeof e === "string" ? e.includes(err) : e?.message?.includes(err))) {
return;
}
console.warn("Error generating autocompletion: ", e);
if (!this.errorsShown.has(e.message)) {
this.errorsShown.add(e.message);
this._onError(e);
}
}
/**
* 准备LLM配置
* 确保模型配置适合代码补全任务
*/
async _prepareLlm() {
const llm = await this._injectedGetLlm();
if (!llm) return undefined;
// 修复模型配置问题
if (llm.model === undefined && llm.completionOptions?.model !== undefined) {
llm.model = llm.completionOptions.model;
}
// 忽略空API密钥
if (llm.providerName === "mistral" && llm.apiKey === "") {
return undefined;
}
// 设置适合补全的温度(如未指定)
if (llm.completionOptions.temperature === undefined) {
llm.completionOptions.temperature = 0.01;
}
// 处理特定模型的配置
if (llm.providerName === "openai") {
llm.useLegacyCompletionsEndpoint = true;
}
return llm;
}
/**
* 取消当前补全请求
*/
cancel() {
this.loggingService.cancel();
}
/**
* 处理用户接受补全的反馈
*/
accept(completionId) {
const outcome = this.loggingService.accept(completionId);
if (!outcome) return;
// 更新括号匹配服务的状态
this.bracketMatchingService.handleAcceptedCompletion(
outcome.completion,
outcome.filepath
);
}
/**
* 记录补全显示事件
*/
markDisplayed(completionId, outcome) {
this.loggingService.markDisplayed(completionId, outcome);
}
/**
* 加载补全选项配置
*/
async _getAutocompleteOptions() {
const { config } = await this.configHandler.loadConfig();
// 合并默认选项和用户配置
const options = {
...DEFAULT_AUTOCOMPLETE_OPTS,
...config?.tabAutocompleteOptions,
};
return options;
}
/**
* 提供内联补全项的主方法
* 这是系统的入口点
*/
async provideInlineCompletionItems(input, token) {
try {
// 创建中止信号(如未提供)
if (!token) {
const controller = this.loggingService.createAbortController(input.completionId);
token = controller.signal;
}
const startTime = Date.now();
const options = await this._getAutocompleteOptions();
// 应用延迟机制
if (await this.debouncer.delayAndShouldDebounce(options.debounceDelay)) {
return undefined;
}
// 获取LLM
const llm = await this._prepareLlm();
if (!llm) return undefined;
// 创建辅助变量对象(包含文件内容、位置等信息)
const helper = await HelperVars.create(
input, options, llm.model, this.ide
);
// 预过滤检查
if (await shouldPrefilter(helper, this.ide)) {
return undefined;
}
// 收集上下文片段
const [snippetPayload, workspaceDirs] = await Promise.all([
getAllSnippets({
helper,
ide: this.ide,
getDefinitionsFromLsp: this.getDefinitionsFromLsp,
contextRetrievalService: this.contextRetrievalService,
}),
this.ide.getWorkspaceDirs(),
]);
// 构建提示词
const { prompt, prefix, suffix, completionOptions } = renderPrompt({
snippetPayload,
workspaceDirs,
helper,
});
// 尝试补全
let completion = "";
// 检查缓存
const cache = await this.autocompleteCache;
const cachedCompletion = helper.options.useCache
? await cache.get(helper.prunedPrefix)
: undefined;
let cacheHit = false;
if (cachedCompletion) {
// 使用缓存结果
cacheHit = true;
completion = cachedCompletion;
} else {
// 判断是单行还是多行补全
const multiline = !helper.options.transform ||
shouldCompleteMultiline(helper);
// 流式生成补全
const completionStream = this.completionStreamer.streamCompletionWithFilters(
token,
llm,
prefix,
suffix,
prompt,
multiline,
completionOptions,
helper,
);
// 收集生成结果
for await (const update of completionStream) {
completion += update;
}
// 如果已中止,返回未定义
if (token.aborted) {
return undefined;
}
// 后处理生成的补全
const processedCompletion = helper.options.transform
? postprocessCompletion({
completion,
prefix: helper.prunedPrefix,
suffix: helper.prunedSuffix,
llm,
})
: completion;
completion = processedCompletion;
}
if (!completion) {
return undefined;
}
// 构建结果对象
const outcome = {
time: Date.now() - startTime,
completion,
prefix,
suffix,
prompt,
modelProvider: llm.providerName,
modelName: llm.model,
completionOptions,
cacheHit,
filepath: helper.filepath,
numLines: completion.split("\n").length,
completionId: helper.input.completionId,
gitRepo: await this.ide.getRepoName(helper.filepath),
};
return outcome;
} catch (error) {
this.onError(error);
return undefined;
}
}
}预过滤系统-提升响应速度的第一道关卡
在向大语言模型发送请求前,系统会通过预过滤机制快速判断当前场景是否适合触发补全,这极大提升了用户体验:
- 在生成补全之前,系统会进行预过滤判断是否应该进行补全:
- 配置检查:检查是否在设置中禁用了自动补全
- 文件检查:检查当前文件是否在禁用列表中
- 语言特定检查:针对特定语言的规则检查
- 编辑器状态检查:多光标时不提供补全
这种细致入微的设计大大提升了用户体验,避免了不必要的干扰。
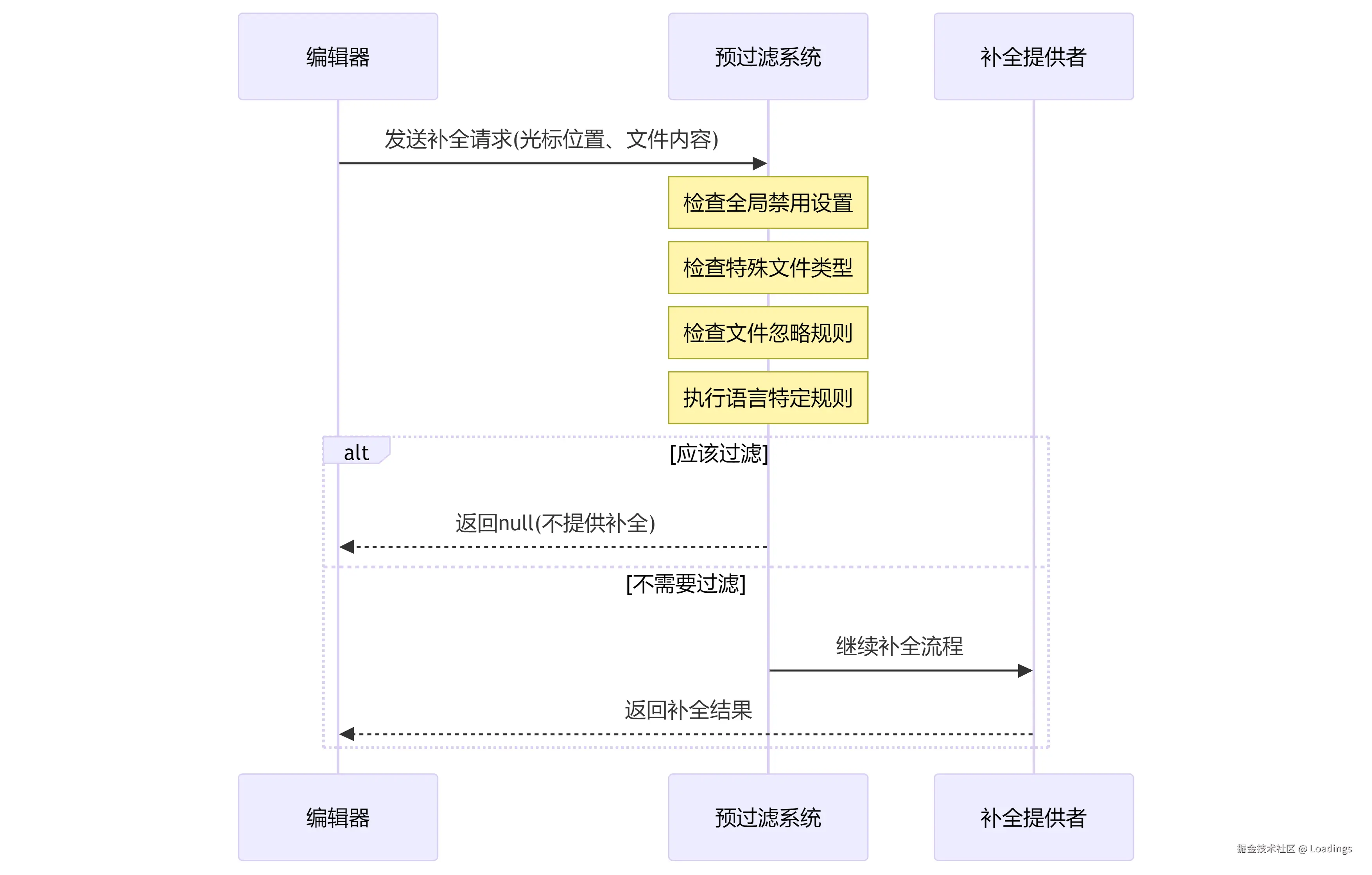
js
/**
* 预过滤主函数
* 决定是否应该提供补全
*/
async function shouldPrefilter(helper, ide) {
// 检查全局禁用设置
if (helper.options.disable) {
return true;
}
// 检查特殊文件
if (helper.filepath === getConfigJsonPath()) {
return true;
}
// 检查文件忽略规则
const disableInFiles = [...(helper.options.disableInFiles ?? []), "*.prompt"];
if (await isDisabledForFile(helper.filepath, disableInFiles, ide)) {
return true;
}
// 对空文件的处理
if (helper.filepath.includes("Untitled") && helper.fileContents.trim() === "") {
return true;
}
// 根据语言特定规则判断
if (await shouldLanguageSpecificPrefilter(helper)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 检查文件是否被忽略
*/
async function isDisabledForFile(currentFilepath, disableInFiles, ide) {
if (disableInFiles) {
// 获取相对路径
const workspaceDirs = await ide.getWorkspaceDirs();
const { relativePathOrBasename } = findUriInDirs(
currentFilepath,
workspaceDirs
);
// 使用忽略模式检查
const pattern = ignore().add(disableInFiles);
if (pattern.ignores(relativePathOrBasename)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* 语言特定的预过滤规则
*/
async function shouldLanguageSpecificPrefilter(helper) {
const line = helper.fileLines[helper.pos.line] ?? "";
// 检查是否在行尾
for (const endOfLine of helper.lang.endOfLine) {
if (line.endsWith(endOfLine) && helper.pos.character >= line.length) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}上下文收集:AI补全的"超能力"来源
AI代码补全最大的优势在于它能理解丰富的上下文,就像拥有"透视眼"一样看到项目的全貌。这是如何实现的,多维度上下文收集:
- 收集当前文件的信息
- 分析文件中的导入语句并找到相关定义
- 识别项目结构中的相关代码
- 从IDE的LSP服务获取相关代码片段
- 收集剪贴板内容
- 最近编辑的范围
- 最近访问的范围
- 获取当前未提交的代码更改
- 将上述获取到的内容整合成整个对象
核心架构设计
上下文收集系统采用模块化设计,主要由以下组件构成:
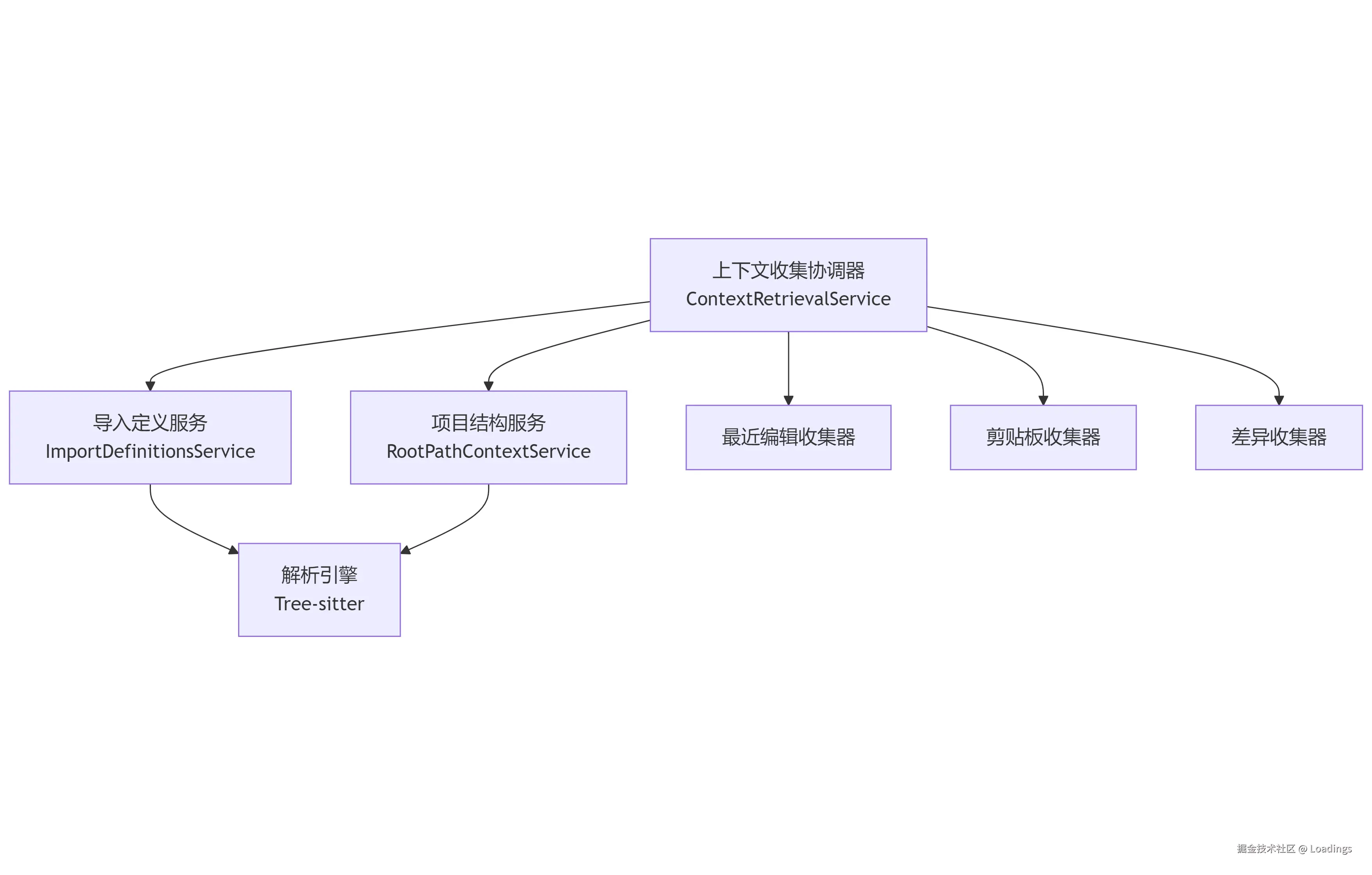
这些组件通过协作完成上下文的全方位收集,每个组件负责特定领域的上下文信息获取。
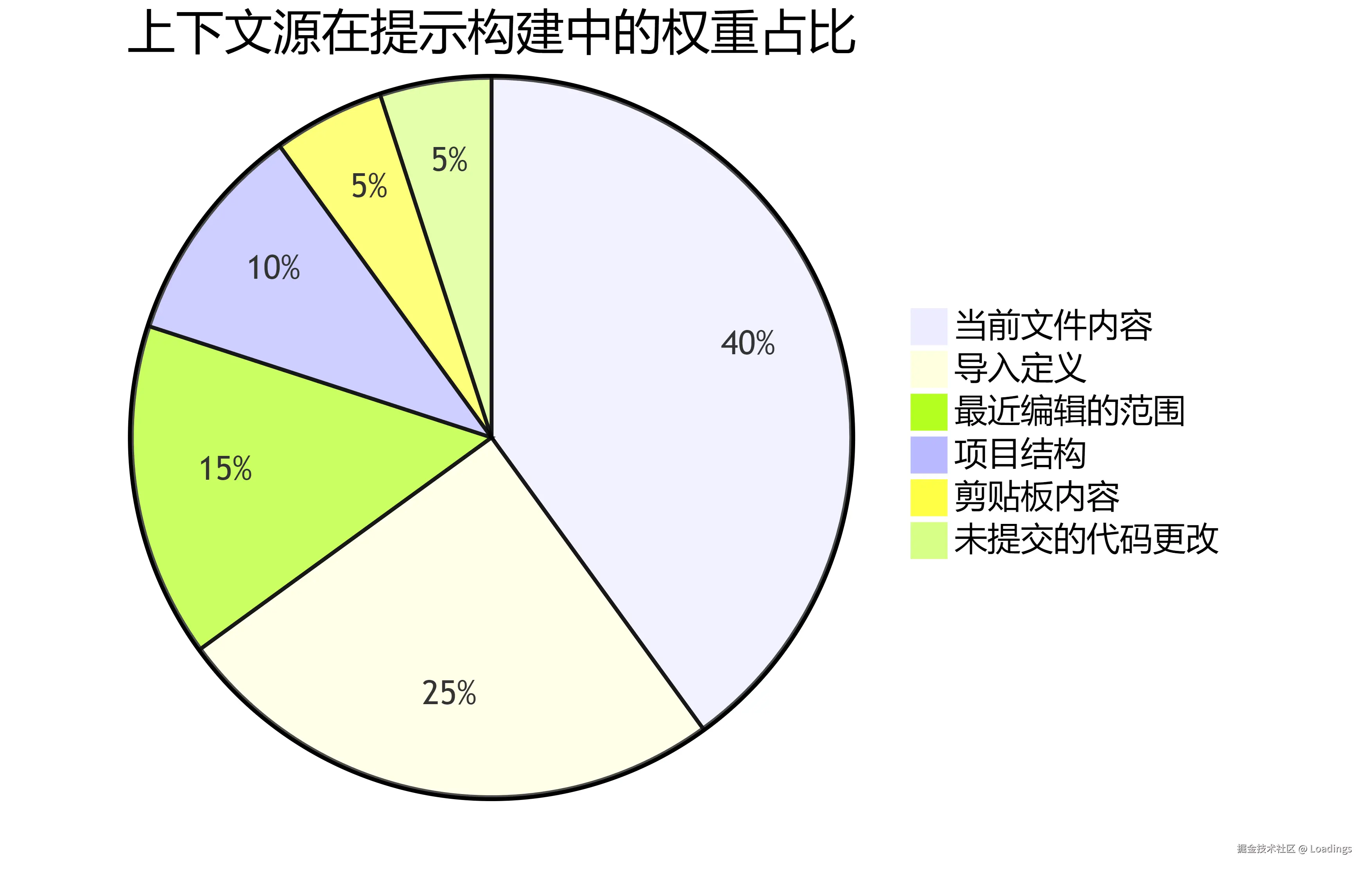
上下文各源影响分析表
| 上下文源 | 收集方法 | 影响程度 | 典型场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 当前文件内容 | 从光标周围提取代码 | 最高 (40%) | 所有补全场景 |
| 导入定义 | 分析导入语句获取相关API定义 | 高 (25%) | 使用导入模块的API |
| 最近编辑的范围 | 记录用户最近编辑的区域 | 中高 (15%) | 延续最近编辑的逻辑 |
| 项目结构 | 分析目录结构和相关文件 | 中 (10%) | 使用项目内其他模块 |
| 剪贴板内容 | 获取用户最近复制的代码 | 低 (5%) | 补全类似复制内容 |
| 未提交的代码更改 | 获取版本控制的未提交更改 | 低 (5%) | 使用最新的代码逻辑 |
实际案例分析
以下是一个实际编码场景中上下文收集的示例,想象你正在开发一个用户管理功能,当你输入到这里时:
当前编辑文件:userService.js
javascript
import { fetchUserProfile, fetchUserSettings } from './userAPI';
function processUser(user) {
const { name, email } = user;
// 光标位置
}系统收集的上下文片段:
- 导入定义(从userAPI.js):
javascript
// fetchUserProfile定义
export function fetchUserProfile(userId) {
return fetch(`/api/users/${userId}/profile`).then(res => res.json());
}
// fetchUserSettings定义
export function fetchUserSettings(userId) {
return fetch(`/api/users/${userId}/settings`).then(res => res.json());
}- 最近编辑的相关代码:
javascript
// 用户最近在另一个文件中编辑的代码
function saveUserData(user) {
const result = validateUser(user);
if (result.valid) {
return updateUserInDatabase(user);
}
return Promise.reject(result.errors);
}- 未提交的代码变更:
diff
@@ -15,6 +15,10 @@
function validateUser(user) {
const errors = [];
if (!user.email) errors.push('Email is required');
+ if (!user.name) errors.push('Name is required');
+
+ // 验证邮箱格式
+ if (!/^[\w.-]+@[\w.-]+\.\w+$/.test(user.email)) errors.push('Invalid email format');
return { valid: errors.length === 0, errors };
}通过融合这些上下文,AI模型可以提供更智能的补全建议,例如:
javascript
function processUser(user) {
const { name, email } = user;
// 验证用户数据
const result = validateUser(user);
if (!result.valid) {
return Promise.reject(result.errors);
}
// 获取用户资料和设置
return Promise.all([
fetchUserProfile(user.id),
fetchUserSettings(user.id)
]).then(([profile, settings]) => {
// 处理用户数据
return { ...user, profile, settings };
});
}这个案例展示了AI代码补全系统如何通过收集多源上下文(导入定义、最近编辑代码和未提交变更),生成符合项目风格和逻辑的智能补全建议。系统不仅理解了导入的API用法,还融合了项目中的验证逻辑和数据处理模式,产生出高度相关的补全结果。
具体实现:
语法分析驱动的上下文理解
系统使用Tree-sitter这一高性能解析器构建抽象语法树(AST),精确理解代码结构而非简单文本匹配,这段代码从AST根节点出发,构建一条通向光标位置的节点路径,帮助系统理解用户正在编辑哪种语法结构(函数、类、循环等)。这是上下文收集的基础,使系统能够智能识别相关代码片段。
ts
export async function getTreePathAtCursor(
ast: Parser.Tree,
cursorIndex: number,
): Promise<AstPath> {
const path = [ast.rootNode];
while (path[path.length - 1].childCount > 0) {
let foundChild = false;
for (const child of path[path.length - 1].children) {
if (child.startIndex <= cursorIndex && child.endIndex >= cursorIndex) {
path.push(child);
foundChild = true;
break;
}
}
if (!foundChild) {
break;
}
}
return path;
}智能符号提取与相关度计算
系统通过识别光标附近的标识符,建立相关代码间的语义连接,系统使用Jaccard相似度算法评估代码片段与当前上下文的相关性,确保最相关的片段被优先包含到提示中。
ts
// 从代码片段中提取符号
export function getSymbolsForSnippet(snippet: string): Set<string> {
const rx = /[\s.,\/#!$%\^&\*;:{}=\-_`~()\[\]]/g;
const symbols = snippet
.split(rx)
.map((s) => s.trim())
.filter((s) => s !== "");
return new Set(symbols);
}
// 计算代码相似度
function jaccardSimilarity(a: string, b: string): number {
const aSet = getSymbolsForSnippet(a);
const bSet = getSymbolsForSnippet(b);
const union = new Set([...aSet, ...bSet]).size;
if (union === 0) return 0;
let intersection = 0;
for (const symbol of aSet) {
if (bSet.has(symbol)) intersection++;
}
return intersection / union;
}导入定义解析机制
AI代码补全的一个关键优势是理解导入的模块和API。系统的导入解析模块实现如下,该实现遵循以下策略:
- 提取光标附近5行前缀和3行后缀
- 识别所有非关键字标识符
- 在导入表中查找这些标识符的定义
- 收集相关定义的代码内容
例如,当用户在fetchUserData函数后输入.时,系统会找到该函数的定义,帮助模型理解可用的方法和属性。
ts
public async getSnippetsFromImportDefinitions(
helper: HelperVars,
): Promise<AutocompleteCodeSnippet[]> {
if (helper.options.useImports === false) {
return [];
}
const importSnippets: AutocompleteCodeSnippet[] = [];
const fileInfo = this.importDefinitionsService.get(helper.filepath);
if (fileInfo) {
const { imports } = fileInfo;
// 提取光标周围的符号
const textAroundCursor =
helper.fullPrefix.split("\n").slice(-5).join("\n") +
helper.fullSuffix.split("\n").slice(0, 3).join("\n");
const symbols = Array.from(getSymbolsForSnippet(textAroundCursor)).filter(
(symbol) => !helper.lang.topLevelKeywords.includes(symbol),
);
// 为每个符号查找导入信息
for (const symbol of symbols) {
const references = imports[symbol];
if (Array.isArray(references)) {
importSnippets.push(...references.map(ref => ({
filepath: ref.filepath,
content: ref.contents,
type: AutocompleteSnippetType.Code,
})));
}
}
}
return importSnippets;
}高级项目结构分析
系统使用RootPathContextService分析项目结构,找出与当前代码语义相关的其他定义,这段代码展示了:
- 递归分析语法树路径上的节点
- 基于节点类型获取相关定义
- 构建层次化的上下文信息
ts
async getContextForPath(
filepath: string,
astPath: AstPath,
): Promise<AutocompleteCodeSnippet[]> {
const snippets: AutocompleteCodeSnippet[] = [];
// 递归构建上下文路径
let parentKey = filepath;
for (const astNode of astPath.filter((node) =>
RootPathContextService.TYPES_TO_USE.has(node.type),
)) {
const key = RootPathContextService.keyFromNode(parentKey, astNode);
// 使用缓存提高性能
const foundInCache = this.cache.get(key);
const newSnippets =
foundInCache ?? (await this.getSnippetsForNode(filepath, astNode));
// 转换为统一格式
snippets.push(...newSnippets.map(item => ({
filepath: item.filepath,
content: item.contents,
type: AutocompleteSnippetType.Code,
})));
// 更新缓存
if (!foundInCache) {
this.cache.set(key, newSnippets);
}
parentKey = key;
}
return snippets;
}多源并行收集与超时保护
为了提高效率,系统并行收集不同来源的上下文,并使用超时保护机制避免单一来源阻塞整体流程,通过这种设计,即使某个来源响应慢或失败,系统仍能在100毫秒内继续处理流程,保证了整体的响应速度。
js
const [
rootPathSnippets, // 项目结构上下文
importDefinitionSnippets, // 导入定义上下文
ideSnippets, // IDE提供的片段
diffSnippets, // 未提交的代码差异
clipboardSnippets, // 剪贴板内容
] = await Promise.all([
racePromise(contextRetrievalService.getRootPathSnippets(helper)),
racePromise(contextRetrievalService.getSnippetsFromImportDefinitions(helper)),
IDE_SNIPPETS_ENABLED ? racePromise(getIdeSnippets(helper, ide, getDefinitionsFromLsp)) : [],
racePromise(getDiffSnippets(ide)),
racePromise(getClipboardSnippets(ide)),
]);
function racePromise<T>(promise: Promise<T[]>): Promise<T[]> {
const timeoutPromise = new Promise<T[]>((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => resolve([]), 100); // 100ms超时
});
return Promise.race([promise, timeoutPromise]);
}智能片段合并与去重
系统不仅收集片段,还会智能合并重叠区域,避免上下文冗余,这种智能合并机制确保系统能够:
- 提供完整的代码上下文
- 避免重复代码片段浪费token额度
- 保留最高相关性分数的代码片段
js
function deduplicateSnippets(
snippets: Required<AutocompleteSnippetDeprecated>[],
): Required<AutocompleteSnippetDeprecated>[] {
// 按文件分组
const fileGroups: {
[key: string]: Required<AutocompleteSnippetDeprecated>[];
} = {};
for (const snippet of snippets) {
if (!fileGroups[snippet.filepath]) {
fileGroups[snippet.filepath] = [];
}
fileGroups[snippet.filepath].push(snippet);
}
// 合并重叠范围
const allRanges = [];
for (const file of Object.keys(fileGroups)) {
allRanges.push(...mergeSnippetsByRange(fileGroups[file]));
}
return allRanges;
}
function mergeSnippetsByRange(
snippets: Required<AutocompleteSnippetDeprecated>[],
): Required<AutocompleteSnippetDeprecated>[] {
if (snippets.length <= 1) {
return snippets;
}
const sorted = snippets.sort(
(a, b) => a.range.start.line - b.range.start.line,
);
const merged: Required<AutocompleteSnippetDeprecated>[] = [];
while (sorted.length > 0) {
const next = sorted.shift()!;
const last = merged[merged.length - 1];
if (merged.length > 0 && last.range.end.line >= next.range.start.line) {
// 合并与前一个片段重叠的部分
last.score = Math.max(last.score, next.score);
last.range.end = next.range.end;
last.contents = mergeOverlappingRangeContents(last, next);
} else {
merged.push(next);
}
}
return merged;
}
js
/**
* 收集所有相关代码片段
* 从多个来源并行收集上下文信息
*/
async function getAllSnippets({helper, ide, getDefinitionsFromLsp, contextRetrievalService}) {
// 获取最近编辑的范围片段
const recentlyEditedRangeSnippets = getSnippetsFromRecentlyEditedRanges(helper);
// 并行获取各类上下文
const [
rootPathSnippets, // 项目结构上下文
importDefinitionSnippets, // 导入定义上下文
ideSnippets, // IDE提供的片段
diffSnippets, // 未提交的代码差异
clipboardSnippets, // 剪贴板内容
] = await Promise.all([
racePromise(contextRetrievalService.getRootPathSnippets(helper)),
racePromise(contextRetrievalService.getSnippetsFromImportDefinitions(helper)),
IDE_SNIPPETS_ENABLED ? racePromise(getIdeSnippets(helper, ide, getDefinitionsFromLsp)) : [],
racePromise(getDiffSnippets(ide)),
racePromise(getClipboardSnippets(ide)),
]);
// 组合所有结果
return {
rootPathSnippets,
importDefinitionSnippets,
ideSnippets,
recentlyEditedRangeSnippets,
diffSnippets,
clipboardSnippets,
recentlyVisitedRangesSnippets: helper.input.recentlyVisitedRanges,
};
}
/**
* 在有限时间内获取结果的promise
* 防止单个上下文源阻塞整个流程
*/
function racePromise(promise) {
const timeoutPromise = new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => resolve([]), 100); // 100ms超时
});
return Promise.race([promise, timeoutPromise]);
}
/**
* 上下文检索服务类
* 负责处理各类上下文的收集
*/
class ContextRetrievalService {
constructor(ide) {
this.ide = ide;
this.importDefinitionsService = new ImportDefinitionsService(this.ide);
this.rootPathContextService = new RootPathContextService(
this.importDefinitionsService,
this.ide
);
}
/**
* 获取从导入语句中提取的上下文
*/
async getSnippetsFromImportDefinitions(helper) {
if (helper.options.useImports === false) {
return [];
}
const importSnippets = [];
const fileInfo = this.importDefinitionsService.get(helper.filepath);
if (fileInfo) {
const { imports } = fileInfo;
// 提取光标附近的符号
const textAroundCursor =
helper.fullPrefix.split("\n").slice(-5).join("\n") +
helper.fullSuffix.split("\n").slice(0, 3).join("\n");
// 过滤出非关键字的符号
const symbols = Array.from(getSymbolsForSnippet(textAroundCursor))
.filter(symbol => !helper.lang.topLevelKeywords.includes(symbol));
// 为每个符号查找导入信息
for (const symbol of symbols) {
const references = imports[symbol];
if (Array.isArray(references)) {
// 转换为代码片段
const snippets = references.map(ref => ({
filepath: ref.filepath,
content: ref.contents,
type: "Code",
}));
importSnippets.push(...snippets);
}
}
}
return importSnippets;
}
/**
* 获取项目结构上下文
*/
async getRootPathSnippets(helper) {
if (!helper.treePath) {
return [];
}
// 通过项目路径获取相关上下文
return this.rootPathContextService.getContextForPath(
helper.filepath,
helper.treePath
);
}
}
/**
* 获取未提交的代码差异(带缓存)
*/
async function getDiffSnippets(ide) {
// 使用时间戳作为缓存键
const currentTimestamp = ide.getLastFileSaveTimestamp ?
ide.getLastFileSaveTimestamp() :
Math.floor(Date.now() / 10000) * 10000; // 每10秒更新一次
// 检查缓存
const cached = diffSnippetsCache.get(currentTimestamp);
if (cached) {
return cached;
}
// 获取差异
let diff = [];
try {
diff = await ide.getDiff(true);
} catch (e) {
console.error("Error getting diff for autocomplete", e);
}
// 转换为片段并缓存
return diffSnippetsCache.set(
currentTimestamp,
diff.map(item => ({
content: item,
type: "Diff",
}))
);
}
/**
* 从最近编辑的范围获取片段
*/
function getSnippetsFromRecentlyEditedRanges(helper) {
if (helper.options.useRecentlyEdited === false) {
return [];
}
// 转换为代码片段
return helper.input.recentlyEditedRanges.map(range => ({
filepath: range.filepath,
content: range.lines.join("\n"),
type: "Code",
}));
}提示词构建:引导AI走向精准补全
收集到上下文后,系统需要构建合适的提示词来指导AI模型生成补全。这是最关键的环节之一
- 模板选择:从预置的提示词模板中pick
- 支持Fill-in-the-Middle, (FIM) 是一种提示词结构,允许模型在给定前缀和后缀的情况下填充中间部分;支持普通补全
- 提示词格式化
- 插入prefix和suffix(光标前后的代码)
- 添加收集的代码片段(snippets)
- 加入文件名、仓库名、语言等特定信息
- 停止词设置:getStopTokens为不同语言和模型设置合适的停止词,用于指示模型停止生成内容的特殊标记,用于控制输出边界
假设当用户在TypeScript文件中编写如下代码时,构建给大模型的提示词示例:
用户代码示例
typescript
// 用户正在编写的代码
function calculateTotal(items: ShoppingItem[]) {
// 光标位置在这里
return total;
}前缀:
typescript
function calculateTotal(items: ShoppingItem[]) {后缀(光标后的代码):
typescript
return total;
}构建GPT或Claude提示词
当使用GPT或Claude等模型进行自动完成时,系统会构建以下"洞填充"风格的提示词:
css
You are a HOLE FILLER. You are provided with a file containing holes, formatted as '{{HOLE_NAME}}'. Your TASK is to complete with a string to replace this hole with, inside a <COMPLETION></COMPLETION> XML tag, including context-aware indentation, if needed. All completions MUST be truthful, accurate, well-written and correct.
## EXAMPLE QUERY:
<QUERY>
function sum_evens(lim) {
var sum = 0;
for (var i = 0; i < lim; ++i) {
{{FILL_HERE}}
}
return sum;
}
</QUERY>
## CORRECT COMPLETION
<COMPLETION>if (i % 2 === 0) {
sum += i;
}</COMPLETION>
TASK: Fill the {{FILL_HERE}} hole. Answer only with the CORRECT completion, and NOTHING ELSE. Do it now.模型可能的响应
模型会生成一个适合上下文的代码补全,填充在<COMPLETION>标签中:
ini
<COMPLETION>
let total = 0;
for (const item of items) {
total += item.price * item.quantity;
}
</COMPLETION>通过专用代码语言模型内置的标签构建提示词
不同的专用代码语言模型使用各自特定的标签系统来执行自动完成任务。以下是主要代码模型使用的标签及其解释:
1. StableCode
标签:
<fim_prefix>- 标记前缀代码的开始<fim_suffix>- 标记后缀代码的开始<fim_middle>- 标记需要模型填充的中间部分的开始<file_sep>- 用于分隔多个文件上下文<|endoftext|>- 标记文本结束</fim_middle>- 标记中间部分的结束</code>- 标记代码块结束
来源: huggingface.co/stabilityai...
2. Qwen Coder
标签:
<|fim_prefix|>- 标记前缀代码的开始<|fim_suffix|>- 标记后缀代码的开始<|fim_middle|>- 标记需要填充的中间部分<|fim_pad|>- 填充标记<|repo_name|>- 标记代码库名称<|file_sep|>- 用于分隔多个文件<|im_start|>- 标记输入消息开始<|im_end|>- 标记输入消息结束
3. Codestral
标签:
[PREFIX]- 标记前缀代码[SUFFIX]- 标记后缀代码+++++- 用于标记文件路径(在多文件模式下)
特点: Codestral使用的标签顺序与其他模型不同,它先标记后缀再标记前缀。
4. CodeGemma
标签:
<|fim_prefix|>- 标记前缀代码<|fim_suffix|>- 标记后缀代码<|fim_middle|>- 标记填充部分<|file_separator|>- 用于分隔多个文件<end_of_turn>- 标记对话轮次结束<eos>- 结束标记
5. StarCoder2
标签:
<fim_prefix>- 标记前缀代码<fim_suffix>- 标记后缀代码<fim_middle>- 标记填充部分<file_sep>- 用于分隔多个文件上下文<|endoftext|>- 标记文本结束
6. CodeLlama
标签:
<PRE>- 标记前缀代码<SUF>- 标记后缀代码<MID>- 标记需要填充的中间部分< EOT >- 结束标记
7. CodeGeeX4
标签:
<|user|>- 标记用户输入开始<|assistant|>- 标记助手回复开始<|code_suffix|>- 标记后缀代码<|code_prefix|>- 标记前缀代码<|code_middle|>- 标记需要填充的中间部分###PATH:- 标记文件路径###LANGUAGE:- 标记编程语言###MODE:BLOCK- 标记补全模式###REFERENCE:- 标记参考代码
标签对比
不同模型的标签系统虽然概念相似,但具体实现有所不同:
- 格式差异: 有些模型使用尖括号
<>,有些使用方括号[],有些使用特殊Unicode字符。 - 顺序差异: 大多数模型采用"前缀-后缀-中间"的顺序,但Codestral采用"后缀-前缀"的顺序。
- 附加信息: 有些模型(如CodeGeeX4)包含文件路径、语言类型和模式等额外信息。
- 多文件支持: 大多数模型都有处理多文件上下文的标记,通常用某种形式的文件分隔符。
这些专用标签系统使得代码模型能够以更紧凑的方式理解补全任务,无需像GPT/Claude那样使用冗长的指令和示例,从而更有效地利用上下文窗口。
"洞填充"方法尤为适合GPT和Claude等通用大型语言模型,它们能通过明确的指令和示例提供高质量的代码补全。与之相比,专用代码模型如CodeLlama、StableCode等则采用不同的方法,主要是因为:这些专用模型在预训练阶段已针对FIM(Fill-In-the-Middle)任务进行了大量训练,使它们能够直接识别如<fim_prefix>、<fim_suffix>等特定标记。此外,洞填充模板需要包含大量示例和详细指令,会占用宝贵的上下文窗口,而专用代码模型使用的标记系统(如<|fim_prefix|>)更为简洁,只需几个标记即可明确任务要求,从而提高了上下文窗口的利用效率
模板对比分析
| 模型 | 提示词结构 | 适用场景 | 特点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Codestral | [SUFFIX]{后缀}[PREFIX]{前缀} | 通用代码补全 | 清晰的标记,有效处理多行上下文 |
| StableCode | <fim_prefix>{前缀}<fim_suffix>{后缀}<fim_middle> | 填空型补全 | 三段式结构,明确标记填空位置 |
| CodeLlama | PRE {前缀} SUF{后缀} MID | 代码续写 | 简洁的标记,空格敏感度较高 |
单文件模型提示词模板示例
js
// 基本Codestral模板
const codestralFimTemplate = {
// 简单的前缀后缀模板
template: "[SUFFIX]{{{suffix}}}[PREFIX]{{{prefix}}}",
// 停止生成的标记
completionOptions: {
stop: ["[PREFIX]", "[SUFFIX]"],
},
};
// 完整案例:
// 输入:
// prefix = "function calculateSum(a, b) {\n "
// suffix = "\n}"
//
// 渲染后的提示词:
// "[SUFFIX]
// }[PREFIX]function calculateSum(a, b) {
// "
//
// 输出示例:
// "return a + b;"多文件 Codestral 模板
js
// 多文件Codestral模板
const multifileCodestralTemplate = {
// 特殊的前缀后缀处理函数
compilePrefixSuffix: (prefix, suffix, filepath, reponame, snippets, workspaceUris) => {
// 获取文件名
function getFileName(snippet) {
return snippet.uri.startsWith("file://") ? snippet.uniquePath : snippet.uri;
}
// 如果没有片段且前缀后缀为空
if (snippets.length === 0) {
if (suffix.trim().length === 0 && prefix.trim().length === 0) {
return [
`+++++ ${getLastNUriRelativePathParts(workspaceUris, filepath, 2)}\n${prefix}`,
suffix,
];
}
return [prefix, suffix];
}
// 获取相对路径
const relativePaths = getShortestUniqueRelativeUriPaths(
[
...snippets.map(snippet =>
"filepath" in snippet ? snippet.filepath : "file:///Untitled.txt"),
filepath,
],
workspaceUris
);
// 格式化片段
const otherFiles = snippets
.map((snippet, i) => {
if (snippet.type === "Diff") {
return snippet.content;
}
return `+++++ ${getFileName(relativePaths[i])} \n${snippet.content}`;
})
.join("\n\n");
// 组合最终结果
return [
`${otherFiles}\n\n+++++ ${getFileName(relativePaths[relativePaths.length - 1])}\n${prefix}`,
suffix,
];
},
// 模板函数
template: (prefix, suffix) => {
return `[SUFFIX]${suffix}[PREFIX]${prefix}`;
},
// 停止标记
completionOptions: {
stop: ["[PREFIX]", "[SUFFIX]", "\n+++++ "],
},
};
// 完整案例:
// snippets = [
// { filepath: "/src/utils.js", content: "function helper() { return true; }", type: "Code" }
// ]
// prefix = "function main() {\n "
// suffix = "\n}"
// filepath = "/src/main.js"
//
// 处理后:
// prefix = "+++++ src/utils.js
// function helper() { return true; }
//
// +++++ src/main.js
// function main() {
// "
// suffix = "\n}"
//
// 渲染后的提示词:
// "[SUFFIX]
// }[PREFIX]+++++ src/utils.js
// function helper() { return true; }
//
// +++++ src/main.js
// function main() {
// "
//
// 输出示例:
// "const result = helper();
// return result;"具体实现:
js
/**
* 提示词渲染主函数
* 根据不同模型和上下文构建最终提示词
*/
function renderPrompt({snippetPayload, workspaceDirs, helper}) {
// 1. 准备基础数据
let prefix = helper.input.manuallyPassPrefix || helper.prunedPrefix;
let suffix = helper.input.manuallyPassPrefix ? "" : helper.prunedSuffix;
if (suffix === "") {
suffix = "\n";
}
// 获取仓库名称
const reponame = getUriPathBasename(workspaceDirs[0] ?? "myproject");
// 2. 获取合适的模板
const {template, compilePrefixSuffix, completionOptions} = getTemplate(helper);
// 3. 过滤和排序代码片段
const snippets = getSnippets(helper, snippetPayload);
// 4. 处理前缀和后缀
if (compilePrefixSuffix) {
// 某些模型需要特殊处理前缀和后缀
[prefix, suffix] = compilePrefixSuffix(
prefix, suffix, helper.filepath, reponame,
snippets, helper.workspaceUris
);
} else {
// 标准处理:格式化片段并添加到前缀
const formattedSnippets = formatSnippets(helper, snippets, workspaceDirs);
prefix = [formattedSnippets, prefix].join("\n");
}
// 5. 渲染最终提示词
const prompt = typeof template === "string"
? renderStringTemplate(
template, prefix, suffix, helper.lang,
helper.filepath, reponame
)
: template(
prefix, suffix, helper.filepath, reponame,
helper.lang.name, snippets, helper.workspaceUris
);
// 6. 获取停止词
const stopTokens = getStopTokens(
completionOptions, helper.lang, helper.modelName
);
// 7. 返回完整结果
return {
prompt,
prefix,
suffix,
completionOptions: {
...completionOptions,
stop: stopTokens,
}
};
}
/**
* 为不同模型选择合适的模板
*/
function getTemplate(helper) {
// 优先使用配置中指定的模板
if (helper.options.template) {
return {
template: helper.options.template,
completionOptions: {},
compilePrefixSuffix: undefined,
};
}
// 否则根据模型选择
return getTemplateForModel(helper.modelName);
}
/**
* 为模型选择适当的模板
*/
function getTemplateForModel(model) {
// Codestral模型模板
if (model.includes("codestral")) {
return {
template: "[SUFFIX]{{{suffix}}}[PREFIX]{{{prefix}}}",
completionOptions: {
stop: ["[PREFIX]", "[SUFFIX]"],
},
};
}
// StableCode模型模板
if (model.includes("stablecode")) {
return {
template: "<fim_prefix>{{{prefix}}}<fim_suffix>{{{suffix}}}<fim_middle>",
completionOptions: {
stop: [
"<fim_prefix>", "<fim_suffix>", "<fim_middle>",
"<file_sep>", "<|endoftext|>", "</fim_middle>", "</code>"
],
},
};
}
// CodeLlama模型模板
if (model.includes("codellama")) {
return {
template: "<PRE> {{{prefix}}} <SUF>{{{suffix}}} <MID>",
completionOptions: {
stop: ["<PRE>", "<SUF>", "<MID>", "< EOT >"]
},
};
}
// 默认模板(适用于most-13b等通用模型)
return {
template: "Complete the following code:\n\n{{{prefix}}}{{{suffix}}}\n\nCompletion:",
completionOptions: {
stop: ["\n\n", "</completion>"]
},
};
}
/**
* 多文件Codestral模板示例
* 用于处理多个文件上下文
*/
const multifileCodestralTemplate = {
// 特殊的前缀和后缀编译函数
compilePrefixSuffix: (prefix, suffix, filepath, reponame, snippets, workspaceUris) => {
function getFileName(snippet) {
return snippet.uri.startsWith("file://") ? snippet.uniquePath : snippet.uri;
}
// 如果没有片段且前缀后缀为空,返回文件路径和前缀
if (snippets.length === 0) {
if (suffix.trim().length === 0 && prefix.trim().length === 0) {
return [
`+++++ ${getLastNUriRelativePathParts(workspaceUris, filepath, 2)}\n${prefix}`,
suffix,
];
}
return [prefix, suffix];
}
// 获取相对路径
const relativePaths = getShortestUniqueRelativeUriPaths(
[
...snippets.map(snippet =>
"filepath" in snippet ? snippet.filepath : "file:///Untitled.txt"),
filepath,
],
workspaceUris
);
// 格式化上下文文件
const otherFiles = snippets
.map((snippet, i) => {
if (snippet.type === "Diff") {
return snippet.content;
}
return `+++++ ${getFileName(relativePaths[i])} \n${snippet.content}`;
})
.join("\n\n");
// 组合最终结果
return [
`${otherFiles}\n\n+++++ ${getFileName(relativePaths[relativePaths.length - 1])}\n${prefix}`,
suffix,
];
},
// 模板函数
template: (prefix, suffix) => {
return `[SUFFIX]${suffix}[PREFIX]${prefix}`;
},
// 停止标记
completionOptions: {
stop: ["[PREFIX]", "[SUFFIX]", "\n+++++ "],
},
};
/**
* 使用Handlebars渲染字符串模板
*/
function renderStringTemplate(template, prefix, suffix, lang, filepath, reponame) {
const filename = getUriPathBasename(filepath);
const compiledTemplate = Handlebars.compile(template);
// 使用模板变量进行渲染
return compiledTemplate({
prefix,
suffix,
filename,
reponame,
language: lang.name,
});
}流式生成与智能过滤:打造极致用户体验
生成补全后,系统并不是简单地将其显示给用户,而是通过一系列精心设计的过滤器对内容进行实时处理,确保补全具有最高品质。
三级过滤机制
- 字符级过滤:在最低层次对每个字符进行处理 检测停止词,如 \n\n 或语言特定标记 防止生成与后缀重叠的内容
- 行级过滤:对完整代码行进行处理 检测并避免重复行 过滤空注释行 移除路径类行(如 // path/to/file.js)
- 语言特定过滤:根据编程语言应用特定规则 Python的缩进处理 JavaScript的括号匹配 各语言特定的代码风格规则
流处理过程可视化图例
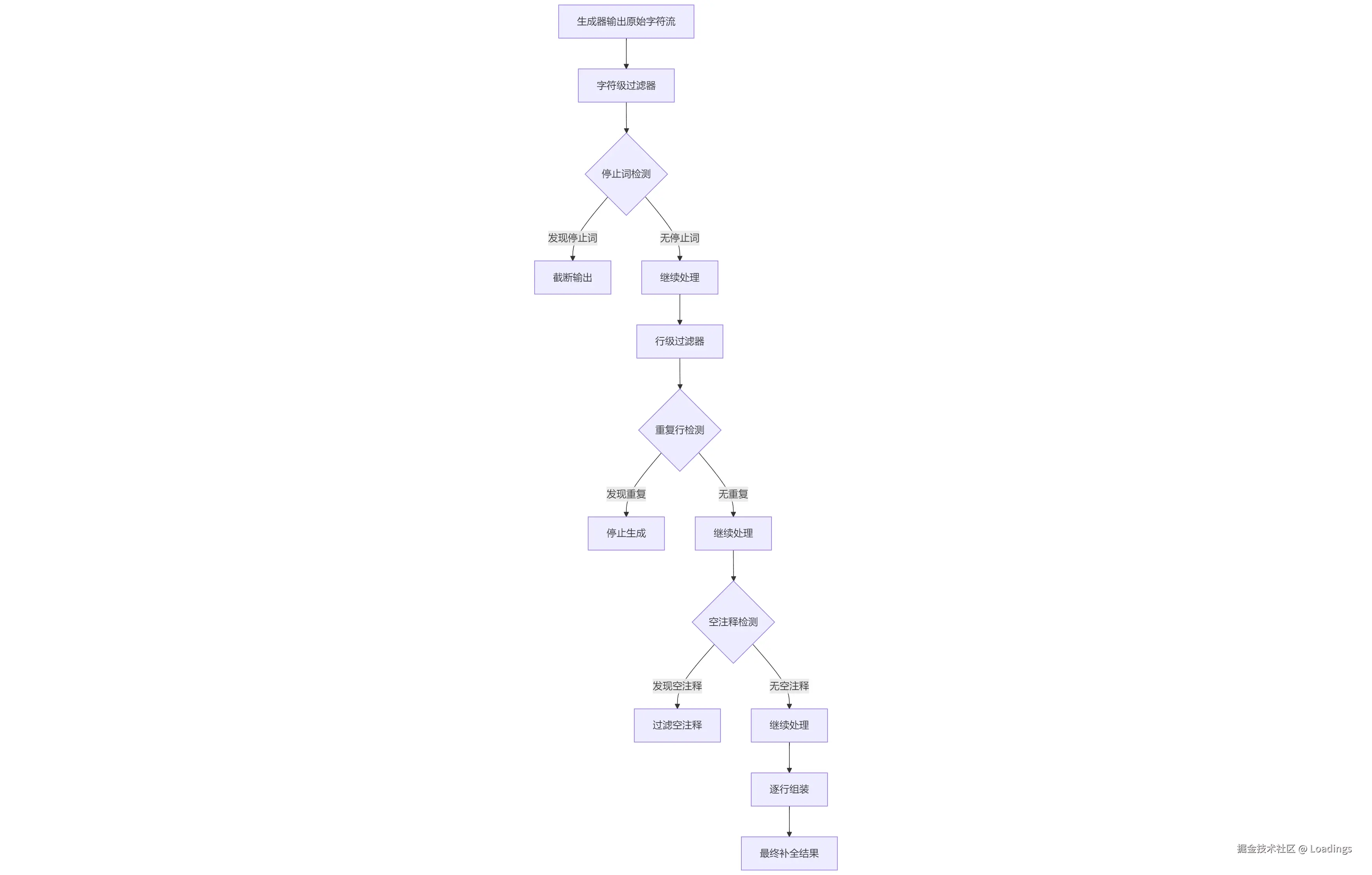
让我们看几个具体例子, 流处理关键步骤示例:
1.字符级过滤 - 停止词检测
js
// 输入流: "return total / len(numbers)\n\ndef another_func"
// 停止词: ["\n\n", "\ndef"]
// 处理过程:
// 检测到停止词"\ndef"在位置24
// 截断在位置24前
// 输出流: "return total / len(numbers)"- 行级过滤 - 重复行检测
python
# 输入流:
# " count = len(numbers)
# average = total / count
# count = len(numbers)"
# 处理过程:
# 检测到第3行与第1行重复
# 截断在第2行结束
# 输出流:
# " count = len(numbers)
# average = total / count"- 行级过滤 - 空注释检测
js
// 输入流:
// " // 计算平均值
// //
// const average = total / count;"
// 处理过程:
// 检测到第2行是空注释
// 移除空注释行
// 输出流:
// " // 计算平均值
// const average = total / count;"这种多层次过滤确保了补全结果的高质量,无需用户手动清理就能直接使用。
具体实现:
js
/**
* 补全流处理器
* 负责流式生成和过滤补全内容
*/
class CompletionStreamer {
constructor(onError) {
this.streamTransformPipeline = new StreamTransformPipeline();
this.generatorReuseManager = new GeneratorReuseManager(onError);
}
/**
* 流式生成补全并应用过滤
*/
async *streamCompletionWithFilters(
token, llm, prefix, suffix, prompt, multiline,
completionOptions, helper
) {
// 1. 获取/复用生成器
const generator = this.generatorReuseManager.getGenerator(
prefix,
(abortSignal) => {
// 根据模型能力选择API
if (llm.supportsFim()) {
return llm.streamFim(prefix, suffix, abortSignal, completionOptions);
} else {
return llm.streamComplete(prompt, abortSignal, {
...completionOptions,
raw: true,
});
}
},
multiline
);
// 2. 定义完全停止函数
const fullStop = () =>
this.generatorReuseManager.currentGenerator?.cancel();
// 3. 处理中断的生成器
const generatorWithCancellation = async function*() {
for await (const update of generator) {
if (token.aborted) {
return;
}
yield update;
}
};
// 4. 应用转换流水线
const initialGenerator = generatorWithCancellation();
const transformedGenerator = helper.options.transform
? this.streamTransformPipeline.transform(
initialGenerator,
prefix,
suffix,
multiline,
completionOptions?.stop || [],
fullStop,
helper
)
: initialGenerator;
// 5. 输出结果
for await (const update of transformedGenerator) {
yield update;
}
}
}
/**
* 流转换管道
* 对生成的内容进行多层过滤和处理
*/
class StreamTransformPipeline {
/**
* 转换流式内容
*/
async *transform(
generator, prefix, suffix, multiline,
stopTokens, fullStop, helper
) {
// 1. 字符级过滤
let charGenerator = generator;
// 处理停止词
charGenerator = stopAtStopTokens(charGenerator, [
...stopTokens,
...STOP_AT_PATTERNS
]);
// 防止生成与后缀重叠
charGenerator = stopAtStartOf(charGenerator, suffix);
// 应用语言特定的字符过滤器
for (const charFilter of helper.lang.charFilters ?? []) {
charGenerator = charFilter({
chars: charGenerator,
prefix,
suffix,
filepath: helper.filepath,
multiline,
});
}
// 2. 行级过滤
let lineGenerator = streamLines(charGenerator);
// 应用基础行过滤器
lineGenerator = stopAtLines(lineGenerator, fullStop);
// 获取光标下方的行
const lineBelowCursor = this.getLineBelowCursor(helper);
if (lineBelowCursor.trim() !== "") {
lineGenerator = stopAtLinesExact(lineGenerator, fullStop, [
lineBelowCursor
]);
}
// 处理重复行
lineGenerator = stopAtRepeatingLines(lineGenerator, fullStop);
// 避免空注释
lineGenerator = avoidEmptyComments(
lineGenerator,
helper.lang.singleLineComment
);
// 避免路径行
lineGenerator = avoidPathLine(lineGenerator, helper.lang.singleLineComment);
// 跳过前缀
lineGenerator = skipPrefixes(lineGenerator);
// 处理双换行
lineGenerator = noDoubleNewLine(lineGenerator);
// 应用语言特定的行过滤器
for (const lineFilter of helper.lang.lineFilters ?? []) {
lineGenerator = lineFilter({ lines: lineGenerator, fullStop });
}
// 在相似行处停止
lineGenerator = stopAtSimilarLine(
lineGenerator,
this.getLineBelowCursor(helper),
fullStop
);
// 应用超时机制
const timeoutValue = helper.options.showWhateverWeHaveAtXMs;
lineGenerator = showWhateverWeHaveAtXMs(lineGenerator, timeoutValue);
// 3. 组合换行符
const finalGenerator = streamWithNewLines(lineGenerator);
for await (const update of finalGenerator) {
yield update;
}
}
/**
* 获取光标下方的行
*/
getLineBelowCursor(helper) {
let lineBelowCursor = "";
let i = 1;
// 查找光标下方第一个非空行
while (
lineBelowCursor.trim() === "" &&
helper.pos.line + i <= helper.fileLines.length - 1
) {
lineBelowCursor =
helper.fileLines[
Math.min(helper.pos.line + i, helper.fileLines.length - 1)
];
i++;
}
return lineBelowCursor;
}
}
/**
* 停止于停止词
*/
function stopAtStopTokens(generator, stopTokens) {
return (async function*() {
let buffer = "";
for await (const chunk of generator) {
buffer += chunk;
// 检查是否包含任何停止词
let shouldStop = false;
let stopIndex = buffer.length;
for (const stop of stopTokens) {
const index = buffer.indexOf(stop);
if (index !== -1 && index < stopIndex) {
stopIndex = index;
shouldStop = true;
}
}
if (shouldStop) {
// 只产出停止词之前的内容
yield buffer.substring(0, stopIndex);
return;
} else {
yield chunk;
}
}
})();
}
/**
* 行流处理
* 将字符流分割成行
*/
function streamLines(charGenerator) {
return (async function*() {
let buffer = "";
for await (const chunk of charGenerator) {
buffer += chunk;
// 查找完整行
const lines = buffer.split("\n");
if (lines.length > 1) {
// 产出完整行
for (let i = 0; i < lines.length - 1; i++) {
yield lines[i];
}
// 保留最后一个不完整行
buffer = lines[lines.length - 1];
}
}
// 最后的缓冲区
if (buffer.length > 0) {
yield buffer;
}
})();
}
/**
* 在相似行处停止
*/
function stopAtSimilarLine(lineGenerator, compareLine, fullStop) {
return (async function*() {
if (!compareLine || compareLine.trim().length < 3) {
for await (const line of lineGenerator) {
yield line;
}
return;
}
for await (const line of lineGenerator) {
yield line;
// 检查相似度
if (isSimilarLine(line, compareLine)) {
fullStop();
return;
}
}
})();
}
/**
* 检查两行是否相似
*/
function isSimilarLine(a, b) {
const trimA = a.trim();
const trimB = b.trim();
// 太短的行不比较
if (trimA.length < 3 || trimB.length < 3) {
return false;
}
// 检查相同前缀
const minLength = Math.min(trimA.length, trimB.length);
const commonPrefixLength = longestCommonPrefix(trimA, trimB);
// 如果有足够长的共同前缀
return commonPrefixLength > minLength * 0.7;
}精细化后处理:最后的品质保障
对模型生成的原始输出进行清理和改进的过程
- 空内容过滤:过滤掉空白或只有空格的补全
- 重复检测:检测并过滤掉重复光标上方行的补全
- 极端重复:检测并过滤掉内容高度重复的补全
- 格式修正:处理空格、换行等格式问题
后处理规则表
| 后处理规则 | 解决问题 | 效果 | 适用模型 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 空白内容检查 | 过滤空补全 | 避免无意义补全 | 全部模型 |
| 重复行检测 | 避免代码重复 | 提高补全简洁度 | 全部模型 |
| 极端重复检测 | 检测大量重复结构 | 拒绝低质量补全 | 全部模型 |
| 空格规范化 | 修复不一致缩进 | 提高代码格式一致性 | 全部模型 |
js
/**
* 后处理函数
* 对生成的内容进行质量检查和优化
*/
function postprocessCompletion({completion, llm, prefix, suffix}) {
// 1. 空内容检查
if (isBlank(completion)) {
return undefined;
}
// 2. 只有空格检查
if (isOnlyWhitespace(completion)) {
return undefined;
}
// 3. 重复检查
if (rewritesLineAbove(completion, prefix)) {
return undefined;
}
// 4. 极端重复检查
if (isExtremeRepetition(completion)) {
return undefined;
}
// 5. 模型特定处理
// 5.1 Codestral模型处理
if (llm.model.includes("codestral")) {
// 处理额外空格
if (completion[0] === " " && completion[1] !== " ") {
if (prefix.endsWith(" ") && suffix.startsWith("\n")) {
completion = completion.slice(1);
}
}
// 处理新行
if (
suffix.length === 0 &&
prefix.endsWith("\n\n") &&
completion.startsWith("\n")
) {
// 移除前导换行符
completion = completion.slice(1);
}
}
// 5.2 Granite模型处理
if (llm.model.includes("granite")) {
// Granite倾向于重复行开始部分
let prefixEnd = prefix.split("\n").pop();
if (prefixEnd) {
if (completion.startsWith(prefixEnd)) {
completion = completion.slice(prefixEnd.length);
} else {
const trimmedPrefix = prefixEnd.trim();
const lastWord = trimmedPrefix.split(/\s+/).pop();
if (lastWord && completion.startsWith(lastWord)) {
completion = completion.slice(lastWord.length);
} else if (completion.startsWith(trimmedPrefix)) {
completion = completion.slice(trimmedPrefix.length);
}
}
}
}
// 6. 格式优化
// 处理空格
if (prefix.endsWith(" ") && completion.startsWith(" ")) {
completion = completion.slice(1);
}
return completion;
}
/**
* 检查内容是否为空
*/
function isBlank(completion) {
return completion.trim().length === 0;
}
/**
* 检查是否只有空白字符
*/
function isOnlyWhitespace(completion) {
const whitespaceRegex = /^[\s]+$/;
return whitespaceRegex.test(completion);
}
/**
* 检查是否重写上方行
*/
function rewritesLineAbove(completion, prefix) {
const lineAbove = prefix
.split("\n")
.filter(line => line.trim().length > 0)
.slice(-1)[0];
if (!lineAbove) {
return false;
}
const firstLineOfCompletion = completion
.split("\n")
.find(line => line.trim().length > 0);
if (!firstLineOfCompletion) {
return false;
}
return lineIsRepeated(lineAbove, firstLineOfCompletion);
}
/**
* 检查是否存在极端重复
*/
function isExtremeRepetition(completion) {
const lines = completion.split("\n");
if (lines.length < 6) {
return false;
}
// 检查重复模式
for (let freq = 1; freq < 3; freq++) {
const lcs = longestCommonSubsequence(lines[0], lines[freq]);
if (lcs.length > 5 || lcs.length > lines[0].length * 0.5) {
let matchCount = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < lines.length; i += freq) {
if (lines[i].includes(lcs)) {
matchCount++;
}
}
// 如果匹配次数超过阈值,认为是极端重复
if (matchCount * freq > 8 || (matchCount * freq) / lines.length > 0.8) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}用户交互-UI
- 显示补全:使用内联补全项显示生成的代码
- 接受补全:用户按下Tab接受完整补全逐字接受
- 拒绝补全:用户按下Esc拒绝补全
- 状态栏控制:用户可通过状态栏开关自动补全功能
js
/**
* VSCode补全提供者
* 实现VSCode的InlineCompletionItemProvider接口
*/
class IDECompletionProvider {
constructor(configHandler, ide, webviewProtocol) {
// 获取补全模型的函数
async function getAutocompleteModel() {
const { config } = await configHandler.loadConfig();
if (!config) return undefined;
return config.selectedModelByRole.autocomplete ?? undefined;
}
// 初始化组件
this.completionProvider = new CompletionProvider(
configHandler,
ide,
getAutocompleteModel,
this.onError.bind(this),
getDefinitionsFromLsp
);
this.recentlyVisitedRanges = new RecentlyVisitedRangesService(ide);
this.recentlyEditedTracker = new RecentlyEditedTracker();
this.configHandler = configHandler;
this.ide = ide;
this.webviewProtocol = webviewProtocol;
}
/**
* 错误处理
*/
onError(e) {
// 处理LLM错误
if (handleLLMError(e)) return;
// 提取错误消息
let message = e.message;
// 处理登录相关错误
if (message.includes("Please sign in")) {
showLoginMessage(
message,
this.configHandler.reloadConfig.bind(this.configHandler),
() => {
void this.webviewProtocol.request("openOnboardingCard", undefined);
}
);
return;
}
// 显示一般错误
showErrorMessage(message, "Documentation").then(val => {
if (val === "Documentation") {
openExternalLink("https://docs.example.com/features/code-completion");
}
});
}
/**
* 提供内联补全项
* 这是VSCode调用的主入口点
*/
async provideInlineCompletionItems(document, position, context, token) {
// 检查状态
const isEnabled = getCompletionStatus() === true;
if (token.isCancellationRequested || !isEnabled) {
return null;
}
// 检查特殊文档类型
if (document.uri.scheme === "vscode-scm") {
return null;
}
// 检查多光标
const editor = getActiveTextEditor();
if (editor && editor.selections.length > 1) {
return null;
}
// 构建输入对象
const input = {
pos: {
line: position.line,
character: position.character,
},
completionId: generateUuid(),
filepath: document.uri.toString(),
recentlyVisitedRanges: this.recentlyVisitedRanges.getSnippets(),
recentlyEditedRanges: await this.recentlyEditedTracker.getRecentlyEditedRanges(),
};
// 调用核心提供者
const outcome = await this.completionProvider.provideInlineCompletionItems(
input,
token
);
if (!outcome) return null;
// Construct the range/text to show
const startPos = selectedCompletionInfo?.range.start ?? position;
let range = new vscode.Range(startPos, startPos);
let completionText = outcome.completion;
const isSingleLineCompletion = outcome.completion.split("\n").length <= 1;
if (isSingleLineCompletion) {
const lastLineOfCompletionText = completionText.split("\n").pop() || "";
const currentText = document
.lineAt(startPos)
.text.substring(startPos.character);
const result = processSingleLineCompletion(
lastLineOfCompletionText,
currentText,
startPos.character
);
if (result === undefined) {
return undefined;
}
completionText = result.completionText;
if (result.range) {
range = new vscode.Range(
new vscode.Position(startPos.line, result.range.start),
new vscode.Position(startPos.line, result.range.end)
);
}
} else {
// Extend the range to the end of the line for multiline completions
range = new vscode.Range(startPos, document.lineAt(startPos).range.end);
}
const completionItem = new vscode.InlineCompletionItem(
completionText,
range,
{
title: "Log Autocomplete Outcome",
command: "continue.logAutocompleteOutcome",
arguments: [input.completionId, this.completionProvider],
},
);
(completionItem as any).completeBracketPairs = true;
return [completionItem];
return [item];
}
/**
* 处理接受事件
*/
accept(completionId) {
this.completionProvider.accept(completionId);
}
}整个补全功能用到的辅助类和工具
js
/**
* 辅助变量类
* 存储和处理当前编辑环境信息
*/
class HelperVars {
/**
* 创建辅助变量实例
*/
static async create(input, options, modelName, ide) {
const helper = new HelperVars();
// 基本输入
helper.input = input;
helper.options = options;
helper.modelName = modelName;
helper.filepath = input.filepath;
// 获取文件内容
const fileContents = await getFileContents(input, ide);
helper.fileContents = fileContents;
helper.fileLines = fileContents.split("\n");
// 位置
helper.pos = input.pos;
// 获取语言信息
helper.lang = getLanguageInfo(helper.filepath);
// 工作区信息
helper.workspaceUris = await ide.getWorkspaceDirs();
// 计算前缀和后缀
helper.fullPrefix = getFullPrefix(fileContents, input.pos);
helper.fullSuffix = getFullSuffix(fileContents, input.pos);
// 计算修剪过的前缀和后缀
helper.prunedPrefix = getPrunedPrefix(helper.fullPrefix, options);
helper.prunedSuffix = getPrunedSuffix(helper.fullSuffix, options);
// 获取树路径
helper.treePath = getTreePath(helper.filepath, helper.fileContents);
return helper;
}
}
/**
* 获取文件内容
*/
async function getFileContents(input, ide) {
// 如果直接提供了文件内容,使用它
if (input.manuallyPassFileContents) {
return input.manuallyPassFileContents;
}
// 否则从IDE读取
return await ide.readFile(input.filepath);
}
/**
* 获取完整前缀
*/
function getFullPrefix(fileContents, pos) {
const lines = fileContents.split("\n");
// 获取光标前所有行
const prefixLines = lines.slice(0, pos.line);
// 加上当前行光标前部分
if (pos.line < lines.length) {
prefixLines.push(lines[pos.line].substring(0, pos.character));
}
return prefixLines.join("\n");
}
/**
* 获取完整后缀
*/
function getFullSuffix(fileContents, pos) {
const lines = fileContents.split("\n");
// 获取光标后所有行
const suffixLines = lines.slice(pos.line + 1);
// 加上当前行光标后部分
if (pos.line < lines.length) {
suffixLines.unshift(lines[pos.line].substring(pos.character));
}
return suffixLines.join("\n");
}
/**
* 根据选项修剪前缀
*/
function getPrunedPrefix(fullPrefix, options) {
// 计算要保留的前缀长度
const prefixTokens = Math.floor(options.maxPromptTokens * options.prefixPercentage);
// 简单估计令牌数(实际实现会更复杂)
if (fullPrefix.length <= prefixTokens * 4) {
return fullPrefix;
}
// 保留后部分
return fullPrefix.slice(-prefixTokens * 4);
}
/**
* 根据选项修剪后缀
*/
function getPrunedSuffix(fullSuffix, options) {
// 计算要保留的后缀长度
const suffixTokens = Math.floor(options.maxPromptTokens * options.maxSuffixPercentage);
// 简单估计令牌数
if (fullSuffix.length <= suffixTokens * 4) {
return fullSuffix;
}
// 保留前部分
return fullSuffix.slice(0, suffixTokens * 4);
}
/**
* 自动补全日志服务
* 跟踪和记录用户与补全的交互
*/
class AutocompleteLoggingService {
constructor() {
this.pendingCompletions = new Map();
}
/**
* 创建中止控制器
*/
createAbortController(completionId) {
const controller = new AbortController();
this.pendingCompletions.set(completionId, {
controller,
startTime: Date.now(),
});
return controller;
}
/**
* 记录显示事件
*/
markDisplayed(completionId, outcome) {
const pending = this.pendingCompletions.get(completionId);
if (pending) {
pending.outcome = outcome;
pending.displayTime = Date.now();
}
}
/**
* 记录接受事件
*/
accept(completionId) {
const pending = this.pendingCompletions.get(completionId);
if (!pending) return undefined;
const outcome = pending.outcome;
if (!outcome) return undefined;
// 计算指标
const displayTime = pending.displayTime || Date.now();
const acceptTime = Date.now();
const metrics = {
genLatency: displayTime - pending.startTime,
acceptLatency: acceptTime - displayTime,
totalLatency: acceptTime - pending.startTime,
};
// 发送遥测
sendTelemetry("code_completion_accept", {
modelName: outcome.modelName,
modelProvider: outcome.modelProvider,
numLines: outcome.numLines,
completionLength: outcome.completion.length,
cacheHit: outcome.cacheHit,
...metrics,
});
this.pendingCompletions.delete(completionId);
return outcome;
}
/**
* 取消所有请求
*/
cancel() {
for (const [completionId, pending] of this.pendingCompletions.entries()) {
pending.controller.abort();
this.pendingCompletions.delete(completionId);
}
}
}
/**
* 延迟处理器
* 防止频繁触发补全请求
*/
class AutocompleteDebouncer {
constructor() {
this.lastRequestTime = 0;
}
/**
* 延迟并判断是否应该放弃请求
*/
async delayAndShouldDebounce(delay) {
const now = Date.now();
const timeSinceLastRequest = now - this.lastRequestTime;
// 如果距离上次请求时间不足,等待
if (timeSinceLastRequest < delay) {
// 等待一段时间
await new Promise(resolve =>
setTimeout(resolve, delay - timeSinceLastRequest)
);
// 由于延迟,可能已有新请求,因此放弃当前请求
if (this.lastRequestTime > now) {
return true;
}
}
this.lastRequestTime = Date.now();
return false;
}
}总结与未来展望
关键技术总结
AI代码补全系统的核心优势在于:
- 多维度上下文理解:不仅读取当前文件,还分析导入关系、项目结构和编辑历史
- 智能预过滤:快速判断何时应该提供补全,避免干扰用户
- 流式处理与实时过滤:在生成过程中动态调整输出质量
- 模型适配:针对不同的AI模型优化提示词结构
- 用户体验优化:缓存、防抖等机制确保响应流畅
未来发展
- 更精准的项目语义理解:构建项目知识图谱,理解代码间的深层依赖关系
- 个性化学习:适应开发者的编码风格和偏好
结语
AI代码补全不仅仅是一个便利工具,它正在改变开发者的编码方式和效率。通过理解其背后的技术原理,我们不仅能更好地利用这些工具,也能参与到这项技术的改进和发展中。
无论你是希望提高自己编码效率的开发者,还是对AI应用于开发工具感兴趣的研究者,希望这篇文章能为你揭开AI代码补全的神秘面纱,让你对这项"魔法"背后的技术有更深入的理解。