用数组栈实现
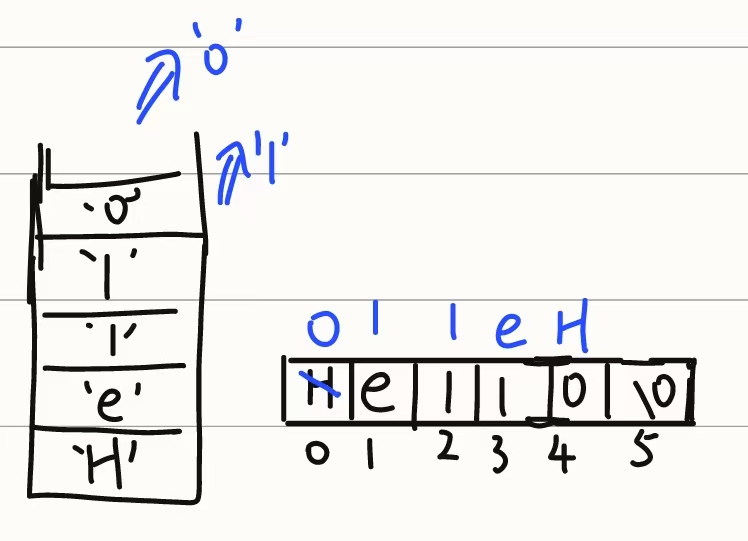
void Reverse(char *C, int len)
{
top = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
push(C[i]);
}
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
C[i] = Top();
pop();
}
}全部函数
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 101
int A[MAX_SIZE];
int top = -1; //栈顶指针,初始为-1,表示栈为空
void push(int x)
{
if (top == MAX_SIZE - 1)
{
printf("栈已满,无法入栈\n");
return;
}
A[++top] = x;
}
void pop()
{
if (top == -1)
{
printf("栈已空,无法出栈\n");
return;
}
top--;
}
void Print()
{
for (int i = 0; i <= top; i++)
{
printf("%c", A[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
int Top()
{
if (top == -1)
{
printf("栈已空,无法取栈顶元素\n");
return -1;
}
return A[top];
}
void Reverse(char *C, int len)
{
top = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
push(C[i]);
}
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
C[i] = Top();
pop();
}
}
int main()
{
char C[51];
printf("请输入一个字符串:");
scanf("%s", C);
int len = strlen(C);
Reverse(C, len);
printf("反转后的字符串为:");
printf("%s\n", C);
return 0;
}用双指针实现(迭代)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
void reverseString(char *str) {
int left = 0;
int right = strlen(str) - 1;
while (left < right) {
// 交换 str[left] 和 str[right]
char temp = str[left];
str[left] = str[right];
str[right] = temp;
// 指针向中间靠拢
left++;
right--;
}
}
int main() {
char str[100];
printf("请输入一个字符串: ");
scanf("%s", str);
reverseString(str);
printf("反转后的字符串: %s\n", str);
return 0;
}链表反转用数组栈
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 100
// 定义链表节点结构体
typedef struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* link;
} Node;
// 栈结构
Node* stack[MAX_SIZE];
int top = -1;
// 栈操作
void push(Node* node) {
if (top == MAX_SIZE - 1) {
printf("栈满了,无法继续压栈\n");
return;
}
stack[++top] = node;
}
Node* pop() {
if (top == -1) {
printf("栈空了,无法出栈\n");
return NULL;
}
return stack[top--];
}
// 链表操作
void insertAtHead(Node** head, int data) {
Node* newNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->link = *head;
*head = newNode;
}
void printList(Node* head) {
Node* temp = head;
while (temp != NULL) {
printf("%d -> ", temp->data);
temp = temp->link;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
// 使用数组栈反转链表
void Reverse(Node** headRef) {
if (*headRef == NULL) {
printf("链表为空\n");
return;
}
Node* temp = *headRef;
// 压栈
while (temp != NULL) {
push(temp);
temp = temp->link;
}
// 弹栈并重建链表
*headRef = pop(); // 新的头结点
temp = *headRef;
while (top != -1) {
temp->link = pop(); // 下一个节点
temp = temp->link;
}
temp->link = NULL; // 最后一个节点
}
// 主函数测试
int main() {
Node* head = NULL;
insertAtHead(&head, 1);
insertAtHead(&head, 2);
insertAtHead(&head, 3);
insertAtHead(&head, 4);
printf("原始链表:\n");
printList(head);
Reverse(&head);
printf("反转后的链表:\n");
printList(head);
return 0;
}压入的是 链表中每个节点的地址,也就是指针