🚀 该系列将会持续整理和更新BBR相关的问题,如有错误和不足恳请大家指正,欢迎讨论!!!
BIoU来自发表在2018年CVPR上的文章: 《Improving Object Localization With Fitness NMS and Bounded IoU Loss》
论文针对现有目标检测方法只关注"足够好"的定位,而非"最优"的框,提出了一种考虑定位质量的NMS策略和BIoU loss。
这里不赘述NMS,只看loss相关的内容。
IoU 是检测性能的主要指标,但直接优化 IoU 很难(不可导、不光滑),因此通常使用 L1/L2 或 SmoothL1 损失,但它们并不直接优化 IoU。 Bounded IoU Loss(BIoU) 通过对 IoU 上界建模,最大化ROI(Region of Interest)和相关的ground truth边界框之间的IoU重叠,使得损失与 IoU 更紧密对应,又具备良好的优化特性。
公式:
 代码来自MMDetection的实现:
代码来自MMDetection的实现:
python
def bounded_iou_loss(pred: Tensor,
target: Tensor,
beta: float = 0.2,
eps: float = 1e-3) -> Tensor:
"""BIoULoss.
This is an implementation of paper
`Improving Object Localization with Fitness NMS and Bounded IoU Loss.
<https://arxiv.org/abs/1711.00164>`_.
Args:
pred (Tensor): Predicted bboxes of format (x1, y1, x2, y2),
shape (n, 4).
target (Tensor): Corresponding gt bboxes, shape (n, 4).
beta (float, optional): Beta parameter in smoothl1.
eps (float, optional): Epsilon to avoid NaN values.
Return:
Tensor: Loss tensor.
"""
pred_ctrx = (pred[:, 0] + pred[:, 2]) * 0.5
pred_ctry = (pred[:, 1] + pred[:, 3]) * 0.5
pred_w = pred[:, 2] - pred[:, 0]
pred_h = pred[:, 3] - pred[:, 1]
with torch.no_grad():
target_ctrx = (target[:, 0] + target[:, 2]) * 0.5
target_ctry = (target[:, 1] + target[:, 3]) * 0.5
target_w = target[:, 2] - target[:, 0]
target_h = target[:, 3] - target[:, 1]
dx = target_ctrx - pred_ctrx
dy = target_ctry - pred_ctry
# 这里的 "×2" 来自中心差异在边界框两侧的对称影响
loss_dx = 1 - torch.max(
(target_w - 2 * dx.abs()) /
(target_w + 2 * dx.abs() + eps), torch.zeros_like(dx))
loss_dy = 1 - torch.max(
(target_h - 2 * dy.abs()) /
(target_h + 2 * dy.abs() + eps), torch.zeros_like(dy))
loss_dw = 1 - torch.min(target_w / (pred_w + eps), pred_w /
(target_w + eps))
loss_dh = 1 - torch.min(target_h / (pred_h + eps), pred_h /
(target_h + eps))
# view(..., -1) does not work for empty tensor
loss_comb = torch.stack([loss_dx, loss_dy, loss_dw, loss_dh],
dim=-1).flatten(1)
loss = torch.where(loss_comb < beta, 0.5 * loss_comb * loss_comb / beta,
loss_comb - 0.5 * beta)
return loss
# 辅助说明BIoU Loss
def smooth_l1_loss(pred: Tensor, target: Tensor, beta: float = 1.0) -> Tensor:
"""Smooth L1 loss.
Args:
pred (Tensor): The prediction.
target (Tensor): The learning target of the prediction.
beta (float, optional): The threshold in the piecewise function.
Defaults to 1.0.
Returns:
Tensor: Calculated loss
"""
assert beta > 0
if target.numel() == 0:
return pred.sum() * 0
assert pred.size() == target.size()
diff = torch.abs(pred - target)
loss = torch.where(diff < beta, 0.5 * diff * diff / beta,
diff - 0.5 * beta)
return lossRIoU来自发表在2020年ACM上的文章: 《Single-Shot Two-Pronged Detector with Rectified IoU Loss》
论文提出了一种基于IoU的自适应定位损失,称为Rectified IoU(RIoU)损失,用于校正各种样本的梯度。校正后的IoU损失增加了高IoU样本的梯度,抑制了低IoU样本的梯度,提高了模型的整体定位精度。
用于解决单阶段目标检测中样本不平衡带来的梯度偏差问题!
但是如果随着IoU的增加而增加局部损失梯度的权重,那么将面临另一个问题,即当回归是完美的(IoU)时,梯度将继续增加→ 1, 这意味着当两个bbox完全重叠(IoU=1)时,将得到最大梯度,这是非常不合理的。
公式:

实现:
python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
def riou_loss(iou: torch.Tensor,
loss_base: torch.Tensor,
alpha: float = 2.0,
gamma: float = 2.0,
threshold: float = 0.5) -> torch.Tensor:
"""
Rectified IoU Loss (RIoU) implementation.
Args:
iou (Tensor): IoU between predicted and target boxes (shape: [N])
loss_base (Tensor): Original IoU-based loss value (e.g., GIoU loss) (shape: [N])
alpha (float): Scaling factor for high IoU samples
gamma (float): Focusing parameter (similar to focal loss)
threshold (float): IoU threshold to apply amplification
Returns:
Tensor: Rectified IoU loss (shape: [N])
"""
# Weight function: amplify high-quality samples
weight = torch.where(
iou >= threshold,
alpha * (iou ** gamma),
iou
)
# Final loss: element-wise weighted
loss = weight * loss_base
return loss.mean()α-IoU来自发表在2021年NeurlPS上的文章:《Alpha-IoU: A Family of Power Intersection over Union Losses for Bounding Box Regression》
边界框回归的核心任务是学习框的预测与真实框之间的匹配程度,IoU是最常见的评价指标。然而现有 IoU 损失(如 GIoU、DIoU、CIoU)虽然考虑了位置和重叠,但它们在优化目标、梯度平滑性或收敛速度上仍有局限。该工作出现的时候已经存在EIoU和Focal-EIoU了。
α-IoU通过一个参数 α 实现灵活控制误差加权,从而提升目标检测精度,并为小数据集和噪声框提供更多鲁棒性。
该论文使用Box-Cox变换将IoU loss变换到α-IoU loss,这是一种统计技术,用于将非正态分布的数据转换为更接近正态分布的形式。该方法由George Box和David Cox在1964年提出,广泛应用于数据预处理步骤中,特别是在需要满足正态性假设的统计分析或机器学习模型构建过程中。


然后推广到GIoU、DIoU和CIoU上,也就是在之前的公式惩罚项上加入α,详细地推导与说明请参考该论文:
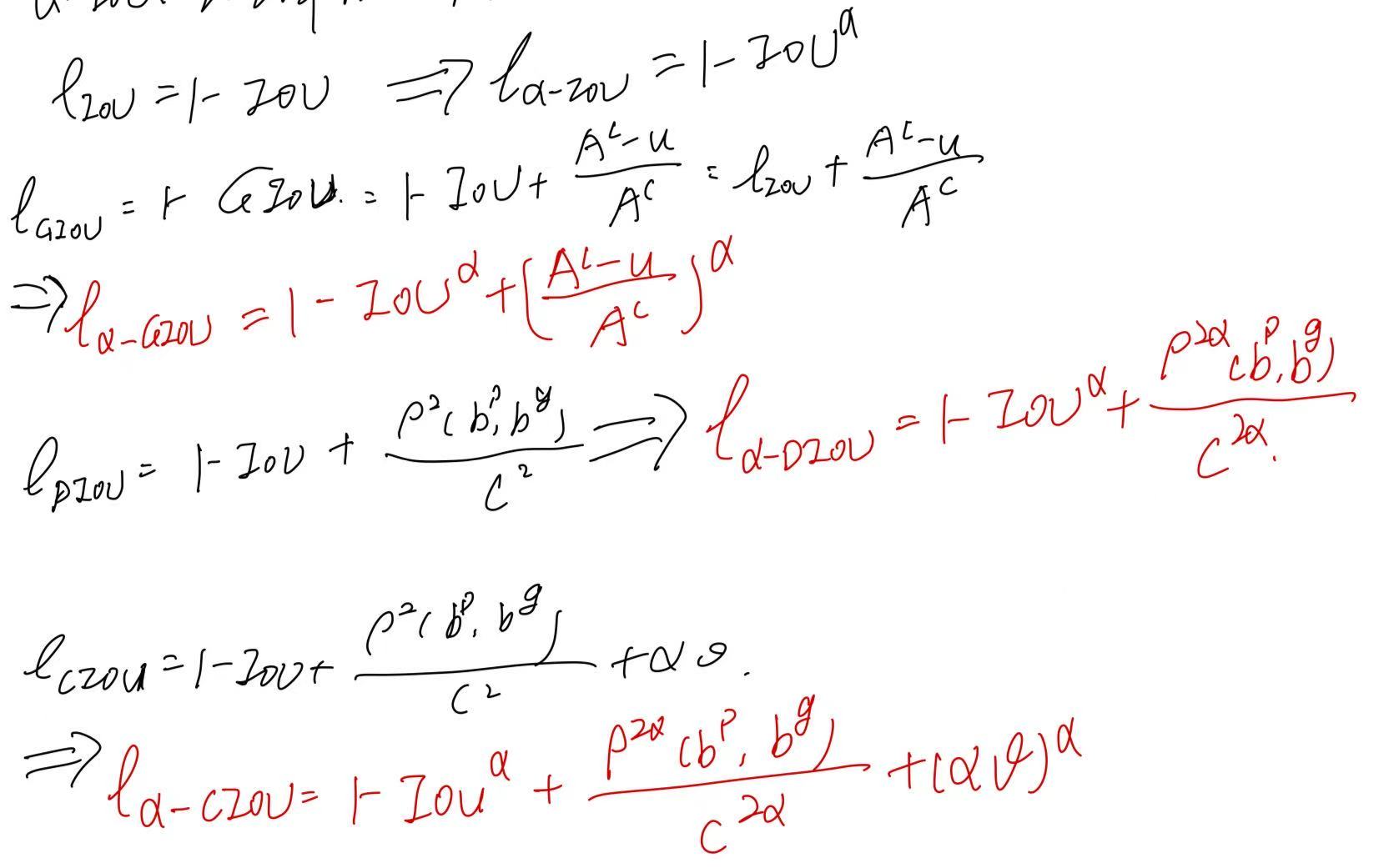 α 对不同的模型或数据集不太敏感,在大多数情况下 α = 3 始终表现良好。α-IoU 损失族可以很容易地应用于在干净和嘈杂的 bbox 设置下改进最先进的检测器,而无需向这些模型引入额外的参数(对训练算法进行任何修改),也不增加它们的训练/推理时间。
α 对不同的模型或数据集不太敏感,在大多数情况下 α = 3 始终表现良好。α-IoU 损失族可以很容易地应用于在干净和嘈杂的 bbox 设置下改进最先进的检测器,而无需向这些模型引入额外的参数(对训练算法进行任何修改),也不增加它们的训练/推理时间。
但是应用到自定义数据集上效果如何还是需要结合具体问题具体分析 !
python
def bbox_alpha_iou(box1, box2, x1y1x2y2=False, GIoU=False, DIoU=False, CIoU=False, alpha=2, eps=1e-9):
# Returns tsqrt_he IoU of box1 to box2. box1 is 4, box2 is nx4
box2 = box2.T
# Get the coordinates of bounding boxes
if x1y1x2y2: # x1, y1, x2, y2 = box1
b1_x1, b1_y1, b1_x2, b1_y2 = box1[0], box1[1], box1[2], box1[3]
b2_x1, b2_y1, b2_x2, b2_y2 = box2[0], box2[1], box2[2], box2[3]
else: # transform from xywh to xyxy
b1_x1, b1_x2 = box1[0] - box1[2] / 2, box1[0] + box1[2] / 2
b1_y1, b1_y2 = box1[1] - box1[3] / 2, box1[1] + box1[3] / 2
b2_x1, b2_x2 = box2[0] - box2[2] / 2, box2[0] + box2[2] / 2
b2_y1, b2_y2 = box2[1] - box2[3] / 2, box2[1] + box2[3] / 2
# Intersection area
inter = (torch.min(b1_x2, b2_x2) - torch.max(b1_x1, b2_x1)).clamp(0) * \
(torch.min(b1_y2, b2_y2) - torch.max(b1_y1, b2_y1)).clamp(0)
# Union Area
w1, h1 = b1_x2 - b1_x1, b1_y2 - b1_y1 + eps
w2, h2 = b2_x2 - b2_x1, b2_y2 - b2_y1 + eps
union = w1 * h1 + w2 * h2 - inter + eps
# change iou into pow(iou+eps)
# iou = inter / union
iou = torch.pow(inter/union + eps, alpha)
# beta = 2 * alpha
if GIoU or DIoU or CIoU:
cw = torch.max(b1_x2, b2_x2) - torch.min(b1_x1, b2_x1) # convex (smallest enclosing box) width
ch = torch.max(b1_y2, b2_y2) - torch.min(b1_y1, b2_y1) # convex height
if CIoU or DIoU: # Distance or Complete IoU https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.08287v1
c2 = (cw ** 2 + ch ** 2) ** alpha + eps # convex diagonal
rho_x = torch.abs(b2_x1 + b2_x2 - b1_x1 - b1_x2)
rho_y = torch.abs(b2_y1 + b2_y2 - b1_y1 - b1_y2)
rho2 = ((rho_x ** 2 + rho_y ** 2) / 4) ** alpha # center distance
if DIoU:
return iou - rho2 / c2 # DIoU
elif CIoU: # https://github.com/Zzh-tju/DIoU-SSD-pytorch/blob/master/utils/box/box_utils.py#L47
v = (4 / math.pi ** 2) * torch.pow(torch.atan(w2 / h2) - torch.atan(w1 / h1), 2)
with torch.no_grad():
alpha_ciou = v / ((1 + eps) - inter / union + v)
# return iou - (rho2 / c2 + v * alpha_ciou) # CIoU
return iou - (rho2 / c2 + torch.pow(v * alpha_ciou + eps, alpha)) # CIoU
else: # GIoU https://arxiv.org/pdf/1902.09630.pdf
# c_area = cw * ch + eps # convex area
# return iou - (c_area - union) / c_area # GIoU
c_area = torch.max(cw * ch + eps, union) # convex area
return iou - torch.pow((c_area - union) / c_area + eps, alpha) # GIoU
else:
return iou # torch.log(iou+eps) or iou