代码解释
- 分子结构定义 :
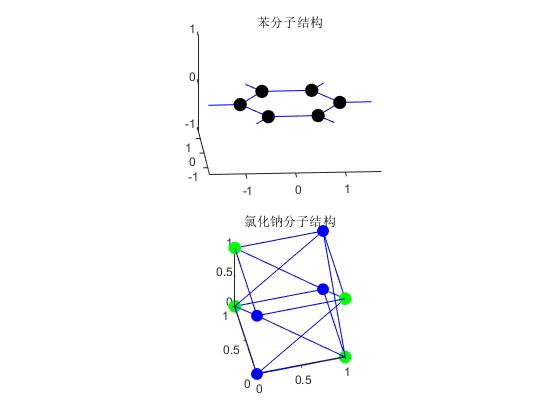
- 苯分子:定义了苯分子中 12 个原子(6 个碳原子和 6 个氢原子)的坐标和原子类型,同时也定义了原子之间的键连接关系。
- 氯化钠分子:定义了一个简单立方晶格的氯化钠结构,包含 8 个原子(4 个钠原子和 4 个氯原子)的坐标和原子类型,以及它们之间的键连接关系。
- 颜色和大小定义:为不同类型的原子定义了不同的颜色和大小,以便在绘制时进行区分。
- 子图布局 :使用
subplot函数创建一个 2x1 的子图布局,分别绘制苯分子和氯化钠分子的 3D 结构。 - 绘制分子结构 :
- 对于每个分子,首先使用
plot3函数绘制原子之间的键。 - 然后使用
scatter3函数根据原子类型绘制不同颜色和大小的球体表示原子。 - 最后使用
title函数为每个子图添加标题,并使用axis equal函数保证坐标轴比例一致,使图形符合 3D 规律。
- 对于每个分子,首先使用
你可以将上述代码复制到 MATLAB 编辑器中运行,就能看到苯分子和氯化钠分子的 3D 结构,不同原子用不同颜色的球体表示。如果需要绘制其他分子,只需按照相同的方式定义原子坐标、原子类型和键连接关系即可。
Matlab
% 苯分子结构
% 原子坐标和类型(1: C, 2: H)
benzene_atoms = [
1 1.0000 0.0000 0.0000; % C1
1 0.5000 0.8660 0.0000; % C2
1 -0.5000 0.8660 0.0000; % C3
1 -1.0000 0.0000 0.0000; % C4
1 -0.5000 -0.8660 0.0000; % C5
1 0.5000 -0.8660 0.0000; % C6
2 1.7320 0.0000 0.0000; % H1
2 0.8660 1.5000 0.0000; % H2
2 -0.8660 1.5000 0.0000; % H3
2 -1.7320 0.0000 0.0000; % H4
2 -0.8660 -1.5000 0.0000; % H5
2 0.8660 -1.5000 0.0000 % H6
];
benzene_bonds = [
1 2;
2 3;
3 4;
4 5;
5 6;
6 1;
1 7;
2 8;
3 9;
4 10;
5 11;
6 12
];
% 氯化钠分子结构(简单立方晶格示例)
% 原子坐标和类型(1: Na, 2: Cl)
nacl_atoms = [
1 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000; % Na1
2 1.0000 0.0000 0.0000; % Cl1
1 1.0000 1.0000 0.0000; % Na2
2 0.0000 1.0000 0.0000; % Cl2
1 0.0000 0.0000 1.0000; % Na3
2 1.0000 0.0000 1.0000; % Cl3
1 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000; % Na4
2 0.0000 1.0000 1.0000 % Cl4
];
nacl_bonds = [
1 2;
1 4;
1 6;
2 3;
2 5;
2 7;
3 4;
3 6;
3 8;
4 5;
4 7;
5 6;
5 8;
6 7;
7 8
];
% 定义颜色和大小
carbon_color = [0 0 0]; % 黑色表示碳原子
hydrogen_color = [1 1 1]; % 白色表示氢原子
sodium_color = [0 0 1]; % 蓝色表示钠原子
chlorine_color = [0 1 0]; % 绿色表示氯原子
carbon_size = 100;
hydrogen_size = 50;
sodium_size = 80;
chlorine_size = 90;
% 创建一个2x1的子图布局
figure;
% 绘制苯分子结构
subplot(2,1,1);
for i = 1:size(benzene_bonds, 1)
atom1 = benzene_atoms(benzene_bonds(i, 1), 2:4);
atom2 = benzene_atoms(benzene_bonds(i, 2), 2:4);
plot3([atom1(1) atom2(1)], [atom1(2) atom2(2)], [atom1(3) atom2(3)], 'b-');
hold on;
end
carbon_indices = benzene_atoms(:,1) == 1;
hydrogen_indices = benzene_atoms(:,1) == 2;
scatter3(benzene_atoms(carbon_indices, 2), benzene_atoms(carbon_indices, 3), benzene_atoms(carbon_indices, 4), carbon_size, carbon_color, 'filled');
scatter3(benzene_atoms(hydrogen_indices, 2), benzene_atoms(hydrogen_indices, 3), benzene_atoms(hydrogen_indices, 4), hydrogen_size, hydrogen_color, 'filled');
title('苯分子结构');
axis equal;
hold off;
% 绘制氯化钠分子结构
subplot(2,1,2);
for i = 1:size(nacl_bonds, 1)
atom1 = nacl_atoms(nacl_bonds(i, 1), 2:4);
atom2 = nacl_atoms(nacl_bonds(i, 2), 2:4);
plot3([atom1(1) atom2(1)], [atom1(2) atom2(2)], [atom1(3) atom2(3)], 'b-');
hold on;
end
sodium_indices = nacl_atoms(:,1) == 1;
chlorine_indices = nacl_atoms(:,1) == 2;
scatter3(nacl_atoms(sodium_indices, 2), nacl_atoms(sodium_indices, 3), nacl_atoms(sodium_indices, 4), sodium_size, sodium_color, 'filled');
scatter3(nacl_atoms(chlorine_indices, 2), nacl_atoms(chlorine_indices, 3), nacl_atoms(chlorine_indices, 4), chlorine_size, chlorine_color, 'filled');
title('氯化钠分子结构');
axis equal;
hold off;代码解释
- 分子结构定义
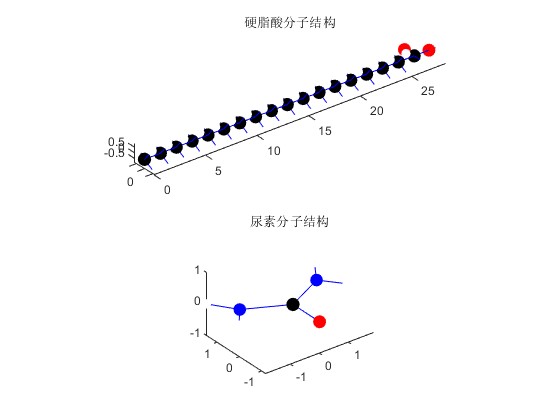
- 硬脂酸:硬脂酸是一种长链脂肪酸,有 18 个碳原子的碳链以及一个羧基。代码里定义了硬脂酸所有原子的坐标与类型,还有原子间的键连接关系。
- 尿素:尿素分子包含一个碳原子、两个氮原子、一个氧原子和四个氢原子。同样定义了其原子坐标、类型以及键连接关系。
- 颜色和大小定义
- 为不同类型的原子(碳、氢、氮、氧)定义了不同的颜色和大小,方便在绘图时区分。
- 子图布局
- 运用
subplot函数创建一个 2x1 的子图布局,分别绘制硬脂酸和尿素的 3D 分子结构。
- 运用
- 绘制分子结构
- 针对每个分子,先利用
plot3函数绘制原子之间的键。 - 接着使用
scatter3函数依据原子类型绘制不同颜色和大小的球体来表示原子。 - 最后使用
title函数为每个子图添加标题,并通过axis equal函数保证坐标轴比例一致,让图形符合 3D 规律。
- 针对每个分子,先利用
你可以把上述代码复制到 MATLAB 编辑器中运行,这样就能看到硬脂酸和尿素的 3D 分子结构,不同原子会用不同颜色的球体表示。
Matlab
% 硬脂酸分子结构
% 原子坐标和类型(1: C, 2: H, 3: O)
stearic_acid_atoms = [
% 碳原子链
1 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000; % C1
1 1.5400 0.0000 0.0000; % C2
1 3.0800 0.0000 0.0000; % C3
1 4.6200 0.0000 0.0000; % C4
1 6.1600 0.0000 0.0000; % C5
1 7.7000 0.0000 0.0000; % C6
1 9.2400 0.0000 0.0000; % C7
1 10.7800 0.0000 0.0000; % C8
1 12.3200 0.0000 0.0000; % C9
1 13.8600 0.0000 0.0000; % C10
1 15.4000 0.0000 0.0000; % C11
1 16.9400 0.0000 0.0000; % C12
1 18.4800 0.0000 0.0000; % C13
1 20.0200 0.0000 0.0000; % C14
1 21.5600 0.0000 0.0000; % C15
1 23.1000 0.0000 0.0000; % C16
1 24.6400 0.0000 0.0000; % C17
1 26.1800 0.0000 0.0000; % C18
% 羧基部分
3 26.1800 1.2300 0.0000; % O1
3 27.6200 0.0000 0.0000; % O2
% 氢原子
2 0.3800 0.9600 0.0000; % H1
2 0.3800 -0.4800 0.8300; % H2
2 0.3800 -0.4800 -0.8300; % H3
2 1.9200 0.9600 0.0000; % H4
2 1.9200 -0.4800 0.8300; % H5
2 1.9200 -0.4800 -0.8300; % H6
2 3.4600 0.9600 0.0000; % H7
2 3.4600 -0.4800 0.8300; % H8
2 3.4600 -0.4800 -0.8300; % H9
2 5.0000 0.9600 0.0000; % H10
2 5.0000 -0.4800 0.8300; % H11
2 5.0000 -0.4800 -0.8300; % H12
2 6.5400 0.9600 0.0000; % H13
2 6.5400 -0.4800 0.8300; % H14
2 6.5400 -0.4800 -0.8300; % H15
2 8.0800 0.9600 0.0000; % H16
2 8.0800 -0.4800 0.8300; % H17
2 8.0800 -0.4800 -0.8300; % H18
2 9.6200 0.9600 0.0000; % H19
2 9.6200 -0.4800 0.8300; % H20
2 9.6200 -0.4800 -0.8300; % H21
2 11.1600 0.9600 0.0000; % H22
2 11.1600 -0.4800 0.8300; % H23
2 11.1600 -0.4800 -0.8300; % H24
2 12.7000 0.9600 0.0000; % H25
2 12.7000 -0.4800 0.8300; % H26
2 12.7000 -0.4800 -0.8300; % H27
2 14.2400 0.9600 0.0000; % H28
2 14.2400 -0.4800 0.8300; % H29
2 14.2400 -0.4800 -0.8300; % H30
2 15.7800 0.9600 0.0000; % H31
2 15.7800 -0.4800 0.8300; % H32
2 15.7800 -0.4800 -0.8300; % H33
2 17.3200 0.9600 0.0000; % H34
2 17.3200 -0.4800 0.8300; % H35
2 17.3200 -0.4800 -0.8300; % H36
2 18.8600 0.9600 0.0000; % H37
2 18.8600 -0.4800 0.8300; % H38
2 18.8600 -0.4800 -0.8300; % H39
2 20.4000 0.9600 0.0000; % H40
2 20.4000 -0.4800 0.8300; % H41
2 20.4000 -0.4800 -0.8300; % H42
2 21.9400 0.9600 0.0000; % H43
2 21.9400 -0.4800 0.8300; % H44
2 21.9400 -0.4800 -0.8300; % H45
2 23.4800 0.9600 0.0000; % H46
2 23.4800 -0.4800 0.8300; % H47
2 23.4800 -0.4800 -0.8300; % H48
2 25.0200 0.9600 0.0000; % H49
2 25.0200 -0.4800 0.8300; % H50
2 25.0200 -0.4800 -0.8300; % H51
2 26.1800 -1.2300 0.0000; % H52
2 28.2600 0.0000 0.0000 % H53
];
stearic_acid_bonds = [
% 碳原子链
1 2;
2 3;
3 4;
4 5;
5 6;
6 7;
7 8;
8 9;
9 10;
10 11;
11 12;
12 13;
13 14;
14 15;
15 16;
16 17;
17 18;
% 羧基部分
18 19;
18 20;
% 氢原子连接
1 21;
1 22;
1 23;
2 24;
2 25;
2 26;
3 27;
3 28;
3 29;
4 30;
4 31;
4 32;
5 33;
5 34;
5 35;
6 36;
6 37;
6 38;
7 39;
7 40;
7 41;
8 42;
8 43;
8 44;
9 45;
9 46;
9 47;
10 48;
10 49;
10 50;
11 51;
11 52;
11 53;
12 54;
12 55;
12 56;
13 57;
13 58;
13 59;
14 60;
14 61;
14 62;
15 63;
15 64;
15 65;
16 66;
16 67;
16 68;
17 69;
17 70;
17 71;
18 72;
18 73
];
% 尿素分子结构
% 原子坐标和类型(1: C, 2: H, 3: N, 4: O)
urea_atoms = [
1 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000; % C
3 1.3300 0.6700 0.0000; % N1
3 -1.3300 0.6700 0.0000; % N2
4 0.0000 -1.2000 0.0000; % O
2 1.8700 1.4700 0.0000; % H1
2 1.8700 0.0000 0.0000; % H2
2 -1.8700 1.4700 0.0000; % H3
2 -1.8700 0.0000 0.0000 % H4
];
urea_bonds = [
1 2;
1 3;
1 4;
2 5;
2 6;
3 7;
3 8
];
% 定义颜色和大小
carbon_color = [0 0 0]; % 黑色表示碳原子
hydrogen_color = [1 1 1]; % 白色表示氢原子
nitrogen_color = [0 0 1]; % 蓝色表示氮原子
oxygen_color = [1 0 0]; % 红色表示氧原子
carbon_size = 100;
hydrogen_size = 50;
nitrogen_size = 90;
oxygen_size = 95;
% 创建一个2x1的子图布局
figure;
% 绘制硬脂酸分子结构
subplot(2,1,1);
for i = 1:size(stearic_acid_bonds, 1)
% 检查索引是否超出范围
if stearic_acid_bonds(i, 1) > size(stearic_acid_atoms, 1) || stearic_acid_bonds(i, 2) > size(stearic_acid_atoms, 1)
fprintf('索引超出范围: 键 %d 连接的原子索引为 (%d, %d)\n', i, stearic_acid_bonds(i, 1), stearic_acid_bonds(i, 2));
continue;
end
atom1 = stearic_acid_atoms(stearic_acid_bonds(i, 1), 2:4);
atom2 = stearic_acid_atoms(stearic_acid_bonds(i, 2), 2:4);
plot3([atom1(1) atom2(1)], [atom1(2) atom2(2)], [atom1(3) atom2(3)], 'b-');
hold on;
end
carbon_indices = stearic_acid_atoms(:,1) == 1;
hydrogen_indices = stearic_acid_atoms(:,1) == 2;
oxygen_indices = stearic_acid_atoms(:,1) == 3;
scatter3(stearic_acid_atoms(carbon_indices, 2), stearic_acid_atoms(carbon_indices, 3), stearic_acid_atoms(carbon_indices, 4), carbon_size, carbon_color, 'filled');
scatter3(stearic_acid_atoms(hydrogen_indices, 2), stearic_acid_atoms(hydrogen_indices, 3), stearic_acid_atoms(hydrogen_indices, 4), hydrogen_size, hydrogen_color, 'filled');
scatter3(stearic_acid_atoms(oxygen_indices, 2), stearic_acid_atoms(oxygen_indices, 3), stearic_acid_atoms(oxygen_indices, 4), oxygen_size, oxygen_color, 'filled');
title('硬脂酸分子结构');
axis equal;
hold off;
% 绘制尿素分子结构
subplot(2,1,2);
for i = 1:size(urea_bonds, 1)
atom1 = urea_atoms(urea_bonds(i, 1), 2:4);
atom2 = urea_atoms(urea_bonds(i, 2), 2:4);
plot3([atom1(1) atom2(1)], [atom1(2) atom2(2)], [atom1(3) atom2(3)], 'b-');
hold on;
end
carbon_indices = urea_atoms(:,1) == 1;
hydrogen_indices = urea_atoms(:,1) == 2;
nitrogen_indices = urea_atoms(:,1) == 3;
oxygen_indices = urea_atoms(:,1) == 4;
scatter3(urea_atoms(carbon_indices, 2), urea_atoms(carbon_indices, 3), urea_atoms(carbon_indices, 4), carbon_size, carbon_color, 'filled');
scatter3(urea_atoms(hydrogen_indices, 2), urea_atoms(hydrogen_indices, 3), urea_atoms(hydrogen_indices, 4), hydrogen_size, hydrogen_color, 'filled');
scatter3(urea_atoms(nitrogen_indices, 2), urea_atoms(nitrogen_indices, 3), urea_atoms(nitrogen_indices, 4), nitrogen_size, nitrogen_color, 'filled');
scatter3(urea_atoms(oxygen_indices, 2), urea_atoms(oxygen_indices, 3), urea_atoms(oxygen_indices, 4), oxygen_size, oxygen_color, 'filled');
title('尿素分子结构');
axis equal;
hold off;