简介
本文将深入分析 commonmark.js 中解析器 Block Parser 部分的源码实现,探讨其如何将 Markdown 文本转换为抽象语法树(AST)。通过分析源码,我们将了解解析器如何按照 CommonMark 规范的 块结构解析阶段 来处理 Markdown 文本,并详细探讨其中的解析策略和规则。
阅读具体的 commonmark.js 实现,我们可以更深刻的理解 CommonMark 规范。
commonmark.js 与 CommonMark 规范 版本 0.31.2。
准备工作
如果您还不知道什么是 Markdown,请先查阅此文档。
为了更好的理解本文的内容,请先下载 commonmark.js 0.31.2 版本的源码,用于对比理解;此外,最好完整阅读 CommonMark 规范,这里有它的中文翻译:CommonMark Spec 中文翻译。
commonmark.js 项目结构
/lib:核心库代码/dist:打包后的发布文件/test:测试文件/bench:基准测试/dingus:在线演示工具/bin:命令行工具rollup.config.js:rollup 打包配置package.json: npm 包配置- 其他工程配置文件...
查看 package.json 的 main 字段和 rollup.config.js 的 input 字段,可以发现源码入口是 /lib/index.js,为了避免干扰,我们只保留最低程度的结构,删除除 /lib 目录外的其他目录,以及非必要的工程配置文件。
删除后的目录结构如下:
markdown
- lib/
- node_modules/
- .editorconfig
- .gitignore
- package.json
- package-lock.json
- rollup.config.js源码阅读流程
源码采用流水线阅读方式,从代码层面的解析入口点开始阅读,按解析流程调试理解,同时穿插规范定义以加深理解,commonmark.js 使用方式如下:
js
import { Parser } 'commonmark';
const parser = new Parser();
const parsed = reader.parse("Hello *world*"); // parsed is a 'Node' treeParser 类定义在 /lib/blocks,我们从它的 parse 方法开始。
为了防止某个阶段过多的代码干扰造成负担,代码示例中通常只保留对应阶段需要的代码,使用 // ... 注释表示被忽略的代码。
块结构解析流程
Markdown 包含块(块引用、列表、段落等)与内联(强调、图片、链接等),Parser 类主要用于解析块节点,以及桥接后续内联节点的解析,它的定义如下:
js
// The Parser object.
function Parser(options) {
return {
doc: new Document(),
parse: parse,
options: options || {},
// ...
};
}从 解析策略-概述 部分可以得出一些信息:
- Markdown 按行解析
- 在解析开始时,首先构建
Document块 Document块是 AST 树的根,可以有任意个子块- 块有
open和closed两种状态
此外,解析流程是具有优先级的,块结构指示符 始终优先 于内联结构指示符,我们始终可以按照 块结构 -> 内联结构 的顺序进行解析,这表明内联结构的标记无法打断块结构,比如:
markdown
- `one
- two`这是一个包含两个项目的列表,而不是一个包含内联代码的列表项在列表中。
Node
我们看上述代码中首先构建的 Document 块的实现:
js
var Document = function() {
var doc = new Node("document", [
[1, 1],
[0, 0]
]);
return doc;
};继承自 Node 类,代码在 /lib/Node.js,大概的类型定义如下:
js
declare class Node {
constructor(nodeType: string, sourcepos: [[number, number], [number, number]]);
// 节点类型
_type: string;
// 父节点
_parent: Node | null;
// 第一个子节点
_firstChild: Node | null;
// 最后一个子节点
_lastChild: Node | null;
// 前一个兄弟节点
_prev: Node | null;
// 后一个兄弟节点
_next: Node | null;
// 块在源码中的位置 [[startLine, startColumn], [endLine, endColumn]]
_sourcepos: [[number, number], [number, number]];
// 是否是打开的块节点
_open: boolean;
// 除块定义字符外的其他字符,用于后续内联解析
_string_content: string | null;
// 将节点作为最后一个子节点添加
appendChild(child: Node): void;
// 将节点作为第一个子节点添加
prependChild(child: Node): void;
// 移除节点
unlink(): void;
// 将节点插入到当前节点之后
insertAfter(sibling: Node): void;
// 将节点插入到当前节点之前
insertBefore(sibling: Node): void;
}Node 类是 AST 树中每个节点的具体实现,通过 _type 属性确定当前的节点类型;上面只包含最基本的类型定义,还有很多用于 不同节点类型解析的辅助字段 。
parse
先看代码:
js
// The main parsing function. Returns a parsed document AST.
var parse = function(input) {
this.doc = new Document();
this.tip = this.doc;
this.refmap = {};
this.lineNumber = 0;
this.lastLineLength = 0;
this.offset = 0;
this.column = 0;
this.lastMatchedContainer = this.doc;
this.currentLine = "";
var lines = input.split(reLineEnding);
var len = lines.length;
if (input.charCodeAt(input.length - 1) === C_NEWLINE) {
// ignore last blank line created by final newline
len -= 1;
}
for (var i = 0; i < len; i++) {
this.incorporateLine(lines[i]);
}
while (this.tip) {
this.finalize(this.tip, len);
}
// ...忽略内联解析代码
return this.doc;
};代码流程大概如下:
-
重置影响解析器的状态
-
源码按行尾拆分为多行
规范中,行尾被定义为
\r、\n或\r\n,commonmark.js 中的正则为/\r\n|\n|\r/ -
忽略最后的空行
-
按顺序调用
incorporateLine方法以分析各行 -
完成并关闭所有未完成的块
关于块结构节点的解析,主要的代码在 incorporateLine 中,它用于分析各行,尝试匹配并创建块,或关闭任意数量的块。
incorporateLine
incorporateLine 方法首先重置一些状态:
js
// Analyze a line of text and update the document appropriately.
// We parse markdown text by calling this on each line of input,
// then finalizing the document.
var incorporateLine = function(ln) {
// ...
this.offset = 0;
this.column = 0;
this.blank = false;
this.lineNumber += 1;
// replace NUL characters for security
if (ln.indexOf("\u0000") !== -1) {
ln = ln.replace(/\0/g, "\uFFFD");
}
this.currentLine = ln;
// ...
}以下是部分字段的释义:
offset:解析器到达当前行内容的字符偏移column:与offset类似,但包含了 tabs(\t)字符的扩展,稍后会解释它blank:到达行尾时,则为truelineNumber:当前行号currentLine:当前行的文本内容
因为 CommonMark 规范将 U+0000(Null 字符)视为不安全字符,并要求使用 U+FFFD(替换字符)替换它,所以我们还必须应用这段代码:
js
// replace NUL characters for security
if (ln.indexOf("\u0000") !== -1) {
ln = ln.replace(/\0/g, "\uFFFD");
}扩展:
U+0000在某些语言中被视为字符串终止符,使用它可能导致字符串意外终止,此特性可能被攻击者利用。来源于 AI。
块结构解析流程 - 步骤 1
查看下一部分代码:
js
var incorporateLine = function(ln) {
// ...
var all_matched = true;
var container = this.doc;
// For each containing block, try to parse the associated line start.
// Bail out on failure: container will point to the last matching block.
// Set all_matched to false if not all containers match.
var lastChild;
while ((lastChild = container._lastChild) && lastChild._open) {
container = lastChild;
this.findNextNonspace();
switch (this.blocks[container.type].continue(this, container)) {
case 0: // we've matched, keep going
break;
case 1: // we've failed to match a block
all_matched = false;
break;
case 2: // we've hit end of line for fenced code close and can return
return;
default:
throw "continue returned illegal value, must be 0, 1, or 2";
}
if (!all_matched) {
container = container._parent; // back up to last matching block
break;
}
}
this.allClosed = container === this.oldtip;
this.lastMatchedContainer = container;
// ...
};要理解这段代码,我们先查看 CommonMark 规范中关于块结构解析的步骤 1:
首先,我们遍历所有 打开 的块,从
Document开始,向内部遍历最后一个子块,直到最深处的open块。每个块都规定了一个条件,如果块要保持打开状态,该行必须满足该条件。例如,块引用需要一个
>字符。段落需要一个非空行。在此阶段,我们可能会匹配所有或部分打开的块。但是,我们暂时无法关闭 未匹配 的块,因为我们可能存在惰性延续行。
用下列 Markdown 举个例子:
markdown> paragraph1 > > paragraph2 惰性延续行在处理第一行时,得到了以下结构:
markdowndocument(open) -> blockquote(open) -> paragraph1(open)现在,由于第二行的内容满足
blockquote块继续打开的条件(仍包含有效的块引用标记>),所以它继续保存打开;消耗了块引用标记
>后,只剩下空白字符串,所以paragraph1不满足继续打开的条件,应该在后续步骤中被关闭。
markdowndocument(open) -> blockquote(open) -> paragraph1(open) # 后续解析步骤中被关闭,现在我们还无法关闭未匹配的块来到第三行,
blockquote继续打开,并添加一个新的paragraph2块:
markdowndocument(open) -> blockquote(open) -> paragraph1(closed) # paragraph1 在上一行的后续解析步骤中被关闭 -> paragraph2(open)最后一行,由于没有匹配的
>标记,blockquote可能 需要被关闭,但当前行内容可能是最后一个open块的惰性延续行,所以我们保持未匹配的块继续打开,等待未来确认关闭。后续解析步骤中,文本内容 "惰性延续行" 被确认为
paragraph2的段落延续行,所以我们仍不能关闭blockquote和paragraph2。最后,所有行都已被分析,所以我们关闭所有打开的块。
回到代码,解释片段:
-
all_matched: 当前行内容是否能匹配所有打开的块 -
container = this.doc:container设置为Document -
lastChild:container的最后一个子块 -
while ((lastChild = container._lastChild) && lastChild._open) { // ... }:从Document开始,向内部迭代最后一个open的块 -
findNextNonspace():找到下一个非空白字符的位置 -
blocks[container.type].continue(this, container):运行匹配,通过container.type运行对应块节点类型的匹配函数,blocks[container.type]是一个通用接口,所有块都实现它,它的接口定义如下:tsdeclare interface BlockContinue { /** * 运行匹配 * * @param parser - 解析器实例 * @param container - 当前块的容器 * @returns 0 = 已匹配 * 1 = 无匹配 * 2 = 当前行被完全处理,可以直接返回 */ continue(parser: Parser, container: Node): 0 | 1 | 2; /** * 完成当前块 * * @param parser - 解析器实例 * @param block - 当前块 */ finalize(parser: Parser, block: Node): void; /** * * @param t - 指定块的类型 * @returns 是否可以包含指定块 */ canContain(t: string): boolean; /** 是否可以包含多行文本 */ acceptsLines: boolean; } -
if (!all_matched) { container = container._parent; break; }:当前行内容不能匹配所有打开的块时,将container备份到父块,此时父块是open的,即最后匹配的块lastMatchedContainer。 -
allClosed:当前行内容是否匹配所有打开的块
findNextNonspace
findNextNonspace 方法用于找到下一个非 \s 或 \t 字符的位置,针对某一行,它可能运行多次,比如:
markdown
> - 无序列表模拟步骤:
findNextNonspace找到>,位置为 0,这是一个blockquotefindNextNonspace找到-,位置为 2,这是blockquote内部的bullet list
来看看它的实现:
js
var findNextNonspace = function() {
var currentLine = this.currentLine;
var i = this.offset;
var cols = this.column;
var c;
while ((c = currentLine.charAt(i)) !== "") {
if (c === " ") {
i++;
cols++;
} else if (c === "\t") {
i++;
cols += 4 - (cols % 4);
} else {
break;
}
}
this.blank = c === "\n" || c === "\r" || c === "";
this.nextNonspace = i;
this.nextNonspaceColumn = cols;
this.indent = this.nextNonspaceColumn - this.column;
this.indented = this.indent >= CODE_INDENT;
};代码大部分比较好理解,从当前 offset 的位置向后迭代,直到遇到行尾或除 \s、\t 的字符。
blank:到达行尾时为truenextNonspace:保存下一个非空白字符的位置nextNonspaceColumn:保存下一个非空白字符的列indent:距上一个column的缩进数量indented:indent是否大于等于 4,不满足其他块的情况下,indent大于等于 4 表示这是一个缩进代码块
我们需要注意这段代码:
js
if (c === "\t") {
i++;
cols += 4 - (cols % 4);
}这里针对 \t 做了额外处理,我们查看 CommonMark 规范中关于 Tabs 的部分:
行中的制表符不会扩展为空格。然而,在空格有助于定义块结构的上下文中,制表符的行为就像它们被带有 4 个字符的制表位的空格替换一样。
这个描述的关键在于,使用 "被带有 4 个字符的制表位的空格替换一样",而不是 "被 4 个空格替换"。
我们查看示例(-> 表示制表符):
markdown
>->这里制表符被扩展为 三个 空格 。
markdown
1.->abc这里制表符被扩展为 两个 空格 。
markdown
->abc这里制表符被扩展为 四个 空格 。
CommonMark 将 tabs 视为 4 字符长度的制表位,在有助于块结构定义的上下文中,tabs 的作用是跳到下一个制表位,而跳过的数量就是它应该被扩展为空格的数量。
可以这样理解 offset 和 column:
offset是实际的字符偏移,\t被它视为一个字符column是块解析时所需要的字符偏移,它包含\t被扩展为指定数量后的空格
CommonMark 中很多块结构都依赖于缩进空格,块解析流程下以 column 为主,比如:
js
->indented code block上述代码中,制表符被扩展为四个空格,满足了缩进代码块的要求,所以这是一个缩进代码块。
块结构解析流程 - 步骤 2
回到 incorporateLine,查看下一部分:
js
var incorporateLine = function(ln) {
var matchedLeaf =
container.type !== "paragraph" && blocks[container.type].acceptsLines;
var starts = this.blockStarts;
var startsLen = starts.length;
// Unless last matched container is a code block, try new container starts,
// adding children to the last matched container:
while (!matchedLeaf) {
this.findNextNonspace();
// this is a little performance optimization:
if (
!this.indented &&
!reMaybeSpecial.test(ln.slice(this.nextNonspace))
) {
this.advanceNextNonspace();
break;
}
var i = 0;
while (i < startsLen) {
var res = starts[i](this, container);
if (res === 1) {
container = this.tip;
break;
} else if (res === 2) {
container = this.tip;
matchedLeaf = true;
break;
} else {
i++;
}
}
if (i === startsLen) {
// nothing matched
this.advanceNextNonspace();
break;
}
}
};当前行在消耗完所有打开块的匹配标记后,通过上述部分的代码,查找新的块开始标记,尝试匹配并创建新块。我们查看块结构解析的步骤 2:
接下来,在消耗完现有区块的延续标记后,我们寻找新的区块起始(例如,
>区块引用)。如果遇到新的区块起始,我们会关闭步骤 1 中未匹配的所有区块,然后将新区块创建为最后一个匹配的容器(
lastMatchedContainer)区块的子区块。
注意这段代码:
js
var matchedLeaf =
container.type !== "paragraph" && blocks[container.type].acceptsLines;之前说过, acceptsLines 用于定义当前块是否接受多行,除段落 paragraph 外,代码块和 HTML 块同样支持多行。与此同时,如果代码块或 HTML 块没有遇到明确的块结束条件,内部的所有字符都被视为文本字符,而不具有 Markdown 含义。
所以,如果 matchedLeaf 初始为 true,则不必进行后续块的解析,因为剩余内容都被视为代码块或 HTML 块的纯文本内容。
这里还存在一个小的性能优化项:
js
// this is a little performance optimization:
if (
!this.indented &&
!reMaybeSpecial.test(ln.slice(this.nextNonspace))
) {
this.advanceNextNonspace();
break;
}reMaybeSpecial 是一个正则实例,规则为 /^[#`~*+_=<>0-9-]/,当上述条件为真时,表示剩余行内容不满足缩进代码块条件及其他块标记开始条件,无需运行块匹配检查。
blockStarts 依然是一个通用接口,所有块定义它且每个块定义不同的匹配条件,它的接口如下:
js
declare interface BlockStartMatcher {
/**
*
* 块开始匹配函数,每当匹配到新块时,关闭所有未匹配的块
*
* @param parser - 解析器
* @param container - 容器节点
* @returns 0 = 无匹配
* 1 = 匹配到容器块,可以继续匹配
* 2 = 匹配到叶块,叶块不包含子块,不能继续匹配
*/
(parser: Parser, container: Node): 0 | 1 | 2;
}没有匹配到任何块开始的条件时,我们前进到下一个非空白字符的位置:
js
if (i === startsLen) {
// nothing matched
this.advanceNextNonspace();
break;
}advanceNextNonspace 方法比较简单:
js
var advanceNextNonspace = function() {
this.offset = this.nextNonspace;
this.column = this.nextNonspaceColumn;
this.partiallyConsumedTab = false;
};块结构解析流程 - 步骤 3
我们继续查看块结构解析的步骤 3:
- 最后,我们查看该行的剩余部分(在诸如
>、列表标记和缩进之类的块标记被使用之后)。这些文本可以合并到最后一个开放块(段落、代码块、标题或原始 HTML)中。
到了这一部分,剩余的行内容都被视为文本,不再参与块解析,留待内联解析时使用,对应这部分的代码为:
js
var incorporateLine = function(ln) {
// ...
// What remains at the offset is a text line. Add the text to the
// appropriate container.
// First check for a lazy paragraph continuation:
if (!this.allClosed && !this.blank && this.tip.type === "paragraph") {
// lazy paragraph continuation
this.addLine();
} else {
// not a lazy continuation
// finalize any blocks not matched
this.closeUnmatchedBlocks();
t = container.type;
if (this.blocks[t].acceptsLines) {
this.addLine();
// if HtmlBlock, check for end condition
if (
t === "html_block" &&
container._htmlBlockType >= 1 &&
container._htmlBlockType <= 5 &&
reHtmlBlockClose[container._htmlBlockType].test(
this.currentLine.slice(this.offset)
)
) {
this.lastLineLength = ln.length;
this.finalize(container, this.lineNumber);
}
} else if (this.offset < ln.length && !this.blank) {
// create paragraph container for line
container = this.addChild("paragraph", this.offset);
this.advanceNextNonspace();
this.addLine();
}
}
this.lastLineLength = ln.length;
};有两个分支:
-
分支 1:剩余文本内容是段落的延续行
addLine用于添加剩余文本到this.tip(在创建新块时,this.tip是最后创建的块;在完成并关闭块时,this.tip是被关闭块的父块):js// Add a line to the block at the tip. We assume the tip // can accept lines -- that check should be done before calling this. var addLine = function() { if (this.partiallyConsumedTab) { this.offset += 1; // skip over tab // add space characters: var charsToTab = 4 - (this.column % 4); this.tip._string_content += " ".repeat(charsToTab); } this.tip._string_content += this.currentLine.slice(this.offset) + "\n"; };注意
partiallyConsumedTab表示有部分消耗的 tabs,比如:markdown1.->段落内容这里由于 tabs 被扩展为两个空格,而列表项需要一个空格,所以剩余一个空格被作为段落内容(内联解析时段落首尾空格被删除)。
-
分支 2:剩余文本内容是代码块、HTML 块的内容,或是一个新的段落。
首先,默认调用
closeUnmatchedBlocks(为了在未创建新块时关闭所有未匹配的块),closeUnmatchedBlocks如下:js// Finalize and close any unmatched blocks. var closeUnmatchedBlocks = function() { if (!this.allClosed) { // finalize any blocks not matched while (this.oldtip !== this.lastMatchedContainer) { var parent = this.oldtip._parent; this.finalize(this.oldtip, this.lineNumber - 1); this.oldtip = parent; } this.allClosed = true; } };从
oldtip向上到lastMatchedContainer的所有块都是未匹配的块,如图所示: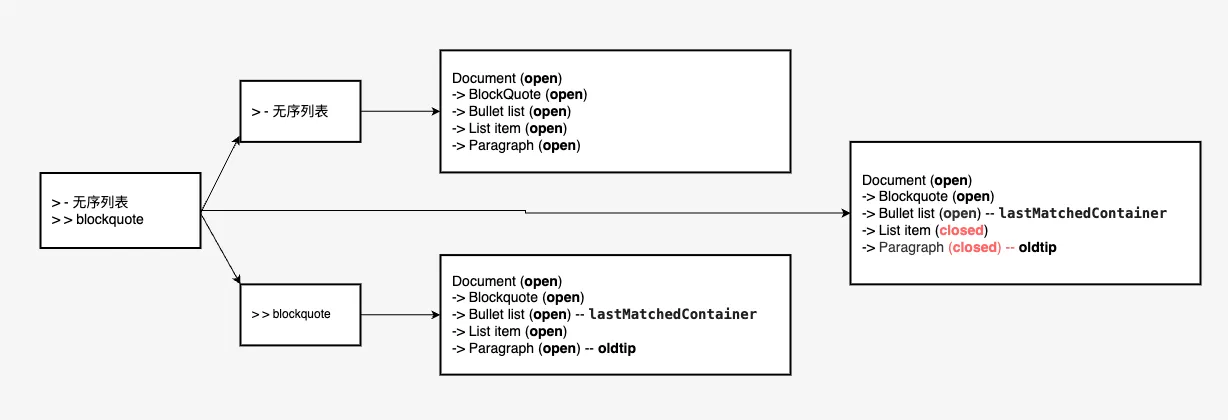
调用
finalize方法以完成并关闭这些块:js// Finalize a block. Close it and do any necessary postprocessing, // e.g. creating string_content from strings, setting the 'tight' // or 'loose' status of a list, and parsing the beginnings // of paragraphs for reference definitions. Reset the tip to the // parent of the closed block. var finalize = function(block, lineNumber) { var above = block._parent; block._open = false; block.sourcepos[1] = [lineNumber, this.lastLineLength]; this.blocks[block.type].finalize(this, block); this.tip = above; };关闭未匹配的块后,将剩余文本内容添加到支持多行的
container(匹配到新块的情况下是最后一个创建的块,否则是lastMatchedContainer):jsif (this.blocks[t].acceptsLines) { this.addLine(); // if HtmlBlock, check for end condition if ( t === "html_block" && container._htmlBlockType >= 1 && container._htmlBlockType <= 5 && reHtmlBlockClose[container._htmlBlockType].test( this.currentLine.slice(this.offset) ) ) { this.lastLineLength = ln.length; this.finalize(container, this.lineNumber); } }这里还检查了 HTML 块的结束条件,满足条件时完成并关闭 HTML 块。
HTML 块在 CommonMark 规范中分为 7 个类型,类型 1 - 5 都有明确的结束标记,类型 6 - 7 以空行作为结束条件。
如果
container不支持多行内容,且删除 Markdown 标记后包含有效文本内容,则添加一个段落:jsif (this.blocks[t].acceptsLines) { } else if (this.offset < ln.length && !this.blank) { // create paragraph container for line container = this.addChild("paragraph", this.offset); this.advanceNextNonspace(); this.addLine(); }addChild用于添加子块到this.tip中,同时更新this.tip引用为新创建的块:js// Add block of type tag as a child of the tip. If the tip can't // accept children, close and finalize it and try its parent, // and so on til we find a block that can accept children. var addChild = function(tag, offset) { while (!this.blocks[this.tip.type].canContain(tag)) { this.finalize(this.tip, this.lineNumber - 1); } var column_number = offset + 1; // offset 0 = column 1 var newBlock = new Node(tag, [ [this.lineNumber, column_number], [0, 0] ]); newBlock._string_content = ""; this.tip.appendChild(newBlock); this.tip = newBlock; return newBlock; };在添加子块时,我们首先检查
this.tip是否可以包含指定块,如果不可以,则完成并关闭this.tip,向上迭代,直到找到最近的可以接受指定块的包含块。比如
this.tip是一个bullet list,则它只能包含list item,在添加非list item的子块时,需要先完成并关闭bullet list。
部分块 BlockContinue 的实现
在 incorporateLine 中,包含了主要的解析流程,还有部分细节隐藏在各个块的独立实现中,在 commonmark.js 被定义为 blocks 与 blockStarts,我们先阅读有关 blocks 的部分。
blocks 的类型可以定义为 BlockContinue,BlockContinue 在 [块结构解析流程 - 步骤 1](#块结构解析流程 - 步骤 1) 中可以看到。
因为部分块(标题、主题分割等)不包含非常有意义的代码,所以这部分块默认忽略,不在本文中解读。
Document
js
({
document: {
continue: function() {
return 0;
},
finalize: function(parser, block) {
removeLinkReferenceDefinitions(parser, block);
return;
},
canContain: function(t) {
return t !== "item";
},
acceptsLines: false
}
})可以看出 document 块始终被匹配,且可以包含除列表项外的所有块。这里注意在完成 document 块时调用了 removeLinkReferenceDefinitions,我们看看这个方法:
js
// Remove link reference definitions from given tree.
var removeLinkReferenceDefinitions = function(parser, tree) {
var event, node;
var walker = tree.walker();
var emptyNodes = [];
while ((event = walker.next())) {
node = event.node;
if (event.entering && node.type === "paragraph") {
var pos;
var hasReferenceDefs = false;
// Try parsing the beginning as link reference definitions;
// Note that link reference definitions must be the beginning of a
// paragraph node since link reference definitions cannot interrupt
// paragraphs.
while (
peek(node._string_content, 0) === C_OPEN_BRACKET &&
(pos = parser.inlineParser.parseReference(
node._string_content,
parser.refmap
))
) {
const removedText = node._string_content.slice(0, pos);
node._string_content = node._string_content.slice(pos);
hasReferenceDefs = true;
const lines = removedText.split("\n");
// -1 for final newline.
node.sourcepos[0][0] += lines.length - 1;
}
if (hasReferenceDefs && isBlank(node._string_content)) {
emptyNodes.push(node);
}
}
}
for (node of emptyNodes) {
node.unlink();
}
};这个方法用于迭代 Document 树,检查每个 Paragraph 段落块是否是有效的链接引用定义,如果是则将链接引用添加到 this.refmap 中。
这里有个奇怪的地方:
js
if (hasReferenceDefs && isBlank(node._string_content)) {
emptyNodes.push(node);
}
for (node of emptyNodes) {
node.unlink();
}依据规范定义,链接引用定义后不能包含其他非空白字符,这里的判断应该始终为真,运行 git log -p -L 244,244:lib/blocks.js | cat 命令查看 if (hasReferenceDefs && isBlank(node._string_content)) { 的首次添加历史,可以找到 df3ea1e80d98fce5ad7c72505f9230faa6f23492 的 commit 记录,但只提到了延迟链接引用定义的检查时机,没有说明这段代码的作用。
为了弄明白这段代码的作用,我们先还原项目结构,删除代码 && isBlank(node._string_content):
js
if (hasReferenceDefs) {
emptyNodes.push(node);
}然后 npm run test 运行测试,会发现以下三个测试用例失败:
markdown
[
foo
]:␣/url
bar
markdown
[foo]:␣/url
"title"␣ok
markdown
[test]:example
""third␣[test]以第一个测试用例说明,这 3 行被当作完成的 Paragraph 段落,但链接引用定义只包含 1,2 行,第 3 行是正常的段落文本,所以需要加上 && isBlank(node._string_content) 这段代码防止将包含正常文本的段落节点删除。
块解析策略中,说明了在段落关闭时检查链接引用定义,commonmark.js 的实现将它推迟到
document块关闭时。
parseReference 是 InlineParser 实例方法,用于解析链接引用,我们留待内联解析部分再讲。
List
js
({
list: {
continue: function() {
return 0;
},
finalize: function(parser, block) {
var item = block._firstChild;
while (item) {
// check for non-final list item ending with blank line:
if (item._next && endsWithBlankLine(item)) {
block._listData.tight = false;
break;
}
// recurse into children of list item, to see if there are
// spaces between any of them:
var subitem = item._firstChild;
while (subitem) {
if (
subitem._next &&
endsWithBlankLine(subitem)
) {
block._listData.tight = false;
break;
}
subitem = subitem._next;
}
item = item._next;
}
block.sourcepos[1] = block._lastChild.sourcepos[1];
},
canContain: function(t) {
return t === "item";
},
acceptsLines: false
}
}
)List 的其他定义都很清晰,主要看 finalize 方法,方法内主要检查列表是 loose 还是 tight 的。
如果列表的任意组成列表项之间以空行分隔,或者任意组成列表项直接包含两个块级元素,且中间有一个空行的,都为
loose列表,反之则为tight列表。
这里的实现比较简单粗暴,判断相邻两个列表项是否包含空行,或列表项的两个相邻直接子块是否包含空行,主要使用 endsWithBlankLine 方法:
js
// Returns true if block ends with a blank line.
var endsWithBlankLine = function(block) {
return block.next &&
block.sourcepos[1][0] !== block.next.sourcepos[0][0] - 1;
};就是判断当前块最后一行的行数与下一块第一行行数的间隔是否大于 1。
blockquote
js
({
block_quote: {
continue: function(parser) {
var ln = parser.currentLine;
if (
!parser.indented &&
peek(ln, parser.nextNonspace) === C_GREATERTHAN
) {
parser.advanceNextNonspace();
parser.advanceOffset(1, false);
if (isSpaceOrTab(peek(ln, parser.offset))) {
parser.advanceOffset(1, true);
}
} else {
return 1;
}
return 0;
},
finalize: function() {
return;
},
canContain: function(t) {
return t !== "item";
},
acceptsLines: false
}
})blockquote 主要在于判断是否能继续匹配的 continue 方法,流程如下:
-
判断是否满足继续的条件(缩进不大于等于 4,第一个非空白字符是
>) -
可以继续匹配
- 跳过空白字符
parser.advanceOffset(1, false)跳过块引用标记>- 如果下一个字符是空格或 tabs,跳过一个空格(块引用标记后允许最多一个空格,且可以是 tabs 扩展的空格)
-
不能匹配
我们说说 advanceOffset 这个方法:
js
var advanceOffset = function(count, columns) {
var currentLine = this.currentLine;
var charsToTab, charsToAdvance;
var c;
while (count > 0 && (c = currentLine[this.offset])) {
if (c === "\t") {
charsToTab = 4 - (this.column % 4);
if (columns) {
this.partiallyConsumedTab = charsToTab > count;
charsToAdvance = charsToTab > count ? count : charsToTab;
this.column += charsToAdvance;
this.offset += this.partiallyConsumedTab ? 0 : 1;
count -= charsToAdvance;
} else {
this.partiallyConsumedTab = false;
this.column += charsToTab;
this.offset += 1;
count -= 1;
}
} else {
this.partiallyConsumedTab = false;
this.offset += 1;
this.column += 1; // assume ascii; block starts are ascii
count -= 1;
}
}
};这个方法有两个参数,count 表示要跳过的字符数量,columns 表示是否以 column 计算(是否包含 tabs 扩展);对于一般 Markdown 标记(eg: -、>)而言,不使用 column。
看这一部分:
js
if (c === "\t") {
charsToTab = 4 - (this.column % 4);
if (columns) {
this.partiallyConsumedTab = charsToTab > count;
charsToAdvance = charsToTab > count ? count : charsToTab;
this.column += charsToAdvance;
this.offset += this.partiallyConsumedTab ? 0 : 1;
count -= charsToAdvance;
} else {
this.partiallyConsumedTab = false;
this.column += charsToTab;
this.offset += 1;
count -= 1;
}
}charsToTab 表示转到下一个制表位所需要的空格数,如果以 column 计算,charsToTab 大于 count 时表示还有剩余的 tabs 扩展空格没有被消耗,即 partiallyConsumedTab = ture。当 partiallyConsumedTab 为真时,我们还没有完全处理这个 tabs 字符,即 this.offset += this.partiallyConsumedTab ? 0 : 1。
List item
查看 continue:
js
({
item: {
continue: function(parser, container) {
if (parser.blank) {
if (container._firstChild == null) {
// Blank line after empty list item
return 1;
} else {
parser.advanceNextNonspace();
}
} else if (
parser.indent >=
container._listData.markerOffset + container._listData.padding
) {
parser.advanceOffset(
container._listData.markerOffset +
container._listData.padding,
true
);
} else {
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
}
})为了满足继续匹配的要求:
-
当前行没有后续内容时,列表项不为空
-
缩进大于等于当前列表项的缩进(markerOffset) + 列表项标记宽(padding)
比如下面
markerOffset为 0,padding为 2(加上无序列表标记-后的空格):markdown- paragraph1 paragraph2列表项要继续,则
paragraph2应该缩进 0 + 2 个空格。
Code block
continue:
js
({
code_block: {
continue: function(parser, container) {
var ln = parser.currentLine;
var indent = parser.indent;
if (container._isFenced) {
// fenced
var match =
indent <= 3 &&
ln.charAt(parser.nextNonspace) === container._fenceChar &&
ln.slice(parser.nextNonspace).match(reClosingCodeFence);
if (match && match[0].length >= container._fenceLength) {
// closing fence - we're at end of line, so we can return
parser.lastLineLength =
parser.offset + indent + match[0].length;
parser.finalize(container, parser.lineNumber);
return 2;
} else {
// skip optional spaces of fence offset
var i = container._fenceOffset;
while (i > 0 && isSpaceOrTab(peek(ln, parser.offset))) {
parser.advanceOffset(1, true);
i--;
}
}
} else {
// indented
if (indent >= CODE_INDENT) {
parser.advanceOffset(CODE_INDENT, true);
} else if (parser.blank) {
parser.advanceNextNonspace();
} else {
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
},
}
})有两个分支:
-
围栏代码块
-
缩进小于等于 3,结束围栏长度大于等于开始围栏长度,则完成并关闭围栏代码块
-
跳过与开始围栏相同长度的缩进空格,后续内容作为代码块内容
比如:
markdown```js abc ```被渲染为:
html<pre> <code class="language-js"> abc</code> </pre>只保留了一个空格,开始围栏前的缩进被删除。
-
-
缩进代码块
- 缩进大于等于 4
- 空行
HTML block
continue:
js
({
html_block: {
continue: function(parser, container) {
return parser.blank &&
(container._htmlBlockType === 6 ||
container._htmlBlockType === 7)
? 1
: 0;
}
}
})当 HTML 块类型为 6 或 7 时,遇到空行即结束,不能继续匹配;类型 1 - 5 的 HTML 块类型必须有明确的块结束条件。
Paragraph
continue:
js
({
paragraph: {
continue: function(parser) {
return parser.blank ? 1 : 0;
}
}
})遇到空行时,段落不能继续。
部分块 BlockStartMatcher 的实现
继续阅读有关 blockStarts 的部分,这部分代码用于匹配并创建块,blockStarts 的类型可定义为 BlockStartMatcher,在 [块结构解析流程 - 步骤 2](#块结构解析流程 - 步骤 2) 部分可以找到。
Blockquote
js
// block quote
function(parser) {
if (
!parser.indented &&
peek(parser.currentLine, parser.nextNonspace) === C_GREATERTHAN
) {
parser.advanceNextNonspace();
parser.advanceOffset(1, false);
// optional following space
if (isSpaceOrTab(peek(parser.currentLine, parser.offset))) {
parser.advanceOffset(1, true);
}
parser.closeUnmatchedBlocks();
parser.addChild("block_quote", parser.nextNonspace);
return 1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}缩进小于 4,第一个非空白字符是 >,后跟一个可选空格,满足条件即创建一个 blockquote 块,在创建新块前,始终调用 closeUnmatchedBlocks 关闭未匹配的块,此时 this.tip 是最后一个打开的块。
ATX heading
js
// ATX heading
function(parser) {
var match;
if (
!parser.indented &&
(match = parser.currentLine
.slice(parser.nextNonspace)
.match(reATXHeadingMarker))
) {
parser.advanceNextNonspace();
parser.advanceOffset(match[0].length, false);
parser.closeUnmatchedBlocks();
var container = parser.addChild("heading", parser.nextNonspace);
container.level = match[0].trim().length; // number of #s
// remove trailing ###s:
container._string_content = parser.currentLine
.slice(parser.offset)
.replace(/^[ \t]*#+[ \t]*$/, "")
.replace(/[ \t]+#+[ \t]*$/, "");
parser.advanceOffset(parser.currentLine.length - parser.offset);
return 2;
} else {
return 0;
}
}缩进小于 4,除行首空白字符外,满足 /^#{1,6}(?:[ \t]+|$)/; 正则模式,即:
- 1 - 6 个
#字符,#字符数量表示对应的标题级别 - 后跟一个空格,或直接到达行尾(ATX 标题支持空内容)
满足条件时,创建一个 ATX heading,同时检查是否有尾部的 # 字符序列,如果有,被解释为 ATX Markdown 标记的一部分。最后返回 2,表示匹配到了叶块,不能再继续匹配新块。
Fenced code block
js
// Fenced code block
function(parser) {
var match;
if (
!parser.indented &&
(match = parser.currentLine
.slice(parser.nextNonspace)
.match(reCodeFence))
) {
var fenceLength = match[0].length;
parser.closeUnmatchedBlocks();
var container = parser.addChild("code_block", parser.nextNonspace);
container._isFenced = true;
container._fenceLength = fenceLength;
container._fenceChar = match[0][0];
container._fenceOffset = parser.indent;
parser.advanceNextNonspace();
parser.advanceOffset(fenceLength, false);
return 2;
} else {
return 0;
}
}缩进小于 4,除行首空白字符外,满足 /^`{3,}(?!.*`)|^~{3,}/ 正则模式,即:
- 3 个或以上
标记,且后续不再包含字符;或 3 个或以上~标记。
满足条件即创建一个围栏代码块,记录围栏相关信息;注意这里没有处理围栏代码块的信息字符串,信息字符串在后续被作为纯文本内容添加到围栏代码块的首行,在 code_block.finalize 中处理。
HTMLBlock
js
// HTML block
function(parser, container) {
if (
!parser.indented &&
peek(parser.currentLine, parser.nextNonspace) === C_LESSTHAN
) {
var s = parser.currentLine.slice(parser.nextNonspace);
var blockType;
for (blockType = 1; blockType <= 7; blockType++) {
if (
reHtmlBlockOpen[blockType].test(s) &&
(blockType < 7 || (container.type !== "paragraph" &&
!(!parser.allClosed && !parser.blank &&
parser.tip.type === "paragraph") // maybe lazy
))
) {
parser.closeUnmatchedBlocks();
// We don't adjust parser.offset;
// spaces are part of the HTML block:
var b = parser.addChild("html_block", parser.offset);
b._htmlBlockType = blockType;
return 2;
}
}
}
return 0;
}缩进小于 4,除行首空白字符外,第一个字符是 <,且:
-
满足 HTML block 类型 1 - 7,其中的一个开始标记条件
-
HTML 块类型不为 7,或 HTML 块类型为 7 时,最后一个打开块不是潜在的惰性延续段落行(类型 7 的 HTML 块无法中断段落)
比如下列 Markdown:
markdownparagraph <custom></custom>被渲染为:
html<p>paragraph <custom></custom></p>而这个:
markdownparagraph <script></script>被渲染为:
html<p>paragraph</p> <script></script>
满足条件时,创建一个 HTML 块。
Setext heading
js
// Setext heading
function(parser, container) {
var match;
if (
!parser.indented &&
container.type === "paragraph" &&
(match = parser.currentLine
.slice(parser.nextNonspace)
.match(reSetextHeadingLine))
) {
parser.closeUnmatchedBlocks();
// resolve reference link definitiosn
var pos;
while (
peek(container._string_content, 0) === C_OPEN_BRACKET &&
(pos = parser.inlineParser.parseReference(
container._string_content,
parser.refmap
))
) {
container._string_content = container._string_content.slice(
pos
);
}
if (container._string_content.length > 0) {
var heading = new Node("heading", container.sourcepos);
heading.level = match[0][0] === "=" ? 1 : 2;
heading._string_content = container._string_content;
container.insertAfter(heading);
container.unlink();
parser.tip = heading;
parser.advanceOffset(
parser.currentLine.length - parser.offset,
false
);
return 2;
} else {
return 0;
}
} else {
return 0;
}
}缩进小于 4,最后一个打开的块时段落,且当前行满足 /^(?:=+|-+)[ \t]*$/ 正则模式,即:
-
一个及以上的
-(一级标题)标记,或一个及以上的=(二级标题)标记比如:
markdownSetext ===
满足条件时,创建一个 Setext 标题。
说到这里,我们需要注意 blockStarts 以数组形式定义,使用 for 循环 从头到尾 尝试匹配块,这体现了块之间的匹配优先级。
以这个 Markdown 举例:
js
Setext
---看完整的段落,这是一个 Setext 标题,但单独看第 2 行,这也可以是一个主题分割;按规范定义,主题分割无法中断 Setext 标题,所以解析为 Setext 标题是正确的,反应在 commonmark.js 代码中就是主题分割的解析定义在 Setext 标题之后。
Thematic break
js
// thematic break
function(parser) {
if (
!parser.indented &&
reThematicBreak.test(parser.currentLine.slice(parser.nextNonspace))
) {
parser.closeUnmatchedBlocks();
parser.addChild("thematic_break", parser.nextNonspace);
parser.advanceOffset(
parser.currentLine.length - parser.offset,
false
);
return 2;
} else {
return 0;
}
}缩进小于 4,除行首空白字符外,满足 /^(?:\*[ \t]*){3,}$|^(?:_[ \t]*){3,}$|^(?:-[ \t]*){3,}$/ 正则模式,即:
- 匹配只包含 3 个及以上的
*、-或_,每个符号之间可以有空格或 tabs。
如之前所说,使用 - 标记的主题分割优先级低于 Setext 标题。
ListItem
js
// list item
function(parser, container) {
var data;
if (
(!parser.indented || container.type === "list") &&
(data = parseListMarker(parser, container))
) {
parser.closeUnmatchedBlocks();
// add the list if needed
if (
parser.tip.type !== "list" ||
!listsMatch(container._listData, data)
) {
container = parser.addChild("list", parser.nextNonspace);
container._listData = data;
}
// add the list item
container = parser.addChild("item", parser.nextNonspace);
container._listData = data;
return 1;
} else {
return 0;
}
},缩进小于 4,最后一个打开块时 List,且解析列表标记数据正常,看看 parseListMarker 方法:
js
// Parse a list marker and return data on the marker (type,
// start, delimiter, bullet character, padding) or null.
var parseListMarker = function(parser, container) {
var rest = parser.currentLine.slice(parser.nextNonspace);
var match;
var nextc;
var spacesStartCol;
var spacesStartOffset;
var data = {
type: null,
tight: true, // lists are tight by default
bulletChar: null,
start: null,
delimiter: null,
padding: null,
markerOffset: parser.indent
};
if (parser.indent >= 4) {
return null;
}
if ((match = rest.match(reBulletListMarker))) {
data.type = "bullet";
data.bulletChar = match[0][0];
} else if (
(match = rest.match(reOrderedListMarker)) &&
(container.type !== "paragraph" || match[1] == 1)
) {
data.type = "ordered";
data.start = parseInt(match[1]);
data.delimiter = match[2];
} else {
return null;
}
// make sure we have spaces after
nextc = peek(parser.currentLine, parser.nextNonspace + match[0].length);
if (!(nextc === -1 || nextc === C_TAB || nextc === C_SPACE)) {
return null;
}
// if it interrupts paragraph, make sure first line isn't blank
if (
container.type === "paragraph" &&
!parser.currentLine
.slice(parser.nextNonspace + match[0].length)
.match(reNonSpace)
) {
return null;
}
// we've got a match! advance offset and calculate padding
parser.advanceNextNonspace(); // to start of marker
parser.advanceOffset(match[0].length, true); // to end of marker
spacesStartCol = parser.column;
spacesStartOffset = parser.offset;
do {
parser.advanceOffset(1, true);
nextc = peek(parser.currentLine, parser.offset);
} while (parser.column - spacesStartCol < 5 && isSpaceOrTab(nextc));
var blank_item = peek(parser.currentLine, parser.offset) === -1;
var spaces_after_marker = parser.column - spacesStartCol;
if (spaces_after_marker >= 5 || spaces_after_marker < 1 || blank_item) {
data.padding = match[0].length + 1;
parser.column = spacesStartCol;
parser.offset = spacesStartOffset;
if (isSpaceOrTab(peek(parser.currentLine, parser.offset))) {
parser.advanceOffset(1, true);
}
} else {
data.padding = match[0].length + spaces_after_marker;
}
return data;
};-
无序列表,第一个非空白字符是
-、+、*,且尾随最少一个空格 -
有序列表,满足
/^(\d{1,9})([.)])/(1-9 个数字,尾随.或)) 正则模式,且尾随最少一个空格
当最后一个打开的块是段落时,列表项不能为空,比如:
markdown
paragraph
*被渲染为惰性延续行:
html
<p>paragraph
*</p>再看这一部分:
js
spacesStartCol = parser.column;
spacesStartOffset = parser.offset;
do {
parser.advanceOffset(1, true);
nextc = peek(parser.currentLine, parser.offset);
} while (parser.column - spacesStartCol < 5 && isSpaceOrTab(nextc));
var blank_item = peek(parser.currentLine, parser.offset) === -1;
var spaces_after_marker = parser.column - spacesStartCol;
if (spaces_after_marker >= 5 || spaces_after_marker < 1 || blank_item) {
data.padding = match[0].length + 1;
parser.column = spacesStartCol;
parser.offset = spacesStartOffset;
if (isSpaceOrTab(peek(parser.currentLine, parser.offset))) {
parser.advanceOffset(1, true);
}
} else {
data.padding = match[0].length + spaces_after_marker;
}这一部分用于确定 padding 的数量,spaces_after_marker 是列表项标记的最后位置到内部第一个非空白字符或行尾的空格数量。
当 spaces_after_marker 大于等于 5 时(缩进代码块),或当内部缩进小于 1 时,或到达行尾时,padding 被设置为列表项标记 + 1 的长度。
反之,padding 被设置为列表项标记 + spaces_after_marker 的长度。
比如:
markdown
1. item
paragraph列表项标记宽度为 2,spaces_after_marker 为 3,则 padding 为 2 + 3。
Indented code block
js
// indented code block
function(parser) {
if (
parser.indented &&
parser.tip.type !== "paragraph" &&
!parser.blank
) {
// indented code
parser.advanceOffset(CODE_INDENT, true);
parser.closeUnmatchedBlocks();
parser.addChild("code_block", parser.offset);
return 2;
} else {
return 0;
}
}缩进大于等于 4,且最后一个打开的块不是段落,因为缩进代码块无法中断段落,同时,缩进后应该包含除 \s、\t 外的字符。
-- end