mmap文件映射视屏:待看...
目录
[问题2: lamba表达式](#问题2: lamba表达式)
[模版封装 3.thread_template](#模版封装 3.thread_template)
线程栈
• 对于Linux进程或者说主线程,简单理解就是main函数的栈空间,在fork的时候,**实际上就是复 制了⽗亲的 stack 空间地址,**然后写时拷⻉(cow)以及动态增⻓。如果扩充超出该上限则栈溢出 会报段错误(发送段错误信号给该进程)。进程栈是唯⼀可以访问未映射⻚⽽不⼀定会发⽣段错 误⸺⸺超出扩充上限才报。
• 然⽽对于主线程⽣成的⼦线程⽽⾔,其 stack 将不再是向下⽣⻓的,⽽是事先固定下来的。线 程栈⼀般是调⽤glibc/uclibc等的 pthread 库接 pthread_create 创建的线程,在⽂件映 射区(或称之为共享区)。其中使⽤ mmap 系统调⽤,这个可以从 glibc 的
nptl/allocatestack.c 中的 allocate_stack 函数中看到:
cpp
mem = mmap (NULL, size, prot,
MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_ANONYMOUS | MAP_STACK, -1, 0);此调⽤中的 size 参数的获取很是复杂,你可以⼿⼯传⼊stack的⼤⼩,也可以使⽤默认的**,⼀般⽽ ⾔就是默认的 8M 。**这些都不重要,重要的是,这种stack不能动态增⻓,⼀旦⽤尽就没了,这是和 ⽣成进程的fork不同的地⽅。在glibc中通过mmap得到了stack之后,底层将调⽤ sys_clone 系 统调⽤:
对于⼦线程的 stack ,**它其实是在进程的地址空间中map出来的⼀块内存区域,**原则上是 线程私有的,但是同⼀个进程的所有线程⽣成的时候,是会浅拷⻉⽣成者的 task_struct 的很多 字段,如果愿意,其它线程也还是可以访问到的,于是⼀定要注意。
每个线程都有自己的栈结构:
独立的上下文:有独立的PCB+TCP(用户层,pthread库内部)
独立的栈:每个线程都有自己的栈结构,要么是进程自己的要么是库中创建进程时mmap申请出来的。
结论:一个线程的数据,其他线程也可以访问:只要拿到对应的地址即可。
代码证明:一个线程的数据,其他线程也可以访问
cpp
//证明:一个线程的数据,其他线程也可以访问:只要拿到对应的地址即可。
#include <sched.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
int *p = nullptr;
void *threadrun(void *args)
{
int a = 123;
p = &a;
while(true) {sleep(1);}
}
int main()
{
pthread_t tid;
pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, threadrun, nullptr);
while(true)
{
std::cout << "*p : " << *p << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
pthread_join(tid, nullptr);
return 0;
}线程封装
线程ID:就是动态库。
线程的封装
以面向对象的形式把线程进行封装
计数器:进程编号: static uint32_t number = 0;
_name:线程名字
_tid:tid
_isdetach:是否被分分离。
_isrunning:是否正在运行,是否调用Start()
Start()线程开始/创建:
--创建线程,pthread_creat
--如果分离,那么就设置线程分离,pthreaddetach
EnableDetach():
是否分离。
Detach():
如果一个线程已经跑起来了,要把它设置为分离状态,用detach()
Enablerunning():
是否已经运行
Stop():停止进程
pthread_cancle
是运行状态才可以stop(),
Join():
如果是分离的那么就不可以Join()
Routine(),写在在public会报错,
因为Routine属于类内的成员函数,默认包含this指针???
_func()回调方法,static没有this指针 ,无法回调房钱成员,
解决:把thos指针传入Routine
简单封装,2.thread
Thread.hpp
cpp
#ifndef _THREAD_H_
#define _THREAD_H_
//一个头文件保护机制,防止头文件被重复包含
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <functional>
namespace ThreadModlue{
static uint32_t number = 1;
class Thread{
using func_t = std::function<void()>;// 添加模版的前身
private:
void Enabledetach(){
std::cout<<"线程被分离了"<<std::endl;
_isdetach = true;
}
void Enablerunning(){
std::cout<<"线程正在运行"<<std::endl;
_isrunning = true;
}
static void* Routine(void*args){//static,没有默认指针,需要在线程创建的时候,通过args传回this指针
Thread* self = static_cast<Thread*>(args);//强转成Thread*类型
self->Enablerunning();
if(self->_isdetach){
self->Enabledetach();
}
self->_func();//调用函数要加上()括号才可以调用
return nullptr;
}
public:
Thread(func_t func)
:_tid(0),
_isdetach(false),
_isrunning(false),
_res(nullptr),
_func(func)
{
_name = "thread - " + std::to_string(number++);
}
void Detach(){
if(_isdetach)
return;
if(_isrunning){
pthread_detach(_tid);
std::cout<<"线程分离成功"<<std::endl;
Enabledetach();
}
}
bool Start(){
if(_isrunning)
return false;//线程正在运行,不可再次启动
int n = pthread_create(&_tid,nullptr,Routine,this);
if( n != 0 ){
std::cerr<<"创建线程错误"<<strerror(n)<<std::endl;
return false;
}else{
std::cout<<"线程创建成功:"<<_name<<std::endl;
return true;
}
}
bool Stop(){
if(_isrunning){
int n = pthread_cancel(_tid);
if(n != 0){
std::cerr<<"线程停止错误:"<<strerror(n)<<std::endl;
return false;
}
else{
_isrunning = false;
std::cout<<"线程停止:"<<_name<<std::endl;
return true;
}
}
}
void Join(){
if(_isdetach){
std::cout<<"已经被分离的线程无法join"<<std::endl;
return;
}
int n = pthread_join(_tid,&_res);
if(n != 0){
std::cerr<<"线程join错误:"<<strerror(n)<<std::endl;
}else{
std::cout << "线程join成功" << std::endl;
}
}
private:
pthread_t _tid;
bool _isdetach;
bool _isrunning;
std::string _name;
void* _res;
func_t _func;
};
}
#endifMain.cc
cpp
#include "Thread.hpp"
#include <unistd.h>
#include <vector>
using namespace ThreadModlue;
int main(){
Thread t([](){
while(true)
{
std::cout << "我是一个新线程: "<< std::endl; // 我的线程的名字是什么呀?debug
sleep(1);
}
});
t.Start();
t.Detach();
sleep(2);
t.Stop();
sleep(2);
t.Join();
return 0;
}Makefile
cpp
test_thread:Main.cc
g++ -o $@ $^ -lpthread
.PHONY:clean
clean:
rm -f test_thread结果:
问题1:
在实现线程的封装过程中,Routine(),写在在public会报错,
因为Routine属于类内的成员函数,默认包含this指针???
这句话怎么理解 ???
cppstatic void* Routine(void*args){ //static,没有默认指针,需要在线程创建的时候,通过args传回this指针 Thread* self = static_cast<Thread*>(args);//强转成Thread*类型 self->Enablerunning(); if(self->_isdetach){ self->Enabledetach(); } self->_func();//调用函数要加上()括号才可以调用 return nullptr; }
pthread_create调用Routine函数,但是Routine没有默认的this指针,
那么就需要在pthread_create的第四个传入Routine的参数传入this指针作为参数才可以
问题2: lamba表达式
cpp
Thread t([](){
while(true)
{
std::cout << "我是一个新线程: "<< std::endl; // 我的线程的名字是什么呀?debug
sleep(1);
}
});模版封装 3.thread_template
Thread.hpp
cpp
#ifndef _THREAD_H_
#define _THREAD_H_
//一个头文件保护机制,防止头文件被重复包含
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <functional>
namespace ThreadModlue{
static uint32_t number = 1;
template<typename T>//这里设置模版类型
class Thread{
using func_t = std::function<void(T)>;// 添加模版的前身 + 模版添加需要传参数!!!
private:
void Enabledetach(){
std::cout<<"线程被分离了"<<std::endl;
_isdetach = true;
}
void Enablerunning(){
std::cout<<"线程正在运行"<<std::endl;
_isrunning = true;
}
static void* Routine(void*args){//static,没有默认指针,需要在线程创建的时候,通过args传回this指针
Thread<T>* self = static_cast<Thread<T>*>(args);//强转成Thread<T*>类型,
self->Enablerunning();
if(self->_isdetach){
self->Enabledetach();
}
self->_func(self->_data);//调用函数要加上()括号才可以调用
return nullptr;
}
public:
Thread(func_t func,T data)//传参 T data
:_tid(0),
_isdetach(false),
_isrunning(false),
_res(nullptr),
_func(func),
_data(data)//初始化参数
{
_name = "thread - " + std::to_string(number++);
}
void Detach(){
if(_isdetach)
return;
if(_isrunning){
pthread_detach(_tid);
std::cout<<"线程分离成功"<<std::endl;
Enabledetach();
}
}
bool Start(){
if(_isrunning)
return false;//线程正在运行,不可再次启动
int n = pthread_create(&_tid,nullptr,Routine,this);
if( n != 0 ){
std::cerr<<"创建线程错误"<<strerror(n)<<std::endl;
return false;
}else{
std::cout<<"线程创建成功:"<<_name<<std::endl;
return true;
}
}
bool Stop(){
if(_isrunning){
int n = pthread_cancel(_tid);
if(n != 0){
std::cerr<<"线程停止错误:"<<strerror(n)<<std::endl;
return false;
}
else{
_isrunning = false;
std::cout<<"线程停止:"<<_name<<std::endl;
return true;
}
}
}
void Join(){
if(_isdetach){
std::cout<<"已经被分离的线程无法join"<<std::endl;
return;
}
int n = pthread_join(_tid,&_res);
if(n != 0){
std::cerr<<"线程join错误:"<<strerror(n)<<std::endl;
}else{
std::cout << "线程join成功" << std::endl;
}
}
~Thread(){}
private:
pthread_t _tid;
bool _isdetach;
bool _isrunning;
std::string _name;
void* _res;
func_t _func;
T _data;
};
}
#endifMain.cc
cpp
#include "Thread.hpp"
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace ThreadModlue;
// 我们可以传递对象吗???
class ThreadData
{
public:
pthread_t tid;
std::string name;
};
void Count(ThreadData td)
{
while (true)
{
std::cout << "我是一个新线程" << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
}
int main()
{
ThreadData td;
Thread<ThreadData> t(Count, td);
t.Start();
sleep(5);
t.Stop();
t.Join();
return 0;
}Makefile
cpp
test_thread:Main.cc
g++ -o $@ $^ -lpthread
.PHONY:clean
clean:
rm -f test_thread
结果
线程局部存储4threadlocal
test.cc
cpp
#include <pthread.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
// 该count叫做线程的局部存储!
int count = 1;
// 线程局部存储有什么用?全局变量,我又不想让这个全局变量被其他线程看到!
// 线程局部存储,只能存储内置类型和部分指针
std::string Addr(int &c)
{
char addr[64];
snprintf(addr, sizeof(addr), "%p", &c);
return addr;
}
void *routine1(void *args)
{
(void)args;
while (true)
{
std::cout << "thread - 1, count = " << count << "[我来修改count], "
<< "&count: " << Addr(count) << std::endl;
count++;
sleep(1);
}
}
void *routine2(void *args)
{
(void)args;
while (true)
{
std::cout << "thread - 2, count = " << count
<< ", &count: " << Addr(count) << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
}
int main()
{
pthread_t tid1, tid2;
pthread_create(&tid1, nullptr, routine1, nullptr);
pthread_create(&tid2, nullptr, routine2, nullptr);
pthread_join(tid1, nullptr);
pthread_join(tid2, nullptr);
return 0;
}Makefile
cpp
test_thread:test.cc
g++ -o $@ $^ -lpthread
.PHONY:clean
clean:
rm -f test_thread结果:
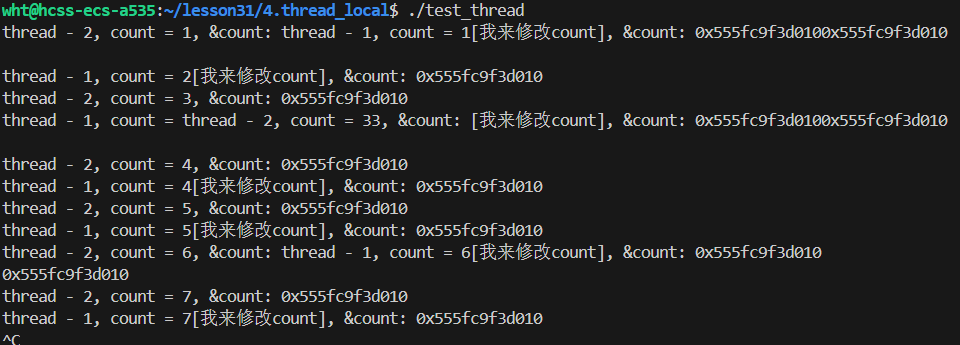
全局变量被两个线程共享 ,线程1修改全局变量count,线程2也可以看得到
添加:__thread
cpp
#include <pthread.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
// 该count叫做线程的局部存储!
__thread int count = 1;
// 线程局部存储有什么用?全局变量,我又不想让这个全局变量被其他线程看到!
// 线程局部存储,只能存储内置类型和部分指针
std::string Addr(int &c)
{
char addr[64];
snprintf(addr, sizeof(addr), "%p", &c);
return addr;
}
void *routine1(void *args)
{
(void)args;
while (true)
{
std::cout << "thread - 1, count = " << count << "[我来修改count], "
<< "&count: " << Addr(count) << std::endl;
count++;
sleep(1);
}
}
void *routine2(void *args)
{
(void)args;
while (true)
{
std::cout << "thread - 2, count = " << count
<< ", &count: " << Addr(count) << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
}
int main()
{
pthread_t tid1, tid2;
pthread_create(&tid1, nullptr, routine1, nullptr);
pthread_create(&tid2, nullptr, routine2, nullptr);
pthread_join(tid1, nullptr);
pthread_join(tid2, nullptr);
return 0;
}结果:
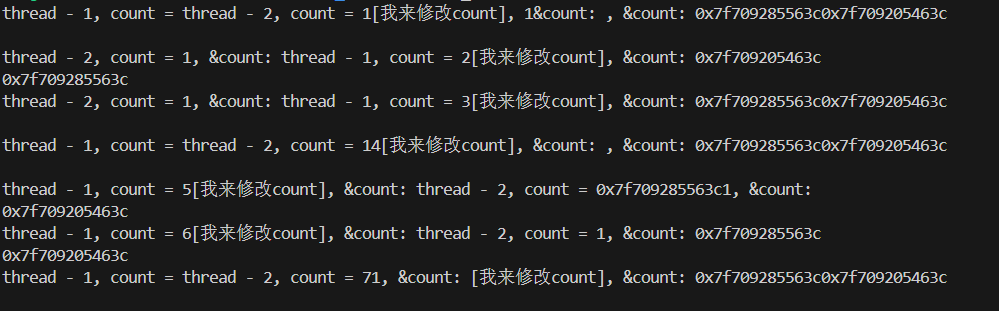
解析:
与上面不同的是,在添加__thread后,线程1修改count,线程2读取的count不再随着线程1 的修改而修改
解释:
添加__thread修饰:该count叫做局部存储
同一个变量名:指向不同的地址
在各自的线程管理块里面创建存储

pthread_setname_np:设置线程的名字。
pthread_getname_np:用于获取线程的名称。
cpp
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_setname_np(pthread_t thread, const char *name);
参数
pthread_t thread:要设置名称的线程 ID。如果设置为 pthread_self(),则表示当前线程。
const char *name:要设置的线程名称。通常是一个简短的字符串,长度通常不超过 16 个字符(包括终止符 \0)。
返回值
成功时返回 0。
失败时返回错误码(如 EINVAL 表示无效参数,EAGAIN 表示名称过长等)。
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_getname_np(pthread_t thread, char *name, size_t len);
参数
pthread_t thread:要获取名称的线程 ID。如果设置为 pthread_self(),则表示当前线程。
char *name:用于存储线程名称的缓冲区。
size_t len:缓冲区的大小。
返回值
成功时返回 0。
失败时返回错误码(如 EINVAL 表示无效参数,ERANGE 表示缓冲区太小等)。用2.thread进行修改
cpp
#ifndef _THREAD_H_
#define _THREAD_H_
//一个头文件保护机制,防止头文件被重复包含
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <functional>
namespace ThreadModlue{
static uint32_t number = 1;
class Thread{
using func_t = std::function<void()>;// 添加模版的前身
private:
void Enabledetach(){
std::cout<<"线程被分离了"<<std::endl;
_isdetach = true;
}
void Enablerunning(){
std::cout<<"线程正在运行"<<std::endl;
_isrunning = true;
}
static void* Routine(void*args){//static,没有默认指针,需要在线程创建的时候,通过args传回this指针
Thread* self = static_cast<Thread*>(args);//强转成Thread*类型
self->Enablerunning();
if(self->_isdetach){
self->Enabledetach();
}
pthread_setname_np(self->_tid, self->_name.c_str());
self->_func();//调用函数要加上()括号才可以调用
return nullptr;
}
public:
Thread(func_t func)
:_tid(0),
_isdetach(false),
_isrunning(false),
_res(nullptr),
_func(func)
{
_name = "thread - " + std::to_string(number++);
}
void Detach(){
if(_isdetach)
return;
if(_isrunning){
pthread_detach(_tid);
std::cout<<"线程分离成功"<<std::endl;
Enabledetach();
}
}
bool Start(){
if(_isrunning)
return false;//线程正在运行,不可再次启动
int n = pthread_create(&_tid,nullptr,Routine,this);
if( n != 0 ){
std::cerr<<"创建线程错误"<<strerror(n)<<std::endl;
return false;
}else{
std::cout<<"线程创建成功:"<<_name<<std::endl;
return true;
}
}
bool Stop(){
if(_isrunning){
int n = pthread_cancel(_tid);
if(n != 0){
std::cerr<<"线程停止错误:"<<strerror(n)<<std::endl;
return false;
}
else{
_isrunning = false;
std::cout<<"线程停止:"<<_name<<std::endl;
return true;
}
}
}
void Join(){
if(_isdetach){
std::cout<<"已经被分离的线程无法join"<<std::endl;
return;
}
int n = pthread_join(_tid,&_res);
if(n != 0){
std::cerr<<"线程join错误:"<<strerror(n)<<std::endl;
}else{
std::cout << "线程join成功" << std::endl;
}
}
private:
pthread_t _tid;
bool _isdetach;
bool _isrunning;
std::string _name;
void* _res;
func_t _func;
};
}
#endif
cpp
#include "Thread.hpp"
#include <unistd.h>
#include <vector>
using namespace ThreadModlue;
int main(){
// Thread t([](){
// while(true)
// {
// std::cout << "我是一个新线程: "<< std::endl; // 我的线程的名字是什么呀?debug
// sleep(1);
// }
// });
// t.Start();
// t.Detach();
// sleep(2);
// t.Stop();
// sleep(2);
// t.Join();
// return 0;
std::vector<Thread> threads;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
threads.emplace_back([]()
{
while(true)
{
char name[128];
pthread_getname_np(pthread_self(), name, sizeof(name));
std::cout << "我是一个新线程: " << name << std::endl; // 我的线程的名字是什么呀?debug
sleep(1);
} });
}
for (auto &thread : threads)
{
thread.Start();
}
for (auto &thread : threads)
{
thread.Join();
}
}同步和互斥
5.mutex代码,加锁和解锁,见一下
cpp// 操作共享变量会有问题的售票系统代码 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <pthread.h> int ticket = 1000; pthread_mutex_t lock = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER; void *route(void *arg) { char *id = (char *)arg; while (1) { pthread_mutex_lock(&lock); if (ticket > 0) // 1. 判断 { usleep(1000); // 模拟抢票花的时间 printf("%s sells ticket:%d\n", id, ticket); // 2. 抢到了票 ticket--; // 3. 票数-- pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock); } else { pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock); break; } } return nullptr; } int main(void) { pthread_t t1, t2, t3, t4; pthread_create(&t1, NULL, route, (void *)"thread 1"); pthread_create(&t2, NULL, route, (void *)"thread 2"); pthread_create(&t3, NULL, route, (void *)"thread 3"); pthread_create(&t4, NULL, route, (void *)"thread 4"); pthread_join(t1, NULL); pthread_join(t2, NULL); pthread_join(t3, NULL); pthread_join(t4, NULL); }
下一篇:线程互斥:



