目录
[P4779 【模板】单源最短路径(标准版)(洛谷)](#P4779 【模板】单源最短路径(标准版)(洛谷))
[743. 网络延迟时间(力扣)](#743. 网络延迟时间(力扣))
[1976. 到达目的地的方案数](#1976. 到达目的地的方案数)
[P1144 最短路计数(洛谷)](#P1144 最短路计数(洛谷))
[P1462 通往奥格瑞玛的道路](#P1462 通往奥格瑞玛的道路)
[2642. 设计可以求最短路径的图类](#2642. 设计可以求最短路径的图类)
[778. 水位上升的泳池中游泳](#778. 水位上升的泳池中游泳)
[787. K 站中转内最便宜的航班](#787. K 站中转内最便宜的航班)
dijkstra算法的运用
先说我对dijkstra的理解吧,然后看完这些东西,再写题,我的第一道题是模版题,可以配合看一下
1,dijkstra的构成,首先是图,链式前向星(邻接表,邻接矩阵)这仨都行哈,节点数量大的话就用链式前向星,邻接表比较方便(我不太用邻接矩阵的),其次是小根堆,他用来保证我们每次找到的节点都离源节点最近的节点。然后是distance_数组用来记录源节点到每个节点的最短距离,初始化为一个很大的值就好(我都设为INT_MAX),没了就这几个。
2,代码,就先建图嘛,然后对上面说的这些结构该初始化的初始化,,小根堆里面先push一下代价0和源节点,因为自己到自己代价为0,distance_数组进行初始化为INT_MAX,接下来就是核心代码,核心代码的解析在下面模版题上有详细注释
P4779 【模板】单源最短路径(标准版)(洛谷)
题目背景
2018 年 7 月 19 日,某位同学在 NOI Day 1 T1 归程 一题里非常熟练地使用了一个广为人知的算法求最短路。
然后呢?
100→60;
Ag→Cu;
最终,他因此没能与理想的大学达成契约。
小 F 衷心祝愿大家不再重蹈覆辙。
题目描述
给定一个 n 个点,m 条有向边的带非负权图,请你计算从 s 出发,到每个点的距离。
数据保证你能从 s 出发到任意点。
输入格式
第一行为三个正整数 n,m,s。 第二行起 m 行,每行三个非负整数 ui,vi,wi,表示从 ui 到 vi 有一条权值为 wi 的有向边。
输出格式
输出一行 n 个空格分隔的非负整数,表示 s 到每个点的距离。
输入输出样例
输入 #1复制
4 6 1 1 2 2 2 3 2 2 4 1 1 3 5 3 4 3 1 4 4输出 #1复制
0 2 4 3说明/提示
样例解释请参考 数据随机的模板题。
1≤n≤105;
1≤m≤2×105;
s=1;
1≤ui,vi≤n;
0≤wi≤109,
0≤∑wi≤109。
本题数据可能会持续更新,但不会重测,望周知。
思路
这题就是个模版提,思路就是上面讲算法解析,配合着看理解就行,因为这题数据给的是1e5我就用链式前向星了
cpp
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n,m,s;
const int N=1e5+10;
struct edge{
int to;
int w;
int next;
}graph[N*2];
int cnt,head[N];
void add_edge(int u,int v,int w){
cnt++;
graph[cnt].to=v;
graph[cnt].w=w;
graph[cnt].next=head[u];
head[u]=cnt;
}
int main(){
cin>>n>>m>>s;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
int u,v,w;
cin>>u>>v>>w;
add_edge(u,v,w);
}
vector<int>distance_(N,INT_MAX);
distance_[s]=0;
//算出s到每个点的最短距离
priority_queue<pair<int,int>,vector<pair<int,int>>,greater<pair<int,int>>> pq;
pq.push({0,s});
while(!pq.empty()){
//先取出来源节点到达当前节点的代价dist,和当前是哪个节点u
int dist=pq.top().first;
int u=pq.top().second;
//记得弹出去,要不然就进行不下去
pq.pop();
//如果到达当前节点的代价比你存的到达当前节点的最小代价大,就continue,这个点就不走了
if(dist>distance_[u]) continue;
//开始遍历图,也就是遍历u,看看u连接的节点把他们扔进堆里面继续进行操作
for(int i=head[u];i;i=graph[i].next){
int to=graph[i].to;
int w=graph[i].w;
//如果之前存的到达to的距离比现在发现的代价大就 更新
if(distance_[to]>dist+w){
distance_[to]=dist+w;
pq.push({distance_[to],to});
}
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cout<<distance_[i]<<' ';
}
}743. 网络延迟时间(力扣)
743. 网络延迟时间 - 力扣(LeetCode)![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/network-delay-time/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/network-delay-time/description/
有
n个网络节点,标记为1到n。给你一个列表
times,表示信号经过 有向 边的传递时间。times[i] = (ui, vi, wi),其中ui是源节点,vi是目标节点,wi是一个信号从源节点传递到目标节点的时间。现在,从某个节点
K发出一个信号。需要多久才能使所有节点都收到信号?如果不能使所有节点收到信号,返回-1。示例 1:
输入:times = [[2,1,1],[2,3,1],[3,4,1]], n = 4, k = 2 输出:2示例 2:
输入:times = [[1,2,1]], n = 2, k = 1 输出:1示例 3:
输入:times = [[1,2,1]], n = 2, k = 2 输出:-1提示:
1 <= k <= n <= 100
1 <= times.length <= 6000
times[i].length == 3
1 <= ui, vi <= n
ui != vi
0 <= wi <= 100所有
(ui, vi)对都 互不相同(即,不含重复边)
思路
其实和上面那个几乎一样,这个就是让你算一下从k节点开始遍历完,所消耗的全部代价,那我们只需要在distance里找出最大值就好,因为distance里存的是源节点到所有节点的最近距离,所以里面当然有源节点所到达的最后一个节点,这个节点李村的就是从源节点走完所有节点的代价
cpp
class Solution {
public:
int networkDelayTime(vector<vector<int>>& times, int n, int k) {
//先建图
vector<vector<pair<int,int>>> graph(n+1);
for(auto &edge:times){
graph[edge[0]].emplace_back(edge[1],edge[2]);
}
//distance,visited数组
vector<int>distance(n+1,INT_MAX);
vector<bool>visited(n+1);
//再建个小根堆
priority_queue<pair<int,int>,vector<pair<int,int>>,greater<pair<int,int>>> hp;
hp.emplace(0,k);//k节点到自己距离为0;
distance[k]=0;
while(!hp.empty()){
auto [dist,u]=hp.top();
hp.pop();
if(visited[u])
continue;
visited[u]=true;
for(auto& [v,w]:graph[u]){
if(!visited[v]&&distance[u]+w<distance[v]){
distance[v]=w+distance[u];
hp.emplace(distance[v],v);
}
}
}
//走完也就是把每个节点都弹出过了,也就脱离循环了
int max1=*max_element(distance.begin()+1,distance.end());
return max1==INT_MAX?-1:max1;
}
};1514.概率最大路径(力扣)
1514. 概率最大的路径 - 力扣(LeetCode)![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-with-maximum-probability/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-with-maximum-probability/
有
n个网络节点,标记为1到n。给你一个列表
times,表示信号经过 有向 边的传递时间。times[i] = (ui, vi, wi),其中ui是源节点,vi是目标节点,wi是一个信号从源节点传递到目标节点的时间。现在,从某个节点
K发出一个信号。需要多久才能使所有节点都收到信号?如果不能使所有节点收到信号,返回-1。示例 1:
输入:times = [[2,1,1],[2,3,1],[3,4,1]], n = 4, k = 2 输出:2示例 2:
输入:times = [[1,2,1]], n = 2, k = 1 输出:1示例 3:
输入:times = [[1,2,1]], n = 2, k = 2 输出:-1提示:
1 <= k <= n <= 1001 <= times.length <= 6000times[i].length == 31 <= ui, vi <= nui != vi0 <= wi <= 100- 所有
(ui, vi)对都 互不相同(即,不含重复边)
思路
这个就是小根堆换成大根堆,这样就能求出最大概率,然后因为是概率存的时候换成double
别的都跟上面一样
cpp
class Solution {
public:
double maxProbability(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<double>& succProb, int start_node, int end_node) {
vector<vector<pair<int,double>>>graph(n);
vector<double>distance_(n,0);
for (int i = 0; i < edges.size(); i++) {
auto& e = edges[i];
graph[e[0]].emplace_back(e[1],succProb[i]);
graph[e[1]].emplace_back(e[0],succProb[i]);
}
priority_queue<pair<double,int>>pq;
pq.push({1,start_node});//自己到自己的概率为1
distance_[start_node]=1;
while(!pq.empty()){
auto [dist,u]=pq.top();
pq.pop();
if(dist<distance_[u]) continue;
for(auto &[to,w]:graph[u]){
if(distance_[to]<w*dist){
distance_[to]=w*dist;
pq.push({distance_[to],to});
}
}
}
return distance_[end_node];
}
};1631.最小体力消耗路径
1514. 概率最大的路径 - 力扣(LeetCode)![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-with-maximum-probability/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-with-maximum-probability/
你准备参加一场远足活动。给你一个二维
rows x columns的地图heights,其中heights[row][col]表示格子(row, col)的高度。一开始你在最左上角的格子(0, 0),且你希望去最右下角的格子(rows-1, columns-1)(注意下标从 0 开始编号)。你每次可以往 上 ,下 ,左 ,右 四个方向之一移动,你想要找到耗费 体力 最小的一条路径。一条路径耗费的 体力值 是路径上相邻格子之间 高度差绝对值 的 最大值 决定的。
请你返回从左上角走到右下角的最小体力消耗值 。
示例 1:
输入:heights = [[1,2,2],[3,8,2],[5,3,5]] 输出:2 解释:路径 [1,3,5,3,5] 连续格子的差值绝对值最大为 2 。 这条路径比路径 [1,2,2,2,5] 更优,因为另一条路径差值最大值为 3 。示例 2:
输入:heights = [[1,2,3],[3,8,4],[5,3,5]] 输出:1 解释:路径 [1,2,3,4,5] 的相邻格子差值绝对值最大为 1 ,比路径 [1,3,5,3,5] 更优。示例 3:
输入:heights = [[1,2,1,1,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,1,1,2,1]] 输出:0 解释:上图所示路径不需要消耗任何体力。提示:
rows == heights.lengthcolumns == heights[i].length1 <= rows, columns <= 1001 <= heights[i][j] <= 106
思路
看题上要求的是啥,他说的最小体力消耗就是,两个相邻格子之间的差值,那我们只要把这个差值作为代价存进小根堆里面就可以用dijkstra算法进行求解了,这里我们还要自己给小根堆构建一个排序,利用结构体,其他的看代码就能理解了
if(c>distance_[a][b]) continue;这里其实我们可以用个visited数组代替,上面的题一样,因为我们利用堆每次走的都是最有效的路,鄋走过的就不用走了
cpp
class Solution {
public:
struct Node{
int x,y,cost;
Node(int x_,int y_,int cost_) : x(x_),y(y_),cost(cost_){}
bool operator>(const Node& other) const{
return cost>other.cost;
}
};
int mv[5]={-1,0,1,0,-1};
int minimumEffortPath(vector<vector<int>>& heights) {
int m=heights.size();
int n=heights[0].size();
//构建小根堆
priority_queue<Node,vector<Node>,greater<Node>>pq;
pq.push({0,0,0});//自己到自己的差值是0
vector<vector<int>>distance_(m+1,vector<int>(n+1,INT_MAX));
distance_[0][0]=0;
while(!pq.empty()){
auto[a,b,c]=pq.top();
pq.pop();
if(a==m-1&&b==n-1) return c;
if(c>distance_[a][b]) continue;
for(int i=0,nx,ny;i<4;i++){
nx=a+mv[i];
ny=b+mv[i+1];
if(nx>=0&&ny>=0&&nx<m&&ny<n){
int nc=max(c,abs(heights[nx][ny]-heights[a][b]));
if(nc<distance_[nx][ny]){
distance_[nx][ny]=nc;
pq.push({nx,ny,nc});
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
};1976. 到达目的地的方案数
你在一个城市里,城市由
n个路口组成,路口编号为0到n - 1,某些路口之间有 双向 道路。输入保证你可以从任意路口出发到达其他任意路口,且任意两个路口之间最多有一条路。给你一个整数
n和二维整数数组roads,其中roads[i] = [ui, vi, timei]表示在路口ui和vi之间有一条需要花费timei时间才能通过的道路。你想知道花费 最少时间 从路口0出发到达路口n - 1的方案数。请返回花费 最少时间 到达目的地的 路径数目 。由于答案可能很大,将结果对
109 + 7取余 后返回。示例 1:
输入:n = 7, roads = [[0,6,7],[0,1,2],[1,2,3],[1,3,3],[6,3,3],[3,5,1],[6,5,1],[2,5,1],[0,4,5],[4,6,2]] 输出:4 解释:从路口 0 出发到路口 6 花费的最少时间是 7 分钟。 四条花费 7 分钟的路径分别为: - 0 ➝ 6 - 0 ➝ 4 ➝ 6 - 0 ➝ 1 ➝ 2 ➝ 5 ➝ 6 - 0 ➝ 1 ➝ 3 ➝ 5 ➝ 6示例 2:
输入:n = 2, roads = [[1,0,10]] 输出:1 解释:只有一条从路口 0 到路口 1 的路,花费 10 分钟。提示:
1 <= n <= 200n - 1 <= roads.length <= n * (n - 1) / 2roads[i].length == 30 <= ui, vi <= n - 11 <= timei <= 109ui != vi- 任意两个路口之间至多有一条路。
- 从任意路口出发,你能够到达其他任意路口。
思路
这个就是增加一个cnt数组来记录源节点到每个节点最短路的路径数,其他的都一样
还有就是这个数要用long long 最开始我就是没弄这个一直过不完,后来把所有int都换了
更新规则:
发现更短路径 :当找到一条比当前记录更短的路径时,需要重置 cnt[i]。
路径长度相同 :当遇到另一条路径长度与当前记录相同时,需要累加 cnt[i]。
cpp
class Solution {
public:
int countPaths(int n, vector<vector<int>>& roads) {
vector<vector<pair<long long,long long>>> graph(n);
for(auto &edge:roads){
graph[edge[0]].push_back({edge[1],edge[2]});
graph[edge[1]].push_back({edge[0],edge[2]});
}
vector<long long>distance_(n,LLONG_MAX);
priority_queue<pair<long long,long long>,vector<pair<long long,long long>>,greater<pair<long long,long long>>>pq;
pq.push({0,0});
distance_[0]=0;
vector<int>cnt(n,0);//记录从起点到每个节点的最短路的个数
cnt[0]=1;
while(!pq.empty()){
auto [w,u]=pq.top();
pq.pop();
if(w>distance_[u]) continue;
for(auto [v,dist]:graph[u]){
if(dist+w<distance_[v]){
distance_[v]=dist+w;
cnt[v]=cnt[u];//如果有更短得多路就取代
pq.push({distance_[v],v});
}
else if(dist+w==distance_[v]){
(cnt[v]+=cnt[u])%=1000000000+7;
}
}
}
return cnt[n-1];
}
};P1144 最短路计数(洛谷)
P1144 最短路计数 - 洛谷![]() https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P1144
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P1144
题目描述
给出一个 N 个顶点 M 条边的无向无权图,顶点编号为 1∼N。问从顶点 1 开始,到其他每个点的最短路有几条。
输入格式
第一行包含 2 个正整数 N,M,为图的顶点数与边数。
接下来 M 行,每行 2 个正整数 x,y,表示有一条连接顶点 x 和顶点 y 的边,请注意可能有自环与重边。
输出格式
共 N 行,每行一个非负整数,第 i 行输出从顶点 1 到顶点 i 有多少条不同的最短路,由于答案有可能会很大,你只需要输出 ansmod100003 后的结果即可。如果无法到达顶点 i 则输出 0。
输入输出样例
输入 #1复制
5 7 1 2 1 3 2 4 3 4 2 3 4 5 4 5输出 #1复制
1 1 1 2 4说明/提示
1 到 5 的最短路有 4 条,分别为 2 条 1→2→4→5 和 2 条 1→3→4→5(由于 4→5 的边有 2 条)。
对于 20% 的数据,1≤N≤100;
对于 60% 的数据,1≤N≤103;
对于 100% 的数据,1≤N≤106,1≤M≤2×106。
思路
这题和上一题没啥区别哈,就是这个无权而已,那就是权重改为1就行,还有就是这个我不知道为啥卡我样例,给我TLE了,最后还是靠加速输入输出才过的,我感觉我没啥能优化的地方了,链式前向星我也用了,,奇怪。
cpp
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n,m;
#define int long long
const int N=2e6+10;
struct edge{
int to;
int next;
}graph[N*2];
int cnt,head[N];
void add_edge(int u,int v){
cnt++;
graph[cnt].to=v;
graph[cnt].next=head[u];
head[u]=cnt;
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
int u,v;
cin>>u>>v;
if (u == v) continue;
add_edge(u,v);
add_edge(v,u);
}
vector<int>distance_(n+1,LLONG_MAX);
distance_[1]=0;
priority_queue<pair<int,int>,vector<pair<int,int>>,greater<pair<int,int>>> pq;
pq.push({0,1});
vector<int>cnt(n+1,0);
cnt[1]=1;
while(!pq.empty()){
int dist=pq.top().first;
int u=pq.top().second;
pq.pop();
if(dist>distance_[u]) continue;
for(int i=head[u];i;i=graph[i].next){
int to=graph[i].to;
if(distance_[to]>dist+1){
distance_[to]=dist+1;
pq.push({distance_[to],to});
cnt[to]=cnt[u];
}
else if(distance_[to]==dist+1){
(cnt[to]+=cnt[u])%=100003 ;
}
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cout<<cnt[i]<<endl;
}
}P1462 通往奥格瑞玛的道路
P1462 通往奥格瑞玛的道路 - 洛谷![]() https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P1462
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P1462
题目背景
在艾泽拉斯大陆上有一位名叫歪嘴哦的神奇术士,他是部落的中坚力量。
有一天他醒来后发现自己居然到了联盟的主城暴风城。
在被众多联盟的士兵攻击后,他决定逃回自己的家乡奥格瑞玛。
题目描述
在艾泽拉斯,有 n 个城市。编号为 1,2,3,...,n。
城市之间有 m 条双向的公路,连接着两个城市,从某个城市到另一个城市,会遭到联盟的攻击,进而损失一定的血量。
每次经过一个城市,都会被收取一定的过路费(包括起点和终点)。路上并没有收费站。
假设 1 为暴风城,n 为奥格瑞玛,而他的血量最多为 b,出发时他的血量是满的。如果他的血量降低至负数,则他就无法到达奥格瑞玛。
歪嘴哦不希望花很多钱,他想知道,在所有可以到达奥格瑞玛的道路中,对于每条道路所经过的城市收费的最大值,最小值为多少。
输入格式
第一行 3 个正整数,n,m,b。分别表示有 n 个城市,m 条公路,歪嘴哦的血量为 b。
接下来有 n 行,每行 1 个正整数,fi。表示经过城市 i,需要交费 fi 元。
再接下来有 m 行,每行 3 个正整数,ai,bi,ci(1≤ai,bi≤n)。表示城市 ai 和城市 bi 之间有一条公路,如果从城市 ai 到城市 bi,或者从城市 bi 到城市 ai,会损失 ci 的血量。
输出格式
仅一个整数,表示歪嘴哦交费最多的一次的最小值。
如果他无法到达奥格瑞玛,输出
AFK。输入输出样例
输入 #1复制
4 4 8 8 5 6 10 2 1 2 2 4 1 1 3 4 3 4 3输出 #1复制
10说明/提示
对于 60% 的数据,满足 n≤200,m≤104,b≤200;
对于 100% 的数据,满足 1≤n≤104,1≤m≤5×104,1≤b≤109;
对于 100% 的数据,满足 1≤ci≤109,0≤fi≤109,可能有两条边连接着相同的城市。
思路
这道题可以看出,血量是边权,那激素我们dijkstra算法里的堆里面的东西,然后又给了另一个变量那就是收费,我们可以想到二分(我没想到,我依旧是笨蛋),里收费这个变量作为二分的东西,因为要我们求收费最小是多少嘛,那我们就二分,一直找到二分后的值,里面当然有个check函数,来判断二分的方向,check里的核心代码就就是dijkstra,利用小根堆然后每次找掉血量最少的路走,然后看走完后血量是不是小于等于b,是的话说明这个二分的答案正确,我们就继续缩减范围,就这样一直重复就好了,当然也可以像题解里面用大根堆,看最后血量有没有从b减到0
cpp
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=1e4+10;
const int M=5e4+10;
struct edge{
int to;
int next;
int w;
}graph[M*2];
int cnt,head[N],f[N];
void add_edge(int u,int v,int w){
cnt++;
graph[cnt].w=w;
graph[cnt].to=v;
graph[cnt].next=head[u];
head[u]=cnt;
}
int n,m,b;
bool check(int x){
vector<int>distance_(N,-1);
//如果开头和结尾已经超过了二分出来的血量就代表这个收费不是正解
if(f[1]>x||f[n]>x) return false;
distance_[1]=b;
priority_queue<pair<int,int>>pq;//构建大根堆 ({剩余血量,节点})
pq.push({b,1});
while(!pq.empty()){
int dist=pq.top().first;
int u=pq.top().second;
pq.pop();
if(dist<distance_[u]) continue;
for(int i=head[u];i;i=graph[i].next){
int to=graph[i].to;
int w=graph[i].w;
if(f[to]>x) continue;
if(distance_[to]<dist-w&&dist-w>=0){
//如果要走的节点to里存的最大血量可以更新
distance_[to]=dist-w;
pq.push({distance_[to],to});
}
}
}
return distance_[n]!=-1;//如果不等于-1说明二分出来的答案可以
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cin>>n>>m>>b;
int l=1e9+10,r=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>f[i];
l=min(l,f[i]);
r=max(r,f[i]);
}
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
int u,v,w;
cin>>u>>v>>w;
if(u==v) continue;
add_edge(u,v,w);
add_edge(v,u,w);
}
int ans=-1;
while(l<=r){
int mid=(l+r)/2;
if(check(mid)){
ans=mid;
r=mid-1;
}
else{
l=mid+1;
}
}
if(ans==-1) cout<<"AFK";
else{
cout<<ans;
}
} 2642. 设计可以求最短路径的图类
给你一个有
n个节点的 有向带权 图,节点编号为0到n - 1。图中的初始边用数组edges表示,其中edges[i] = [fromi, toi, edgeCosti]表示从fromi到toi有一条代价为edgeCosti的边。请你实现一个
Graph类:
Graph(int n, int[][] edges)初始化图有n个节点,并输入初始边。addEdge(int[] edge)向边集中添加一条边,其中edge = [from, to, edgeCost]。数据保证添加这条边之前对应的两个节点之间没有有向边。int shortestPath(int node1, int node2)返回从节点node1到node2的路径最小 代价。如果路径不存在,返回-1。一条路径的代价是路径中所有边代价之和。示例 1:
输入: ["Graph", "shortestPath", "shortestPath", "addEdge", "shortestPath"] [[4, [[0, 2, 5], [0, 1, 2], [1, 2, 1], [3, 0, 3]]], [3, 2], [0, 3], [[1, 3, 4]], [0, 3]] 输出: [null, 6, -1, null, 6] 解释: Graph g = new Graph(4, [[0, 2, 5], [0, 1, 2], [1, 2, 1], [3, 0, 3]]); g.shortestPath(3, 2); // 返回 6 。从 3 到 2 的最短路径如第一幅图所示:3 -> 0 -> 1 -> 2 ,总代价为 3 + 2 + 1 = 6 。 g.shortestPath(0, 3); // 返回 -1 。没有从 0 到 3 的路径。 g.addEdge([1, 3, 4]); // 添加一条节点 1 到节点 3 的边,得到第二幅图。 g.shortestPath(0, 3); // 返回 6 。从 0 到 3 的最短路径为 0 -> 1 -> 3 ,总代价为 2 + 4 = 6 。提示:
1 <= n <= 1000 <= edges.length <= n * (n - 1)edges[i].length == edge.length == 30 <= fromi, toi, from, to, node1, node2 <= n - 11 <= edgeCosti, edgeCost <= 106- 图中任何时候都不会有重边和自环。
- 调用
addEdge至多100次。- 调用
shortestPath至多100次。
思路
其实没啥思路哈,和上面的都一样,也就是个模版,当练手用得了
cpp
class Graph {
public:
using pii=pair<int,int>;
vector<vector<pii>>graph;
Graph(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) :graph(n){
for(auto e:edges){
graph[e[0]].push_back({e[1],e[2]});
}
}
void addEdge(vector<int> edge) {
graph[edge[0]].push_back({edge[1],edge[2]});
}
int shortestPath(int node1, int node2) {
vector<int>distance_(graph.size()+1,INT_MAX);
priority_queue<pii,vector<pii>,greater<pii>>pq;
distance_[node1]=0;
pq.push({0,node1});
while(!pq.empty()){
auto [dist,u]=pq.top();
pq.pop();
if(u==node2) return dist;
if(dist>distance_[u]) continue;
for(auto [v,w]:graph[u]){
if(w+dist<distance_[v]){
distance_[v]=w+dist;
pq.push({distance_[v],v});
}
}
}
return -1;
}
};
/**
* Your Graph object will be instantiated and called as such:
* Graph* obj = new Graph(n, edges);
* obj->addEdge(edge);
* int param_2 = obj->shortestPath(node1,node2);
*/778. 水位上升的泳池中游泳
在一个
n x n的整数矩阵grid中,每一个方格的值grid[i][j]表示位置(i, j)的平台高度。当开始下雨时,在时间为
t时,水池中的水位为t。你可以从一个平台游向四周相邻的任意一个平台,但是前提是此时水位必须同时淹没这两个平台。假定你可以瞬间移动无限距离,也就是默认在方格内部游动是不耗时的。当然,在你游泳的时候你必须待在坐标方格里面。你从坐标方格的左上平台
(0,0)出发。返回 你到达坐标方格的右下平台(n-1, n-1)所需的最少时间 。示例 1:
输入: grid = [[0,2],[1,3]] 输出: 3 解释: 时间为0时,你位于坐标方格的位置为
(0, 0)。
此时你不能游向任意方向,因为四个相邻方向平台的高度都大于当前时间为 0 时的水位。 等时间到达 3 时,你才可以游向平台 (1, 1). 因为此时的水位是 3,坐标方格中的平台没有比水位 3 更高的,所以你可以游向坐标方格中的任意位置示例 2:
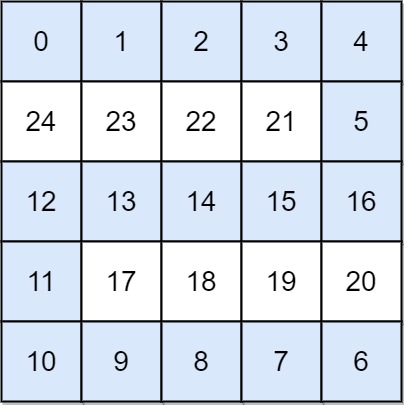
输入: grid = [[0,1,2,3,4],[24,23,22,21,5],[12,13,14,15,16],[11,17,18,19,20],[10,9,8,7,6]] 输出: 16 解释: 最终的路线用加粗进行了标记。 我们必须等到时间为 16,此时才能保证平台 (0, 0) 和 (4, 4) 是连通的提示:
n == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= n <= 500 <= grid[i][j] < n2grid[i][j]中每个值 均无重复
思路
其实和上面那个最小体力消耗的题差不多,我们依旧是按照步骤来就行,不同的是存进去的堆的值是不一样的,其他偶数一样,看代码其实就好了
cpp
class Solution {
public:
struct Node{
int x;
int y;
int cost;
Node(int x_,int y_,int cost_):x(x_),y(y_),cost(cost_){}
bool operator>(const Node& other) const{
return cost>other.cost;
}
};
int move[5]={-1,0,1,0,-1};
int swimInWater(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int m=grid.size();
int n=grid[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> dis(m,vector<int>(n,INT_MAX));
priority_queue<Node,vector<Node>,greater<Node>> hp;
hp.emplace(0,0,grid[0][0]);
dis[0][0]=grid[0][0];
while(!hp.empty()){
auto[x,y,dist]=hp.top();
hp.pop();
if(dist>dis[x][y])
continue;
if(x==m-1&&y==n-1){
return dist;
}
for(int i=0,nx,ny;i<4;i++){
nx=x+move[i];
ny=y+move[i+1];
if(nx>=0&&ny>=0&&nx<m&&ny<n){
int nc=max(dist,grid[nx][ny]);
if(nc<dis[nx][ny]){
dis[nx][ny]=nc;
hp.emplace(nx,ny,dis[nx][ny]);
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
};787. K 站中转内最便宜的航班
787. K 站中转内最便宜的航班![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/cheapest-flights-within-k-stops/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/cheapest-flights-within-k-stops/
有
n个城市通过一些航班连接。给你一个数组flights,其中flights[i] = [fromi, toi, pricei],表示该航班都从城市fromi开始,以价格pricei抵达toi。现在给定所有的城市和航班,以及出发城市
src和目的地dst,你的任务是找到出一条最多经过k站中转的路线,使得从src到dst的 价格最便宜 ,并返回该价格。 如果不存在这样的路线,则输出-1。示例 1:
输入: n = 4, flights = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[2,0,100],[1,3,600],[2,3,200]], src = 0, dst = 3, k = 1 输出: 700 解释: 城市航班图如上 从城市 0 到城市 3 经过最多 1 站的最佳路径用红色标记,费用为 100 + 600 = 700。 请注意,通过城市 [0, 1, 2, 3] 的路径更便宜,但无效,因为它经过了 2 站。示例 2:
输入: n = 3, edges = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[0,2,500]], src = 0, dst = 2, k = 1 输出: 200 解释: 城市航班图如上 从城市 0 到城市 2 经过最多 1 站的最佳路径标记为红色,费用为 100 + 100 = 200。示例 3:
输入:n = 3, flights = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[0,2,500]], src = 0, dst = 2, k = 0 输出:500 解释: 城市航班图如上 从城市 0 到城市 2 不经过站点的最佳路径标记为红色,费用为 500。提示:
1 <= n <= 1000 <= flights.length <= (n * (n - 1) / 2)flights[i].length == 30 <= fromi, toi < nfromi != toi1 <= pricei <= 104- 航班没有重复,且不存在自环
0 <= src, dst, k < nsrc != dst
思路
整体就是个dijkstra,但是这次相当于分层图最短路了,用bfs当然也是可以的,分层图就是现在又有个另一个限制,我们要保证在k次转飞机路线内才行,所以我们就把distance数组变成二维记录走到每个节点时已经转运了几次,还有堆里面也加上这玩意,就行了,还是很有意思的哈哈
cpp
class Solution {
public:
using tiii=tuple<int, int, int>;
int findCheapestPrice(int n, vector<vector<int>>& flights, int src, int dst, int k) {
//建图
vector<vector<pair<int,int>>> graph(n);
for(auto &edge:flights){
graph[edge[0]].push_back({edge[1],edge[2]});
}
//建堆
priority_queue<tiii,vector<tiii>,greater<>>pq;
//distance_表
vector<vector<int>> distance_(n,vector<int>(k+2,INT_MAX));
//初始化
distance_[src][k+1]=0;
pq.push({0,src,k+1});
int ans=0;
while(!pq.empty()){
auto [dist,u,remain]=pq.top();
pq.pop();
if(u==dst) return dist;
if(remain==0) continue;
if(dist>distance_[u][remain]) continue;
for(auto [v,w]:graph[u]){
int new_remain=remain-1;
if(dist+w<distance_[v][new_remain]){
distance_[v][new_remain]=dist+w;
pq.push({distance_[v][new_remain],v,new_remain});
}
}
}
return -1;
}
};结束咯,之后还会接着写的,记得来看哈,有啥错误可以告诉我,我去改