任务
1、采用 Kmeans 算法实现 2D 数据自动聚类,预测 V1=80,V2=60 数据类别;
2、计算预测准确率,完成结果矫正
3、采用 KNN、Meanshift 算法,重复步骤 1-2
代码工具:jupyter notebook
视频资料
无监督学习:15.17 无监督学习_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
Kmeans-KNN-Meanshift:16.18 Kmeans-KNN-Meanshift_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
Kmean 实战(1):17.20 Kmeans实战(1)_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
Kmean 实战(2):18.21 Kmeans实战(2)_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
KNN-meanshift:19.22 KNN-Meanshift_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
数据准备
数据集:kmeans_knn_meanshift_data.csv
链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1i0IxtE6rBKHIb-2kbX1NkA 提取码: 8497
python
#load the data
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
data = pd.read_csv('kmeans_knn_meanshift_data.csv')
data.head()
python
#看一下 labels 里面有多少类别
pd.value_counts(y)
python
#数据可视化
%matplotlib inline
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
fig1 = plt.figure()
plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'], X.loc[:,'V2'])
plt.title("un-labled data")
plt.xlabel('V1')
plt.ylabel('V2')
plt.show()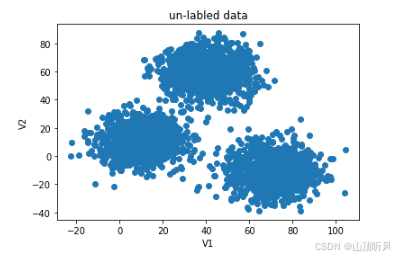
python
fig1 = plt.figure()
label0 = plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==0], X.loc[:,'V2'][y==0])
label1 = plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==1], X.loc[:,'V2'][y==1])
label2 = plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==2], X.loc[:,'V2'][y==2])
plt.title("labeled data")
plt.xlabel('V1')
plt.ylabel('V2')
plt.legend((label0, label1, label2),('label0','label1','label2'))
plt.show()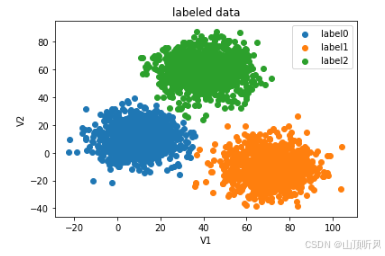
python
print(X.shape, y.shape) # (3000, 2) (3000,)Kmeans 算法(无监督)
创建模型并训练
python
# set the model
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
KM = KMeans(n_clusters = 3, random_state = 0)
KM.fit(X)
原始数据可视化
python
centers = KM.cluster_centers_ # 三个中心点
fig3 = plt.figure()
#画原图
label0 = plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==0], X.loc[:,'V2'][y==0])
label1 = plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==1], X.loc[:,'V2'][y==1])
label2 = plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==2], X.loc[:,'V2'][y==2])
plt.title("labeled data")
plt.xlabel('V1')
plt.ylabel('V2')
plt.legend((label0, label1, label2),('label0','label1','label2'))
#展示中心点
plt.scatter(centers[:,0], centers[:,1])
plt.show()
预测 V1=80,V2=60 数据类别
python
# test data :V1 = 80, V2 = 60
y_predict_test = KM.predict([[80,60]])
print(y_predict_test) # [1]
python
#predict based on training data
y_predict = KM.predict(X)
# 打印出预测数据的分布
print(pd.value_counts(y_predict), pd.value_counts(y))
#发现与原始数据分布好像不太一样
python
#看下准确率
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
accuracy = accuracy_score(y, y_predict)
print(accuracy) # 0.0023333333333333335, 可以看出准确率很低预测数据与原数据一起展示
python#数据画出来看看哪里的问题 fig4 = plt.subplot(121)# 一行两列,画第一列 #画预测图================================================== label0 = plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y_predict==0], X.loc[:,'V2'][y_predict==0]) label1 = plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y_predict==1], X.loc[:,'V2'][y_predict==1]) label2 = plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y_predict==2], X.loc[:,'V2'][y_predict==2]) plt.title("predicted data") plt.xlabel('V1') plt.ylabel('V2') plt.legend((label0, label1, label2),('label0','label1','label2')) #展示中心点 plt.scatter(centers[:,0], centers[:,1]) #画原图================================================== fig5 = plt.subplot(122) label0 = plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==0], X.loc[:,'V2'][y==0]) label1 = plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==1], X.loc[:,'V2'][y==1]) label2 = plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==2], X.loc[:,'V2'][y==2]) plt.title("labled data") plt.xlabel('V1') plt.ylabel('V2') plt.legend((label0, label1, label2),('label0','label1','label2')) #展示中心点 plt.scatter(centers[:,0], centers[:,1]) plt.show() # 从下图可以看到,类别是区分出来了,但是类别名称不对; # 这很正常,无监督式学习就是把类别区分出来至于取什么名称,那不一定 # 但是,如果已原数据的标签,可以将预结果的类别名称进行校正

类别校正
python
# correct the results
y_corrected = []
for i in y_predict:
if i == 0:
y_corrected.append(1)
elif i == 1:
y_corrected.append(2)
else:
y_corrected.append(0)
print(pd.value_counts(y_corrected), pd.value_counts(y))
python
# 看下校正后的准确率是多少
print(accuracy_score(y, y_corrected)) # 0.997
python
y_corrected = np.array(y_corrected)
print(type(y_corrected)) # <class 'numpy.ndarray'>校正后重新可视化
python
#画出校正后的图形,y_predict 换成 y_corrected
fig6 = plt.subplot(121)# 一行两列,画第一列
#画预测图==================================================
label0 = plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y_corrected==0], X.loc[:,'V2'][y_corrected==0])
label1 = plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y_corrected==1], X.loc[:,'V2'][y_corrected==1])
label2 = plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y_corrected==2], X.loc[:,'V2'][y_corrected==2])
plt.title("corrected data")
plt.xlabel('V1')
plt.ylabel('V2')
plt.legend((label0, label1, label2),('label0','label1','label2'))
#展示中心点
plt.scatter(centers[:,0], centers[:,1])
#画原图==================================================
fig7 = plt.subplot(122)
label0 = plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==0], X.loc[:,'V2'][y==0])
label1 = plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==1], X.loc[:,'V2'][y==1])
label2 = plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==2], X.loc[:,'V2'][y==2])
plt.title("labeled data")
plt.xlabel('V1')
plt.ylabel('V2')
plt.legend((label0, label1, label2),('label0','label1','label2'))
#展示中心点
plt.scatter(centers[:,0], centers[:,1])
plt.show() 
KNN 算法(有监督)
python
#3、采用 KNN、Meanshift 算法,重复步骤 1-2
X.head()
y.head()
创建模型并训练
python
#establish a KNN model(KNN 是 监督式)
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
KNN = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors = 3)
KNN.fit(X, y)
进行预测
#predict based on the test data V1=80, V2=60
y_predict_knn_test = KNN.predict([[80,60]])
y_predict_knn = KNN.predict(X) # 训练数据使用 KNN的预测结果
print(y_predict_knn_test) # 结果:[2]
print('knn accureacy:', accuracy_score(y, y_predict_knn)) #knn accureacy: 1.0, 全部正确
python
#打印出通过 KNN模型预测结果的分布,以及原来数据的分布
print(pd.value_counts(y_predict_knn), pd.value_counts(y)) # 可以看出完全一样
可视化
python
#画图 KNN
fig8 = plt.subplot(121)# 一行两列,画第一列
#画预测图==================================================
label0 = plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y_predict_knn==0], X.loc[:,'V2'][y_predict_knn==0])
label1 = plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y_predict_knn==1], X.loc[:,'V2'][y_predict_knn==1])
label2 = plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y_predict_knn==2], X.loc[:,'V2'][y_predict_knn==2])
plt.title("KNN results")
plt.xlabel('V1')
plt.ylabel('V2')
plt.legend((label0, label1, label2),('label0','label1','label2'))
#展示中心点
plt.scatter(centers[:,0], centers[:,1])
#画原图==================================================
fig9 = plt.subplot(122)
label0 = plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==0], X.loc[:,'V2'][y==0])
label1 = plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==1], X.loc[:,'V2'][y==1])
label2 = plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==2], X.loc[:,'V2'][y==2])
plt.title("labeled data")
plt.xlabel('V1')
plt.ylabel('V2')
plt.legend((label0, label1, label2),('label0','label1','label2'))
#展示中心点
plt.scatter(centers[:,0], centers[:,1])
plt.show() 
Meanshift 算法(无监督)
创建模型并训练
python
#try the meanshift model,当只有数据,不知道能分成几个类别的时候使用,可以自动聚类出类别
from sklearn.cluster import MeanShift, estimate_bandwidth
# obtain the bandwidth
bw = estimate_bandwidth(X, n_samples = 500) # n_samples :使用多少个样本点来估计带宽
print(bw) # 30.84663454820215, 带宽是 30
# 通过数据观察,横向X轴 150,纵向Y轴100,所以估出来 是 30 左右
python
# establish the meanshift model( This is an un-supervised model.)
ms = MeanShift(bandwidth = bw)
ms.fit(X)
进行预测
python
y_predict_ms = ms.predict(X)
print(pd.value_counts(y_predict_ms), pd.value_counts(y))# 自动归成了三类
#通过与原始数据的对比可以看出,与原始数据的类别名称不同
可视化
python
#画图,meanshift
fig9 = plt.subplot(121)# 一行两列,画第一列
#画预测图==================================================
label0 = plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y_predict_ms==0], X.loc[:,'V2'][y_predict_ms==0])
label1 = plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y_predict_ms==1], X.loc[:,'V2'][y_predict_ms==1])
label2 = plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y_predict_ms==2], X.loc[:,'V2'][y_predict_ms==2])
plt.title("ms results")
plt.xlabel('V1')
plt.ylabel('V2')
plt.legend((label0, label1, label2),('label0','label1','label2'))
#展示中心点
plt.scatter(centers[:,0], centers[:,1])
#画原图==================================================
fig10 = plt.subplot(122)
label0 = plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==0], X.loc[:,'V2'][y==0])
label1 = plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==1], X.loc[:,'V2'][y==1])
label2 = plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==2], X.loc[:,'V2'][y==2])
plt.title("labeled data")
plt.xlabel('V1')
plt.ylabel('V2')
plt.legend((label0, label1, label2),('label0','label1','label2'))
#展示中心点
plt.scatter(centers[:,0], centers[:,1])
plt.show()
#通过图形发现,橙色部分是一样的,另两种类别反了
类别校正
python
# correct the results
y_corrected_ms = []
for i in y_predict_ms:
if i == 0:
y_corrected_ms.append(2)
elif i == 1:
y_corrected_ms.append(1)
elif i == 2:
y_corrected_ms.append(0)
print(pd.value_counts(y_corrected_ms), pd.value_counts(y))
python
# convert the results to numpy array
y_corrected_ms = np.array(y_corrected_ms)
print(type(y_corrected_ms))# <class 'numpy.ndarray'>
python
#画预测图==================================================
label0 = plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y_corrected_ms==0], X.loc[:,'V2'][y_corrected_ms==0])
label1 = plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y_corrected_ms==1], X.loc[:,'V2'][y_corrected_ms==1])
label2 = plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y_corrected_ms==2], X.loc[:,'V2'][y_corrected_ms==2])
plt.title("ms corrected results")
plt.xlabel('V1')
plt.ylabel('V2')
plt.legend((label0, label1, label2),('label0','label1','label2'))
#展示中心点
plt.scatter(centers[:,0], centers[:,1])
#画原图==================================================
fig12 = plt.subplot(122)
label0 = plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==0], X.loc[:,'V2'][y==0])
label1 = plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==1], X.loc[:,'V2'][y==1])
label2 = plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==2], X.loc[:,'V2'][y==2])
plt.title("labeled data")
plt.xlabel('V1')
plt.ylabel('V2')
plt.legend((label0, label1, label2),('label0','label1','label2'))
#展示中心点
plt.scatter(centers[:,0], centers[:,1])
plt.show() 
kmeans \ knn \ meanshift 总结
kmens \ meanshift: un-supervised, training data: X;
kmeans: need the category number;
meanshift:need to calculate the bandwidth;
knn: supervised: training data:X\y