目录
题目描述
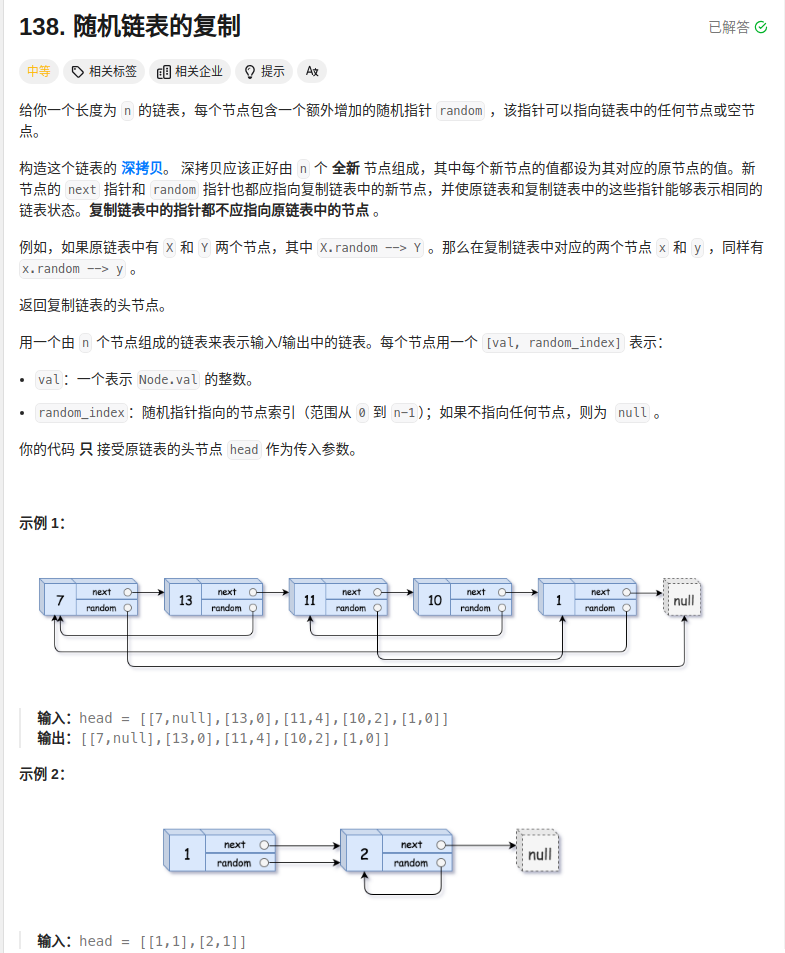
问题的关键是,random指针指向的是原链表的结点,这个原链表的结点对应哪一个新链表的结点呢?有两种办法。一是用哈希表。另一种是复制原链表的每一个结点,并将新结点接在原结点的后面组成一个长度加倍的链表,这样原结点的直接后继就是该原结点对应的新结点。
方法一、使用哈希表
unordered_map<Node*,Node*> new_table;//键是原链表中的旧结点,值是新链表中的新结点
unordered_map<Node*,Node*> random_table;//键是原链表中的旧结点,值是该旧结点的random指针指向的结点
cpp
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
Node* next;
Node* random;
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
next = NULL;
random = NULL;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
if(head == nullptr)
return nullptr;
unordered_map<Node*,Node*> new_table;//键是原链表中的旧结点,值是新链表中的新结点
unordered_map<Node*,Node*> random_table;//键是原链表中的旧结点,值是该旧结点的random指针指向的结点
Node* newHead = nullptr;
Node* newTail = nullptr;
Node* cur = head;
//第一步,建立新链表
while(cur){
Node* node = new Node(cur->val);
new_table.insert({cur,node});
random_table.insert({cur,cur->random});
if(newHead == nullptr){
newHead = node;
newTail = node;
}else{
newTail->next = node;
newTail = node;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
//第二步,设置新链表结点的random指针
for(const auto& [old_node,new_node] : new_table)
{
if(random_table[old_node]){
new_node->random = new_table[random_table[old_node]];
}
}
return newHead;
}
};实际上前面做法中的random_table是可以不需要的。
cpp
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
Node* next;
Node* random;
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
next = NULL;
random = NULL;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
if(head == nullptr)
return nullptr;
unordered_map<Node*,Node*> new_table;//键是原链表中的旧结点,值是新链表中的新结点
Node* newHead = nullptr;
Node* newTail = nullptr;
Node* cur = head;
//第一步,建立新链表
while(cur){
Node* node = new Node(cur->val);
new_table.insert({cur,node});
if(newHead == nullptr){
newHead = node;
newTail = node;
}else{
newTail->next = node;
newTail = node;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
cur = head;
Node* new_cur = newHead;
//第二步,设置新链表结点的random指针
while(cur){
if(cur->random){
new_cur->random = new_table[cur->random];
}
cur = cur->next;
new_cur = new_cur->next;
}
return newHead;
}
};方法二、不使用哈希表
第一步,复制每一个旧结点,并将新结点接在旧结点的后面组成新旧结点交替出现的长度翻倍的大链表。
第二步,设置新结点的random指针。
第三步,从大链表中提取出新结点组成新链表,并将原链表复原。
需要着重强调的是,第二步和第三步必须分开来做。
cpp
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
Node* next;
Node* random;
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
next = NULL;
random = NULL;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
if(head == nullptr)
return nullptr;
Node* cur = head;
//复制每一个旧结点,并将新结点接在旧结点的后面
while(cur){
Node* node = new Node(cur->val);
Node* temp = cur->next;
node->next = cur->next;
cur->next = node;
cur = temp;
}
cur = head;
//设置新结点的random指针
while(cur){
if(cur->random)
cur->next->random = cur->random->next;
cur = cur->next->next;//原链表向前走一位
}
Node* new_head = nullptr;
Node* new_tail = nullptr;
cur = head;
//提取出新结点组成新链表,并将原链表复原
while(cur){
if(new_head == nullptr){
new_head = cur->next;
new_tail = cur->next;
}else{
new_tail->next = cur->next;
new_tail = cur->next;
}
cur->next = cur->next->next;//复原原链表
cur = cur->next;//原链表向前走一步
}
return new_head;
}
};