引言:队列是一种先进先出(First In First Out, FIFO)的线性数据结构,只允许在队尾(rear)插入元素,在队头(front)删除元素。本章介绍队列,包括其实现。
**1.**队列的概念及结构
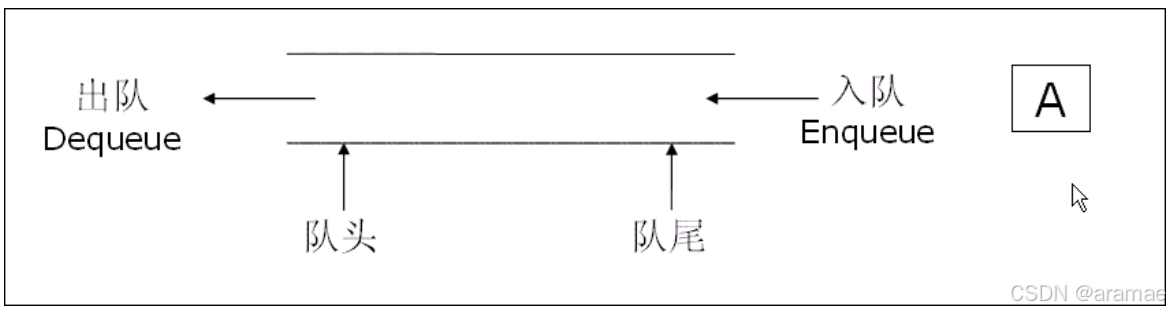
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出 FIFO(First In First Out) 入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾 出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头
**2.**队列的实现
队列也可以数组和链表的结构实现,使用链表的结构实现更优一些,因为如果使用数组的结构,出队列在数 组头上出数据,效率会比较低。
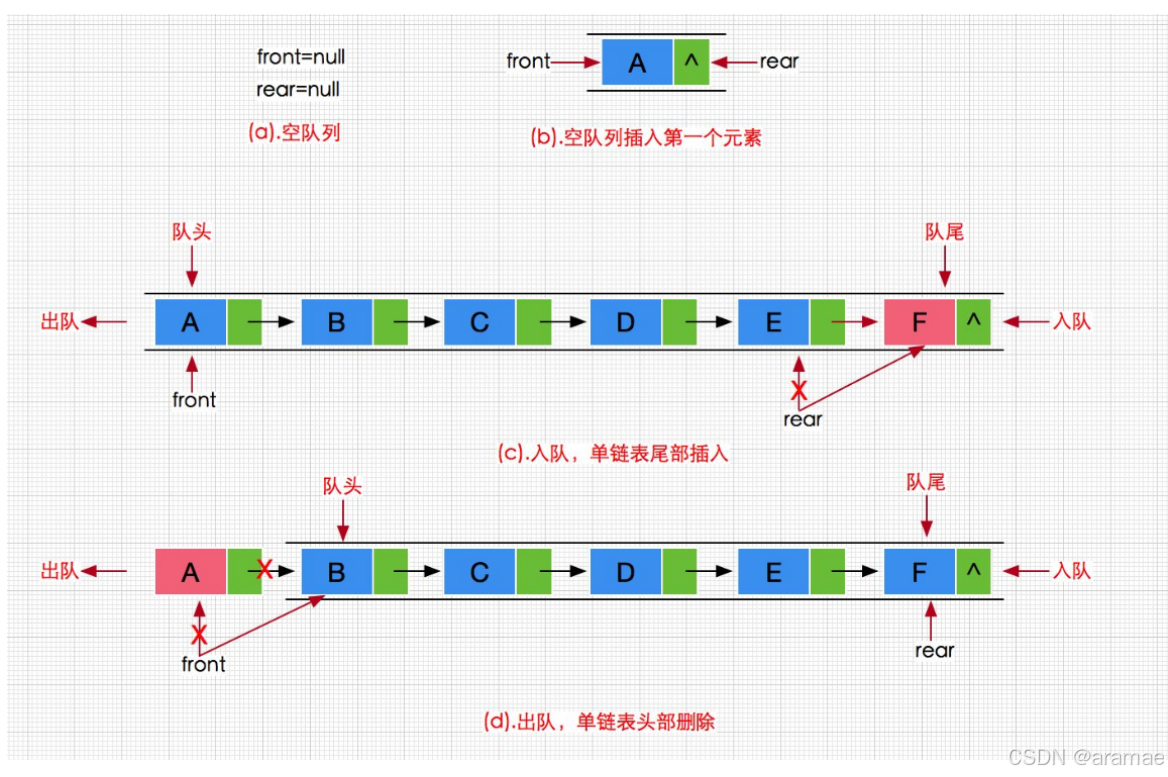
下面实现一个动态队列(链表)
cpp
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<assert.h>
//队列性质:先进先出 //
/* 1.队列初始化
2.队列销毁
3. 入对列
4.出队列
5.判空
6.返回队列长度
7.返回队头数据
8.返回队尾数据
*/
//用单链表实现队列
//使用两个结构体
//一个表示链表的节点的构成
//一个用来描述队列
typedef int QDatatype;
//队列的节点
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode* next;
QDatatype data;
}QNode;
//描述队列
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* head;//队头位置
QNode* tail;//队尾位置
int size;//队列长度
}Queue;
//判空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size == 0;
}
//初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = NULL;
pq->tail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
//销毁队列
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while(cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = NULL;
cur = next;
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
//入队列
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDatatype x)
{
//创建新的节点
QNode* newnode =(QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if(newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return ;
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if(pq->head==NULL)
{
assert(pq->tail == NULL);
pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->tail->next = newnode;
pq->tail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
//出队列
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head!=NULL);
if(pq->head->next == NULL)
{
free(pq->head);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
else
{
QNode* next = pq->head->next;
free(pq->head);
pq->head = next;
}
pq->size--;
}
//返回队列长度
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}
//返回队头数据
QDatatype QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->head->data;
}
//返回队尾数据
QDatatype QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->tail->data;
}
//打印队列
void QueuePrint(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while(cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
printf("%d ",cur->data);
cur =next;
}
}
int main()
{
Queue pq;//定义一个队列
//下面来实现一下队列的基本功能
//1.初始化
QueueInit(&pq);
//2.向队列中放入数据//这里试放8个
QueuePush(&pq, 1);
//打印出来看一下 //1
printf("%d\n", QueueFront(&pq));
//继续放
QueuePush(&pq, 2);
QueuePush(&pq, 3);
QueuePush(&pq, 4);
QueuePush(&pq, 5);
QueuePush(&pq, 6);
QueuePush(&pq, 7);
QueuePush(&pq, 8);
//这里我们可以再添加一个函数,用来打印整个对列
//便于我们观察整个队列的变化
QueuePrint(&pq);
printf("\n");
//3.出队列 ,这里选择出四个数据
QueuePop(&pq);
QueuePop(&pq);
QueuePop(&pq);
QueuePop(&pq);
//再观察队列里的数据
QueuePrint(&pq);
printf("\n");
QueuePop(&pq);
//观察此时 队头,队尾数据和队列长度
// 6 8 3
printf("%d ",QueueFront(&pq));
printf("%d ",QueueBack(&pq));
printf("%d ",QueueSize(&pq));
return 0;
}